La pérdida gestacional precoz acontece en el 10-20% de todas las gestaciones clínicas, siendo el 85% previos a la semana 12 de amenorrea. El aborto involuntario conlleva una carga muy significativa en los recursos destinados a sanidad, alcanzado un coste económico nacional en Reino Unido de 471 millones de libras esterlinas por año (533,06 millones de euros), cifra extrapolable a otros países industrializados. Según una revisión sistemática reciente no hay ensayos bien diseñados en gestaciones del primer trimestre que arrojen una evidencia consolidada sobre cuál es el mejor método de tratamiento de aborto del primer trimestre y existen diferentes estudios que han tratado de evidenciar reducción de costes con resultados contradictorios.
Material y métodosSe realiza un estudio de diseño observacional, retrospectivo y longitudinal. Se revisaron 892 pacientes diagnosticadas de aborto espontáneo durante el primer trimestre de gestación, en el periodo comprendido entre enero de 2013 y diciembre de 2016.
En nuestro estudio hemos querido evaluar la efectividad del misoprostol vaginal como tratamiento médico para el aborto espontáneo en el primer trimestre, en comparación con el legrado obstétrico/evacuador y, cuantificar la diferencia en los costos de ambos procedimientos a través de un estudio de minimización de costes.
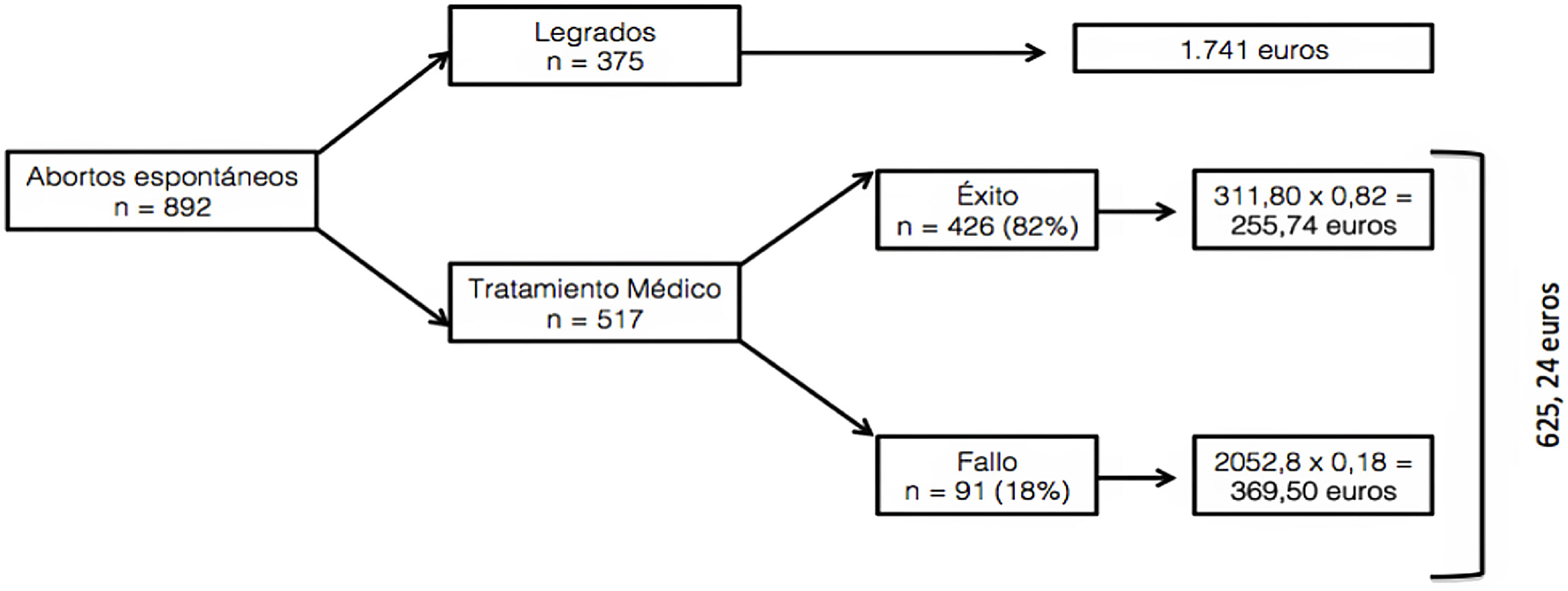
ResultadosDe las 892 pacientes reclutadas, se realizó tratamiento médico con misoprostol en 517 (57,95%) y tratamiento quirúrgico mediante legrado evacuador en 375 (42,05%).
La efectividad del tratamiento médico fue del 82% (426/517). Con respecto al tratamiento quirúrgico la efectividad resultó del 100%. La tasa de éxito del tratamiento médico fue superior en el subgrupo de pacientes con aborto incompleto (92,9%), en comparación con los grupos de gestación anembrionada (85,7%) y aborto diferido (78,2%).
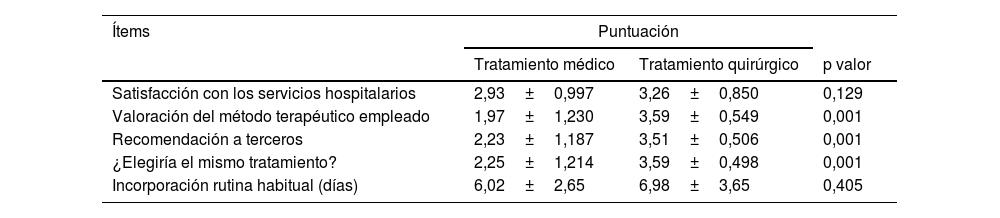
ConclusionesEl tratamiento médico del aborto es un manejo seguro y aceptado por las pacientes. La selección adecuada de las pacientes candidatas conlleva un aumento en la tasa de éxito y la disminución de costes. En nuestro estudio se determinó un importante ahorro total de 576.847,92 € (37,14%) respecto al tratamiento quirúrgico. Dado que la efectividad es comparable y la satisfacción de las pacientes alta, aunque mejorable, consideramos, que con la adecuada información y homogeneización del tratamiento aplicado, aumentará.
Early pregnancy loss occurs in 10-20% of all clinical pregnancies, 85% being prior to week 12 of amenorrhea. Miscarriage entails a very significant burden on healthcare resources, reaching a national economic cost in the United Kingdom of £471 million per year (€533.06 million), a figure that can be extrapolated to other industrialized countries. According to a recent systematic review, there are no well-designed trials in first-trimester pregnancies that provide consolidated evidence on what is the best first-trimester abortion treatment method, and there are different studies that have tried to demonstrate cost reduction with contradictory results.
Material and methodsAn observational, retrospective and longitudinal design study was carried out. 892 patients diagnosed with spontaneous abortion during the first trimester of pregnancy were reviewed, in the period between January 2013 and December 2016.
In our study, we wanted to evaluate the efficacy of vaginal misoprostol as a medical treatment for spontaneous abortion in the first trimester, in comparison with obstetric curettage-evacuator, and to quantify the difference in the costs of both procedures through a cost minimization study. costs.
ResultsOf the 892 recruited patients, medical treatment with misoprostol was performed in 517 (57.95%) and surgical treatment by curettage in 375 (42.05%).
The effectiveness of medical treatment was 82% (426/517). With respect to surgical treatment the effectiveness of 100%. The success rate of medical treatment was higher in the subgroup of patients with incomplete abortion (92.9%), compared to the anembryonic gestation (85.7%) and delayed abortion (78.2%) groups.
ConclusionsThe medical treatment of abortion is a safe management and accepted by the patients. The adequate selection of candidate patients leads to an increase in the success rate and a decrease in costs. In our study, an important total saving of €576,847.92 (37.14%) with respect to surgical treatment will be reduced. Given that the effectiveness is comparable and patient satisfaction is high, although it could be improved, we believe that with adequate information and homogenization of the applied treatment, it is safe.