The incidence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) is 10–20/106inhabitants/year.1 It is the most common tumour of mesenchymal origin in the digestive tract and constitutes 1–2% of gastrointestinal neoplasms.2 The duodenal location is rare, corresponding to 5–7%, behind GISTs in a gastric (50–70%) and small intestinal (20–30%) location, and the association with neurofibromatosis type 1 is infrequent.2 The most accepted treatment is surgical resection with free margins, along with imatinib therapy in metastatic cases or recurrent disease and as neoadjuvant therapy for large lesions or complex locations.3 The duodenal location of GISTs is the most complex with relation to surgical treatment, although there are different options based on the duodenal area where the lesion is located and the relationship to adjacent organs.4 There are few articles published on this topic, generally isolated cases or short series.3–6
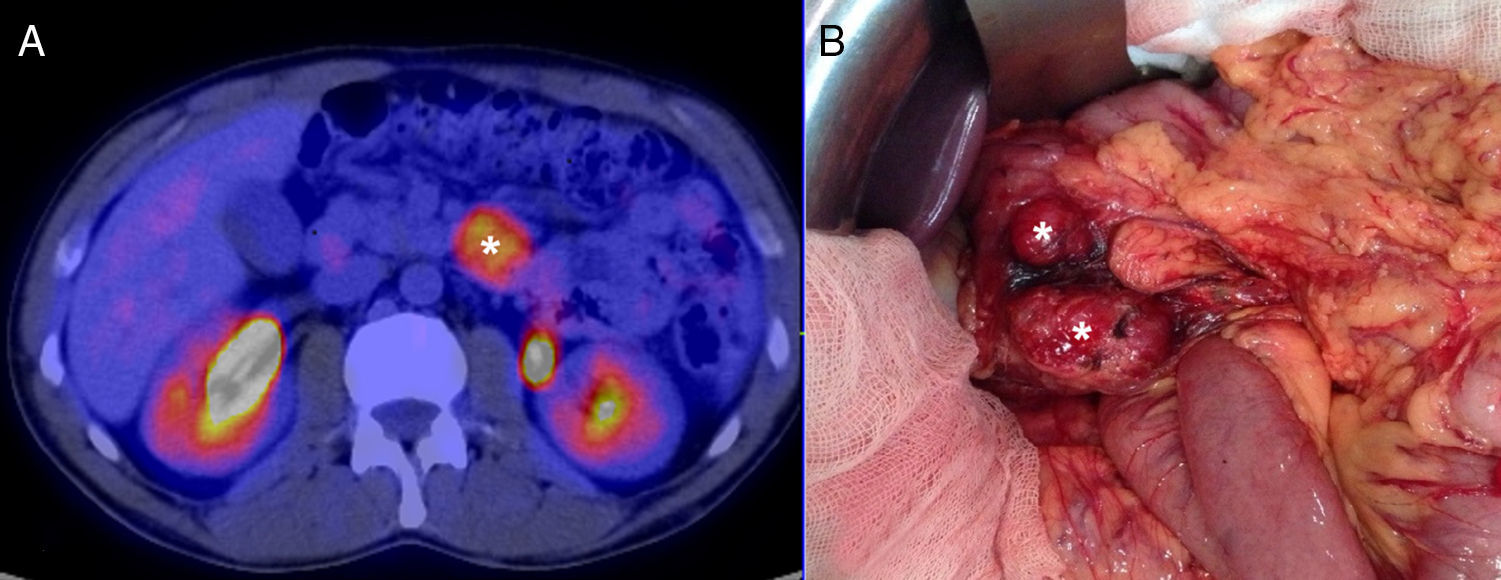
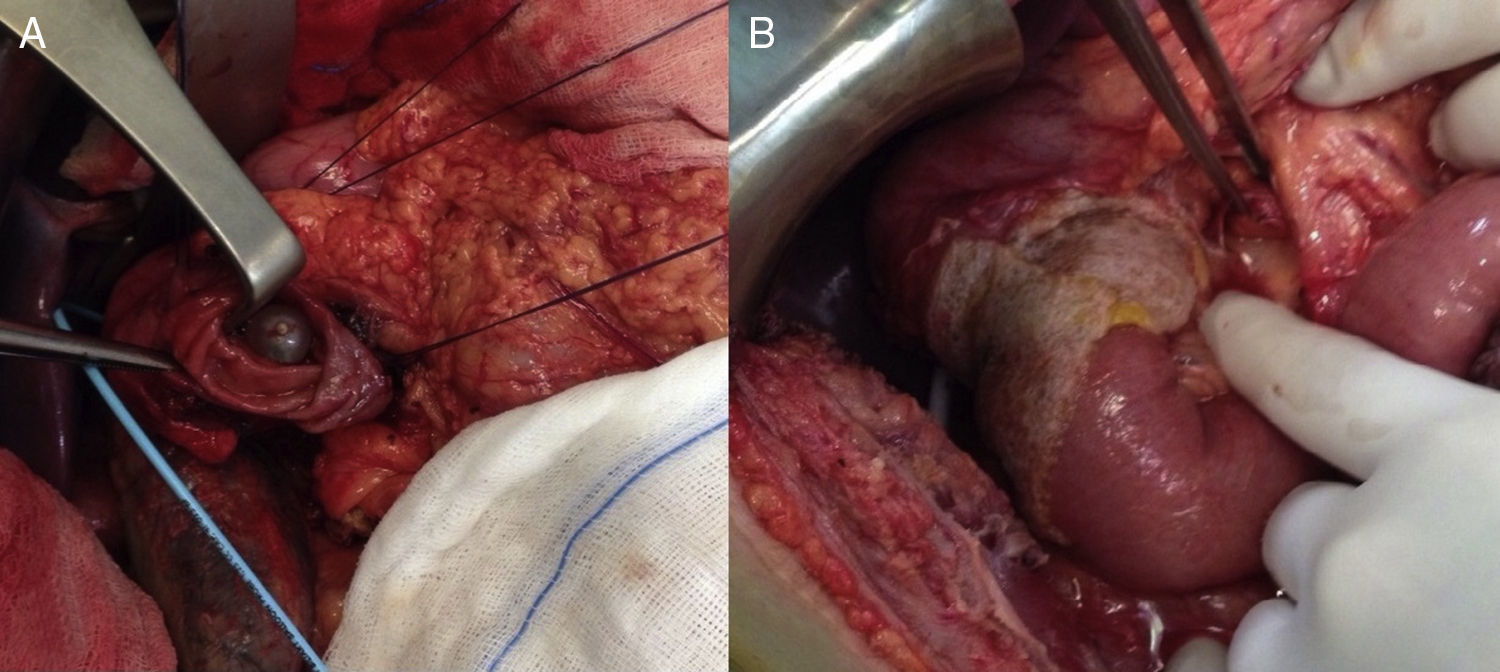
We present the case of a 40-year-old man with neurofibromatosis type 1 undergoing treatment for anaemia of 2 months evolution, and in the last full blood count he presented haemoglobin of 6mg/dl. The patient was asymptomatic, with the exception of dark faeces. The upper gastrointestinal tract endoscopy (UGIE) of the third part of the duodenum showed a 3–4cm ulcerated tumour with a stable adhered clot. No biopsies were taken due to the risk of bleeding. A second UGIE was performed 4 days later, with a pathological anatomy outcome of duodenal ulcer with regenerative changes on the borders. After the abdominal CT scan, which identified a lesion in the third part of the duodenum, without being able to reach a conclusion about the nature thereof, a PET/CT scan was performed (Fig. 1A), diagnosing him with a 4cm poorly-delimited hypermetabolic duodenal lesion, suggestive of a neoplastic lesion, with no other lesions (Fig. 1B). A surgical intervention was carried out, finding, via visual inspection and palpation, two lesions smaller than 1cm of neoplastic appearance in the proximal jejunum together with two others (1×1 and 4×3cm) on the non-pancreatic side of the third part of the duodenum, with the latter probably causing the symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding. No other lesions were found in the intestine or stomach. Given the lack of a histological perioperative diagnosis of the lesion and with this being important for the surgical approach to follow, an intraoperative biopsy was performed, reporting a GIST. Since the lesion was located in the third part of the duodenum, it had to be ensured that the opening of the bile duct—located in the second part of the duodenum, next to the resection area—was not injured, therefore a cholecystectomy was performed along with identification of the ampulla of Vater by means of bile duct canalisation with a Fogarty probe via the cystic duct. After identification, a duodenectomy of the third and fourth parts of the duodenum was performed, including the lesions in the contiguous proximal jejunum (Fig. 2A). The intestinal tract was reconstructed via duodenal-jejunal termino-terminal anastomosis and placement of a TachoSil® patch (Fig. 2B). The post-operative period proceeded without complications, with discharge after 8 days. The pathological anatomy report showed the presence of a multiple stromal tumour (4 lesions) of low degree of malignancy (<4cm and <5 mitotic figures per 50HPF) and positive c-kit, receiving no adjuvant oncological treatment. Two months after the surgical intervention, a capsule endoscopy was performed, ruling out the existence of other lesions throughout the digestive tract that may not have been detected intra-operatively. The patient was asymptomatic and had no relapses at 15 months.
In 5–7% of cases, the GIST was located in the duodenum, and most caused symptoms related to gastrointestinal bleeding.2,7 Five per cent of cases occurred in the context of familial syndrome (Carney-Stratakis, Carney triad, familial GIST and neurofibromatosis), with neurofibromatosis type 1 being the most common, as in our case.2,5 The second part of the duodenum is most affected.4,7 GIST spreads haematogenously, with exceptional spreading via lymphatic and local infiltration. Therefore the objective of surgery is complete resection of the lesions with free margins, with lymphadenectomy not recommended.3,7–9
A diagnosis of GIST is based on the UGIE and an abdominal CT or MRI scan, with a PET/CT scan being helpful in the event of any diagnostic doubt, as occurred in the described case.3,5,7,10
The surgical options for duodenal GISTs are cephalic duodenopancreatectomy (CDP), complete duodenectomy with preservation of the pancreatic head, partial duodenectomy and wedge resection. The different locations in the duodenum, tumour size and the possibility of R0 resection qualify the type of surgery,1,7,8 although the ideal surgical approach is still not well established despite the different studies that compare the oncological results with the different resection techniques.7,8,10
For tumours located in the distal, third, and fourth parts of the duodenum, CDP seems to be an excessively aggressive option, while other options could be considered, such as local wedge resection or partial duodenectomy, as was done in our case, reserving CDP for large tumours and those located in the medial wall of the duodenum with involvement of the adjacent pancreas.1,3,7,8 The above conservative options could also be considered a surgical option in tumours located in the first and second parts of the duodenum, when the lesion is located in the lateral wall, it is small, and it is verified that there is no involvement of the papillary area, reserving CDP for the rest of cases or complete duodenectomy with preservation of the pancreatic head in select cases.1,3,7–9
The tumour size and mitotic count are the determining factors of survival.1,4,9 Adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy with imatinib is indicated in patients with GISTs that are very large, metastatic, recurrent or in complex locations, such as the duodenum.3 It was not suggested as neoadjuvant therapy in our case since there was no perioperative pathological anatomy diagnosis.
Please cite this article as: Palomeque Jiménez A, Rubio López J, Pérez Cabrera B, Jiménez Ríos JA. Duodenectomía parcial como opción terapéutica de un tumor del estroma gastrointestinal duodenal múltiple, asociado a neurofibromatosis tipo 1. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;40:534–536.