The present study captures the essential role of environmental and social innovation driving success of entrepreneurs in the presence of knowledge sharing culture as a mediator and green volunteer behaviour as a moderator. With a particular focus on Vietnam, the study selects manufacturing SMEs because of their bigger role in Vietnam's economy. Since, SMEs foster innovation which is crucial for sustainability and competitive advantage. Therefore, it is imperative to assess the relationship in SMEs context. With quantitative approach, the study collected data from Vietnam's manufacturing SMEs, examining how social innovation focusing on societal needs; environmental innovation emphasizing on environmentally friendly practices contribute to entrepreneurial success. The study used PLS methodology to assess the linkage among variables. Outcomes of the study reveal that both kind of innovations are crucial for entrepreneurial success, however, their significance remarkably enhances when knowledge sharing culture mediates the relationship. This partially mediate role of knowledge sharing culture demonstrates that organizational culture builds on knowledge sharing idea promotes innovative idea, encouraging entrepreneurs to cultivate collaborative environment that further improves the efficacy of innovative ideas. The outcomes also indicated that green volunteer behaviour insignificantly moderates among knowledge-sharing culture and entrepreneurial success. The absence of moderation indicates that even with a focus on environmental goal, green volunteer behavior seems to have no direct alignment with prompt business goals of entrepreneurial success. Hence, the chances are greater that it may dilute the effect of knowledge sharing culture on environmental success.
Sustainability innovation is a broader view that conceptualizes variety of innovation paradigms toward sustainability. Sustainability innovation aimed at minimizing adverse effect of organizations on environment and society while assuring sustainable economic growth of firm (Olanrewaju et al., 2020; Ten, 2022). Since, economic growth and population are two major factors of higher emissions and resource consumption, hence, put great burden on environment (UN, 2019). Therefore, with negative social and environmental outcomes and unfavorable trend, stakeholder pressure on organization forces firms to address these challenges. In continuation of this, the external pressure on firms obliges firms to advocate sustainability principles while surviving in highly competitive market due to globalization and technological advancement. In the light of positive view, these pressures develop an internal motivation due to which they tend to be more involved in sustainability innovation to drive sustainable performance. From revisionist perspective, sustainability innovation ensures firm's success in a way that it enhances firm's competitive advantage in the direction of sustainability (Inegbedion et al., 2021; Wadhwani et al., 2020).
Linking the debate within the context of entrepreneurial success, entrepreneurs require a clear and transparent understanding of their customers and market, the proper network of support, and a solid business plan. They should be adaptable and persistent and are willing to grow and learn as their business evolves. Hence, entrepreneurship is a rewarding and dynamic career path that enables individuals to transform their creative ideas into a successful business, while contributing to generating new jobs and the economy (Aljuwaiber, 2021; Nathan et al., 2022). In this context, knowledge-sharing culture fosters innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning which is important for firms to stay competitive and stay ahead in the market. In knowledge shared culture (KSC), employees feel trusted and valued and more committed and engaged to their work. They are more likely to feel acknowledged and realize that their contributions and ideas are heard and valued (Ahmad & Karim, 2019; Sun et al., 2022). On the other hand, Green volunteer behavior (GVB) defines the actions taken by individuals who choose to involve themselves in environmental activities that not only promote sustainability but also protect the environment. This may include planting trees, clean-up efforts, advocating for the environmental cause, and minimizing waste. GVB is encouraged by the need to impact positively on the environment, thus creating a sustainable and green future. This behavior is derived from personal beliefs, values, and social responsibility as well as the urge to give back to society (Ones et al., 2018; Zhang & Zhao, 2021). Hence these factors play a significant role in enhancing entrepreneurial success.
In this study, the manufacturing industry of Vietnam has been selected to analyse the impacts on the success of entrepreneurial firms. The manufacturing industry of Vietnam has had significant growth in the past few years and is contributing highly to the economy of the country (Canh et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2022). The industry consists of small and medium-sized enterprises, thus making up the majority of the manufacturing industry in Vietnam (Hue, 2019). Entrepreneurship has a significant role in the growth of the manufacturing sector in Vietnam. The country has an encouraging and motivated environment with highly skilled workers and a rapidly growing consumer market. This created a lot of foreign investment and introduced many opportunities for local entrepreneurs to bring new technologies and products to the market and the development of new businesses (Cheng et al., 2022; de Oliveira et al., 2021). In the past few years, the Vietnamese government has taken initiatives in supporting entrepreneurship and innovation in the manufacturing sector by supporting research and development, providing tax incentives, and improving access to finance. This has helped in creating a favourable environment for entrepreneurs and has motivated people to start a new business in the manufacturing sector (Ju et al., 2023; Nguyen et al., 2021). However, the entrepreneurial industry in Vietnam is still facing some constraints despite these benefits due to which they are still lacking behind in the entrepreneurial culture. To make entrepreneurial firms successful it is important to focus not only on external factors but also on internal aspects (Lee et al., 2021).
The role of SMEs is bigger in advancing modern growth of Vietnam. In 2019, SMEs added 50% contribution in Vietnam's GDP, hence, responsible for 50% of the total employment (Roxas, 2021). It is argued that SMEs growth positioned itself in vibrant local economy due to sustainable growth and stability (Jaax, 2020; Tran-Thi-Thanh & Nguyen-Thi-Phuong, 2023). Since, the country has an active participation in international economic and social affairs, therefore, it faces immense pressure from international bodies due to the commitment made to UN agenda 2030. This eventually shifts the pressure on SMEs as well to address social and environmental challenges that may affect businesses. The growing interest and current situation encourage scholars to find out the factors that help Vietnam's SMEs to design strategies and develop capabilities. By identifying the factors SMEs are able to become an enabler of sustainable model that is a particular need of modern Vietnam (Venkataraman, 2019).
Existing literature also reveals that small and medium enterprises of Vietnam are quite innovative, however, their innovation capability is limited in terms of scope and orientation. Innovations, particularly represent minor changes in existing produces/success to gain access to market segments (OECD, 2021). This is due to the fact that Vietnamese SMEs have limited resources and government support that is required for embracing innovation at organizational level. Hence, affecting SMEs competitiveness. Therefore, knowledge sharing culture which is a source of innovation is a right choice of being mediator as it builds strong bridge between social and environmental innovation and entrepreneurial success. TO discuss it further, the study particular focuses manufacturing SMEs because literature on innovation and SMEs performance particularly in Vietnamese context is viewed from different angles (Canh et al., 2019). Existing literature mainly emphasizes on open innovation or product innovation and traditional firm performance, while neglecting the sustainability factor. In addition to this, economy of Vietnam is still in its early phase in the context of innovation. Since, the economy of the country is export-oriented and majority SMEs involve in export-value chain, therefore, they yield high proportion (OECD, 2021).
The above scenario motivates researchers to analyze the role of various factors such as knowledge-sharing culture, social innovation, environmental innovation, and GVB in the entrepreneurial firms of manufacturing sectors. Because in Vietnam, the future of the manufacturing industry looks bright with increased growth, thus increased competitiveness is expected in the coming years. Entrepreneurs in the industry are reluctant to play a significant role in this growth, creating new business ideas and technologies, creating jobs, and contributing to economic development. To achieve these goals organizations must focus on the various factors which play an important role in making entrepreneurial firms successful. Thereby, from theoretical perspective, sustainability innovation factors such as social innovation and environmental innovation are the most suitable predictors that inject success to entrepreneurial firms particularly in the presence of knowledge sharing culture and green volunteer behavior. However, in contextual manner, it is imperative to evaluate the proposed relationship due to the existence of contradictory evidences documented in the literature. A holistic study addressing these concerns in Vietnamese context provides variety of implications as it extends the literature on sustainability innovation and entrepreneurial success by integrating knowledge sharing culture as a mediator and green volunteer behavior as a moderator.
The study is comprised of five sections. Section 1 reflects on the theme of study. Section 2 highlights the synthesized literature; further section 3 consists of the methodology and data collection part. Section 4 analyses the discussions, theoretical and managerial implications as well as the conclusions and limitations.
Literature reviewIn Vietnam, entrepreneurship is facing significant development and growth in the past few years. There are a few factors that are playing a significant role not only in the growth of entrepreneurial firms but also motivates and encouraging society to initiate innovative business ventures. These factors include governments support, the growing technology sector, and favourable economic conditions. Further, free trade agreements, skilled labor, growing infrastructure, and labor cost advantage are also playing significant roles not only in encouraging the local communities but also in foreign investments to initiate business ventures in the manufacturing industry of Vietnam (Yang, 2019). The entrepreneurial firms in the manufacturing sector offer many opportunities for the success and growth of the country. The factors which contribute to the development and success of the economy include innovation, efficiency, supply chain management, and the global market. The manufacturing industry often needs significant investments in facilities, equipment, and personnel, which can be obtained through various sources such as investors, venture capital, and government grants (Ngo, 2021). Despite these factors, entrepreneurial firms are facing a lot of challenges such as limited access to network opportunities and mentorship, lack of experienced entrepreneurs, and lack of regulatory and legal support for start-ups. To tackle these challenges some factors, play a significant role in making entrepreneurial firms successful. These factors include social innovation, environmental innovation, KSC, and GVB and their relationship has been discussed in this paper.
Social innovation and entrepreneurial successSocial innovation refers to designing and implementing new solutions or ideas in improving the well-being of the environment. However, entrepreneurial success indicates the achievement of operational and financial goals by a start-up (Nguyen et al., 2021). The association between social innovation and entrepreneurial success is well-stated in existing literature. Social innovation which focuses on addressing social issues appears be a significant driver as it offers variety of opportunities to entrepreneurs. Studies highlight that entrepreneurs who tend to be more involved in social innovation are the one who better acknowledge unaddressed social needs. This way they are able to add value to traditional concept of business models. Literature exerts that development of cooperative business framework boost social innovative performance which further leads to entrepreneurial success (Doern et al., 2019; Kuczewska & Tomaszewski, 2022). This happens due to the supportive innovation network and resource sharing environment. In addition to this, studies also highlight that social innovation helps firms in improving their competitive edge along with their reputation as both are critical elements of successful business. Another study supports the idea that introducing creativity and emotional intelligence factors in the domain of social entrepreneurship helps firms to build smooth connection between social innovation and entrepreneurial success. The comprehensive view on social and technological entrepreneurship unwarps that integrating both domains’ results in strategic advantage for entrepreneurs, highlighting a significant role of social innovation in entrepreneurial outcomes. The conclusive remarks unfold the positive association between social innovation and entrepreneurial success with this argument that social innovation creates a path through which not only societal challenges can be addressed but successful ventures can be born with long-term sustainability (Ho & Yoon, 2022; Le & Ikram, 2022).
Hypothesis 1 social innovation and entrepreneurial success are positively related.
A well-documented literature clearly highlights a strong link between environmental innovation and entrepreneurial success. Environmental innovation, a broader perspective, comprises of novel practices, products or processes that have one singular aim; to reduce negative impact on environment (Watson et al., 2018).. Due to its distinct nature, it has been recognized as a vital component of entrepreneurial success. Studies sketches the idea that organizations when highly engage in environmental innovation, often experience superior performance as equipped with innovative ideas, they are capable of differentiating themselves from competitors while fulfilling burgeoning demand of consumers for sustainable products. Literature also encompasses that environmental entrepreneurial orientation significantly affect firm's performance as it refines competitive edge of firms through sustainable practices. In addition to this, sustainable entrepreneurship is blended with innovation with an aim to address environmental and social challenges, injecting firms with long-term sustainability and profitability (Burca et al., 2022; Wittmayer et al., 2019). This is due to the fact that eco-innovative firms often draw investors attention, develops an ability to minimize costs through the efficient use of resources. This helps them to build their reputation and makes their position strong in market. Studies also idealize that environmental innovation facilitate entrepreneurs to differentiate their products and attract environmentally conscious consumers, leading to entrepreneurial success. Evidences also showcase that embracing environmental innovation means that firms are able to develop long-term viability of businesses (Awan & Sroufe, 2020; Wang, 2022). Since, environmental regulations become more rigid due to recent environmental issues, therefore, entrepreneurs who integrate environmental perspective into their innovative models, experience less legal risks and assure business continuity. Environmental innovation also brings up new market opportunities especially in those sectors where sustainability is a major concern (Ones et al., 2018; Zhang & Zhao, 2021)s. Hence, give access to entrepreneurs to tap into sustainable markets assuring long-run success. Therefore, it can be concluded that environmental innovation in entrepreneurial ventures not only ease the pressure of stakeholders and regulatory bodies but also allows firms to be connect with broader market trends, resulting in entrepreneurial success (Block et al., 2023).
Hypothesis 2 environmental innovation and entrepreneurial success are positively correlated.
Knowledge sharing is the exchange of experiences, ideas, and information with an organization or community. In this current era, organizations should effectively share information to gain a competitive edge for themselves (Sulistiawan et al., 2022). In this culture of sharing knowledge, social innovation plays a significant role. Muafi (2020), also highlights that social innovation help in designing new and innovative strategies, policies, and ideas to tackle environmental, cultural, and social challenges. Social innovation offers a variety of benefits in promoting knowledge-sharing culture. Social innovation encourages collaboration among organizations and individuals which helps in developing an inclusive and open environment for knowledge sharing. Social innovation support and empower employees by promoting a knowledge-sharing culture, thus help to help organizations in designing effective and creative solutions. With the help of leveraging technologies such as online platforms, social media, and blogs, firms can easily share and exchange their ideas and knowledge about the challenges with customers, employees, and partners. Further, social innovation also promotes transparency, which helps the organizations and employees to develop the trust to openly share their experiences and knowledge (Pansuwong et al., 2023). Gui et al. (2022), also mentioned in their study that the world is changing rapidly, with each passing day new technologies and strategies has been introduced in the business world, due to which employees, managers, or organization especially entrepreneurial firms must exchange their knowledge. Through this culture of knowledge sharing, organizations will remain up to date about the latest trends in the business world. Social innovation plays a significant role in supporting the development and learning process which promotes the culture of knowledge sharing.
It is also argued that strong KSC assists in facilitating the social innovation of the process by motivating the employees to share their expertise, skill, ideas, and perspectives. This leads to the creation of innovative solutions to social issues and in identifying the opportunities for social innovation and in this regard, KSC plays a crucial role in fostering the process of social innovation within an organization (Malik, 2022). Social innovation helps entrepreneurial firms in developing their brand image and reputation and attracting investors and customers, by differentiating their firms from other competitors. By dealing with societal challenges and enhancing society's well-being, entrepreneurial firms not only help in achieving operational and financial goals but also make a positive impact on the environment (Maziriri et al., 2024). However, the social innovation and entrepreneurial success relationship may face some trade-offs and challenges. In this regard, KSC plays a mediating role in dealing with these challenges. KSC encourages transparency and openness through collaboration, which helps in aligning the balance between entrepreneurial firms and social innovation (Ratten & Usmanij, 2021; Vavrek & Kovářová, 2021). Moreover, the continuous sharing of knowledge within the organizations will help to eradicate the risks linked with social innovations, thus creating success chances (Saeed et al., 2019). This discussion indicates that KSC has a positive impact and helps in making a strong and impactful relationship between these variables
Environmental innovation refers to the company's implementation focusing on environmental issues through innovative manufacturing processes, marketing, and products. It supports various innovative development of the latest technologies as well as sustainable and green strategies and practices. Cillo et al. (2022), highlighted that in past few years, the role of environmental innovation in the culture of knowledge sharing has gained huge attention, especially in the entrepreneurial sectors. Environmental innovation through fostering the exchange and collaboration of information and ideas among employees and organizations can have a significant impact on KSC. Environmental innovation encourages the coordination and collaboration between different stakeholders and partners including non-government, government, or business organizations. Chatterjee et al. (2022), determined that this coordination promotes knowledge sharing and builds openness and trust. Moreover, environmental innovation assists in the utilization of emerging and innovative technologies such as information communication technology, providing platforms for knowledge sharing and creating a positive impact. Further, with the help of environmental innovation, organizations are able to incorporate green and sustainable practices which benefit environment leading to the awareness of sustainability issues, hence, emphasizing the effective role of learning culture and knowledge sharing. This discussion above indicates that environmental innovation promotes knowledge sharing culture and exchange of ideas which help individuals to work together to deal with or tackle environmental or industrial issues (Al Shammre et al., 2023; Tajpour et al., 2023).
Previous studies done by the researcher have shown that a culture of knowledge sharing is crucial for the success of designing and implementing innovative ideas. Yang et al. (2018), highlight that environmental innovation assists in introducing innovative processes, technologies, or products that benefit environment. Environmental innovation and KSC can work together, leading to the success of enterprises. Environmental innovation increases efficiency, customer engagement, loyalty, and minimizes cost, and also helps in improving the company's brand image. Environmental innovation may face constraints due to a lack of knowledge sharing as knowledge sharing refers to practices, attitudes, and norms, thus supporting ideas and information sharing. Strong and effective knowledge-sharing leads to innovation, creativity, responsiveness, and agility in organizations (Hudáková et al., 2023; Yasir et al., 2023). For the success of entrepreneurial firms, employees must be well aware of the latest and innovative green practices to maintain the sustainability of the industry. Knowledge sharing helps organizations to understand the importance of environmental innovation for a competitive edge of the organizations. Knowledge sharing culture through open communication, continuous learning, collaboration, and recognition promotes environmental innovation which in return lead to firms’ success. From this discussion above it has been analysed that knowledge sharing act as a bridge and make the relationship strong between environmental innovation and entrepreneurial success (Ahmed et al., 2023; Shehzad et al., 2023).
Hypothesis 3 knowledge-sharing culture mediates the relationship between social innovation and entrepreneurial success.
Hypothesis 4 knowledge-sharing culture mediates the relationship between environmental innovation and entrepreneurial success.
Green volunteer behavior indicates the activities and practices related to environmental protection, conservation, and sustainability that individuals engage in voluntarily. These behaviors have a crucial impact on the KSC and entrepreneurial success. In entrepreneurial firms, where KSC is more prevalent, employees are encouraged to share or exchange their information, and ideas and collaborate, resulting in improved problem-solving capabilities and increased innovation. Arfi et al. (2018), mentioned that when employees and organizations are involved in green volunteer activities and practices, then they have the opportunity of collaborating outside of the workplace and develop relationships of trust and openness in society. Organizations that encourage green behavior determined the environmentally conscious and socially responsible image within the business environment. In short, the employees with green behavior have a keen interest in handling environmental consequences and KSC would help in promoting this behavior which leads to firms’ success.
Hypothesis 5 green volunteer behavior moderates the relationship between knowledge-sharing culture and entrepreneurial success.
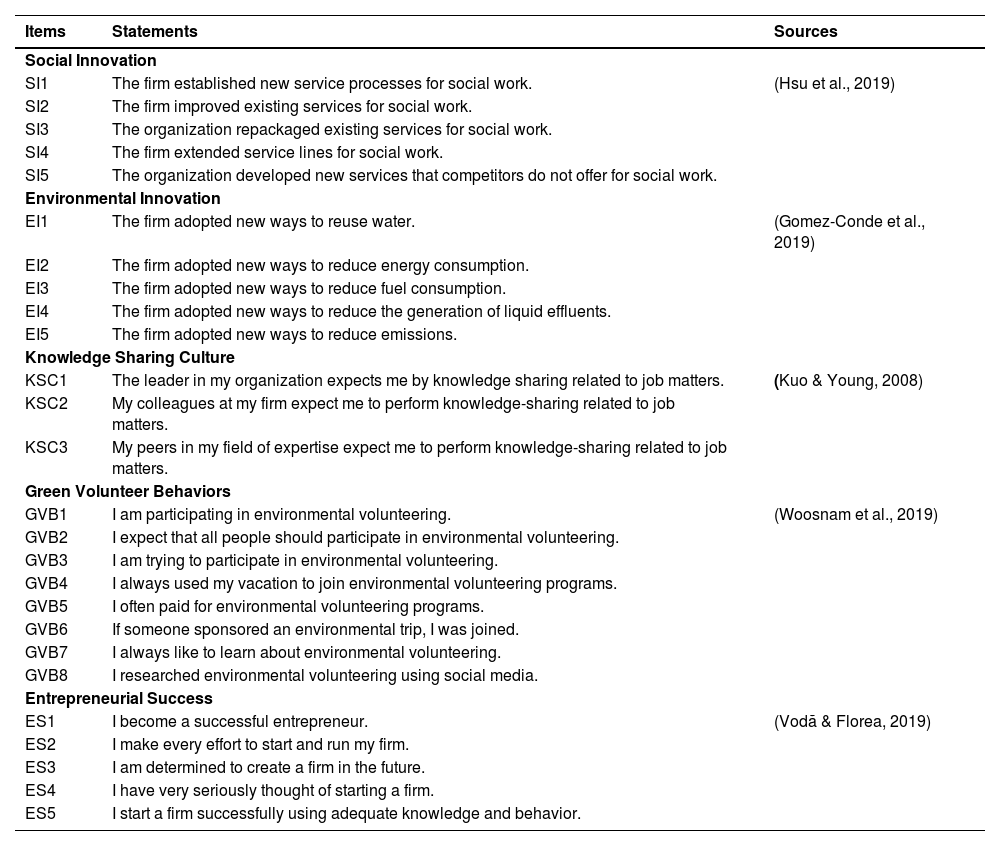
The research investigates the impact of social and environmental innovation on entrepreneurial success and also investigates the mediating role of knowledge-sharing culture. In addition, the research also analyses the moderating role of green volunteer behavior in the manufacturing industry of Vietnam. These surveys were taken from previous studies such as social innovation has five question statements adopted from Hsu et al. (2019), environmental innovation also has five question statements adopted from Gomez-Conde, Lunkes, and Rosa (2019), knowledge sharing culture have three question statements adopted from Kuo & Young (2008), green volunteer behavior has eight question statements adopted from Woosnam et al. (2019) and entrepreneurial success has five question statements adopted from Vodă & Florea (2019). These question statements are given in Table 1.
Measurement of the constructs
| Items | Statements | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Social Innovation | ||
| SI1 | The firm established new service processes for social work. | (Hsu et al., 2019) |
| SI2 | The firm improved existing services for social work. | |
| SI3 | The organization repackaged existing services for social work. | |
| SI4 | The firm extended service lines for social work. | |
| SI5 | The organization developed new services that competitors do not offer for social work. | |
| Environmental Innovation | ||
| EI1 | The firm adopted new ways to reuse water. | (Gomez-Conde et al., 2019) |
| EI2 | The firm adopted new ways to reduce energy consumption. | |
| EI3 | The firm adopted new ways to reduce fuel consumption. | |
| EI4 | The firm adopted new ways to reduce the generation of liquid effluents. | |
| EI5 | The firm adopted new ways to reduce emissions. | |
| Knowledge Sharing Culture | ||
| KSC1 | The leader in my organization expects me by knowledge sharing related to job matters. | (Kuo & Young, 2008) |
| KSC2 | My colleagues at my firm expect me to perform knowledge-sharing related to job matters. | |
| KSC3 | My peers in my field of expertise expect me to perform knowledge-sharing related to job matters. | |
| Green Volunteer Behaviors | ||
| GVB1 | I am participating in environmental volunteering. | (Woosnam et al., 2019) |
| GVB2 | I expect that all people should participate in environmental volunteering. | |
| GVB3 | I am trying to participate in environmental volunteering. | |
| GVB4 | I always used my vacation to join environmental volunteering programs. | |
| GVB5 | I often paid for environmental volunteering programs. | |
| GVB6 | If someone sponsored an environmental trip, I was joined. | |
| GVB7 | I always like to learn about environmental volunteering. | |
| GVB8 | I researched environmental volunteering using social media. | |
| Entrepreneurial Success | ||
| ES1 | I become a successful entrepreneur. | (Vodă & Florea, 2019) |
| ES2 | I make every effort to start and run my firm. | |
| ES3 | I am determined to create a firm in the future. | |
| ES4 | I have very seriously thought of starting a firm. | |
| ES5 | I start a firm successfully using adequate knowledge and behavior. | |
The respondents of the study were selected based on simple random sampling. The surveys were sent to the employers through emails and personal visits. Total 564 surveys to the employers, but only 294 were received and used for analysis. These valid responses have around 52.13 percent response rate. The study also applied PLS methodology to check the model reliability and validity. It is an effective data analysis tool for primary data analysis. The study also chose PLS-SEM method over others because it is an appropriate model to deal with complex models comprises of multiple constructs and indicators. PLS-SEM compared to SEM also offers simplified analysis and is less bothered by issues related to sample size (Ramli et al., 2018). Besides, normally-distributed data is not a requirement in case of PLS-SEM, hence, an appropriate choice for data set that deviates from normality. PLS-SEM also allows researchers to assess the relationship between constructs even with smaller sample size. Since, the method emphasizes on explained variance in exogenous variables, hence, useful for predictive purposes (Dash & Paul, 2021). Moreover, it checks the items as well as the variables’ correlation using measurement model assessment. Items correlation was examined with the help of factor loadings, and it should be larger than 0.50. Moreover, item correlation is also analysed with the help of composite reliability (CR), and it should be greater than 0.70. Additionally, item correlation is also investigated with the help of Alpha, and it should be higher than 0.70. Finally, the correlation of the items is also analysed with the help of average variance extracted (AVE), and it should be greater than 0.5
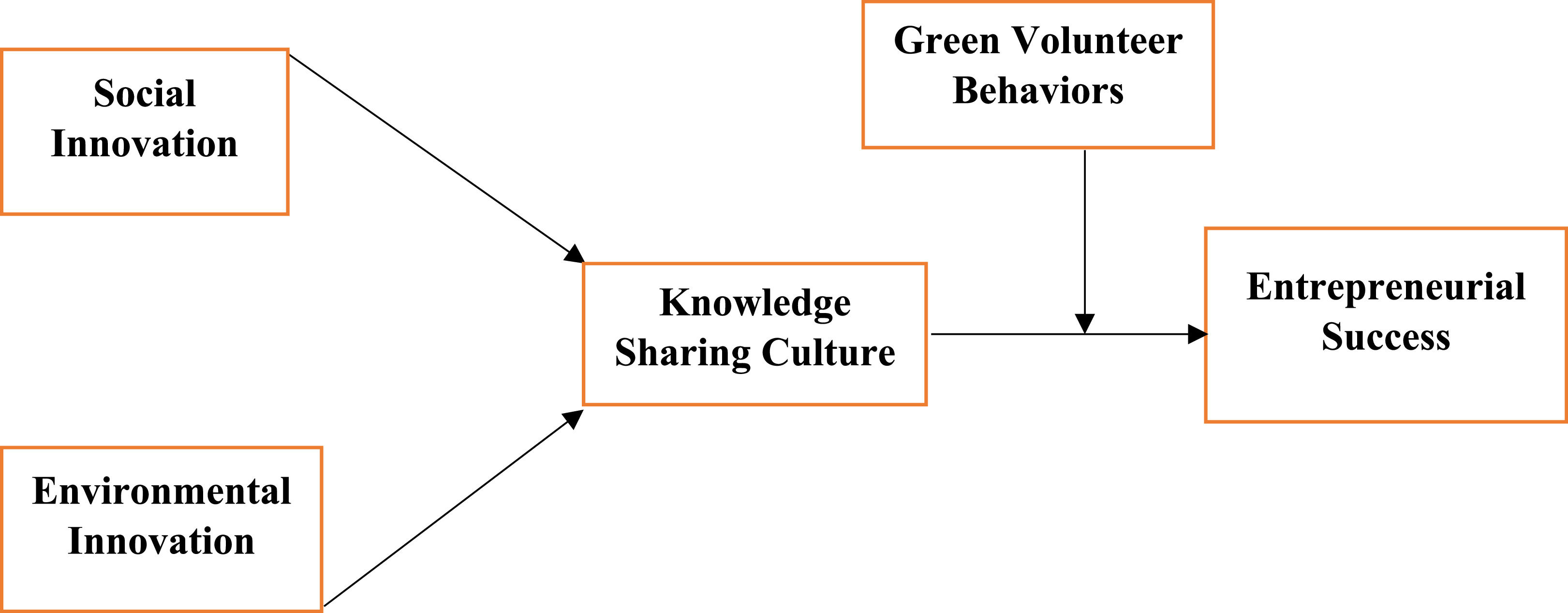
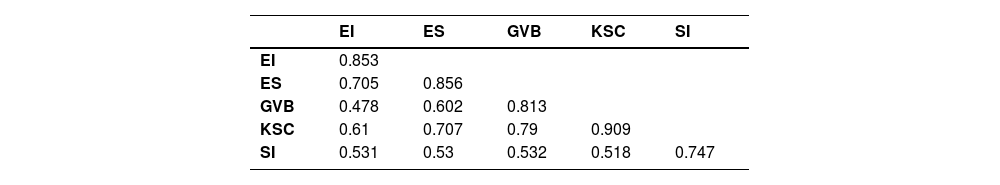
In contrast, the variables’ correlation was assessed via Fornell Larcker, and “the standard criterion is that the first value is larger than the other values in the same column.” Finally, it was also examined through Heterotrait Monotrait (HTMT). In addition, the association among variables has also been examined using structural model assessment. The linkage among constructs was examined using t- values that should be larger than 1.96 and p-values that should be lower than 0.05. Finally, the study used two independent variables, social innovation (SI) and environmental innovation (EI), while knowledge sharing culture (KSC) was used as a mediating variable, green volunteer behavior (GVB) was used as moderating variable, and entrepreneurial success (ES) used as the dependent variable (See fig. 1).
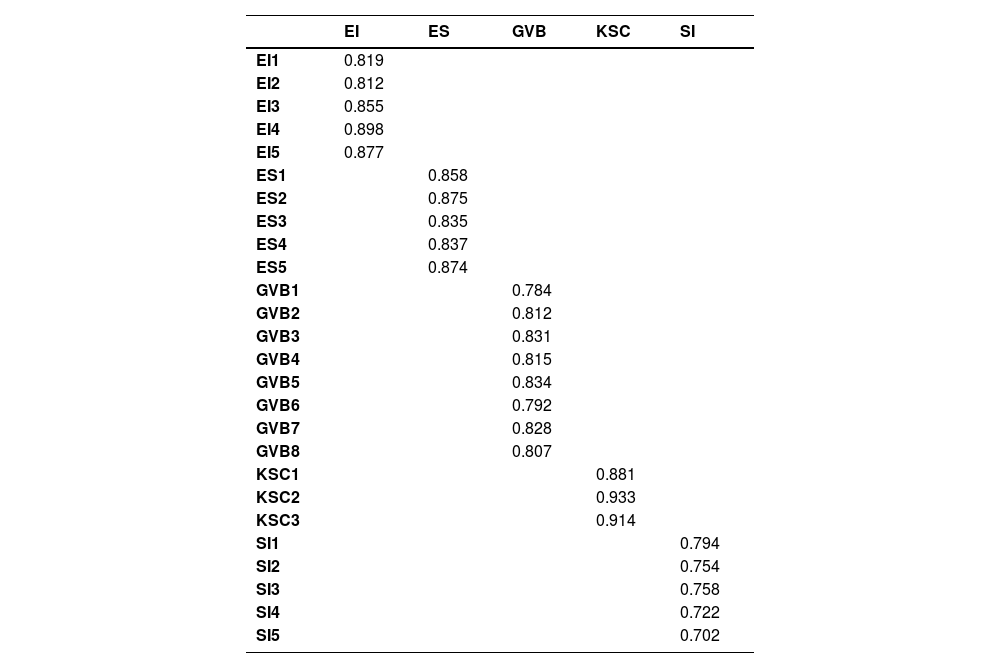
ResultsFindings of Table 2 show the correlation between items. Items correlation was examined with the help of factor loadings, and values are greater than 0.5. These outcomes show a high correlation among items.
In addition, the study findings show the correlation between items and are analysed with the help of CR, and values are larger than 0.70. Additionally, item correlation is also investigated with the help of Alpha, and values are larger than 0.70. Finally, item correlation is also analysed with the help of AVE, and values are larger than 0.50. These outcomes show a high correlation among items. These outcomes are mentioned in Table 3.
The outcomes of Fornell Larcker presented in Table 4 show a low correlation among variables.
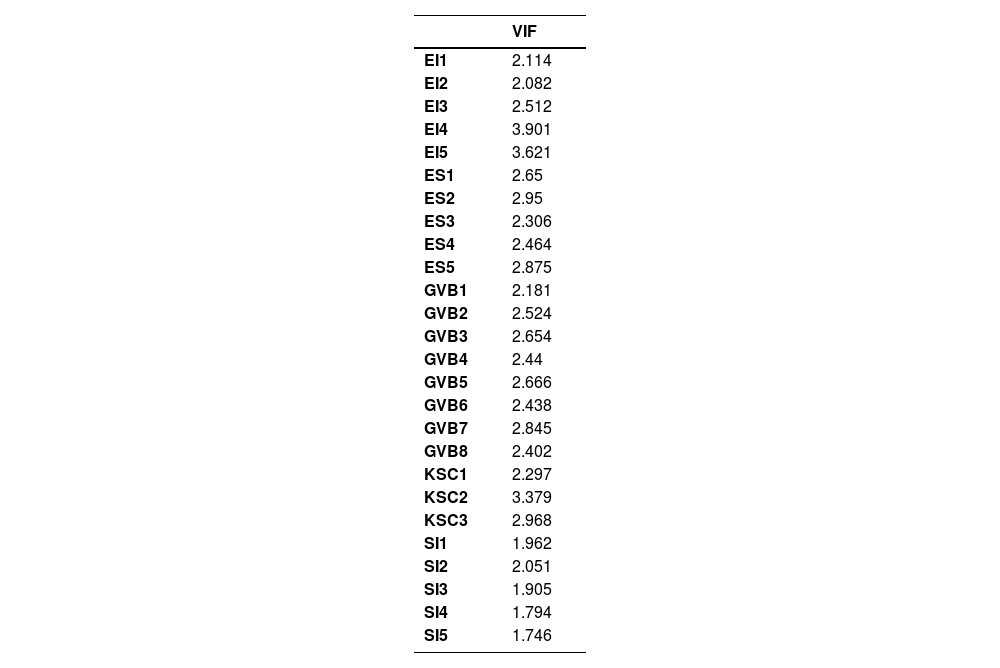
Test of variance inflation factors was also performed for the detection of multicollinearity. As the values of each variable's respective item is less than or equal to 3. So, it indicates that multicollinearity is not present in the data. Table 5 shows the VIF results.
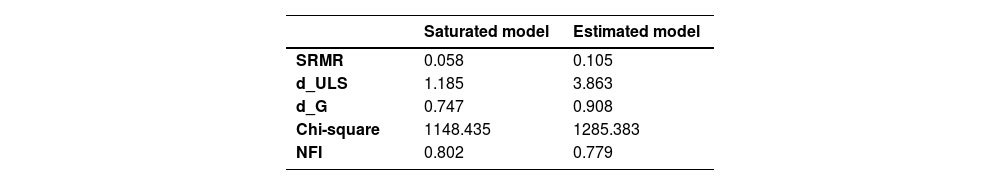
The researcher has also tested model fitness and the results have been reported in table 6. There were five indices in model fitness through which the results have been reported. Both the saturated and estimated model has depicted satisfactory values against all the indices including SRMR, d_ULS, d_D, Chi-square and NFI and it can be observed that the model is fit and significant therefore path analysis can be performed.
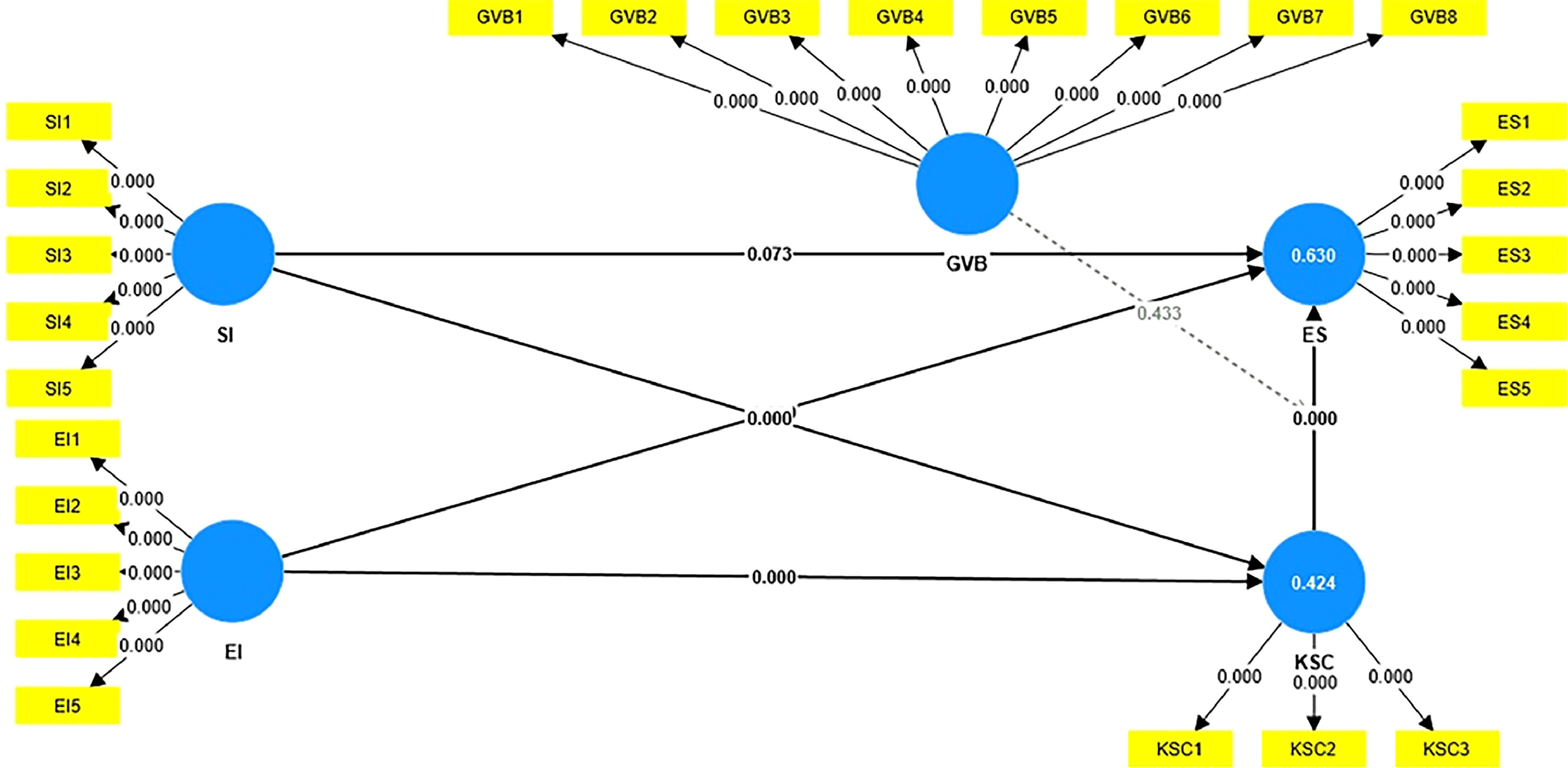
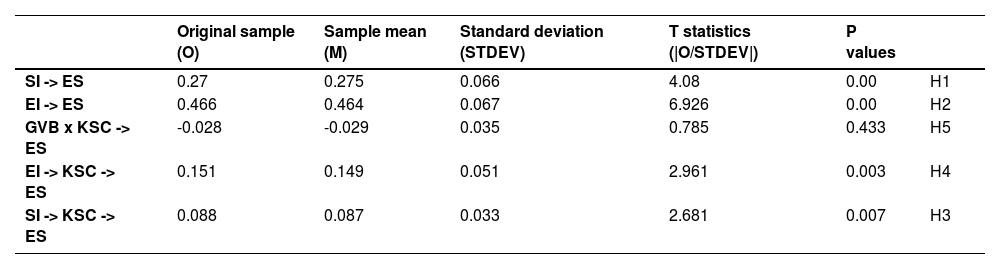
Table 7 depicts the results of different hypothesized paths including the direct and indirect effects. Results indicates that SI and EI significantly impacts entrepreneurial success, Therefore the hypothesis 1 and 2 have been accepted. P-values against the direct effects is 0.00 which shows the significant association among variables. The positive and significant association of SI with ES explains that social innovation addresses the societal needs through novel products/services or processes that allows existing markets to expand further. This not only stimulates sustainable growth but also ensure entrepreneurial success. The results also highlight that entrepreneur with social innovation creates value for businesses and society. Resulting in sustainable business model and long-term economic benefits. In addition to this, the positive and significant relationship between EI and ES also implies that entrepreneurs when integrate environmental innovation in their current business practices, they experience greater success. This is because enhanced competitive advantage, improved market position, long-term cost savings, high capital influx, less legal penalties and high profitability.
Path analysis
Results also depicts that GVB insignificantly moderates the relationship between KSC and ES. So, H5 has been rejected. The absence of moderating role of green volunteer behaviour indicates that even with a focus on environmental goal, green volunteer behavior seems to have no direct alignment with prompt business goals of entrepreneurial success. Hence, the chances are greater that it may dilute the effect of knowledge sharing culture on environmental success. Also, green volunteer behavior sometimes diverts the businesses’ resources from their core operations which could negatively affect the relationship between knowledge sharing culture and entrepreneurial success. The focus on sustainability over profitability due to volunteer behavior often reduce the effectiveness of knowledge sharing culture aimed at ES. A negative path coefficient also highlights other factors such as cultural mismatch that subdue the relationship of KSC with ES.
Findings also highlight the significant role of KSC as a mediator between EI, SI and ES, therefore H3 and H4 have been accepted. P-values for this relationship is 0.003 and 0.007 which meets the threshold criteria of significant probability values. Therefore, the mediating hypothesis have been accepted (See Fig. 2). Findings articulate the knowledge sharing culture partially mediates the relationship. A strong mediation case in the context of KSC indicates that sacred information and novel ideas linked to environmental and social innovation when easily float in environment, makes easier for entrepreneurs to leverage these ideas to achieve success. Knowledge sharing culture also encourage firms to be responsive and adaptable to embrace the change and new market trends. Hence, ensure the long-run success.
DiscussionsThe result has shown the positive role of social innovation in entrepreneurial success in the manufacturing industry of Vietnam. Social innovation has a distinctive characteristic from traditional business as it prioritizes social impact as many social innovations are designed and created to be economically viable, ensuring sustainability and long-term success. The previous study done by Arsawan et al. (2022) also highlights that social innovation has contributed to the awareness for firms to address more environmental and social challenges and focus on the resources and tools that enable organizations to develop innovative solutions. Moreover, the past research done by Wittmayer et al. (2019), also determined the significance of social innovation and how social innovation is transforming the business world. Social innovation can create a meaningful impact and is an important tool to tackle environmental challenges. By encouraging KSC, social innovation also encourages continuous development. Employees can have access to new perspectives and are encouraged to express themselves, leading to dynamic organizations. Roblek et al. (2019), also mentioned in their study that social innovation not transforms business practices but also induces positive changes in the environment. Social innovation would be able to promote the KSC only when the organizations can embrace the change and are willing to invest in the technologies that support KSC. In short, social innovation helps in promoting the culture of KS. Through collaboration, innovative technologies, transparency, and supporting continuous learning, social innovation assists entrepreneurial firms to become competitive and dynamic in the business world. The results have also shown a positive role environmental innovation in promoting the entrepreneurial success in the manufacturing industry of Vietnam. Consistent with literature, Fernando et al. (2019), also highlighted the importance of environmental innovation. Environmental innovation refers to the development of innovative technologies, the circular economy adoption, or implement green practices. As environmental innovation is more concerned with sustainable practices, it also encourages the KSC. As environmental innovation is significant in combating environmental challenges which can be done when organizations have knowledge sharing culture, information, and ideas. With KSC, employees feel empowered and able to express their ideas which in turn leads to the success of the entrepreneurial firms.
The result showed the positive role of KSC in entrepreneurial success. Prior study of Oyemomi et al. (2019), also supports the findings. Organizations having strong KSC will help in making the organizations successful. When organizations promote KSC, employees would able to share their views, knowledge, information, and ideas, thus providing innovative solutions. KSC provides collaboration, open communication, continuous learning, trust, and empowerment within the organizations. All these factors not only make the entrepreneurial firms of the manufacturing industry successful but also help them in earning competitive edge. Findings confirmed that knowledge-sharing culture is a significant mediator between social innovation and entrepreneurial success. It has been concluded from our research that a strong KSC facilitates social innovation to gain the firm's goals and at the same time, helps to tackle all the challenges in the industry. KSC through various pieces of training, leadership guidance, and online webinars helps in assisting the social innovation and entrepreneurial firms’ success.
Findings confirmed the positive mediating impact of KSC between environmental innovation and entrepreneurial success. In our study, it has been concluded that KSC and environmental innovation can work together for the success of entrepreneurship. In the past few years, sustainability has gained huge attention worldwide, so entrepreneurial organizations must manage their brand image with the help of green practices. Through KSC, new and innovative solutions can be designed which tackle the challenges of the environment. In this current era, for the success of entrepreneurial firms, organizations need to implement sustainable practices in their business operations. It has been concluded from our result that KSC not only facilitates environmental innovation but also leads to the success of the organizations. As far as the moderating hypothesis is concerned, results depicted that green volunteer behaviour is an insignificant moderator between knowledge sharing and entrepreneurial success. Although, it can be considered that knowledge sharing culture within a business can directly leads to entrepreneurial success (Audretsch et al., 2020; Laily & Ernawati, 2020). A firm promoting a learning culture within its business can expect the employees to grow by learning and development, thereby leading to entrepreneurial success.
Theoretical implicationEntrepreneurship has gained huge attention from the business world in the past few years because it has been considered a significant engine for innovation and growth in new business ventures and driving economic development. In Vietnam, entrepreneurship has a significant role in developing the manufacturing industry. In Southeast Asia, Vietnam is considered one of the fastest-growing economies, and the sector of manufacturing is helping the country to achieve this success. The manufacturing sector of the country has seen a remarkable transformation in the past few years, with entrepreneurship being a crucial driver of this growth. However, the entrepreneurial sectors of Vietnam are still facing some challenges which can be tackled through this model. In this study, the role of social innovation and environmental innovation in KSC is studied and it has been analyzed how these variables encourage and promote the KSC which then helps the organizations to make them successful. This study also investigates the impact of KSC on entrepreneurial success. Further, this paper also studies the mediating role of KSC between social innovation, environmental innovation, and entrepreneurial success. Further, this study also analyses the moderating role of green volunteer behavior between KSC and entrepreneurial success. In the past, no future research has been conducted on the entrepreneurial firms of the manufacturing sector of Vietnam. The manufacturing sector of the industry is still facing some challenges in entrepreneurial firms and this study will not only help them in highlighting the factors which contribute to their success but also provide assistance in making the environment sustainable by utilizing green behavior. As the manufacturing industry of Vietnam is also facing a sustainability crisis, this study will surely help the industry tackle environmental issues.
Managerial implicationsIn the past few years, entrepreneurial firms have gained huge attention worldwide. Not only the population of the world is increasing but also the job crisis and environmental issues have been raised. To overcome these issues, entrepreneurship and green practices have been encouraged and motivated. Government, policy-making, and regulatory bodies are encouraging industries to focus on new and innovative business ventures who are not on environmentally friendly but also create jobs for people. In Vietnam, the manufacturing industry is one of the biggest contributors to economic development. Entrepreneurship has played a significant role in transforming the manufacturing industry of Vietnam, by designing and producing innovative solutions, improving productivity, and enhancing economic growth. Vietnam's government has taken measures in creating a supportive environment for new business ventures. These measures include providing financial support, legal framework, and streamlining administrative processes for entrepreneurs but still, entrepreneurial firms are facing a lot of challenges to sustain in the market. This paper provides guidelines for managers, policymakers, and industrialists regarding the success of entrepreneurial business firms. This study determined the positive role of social innovation and environmental innovation in KSC. Social and environmental innovation not only motivates the KSC but also helps the workers to share and exchange their information, helping the firms in creating innovative solutions. Further, this study also highlights the mediating role of KSC between social innovation, environmental innovation, and entrepreneurial success. Organizations with a culture of knowledge sharing, develop openness, trust, and transparency among individuals and organizations. Everyone has their capabilities, skills, and ideas, and sharing them will help the firms to provide solutions to the crisis which the industry is facing. Further, this study also investigates the moderating role of green volunteer behavior between KSC and entrepreneurial success. Green behavior is very crucial to tackle the negative impact produced by manufacturing firms on the environment. The research guides the policymakers in making policies related to entrepreneurial success using a knowledge-sharing culture and social and environmental innovation. Green behavior encourages workforce to work with affirmation and share their information to tackle the environmental crisis. This behavior not only maintains the brand image but also helps the firms to gain a competitive edge, resulting in the success of the firms.
ConclusionTo increase resiliency, connectivity among supply chains, and diversity as well as less dependence on any specific country in the global business, Vietnam is becoming one of the best destinations for manufacturing investment because of its production costs, strategic location, competitive labour, and shipping advantages. However, entrepreneurship is a huge contributor to the success of the manufacturing industry of Vietnam. Entrepreneurship has significant importance in the development of small and medium enterprises. SMEs are considered the key driver for the manufacturing sector, thus promotes economic growth. Entrepreneurs with the help of innovative and creative ideas led to the development of new services and products and improving the existing market. In Vietnam, entrepreneurs use their creativity to tackle environmental issues that the country is facing due to increased business activities. Governments are taking initiatives to encourage and motivate individuals to move towards entrepreneurship with green practices. They are also providing financial assistance and legal support to these new and innovative business ventures. However, entrepreneurial organizations are still experiencing issues and this paper made an attempt to address such challenges.
As has been discussed earlier, that green behavior culture assists organizations to adopt green practices to tackle the negative environmental crisis. The manufacturing industry of Vietnam has created a lot of environmental damage in the country, so it is important for organizations to have green practices, thus minimizing the use of hazardous materials and proper utilization of natural resources. Further, organizations having a strong culture of knowledge sharing will help the firms to succeed, as all the employees have their thinking, skills, and knowledge. By exchanging their information and ideas, it will develop an environment of trust and openness which lead to the development of innovative solutions. Employees in such a culture also feel a sense of acknowledgment and empowerment, encouraging and motivating them to fully participate in the success of the country. Since, it has also been confirmed that knowledge sharing culture mediates the relationship of social and environmental innovation with entrepreneurial success, therefore, firms are advised to promote the culture where knowledge can be floated without any restriction. This allows individuals to nurture the growth of innovative ideas, eventually leading to entrepreneurial success. Development of training programs aimed at social and environmental innovation also help individuals to build understanding regarding the significance of such aspects that are crucial to have lasting impact on business. Taking advantage of advanced technology on entrepreneurial platforms means promoting collaborative tools that allows individuals to share creative ideas, thus, adding their significant part into entrepreneurial success. The direct association of social and environmental innovation with entrepreneurial success also indicates that this kind of innovations not only addresses societal and environmental challenges but also ensures firm success. Thus, SMEs should integrate these innovations with their core operations as it would not optimize their environmental resource to reduce the risk of legal challenges and potential challenges but also helps in building a strong relationship with stakeholders. Hence, implementing such practices help manufacturing SMEs of Vietnam to take maximum leverage of these benefits to achieve success that is already evident in the study findings. The insignificant role of green volunteer behaviour as moderator also offers guidelines. The absence of moderation suggests the need of re-assessing the type green volunteer activities. Because their alignment with core business strategies decides the fate of positive entrepreneurial outcomes. These findings also guide entrepreneurs to reconsider the allocation of resources dedicated to the activities that are directly related to knowledge sharing culture and entrepreneurial success. Since negative path coefficient highlight that green volunteer rather seems to be a burden, therefore, it is necessary for organization to closely evaluate their structured patterns because if they are deviating from primary business objectives, then they are distraction for the organization rather than a value-adding element. By considering these suggestions, firms are able to navigate the complex mechanism of green volunteer behaviour with the assurance of entrepreneurial success.
This study has some limitations which should be addressed in future studies. First, this study has analysed the impact of variables such as social innovation and environmental innovation on knowledge-sharing culture. In the future, more variables such as product innovation, and green innovation can also be used in the study to determine their role and impact on knowledge-sharing culture. Second, this study has only used one mediator such as knowledge sharing culture between social innovation, environmental innovation, and entrepreneurial success. However, knowledge adoption, knowledge creation, and application of knowledge can also be used as mediators, in the future to study their impact on entrepreneurial success. Third, in this paper, only one moderator such as green volunteer behavior is used between entrepreneurial success and KSC. However, more moderators such as green practices, and green human resource management can also be used to study their moderating impact on KSC and entrepreneurial success. Last, this research has been conducted on the manufacturing industry of developing countries which might not apply to developed countries. In the future, this model can be used to study developed countries and other industries such as services can also be used to study these variables.
CRediT authorship contribution statementChia-Yang Lin: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology. Ka Yin Chau: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Massoud Moslehpour: Project administration, Supervision, Validation.