The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the presence and impact of Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms, physical and psychological disturbances on patients’ QoL after sleeve gastrectomy (SG), Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS).
MethodsA prospective, observational, cross-sectional, comparative study was carried-out. GI symptoms and patients’ QoL were evaluated by the SF-36 questionnaire and the GI quality of life index (GIQLI). Correlation between GI symptoms, psychological disturbances and QoL scores was analysed.
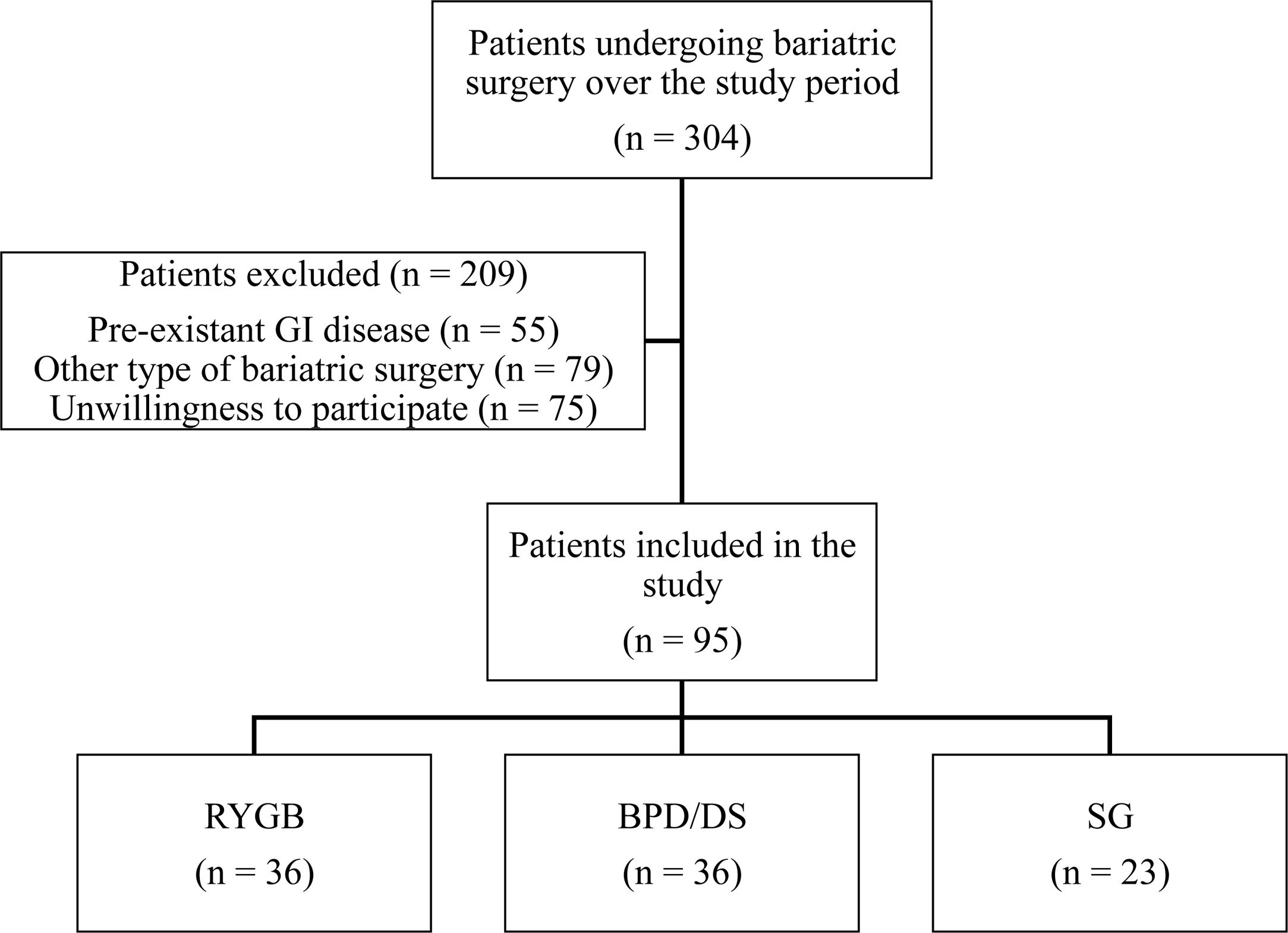
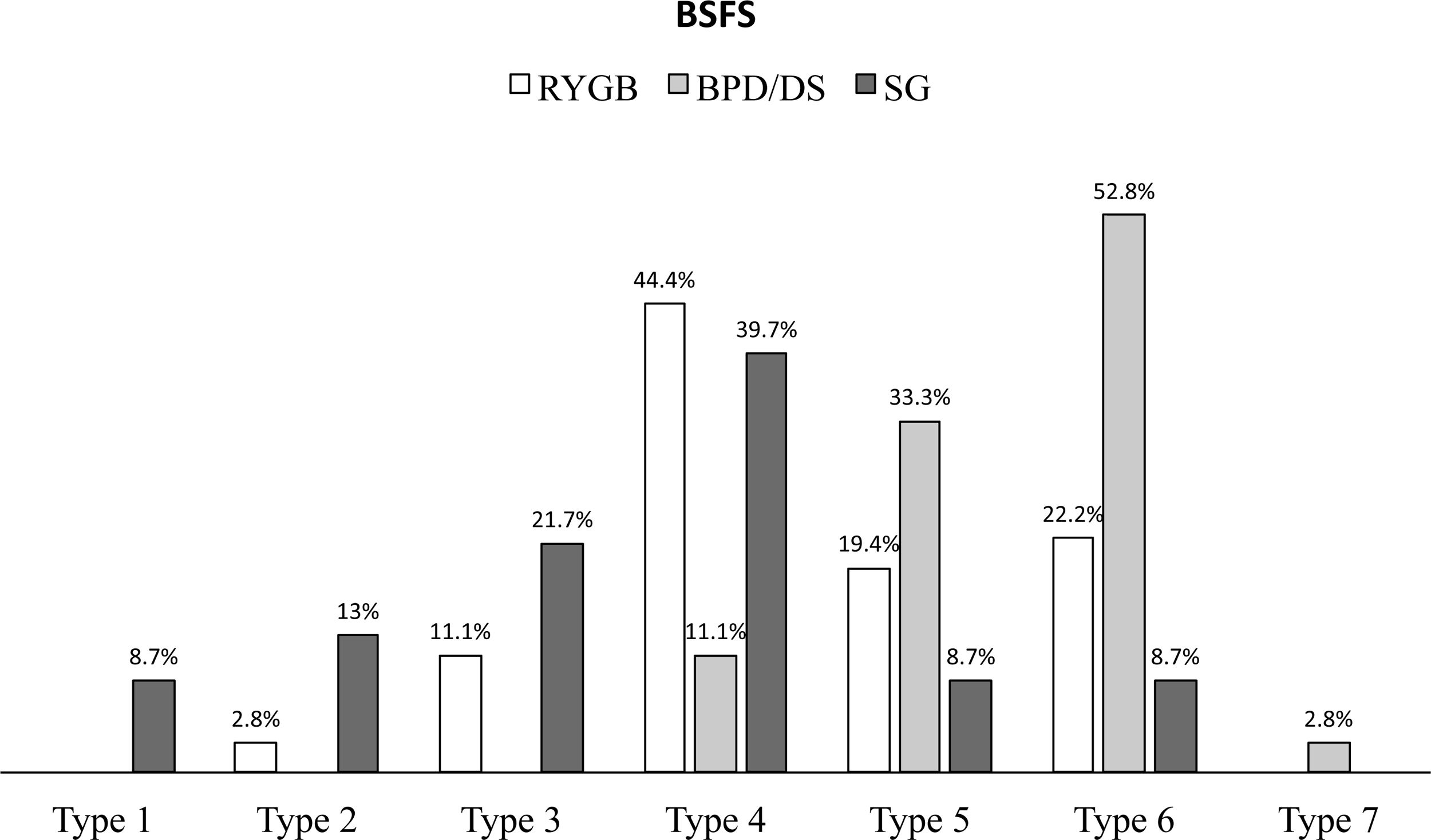
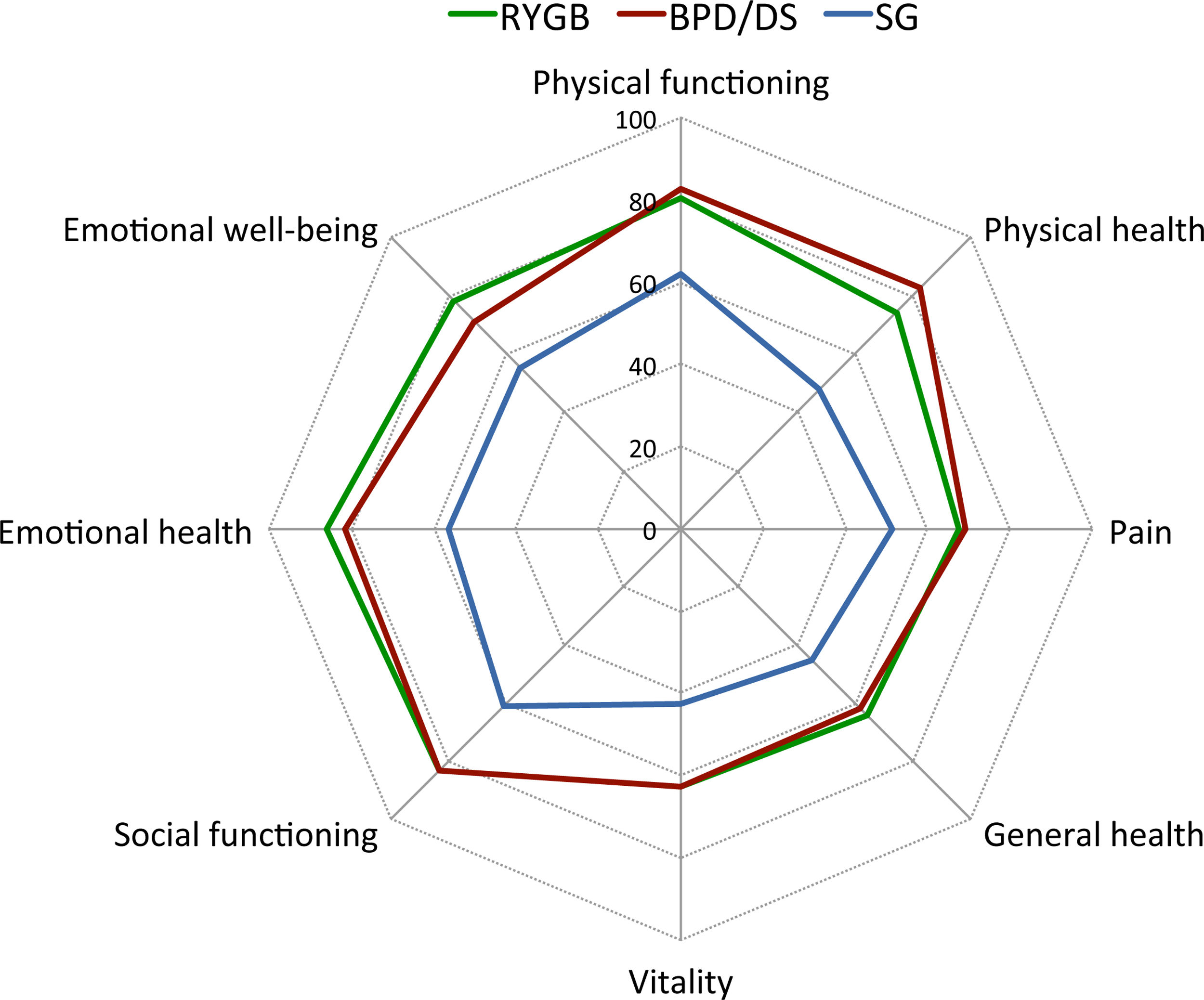
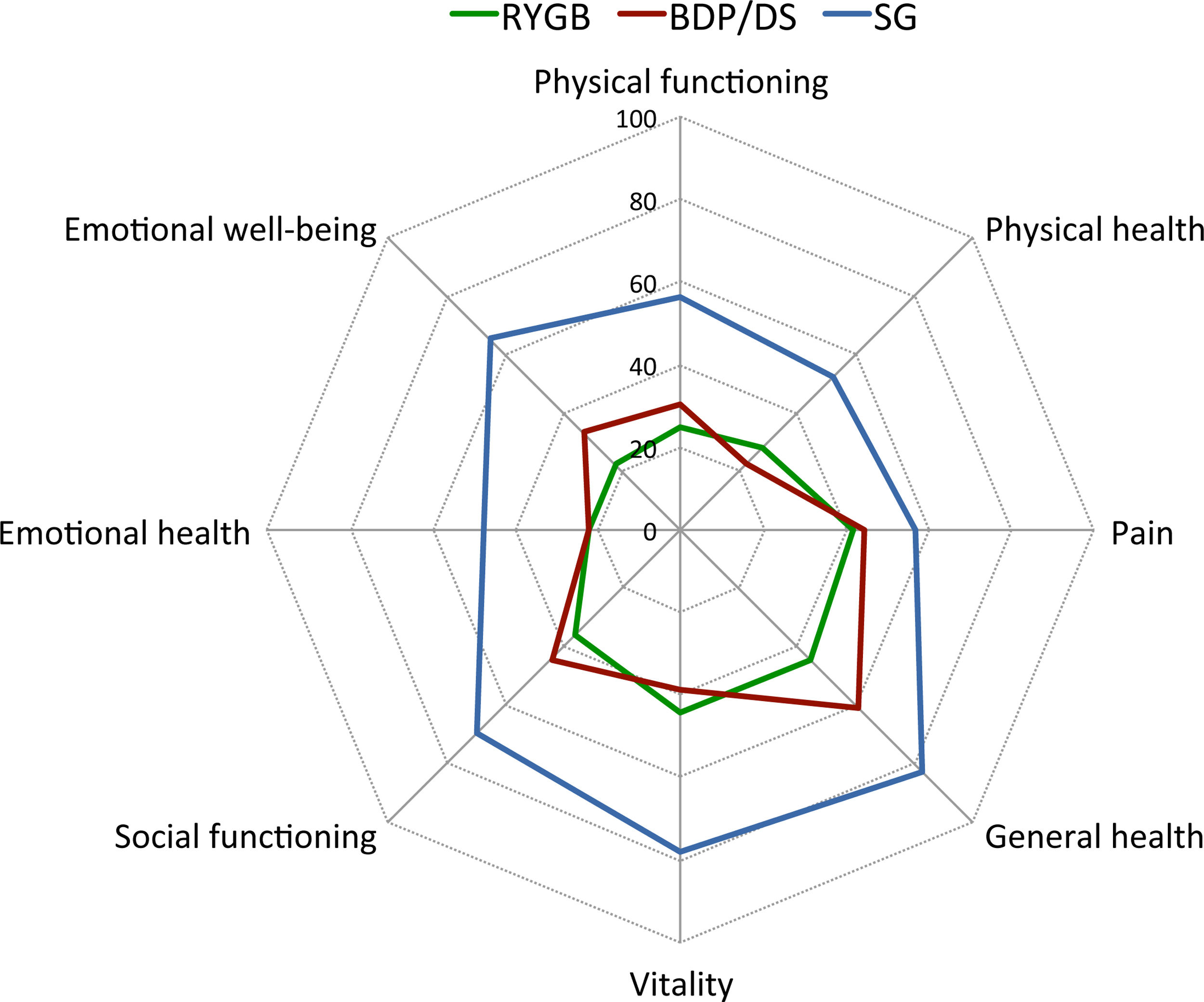
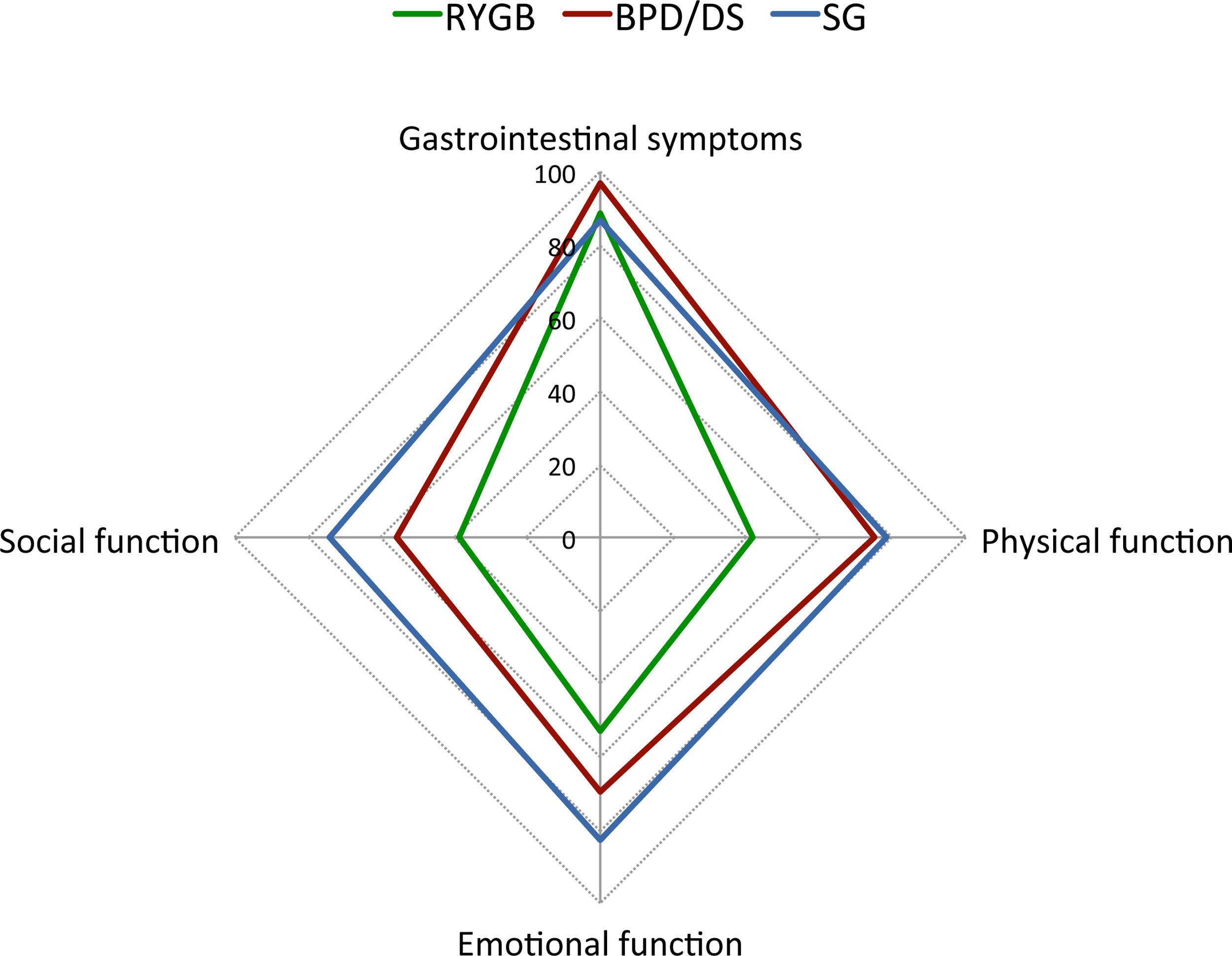
Results95 patients were included (mean age 50.5 years, range 22–70; 76 females). Presence of GI symptoms was a consistent finding in all patients, and postprandial fullness, abdominal distention and flatulence had a negative impact on patients’ QoL. Patients after SG showed a worsening of their initial psychological condition and the lowest QoL scores. Patients after RYGB showed the best GI symptoms-related QoL.
ConclusionsBoth restrictive and malabsorptive bariatric surgical procedures are associated with GI symptoms negatively affecting patients’ QoL. Compared to SG and BPD/DS, patients after RYGB showed the best GI symptoms-related QoL, which can be used as additional information to help in the clinical decision making of the bariatric procedure to be performed.
El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar y comparar la presencia e impacto de los síntomas gastrointestinales (GI), los cambios físicos y psicológicos en la calidad de vida (CV) de los pacientes sometidos a tubulación gástrica (TG), bypass gástrico en Y de Roux (BGYR) y derivación biliopancreática con cruce duodenal (DBP/CD).
MétodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo, observacional, transversal y comparativo. Los síntomas gastrointestinales y la CV de los pacientes fueron evaluados mediante el cuestionario SF-36 y el índice gastrointestinal de calidad de vida (GIQLI). Se analizó la relación entre los síntomas gastrointestinales, los trastornos psicológicos y las puntuaciones de CV.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 95 pacientes (edad media: 50,5 años, rango: 22-70; 76 mujeres). La presencia de síntomas gastrointestinales fue un hallazgo constante en todos los pacientes, y la pesadez posprandial, la distensión abdominal y la flatulencia tuvieron un impacto negativo en la CV de los pacientes. Los pacientes después de la TG mostraron un empeoramiento de su estado psicológico inicial y unas puntuaciones más bajas en la CV. Los pacientes después del BGYR presentaron la mejor CV relacionada con los síntomas gastrointestinales.
ConclusionesLos procedimientos de cirugía bariátrica tanto restrictivos como malabsortivos se asocian a síntomas GI que afectan negativamente la CV de los pacientes. En comparación con la TG y la DBP/CD, los pacientes tras el BGYR presentaron la mejor CV relacionada con los síntomas GI, lo que puede utilizarse como información adicional para ayudar en la toma de decisiones clínicas sobre el procedimiento bariátrico a realizar.