Efficacy of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in combination with renin–angiotensin-system (RAS) blockers for CKD remains controversial. We conducted this meta-analysis to explore the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors combining with RAS blockers on cardiovascular outcomes in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
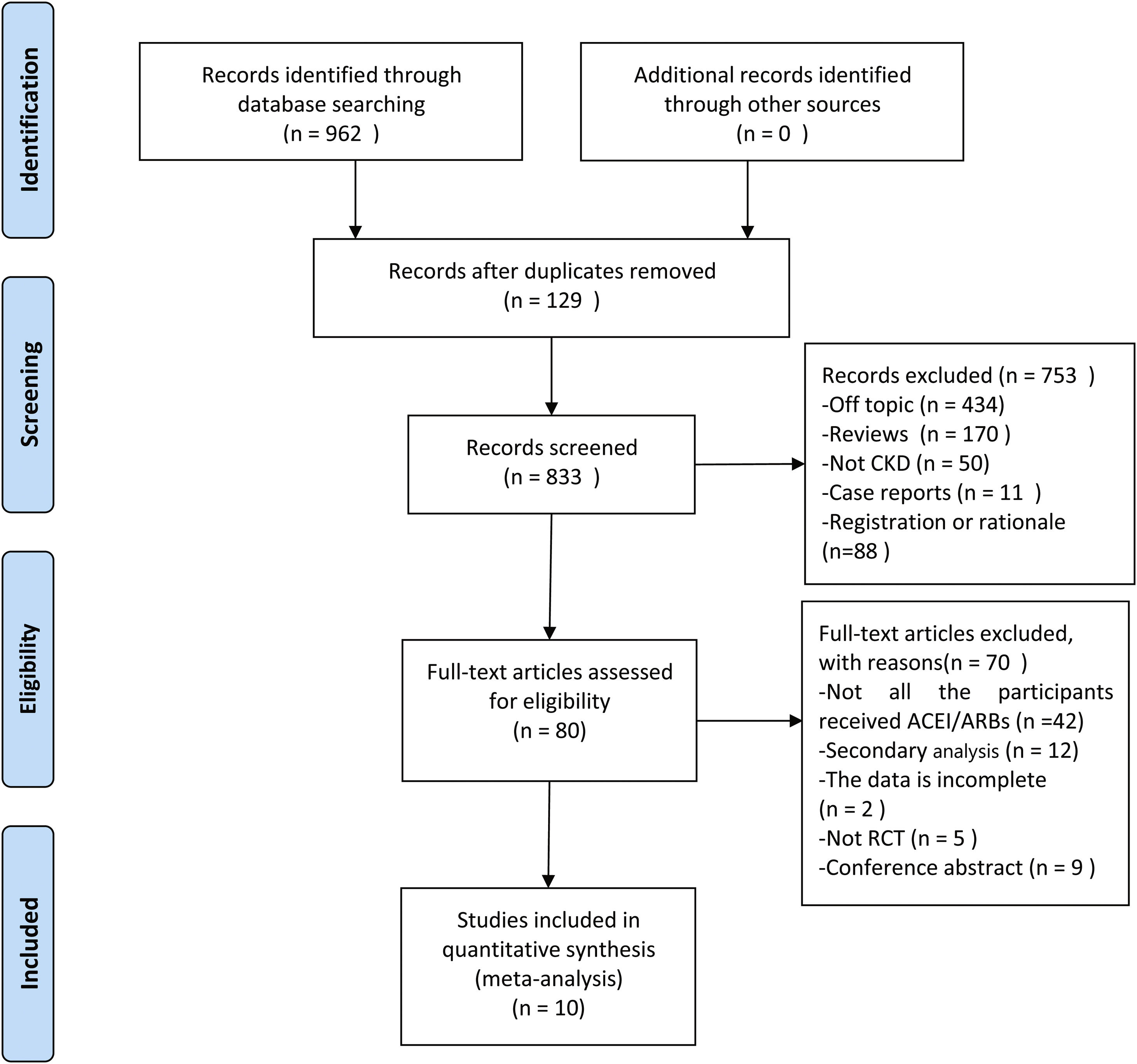
MethodsWe searched Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases with the following keywords.
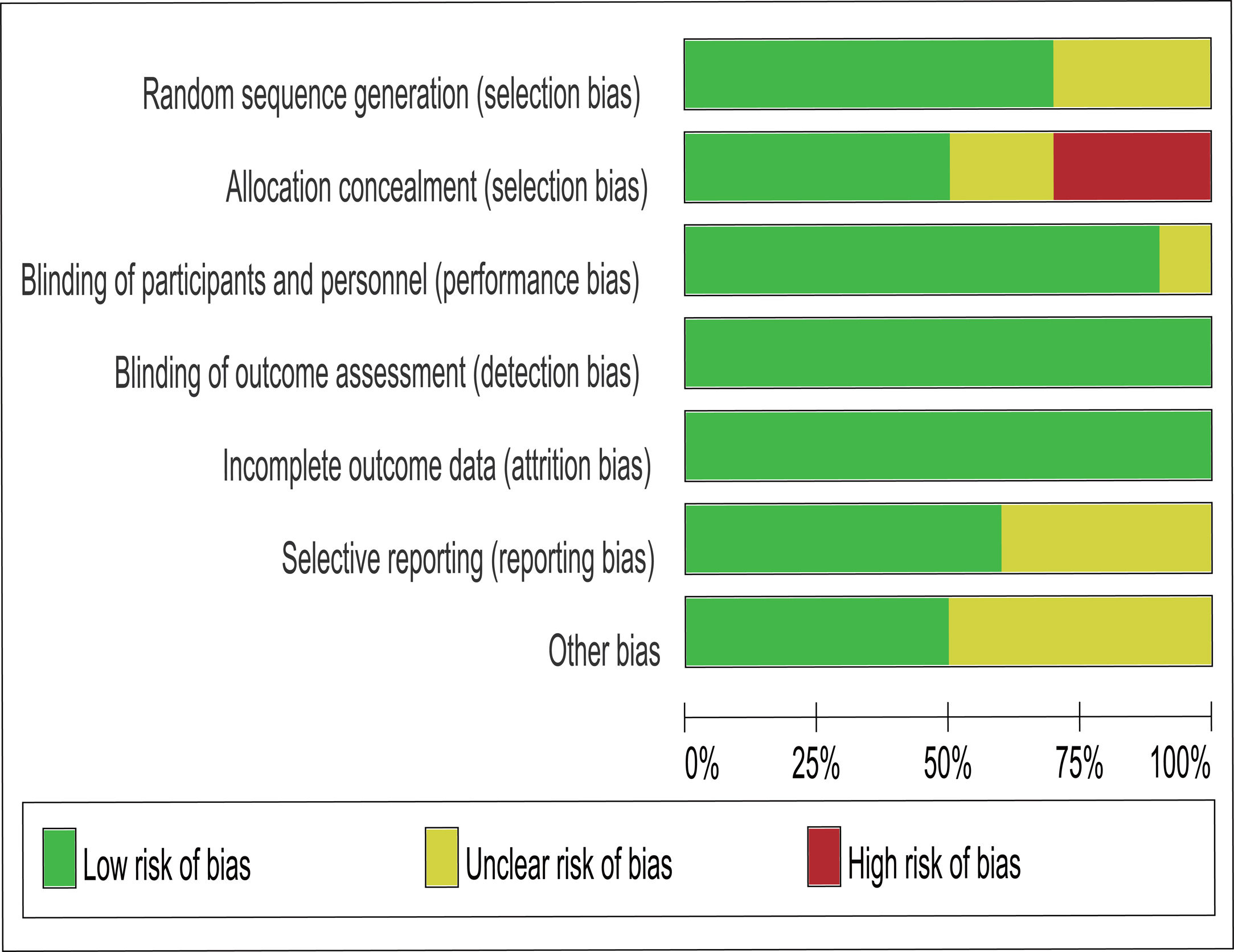
“Renal Insufficiency, Chronic” or “Diabetic Nephropathies” and “Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors”. We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) based on angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) or angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) therapy. The outcome events included cardiac and renal outcomes and other adverse events. This study is registered with PROSPERO: CRD42020218337.
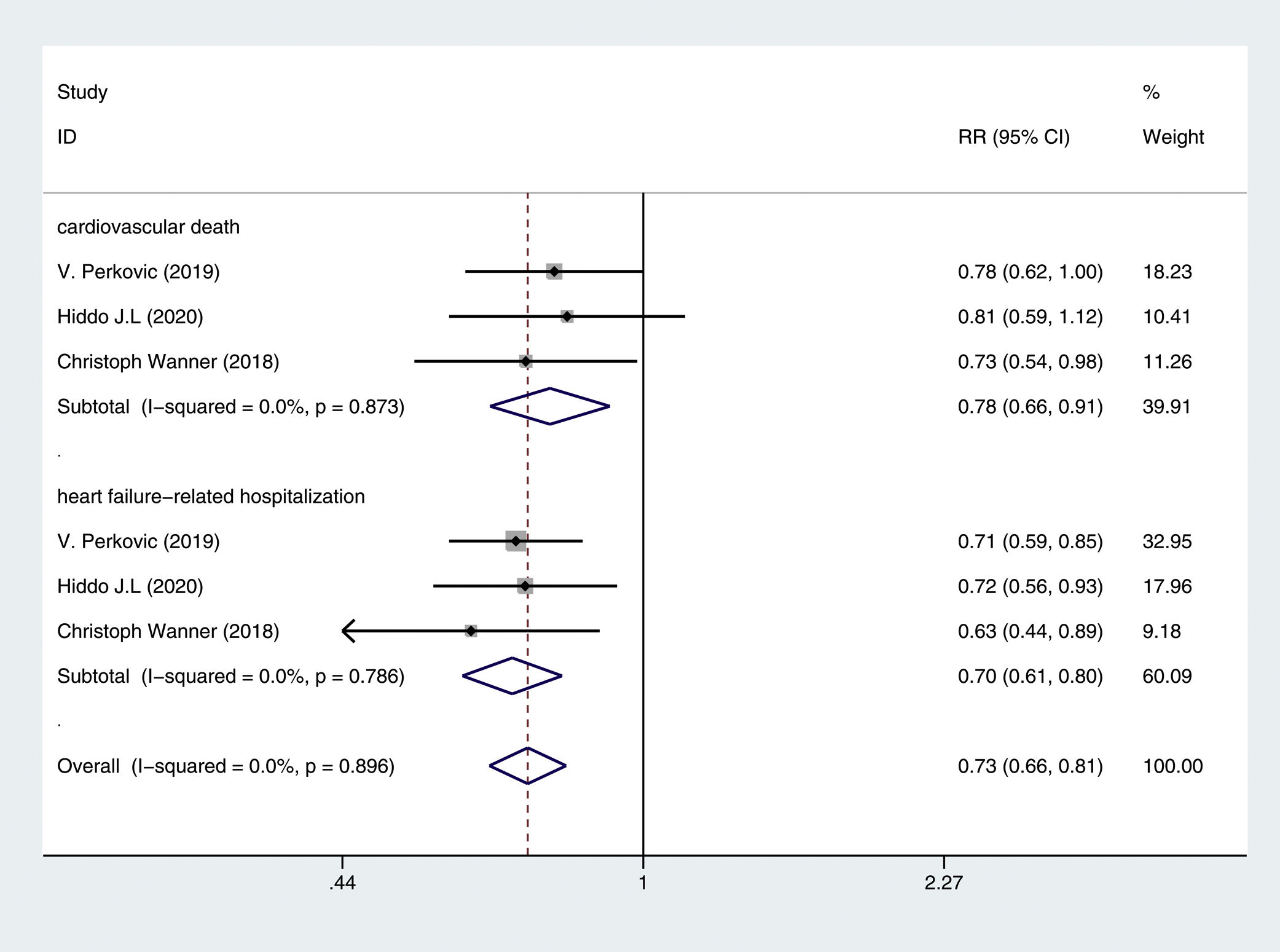
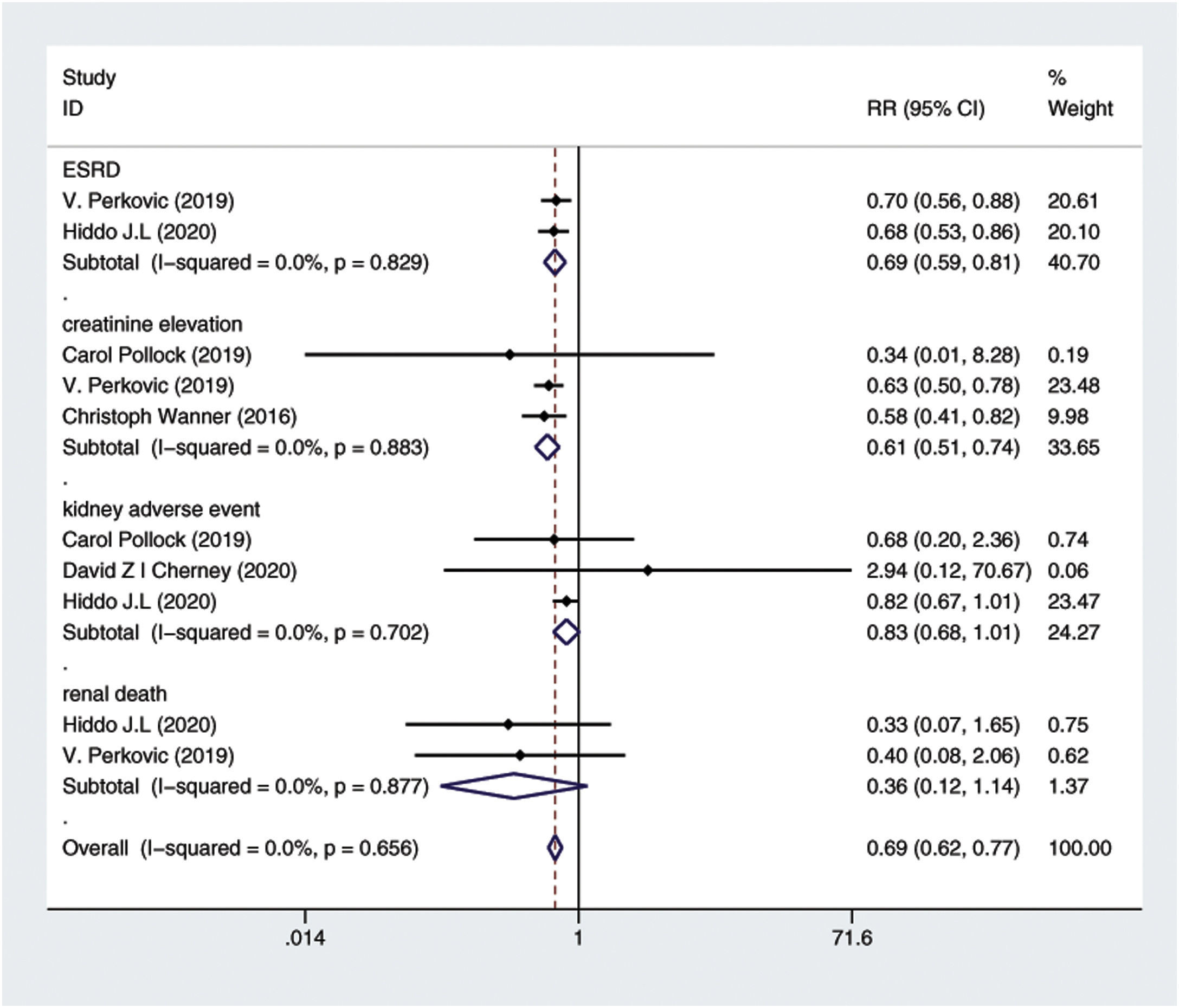
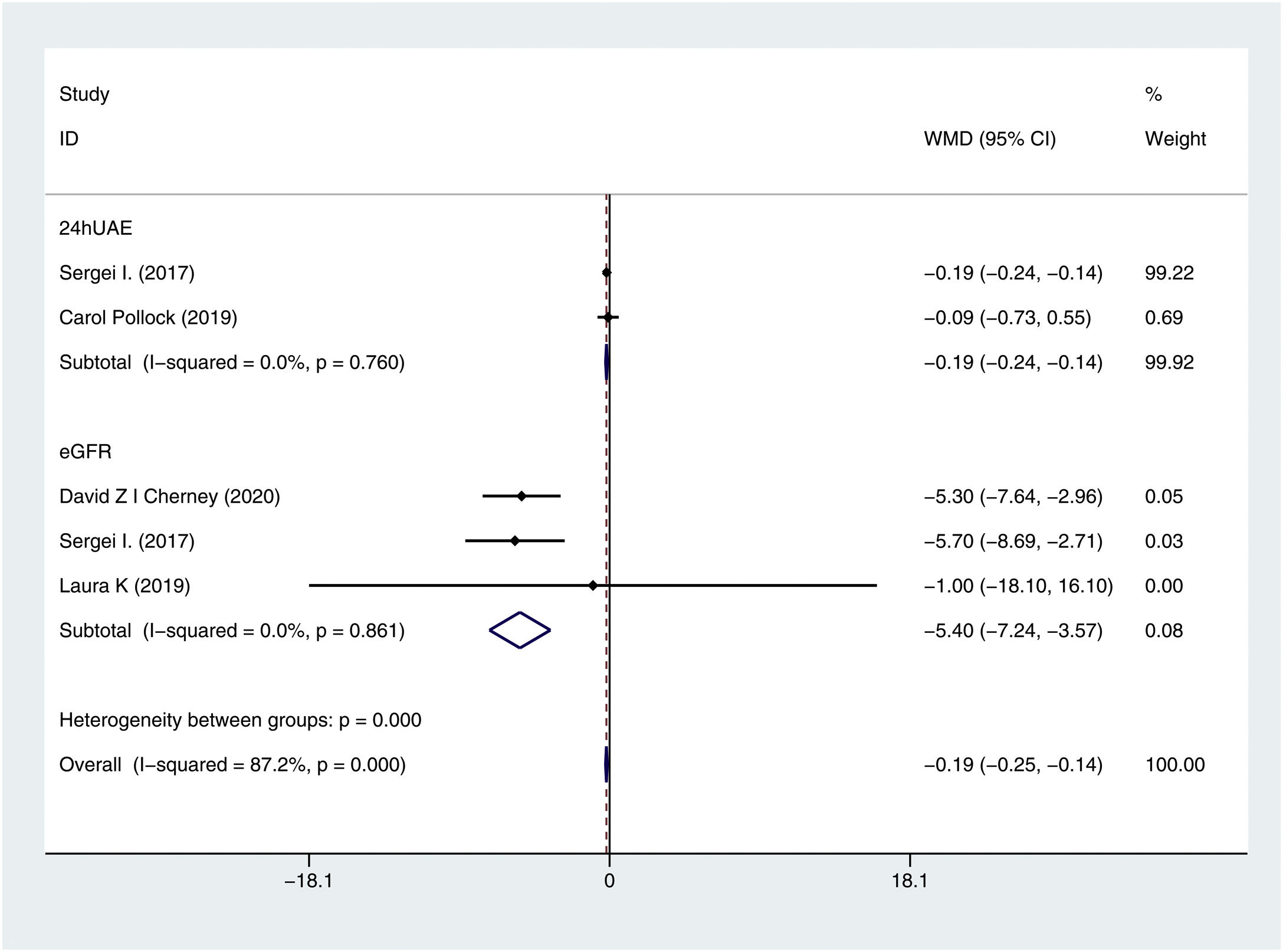
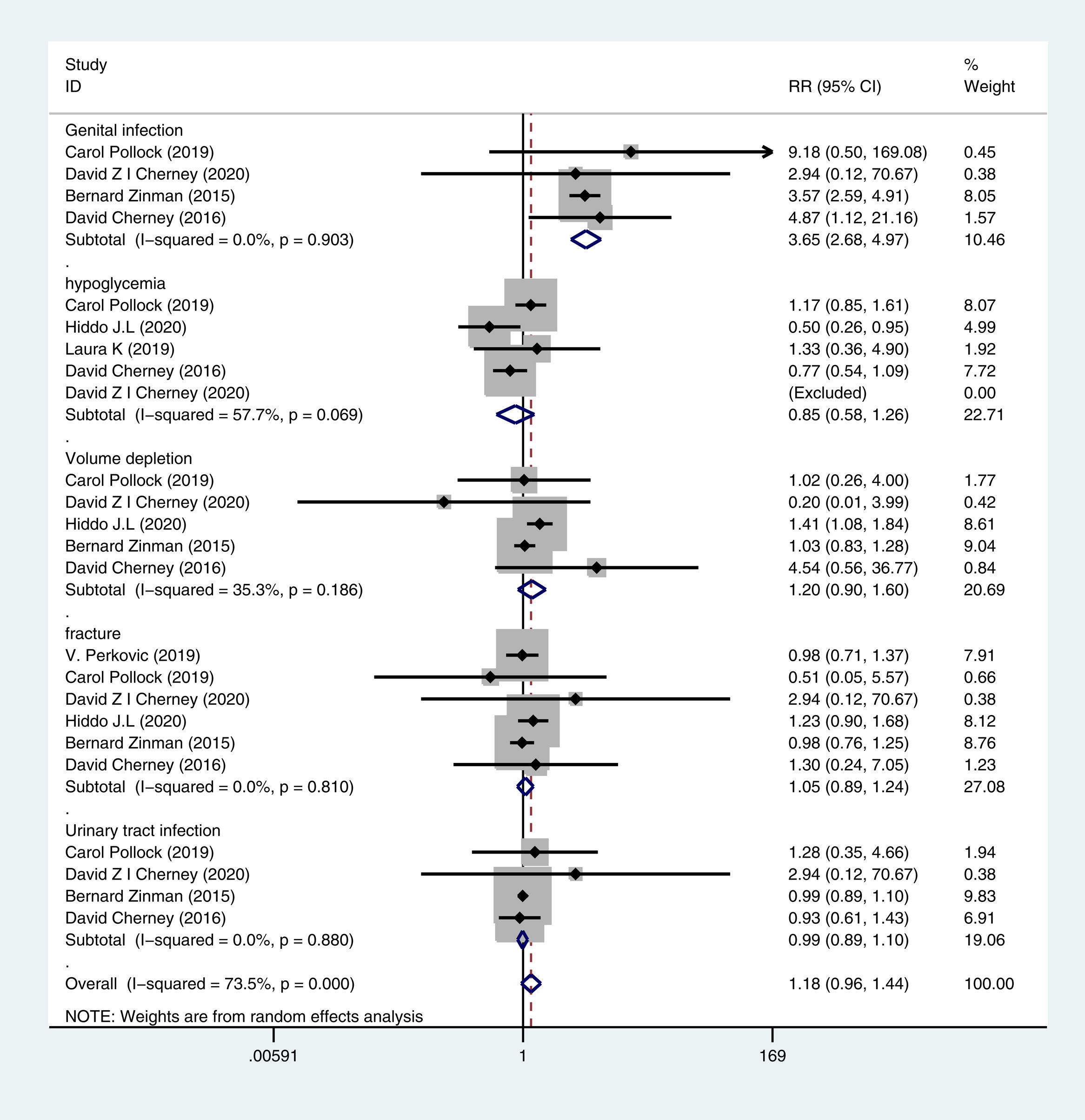
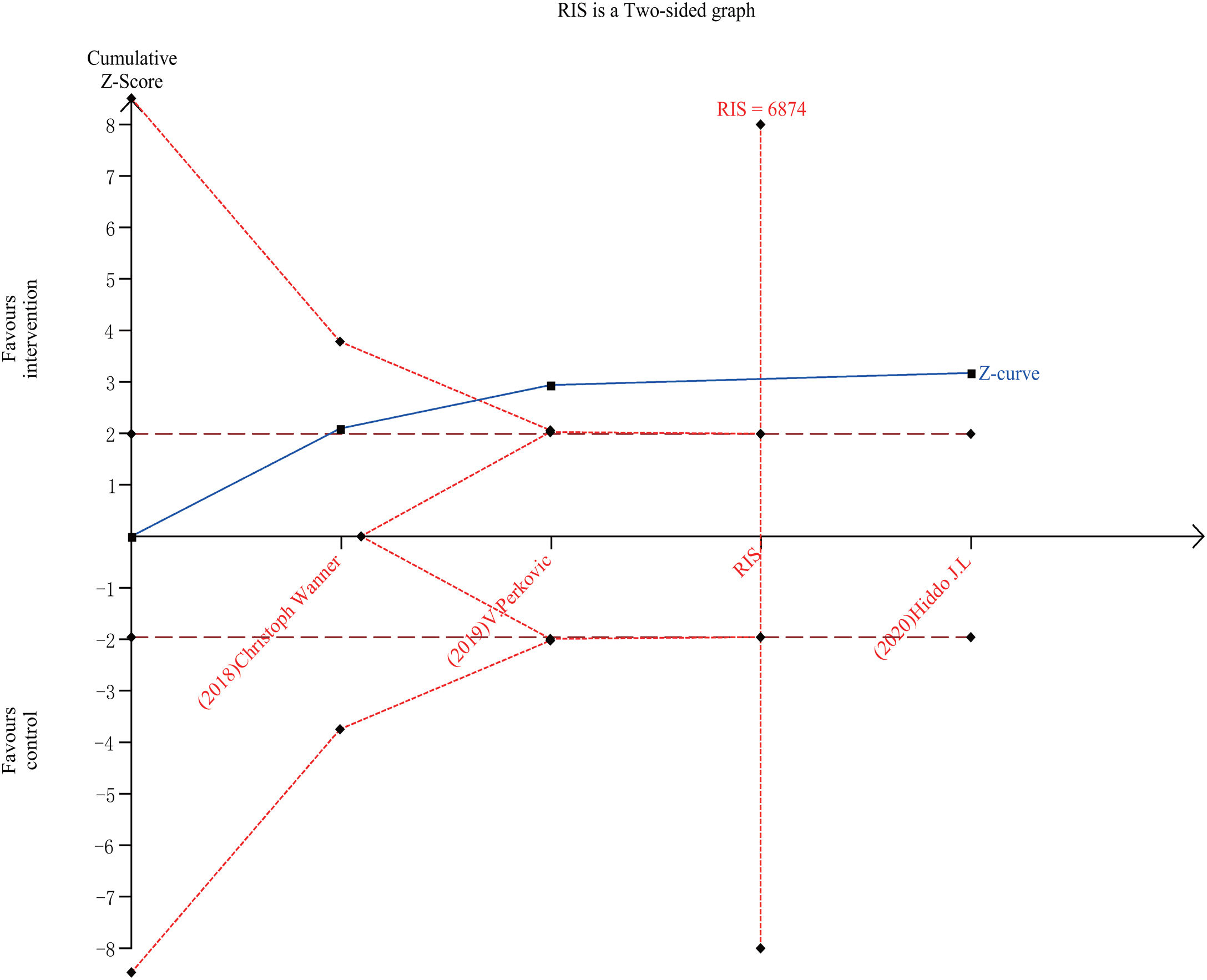
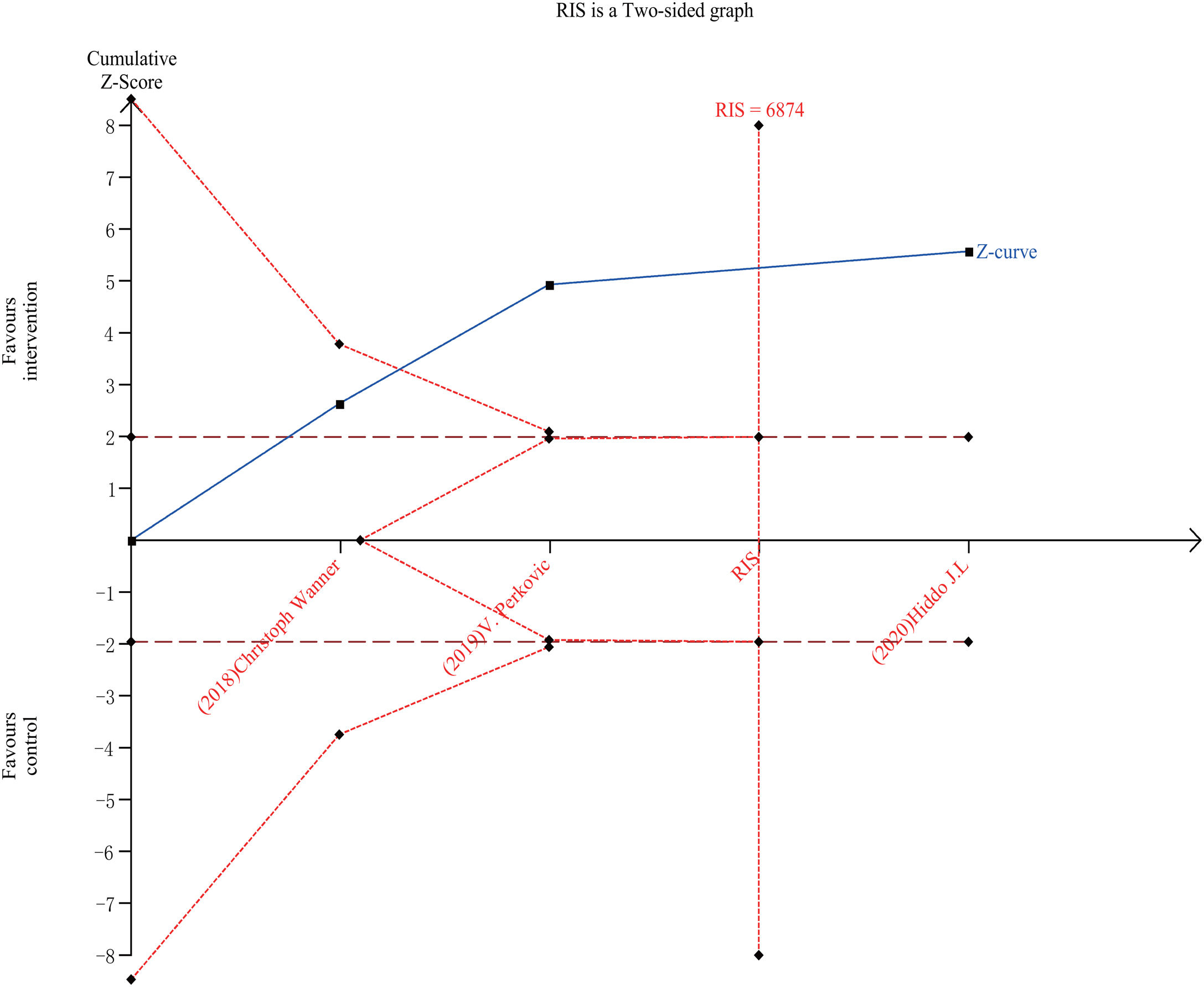
ResultsTen RCTs including 16,983 CKD patients met the inclusion criteria. Compared with placebo plus RAS blockers, SGLT2 inhibitors plus RAS blockers significantly reduced cardiovascular mortality and heart failure-related hospitalization rates (RR=0.78, 95% CI: 0.66–0.91, p=0.002; RR=0.7, 95% CI: 0.61–0.8, p=0.000). We also performed trials sequential analysis (TSA) and the results indicated that our results are reliable. Additionally, it significantly reduced the 24-h urinary albumin excretion rate (24hUAE) and the creatinine elevation rate (WMD=−0.19, 95% CI: −0.24 to −0.14; RR=0.61, 95% CI: 0.51–0.74, p=0.000), delayed progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (RR=0.69, 95% CI: 0.59–0.81, p=0.000). Further, it had no significant effect on the incidence of renal-related adverse events or renal-related mortality. Although it decreased the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (WMD=−5.4, 95% CI: −7.24 to −3.57), this effect was reversible.
ConclusionsThese data provide a well-document testimonial of the benefits of the combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors and RAS blockers for cardiovascular and renal outcomes in CKD patients.
La eficacia de los inhibidores del cotransportador de sodio-glucosa 2 (SGLT2) en combinación con los bloqueadores del sistema renina-angiotensina (SRA) para la enfermedad renal crónica (ERC) sigue siendo controvertida. Se realizó este metaanálisis para explorar el efecto de los inhibidores del SGLT2 en combinación con los bloqueadores del SRA sobre los resultados cardiovasculares en los pacientes con ERC.
MétodosSe realizaron búsquedas en las bases de datos Embase, PubMed, Web of Science y Cochrane Library con las siguientes palabras clave: «Renal Insufficiency, Chronic» o «Diabetic Nephropathies» y «Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors». Se incluyeron ensayos controlados aleatorios (ECA) basados en el tratamiento con inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina (IECA) o bloqueadores de los receptores de la angiotensina II (BRA). Los eventos de resultado incluyeron resultados cardíacos y renales y otros eventos adversos. Este estudio está registrado en PROSPERO: CRD42020218337.
ResultadosDiez ECA que incluían 16.983 pacientes con ERC cumplieron los criterios de inclusión. En comparación con el placebo más bloqueadores del SRA, los inhibidores de SGLT2 más bloqueadores del SRA redujeron significativamente la mortalidad cardiovascular y las tasas de hospitalización relacionadas con la insuficiencia cardíaca (RR=0,78; IC del 95%: 0,66 a 0,91; p=0,002; RR=0,7; IC del 95%: 0,61 a 0,8; p=0,000). También se realizó un análisis secuencial de ensayos (TSA) y los resultados indicaron que nuestros resultados son fiables. Además, redujo significativamente la tasa de excreción urinaria de albúmina en 24h (24h UAE) y la tasa de elevación de creatinina (DMP=−0,19; IC del 95%: −0,24 a −0,14; RR=0,61; IC del 95%: 0,51 a 0,74; p=0,000), retrasó la progresión a la enfermedad renal terminal (ESRD) (RR=0,69; IC del 95%: 0,59 a 0,81; p=0,000). Además, no tuvo un efecto significativo sobre la incidencia de eventos adversos relacionados con el riñón o la mortalidad relacionada con el riñón. Aunque disminuyó la tasa de filtración glomerular estimada (TFGe) (DMP=−5,4; IC del 95%: −7,24 a −3,57), este efecto fue reversible.
ConclusionesEstos datos proporcionan un testimonio bien documentado de los beneficios del uso combinado de inhibidores de SGLT2 y bloqueadores del SRA para los resultados cardiovasculares y renales en pacientes con ERC.