La hipertensión arterial pulmonar (HAP) es una enfermedad grave y progresiva, con elevada mortalidad. El diagnóstico precoz e inicio de tratamiento temprano mejora el pronóstico. Los pacientes con esclerodermia tienen riesgo elevado de desarrollar HAP. La única estrategia de cribado establecida y validada (ecocardiograma y/o algoritmo DETECT) reconoce la enfermedad cuando ya está avanzada, a pesar de encontrarse en una fase preclínica. La ergoespirometría (CPET) detecta afectación vascular pulmonar en fases más precoces.
MétodosEstudio prospectivo de los 52 pacientes consecutivos diagnosticados de esclerodermia en nuestra área sanitaria, durante 2 años (2018 y 2019). A todos se les realizó CPET, además del cribado sistemático anual. Se comparó la sensibilidad para detectar HAP del cribado actual frente a la CPET. Para confirmar la presencia de HAP se realizó un cateterismo cardiaco derecho (CCD). En caso de mantener la sospecha de HAP en CPET, pero con CCD en reposo no confirmatorio, se continuó con CCD de esfuerzo.
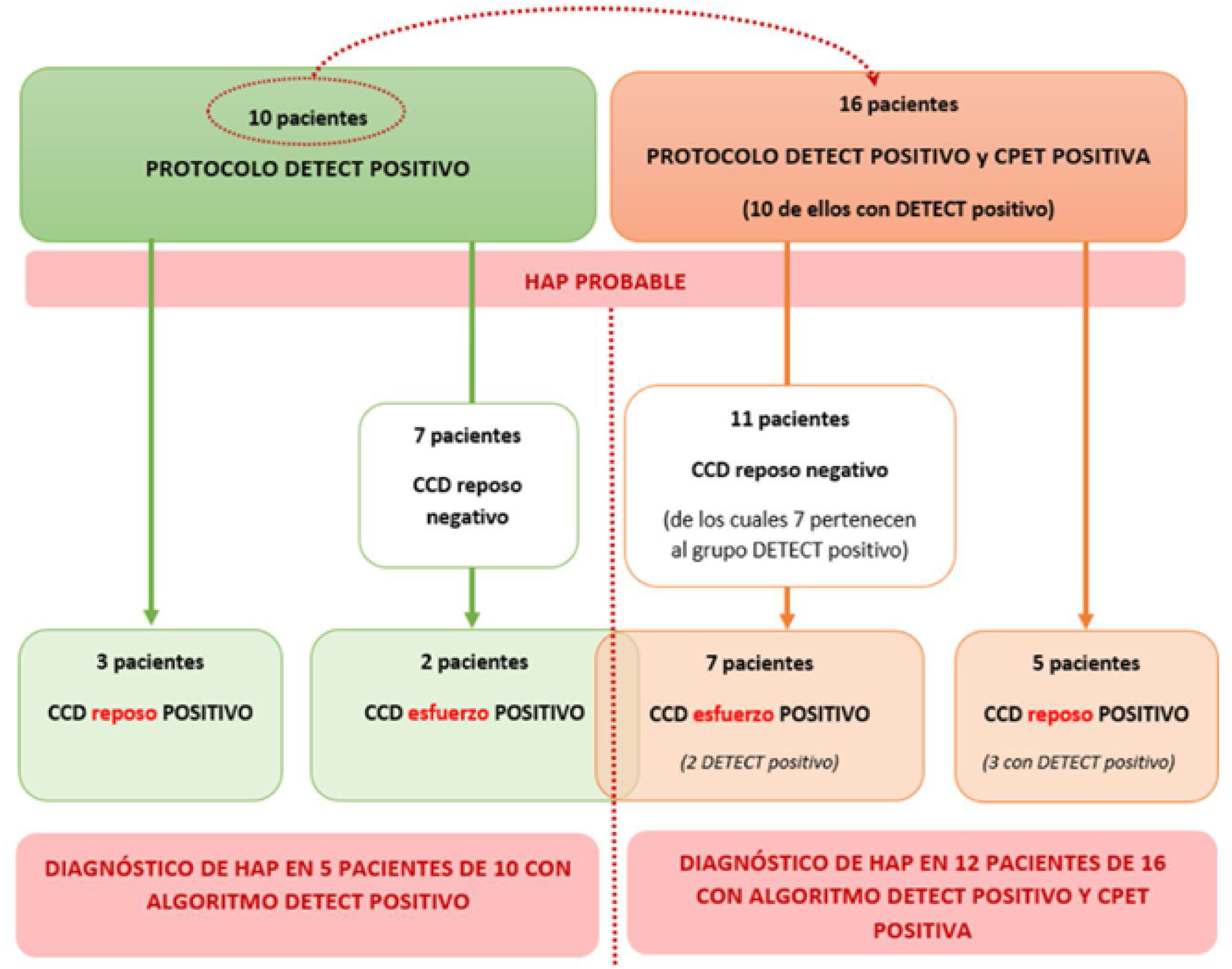
ResultadosSe realizaron 52 CPET, de las cuales 16 indicaron HAP. El CCD de reposo confirmó HAP en 5 pacientes y el CCD de esfuerzo en otros 7 (sensibilidad diagnóstica de CPET junto con el cateterismo de reposo y esfuerzo del 100%). De esos 16 pacientes, DETECT habría identificado 10, de los cuales el CCD de reposo confirmó HAP en 3 y el de esfuerzo en otros 2 (sensibilidad del algoritmo diagnóstico establecido según guías del 70%).
ConclusionesLa CPET y el CCD de esfuerzo podrían reconocer HAP más precozmente que el cribado establecido en pacientes con esclerodermia, permitiendo adelantar el diagnóstico.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe, high mortality and progressive disease. Early diagnosis and treatment improves the prognosis. Patients with scleroderma disease presents high risk of developing PAH. Established screening strategies – echocardiogram and DETECT algorithm – recognize the disease when it is already advanced. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) detects pulmonary vascular injury in earlier stages.
MethodsProspective study of 52 consecutive patients diagnosed of scleroderma in our health area, during 2 years (2018 and 2019). All of them undergo CPET, in addition to the annual systematic screening. Sensitivity of current PAH screening is compared to CPET. To confirm the presence of PAH, right heart catheterization (RHC) is performed. In case of suspected PAH in CPET, but non-confirmatory right heart catheterization at rest, patients carried out exercise RHC.
ResultsFifty-two CPET were performed, of which 16 suggested PAH. Resting RHC confirmed PAH in 5 patients and exercise RHC in 7 (diagnostic sensitivity of CPET together with rest and exercise catheterization of 100%). Of these 16 patients, DETECT had identified 10, of whom resting RHC confirmed PAH in 3 and exercise RHC in 2 (guideline-based diagnostic algorithm sensitivity 70%).
ConclusionsCPET and exercise RHC could detect PAH earlier than established screening in patients with scleroderma disease, allowing early diagnosis.