This research aims to determine the correlation of bioaerosol pollution with temperature, humidity, and lighting in the ICU for measurement in morning and midday.
MethodsThe research was an observational analytic with a cross-sectional study design conducted in Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo hospital. The sample of the research consisted of 8 ICU rooms. The data were analyzed using the Spearman test.
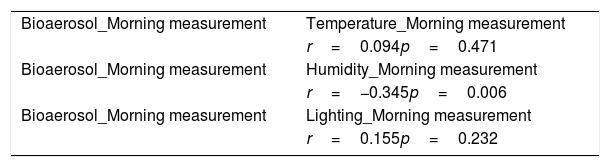
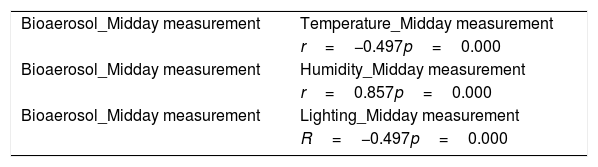
ResultsThe total of bioaerosol in the morning ranged from 320–1885CFU/m3 and the total of bioaerosol in midday ranged from 366–1895CFU/m3. The result showed that the humidity factor correlated with the total of microbial (p=0.006) but the temperature (p=0.471) and lighting (p=0.232) did not correlate with the total of bioaerosol for morning measurement. While the temperature, humidity and lighting factors correlated with the total of bioaerosol (p=0.000) for midday measurement.
ConclusionThe quality of bioaerosol correlates with temperature, humidity, and lighting. For further improvement designing well-built HVAC.