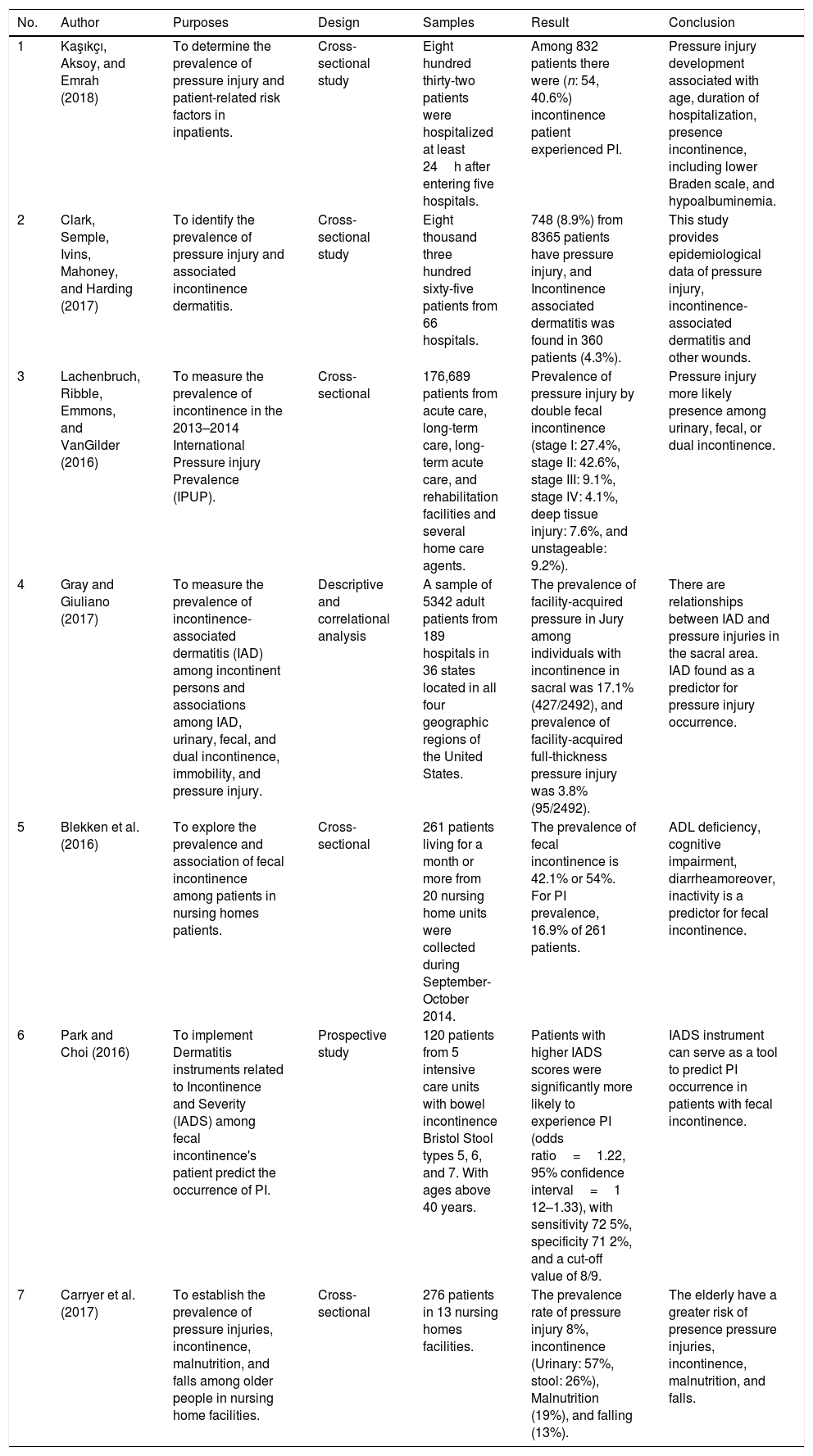
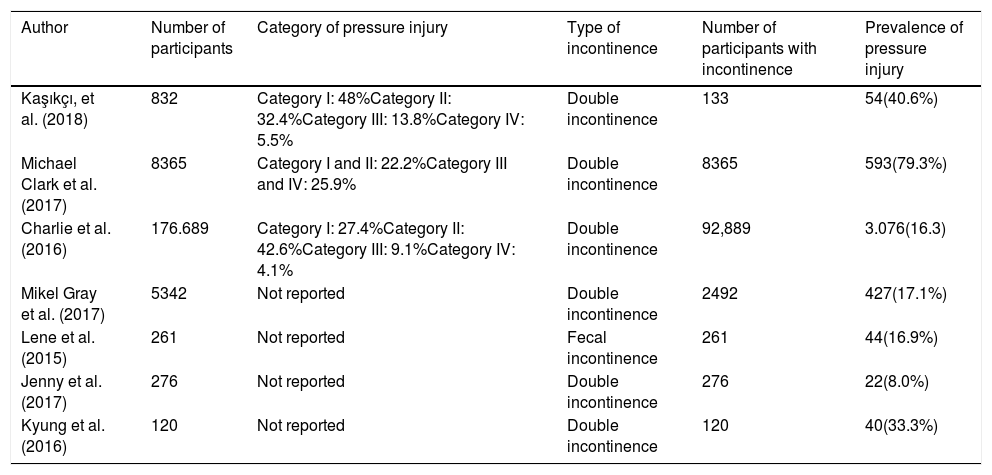
This study was conducted to identify the prevalence of pressure injury (PI) in patients with incontinence.
MethodWe searched articles through PubMed, Science Direct, ProQuest, EBSCO, COCHRANE, and DOAJ. We identified 138 articles from electronic databases published from 2015 to 2019; all of these articles were clinical studies. We obtained seven articles that met the inclusion criteria consisting of 4 cross-sectional articles, one cross-sectional cohort, one prospective study.
ResultsThe prevalence of PI varied incontinence patients, starting from 8.0% of 276 patients, 16.3% of 176,689 patients, 16.9% of 261 patients 30.3% of 8365 patients, 33.3% of 120 patients, 40.6% of 832 patients and 17.1% of 5342 patients.
ConclusionOur study suggests that the prevalence of PI in patients with varied incontinence, and highest in patients with double incontinences (urine and feces).