To investigate the association between left ventricular structure and disease severity in COPD patients.
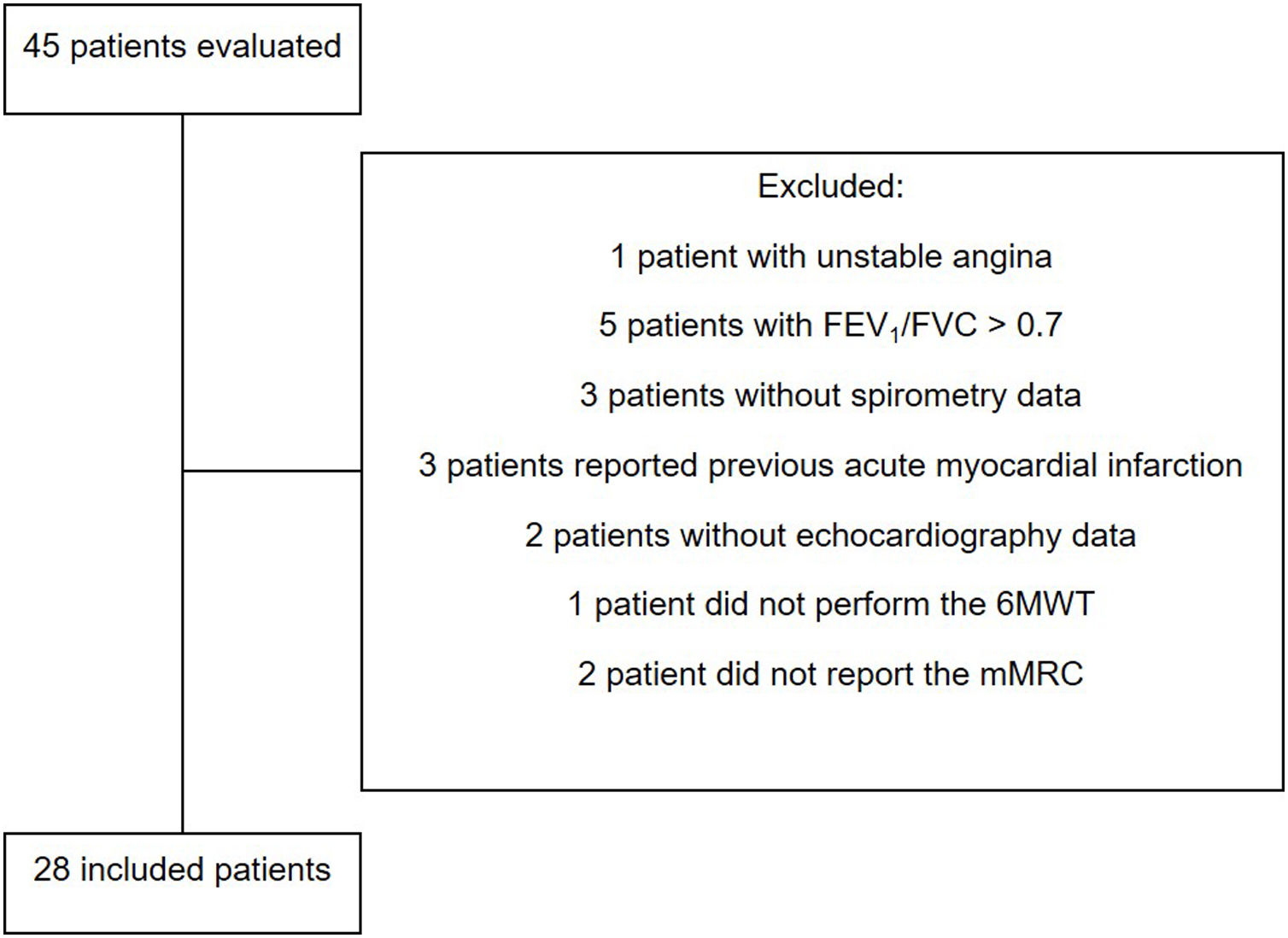
MethodsTwenty-eight COPD patients were stratified according to the disease severity, using the BODE index, into Lower (n=17) and Higher (n=11) groups, composed of patients with lower severity (BODE <5) and higher severity (BODE ≥5), respectively. Left ventricle (LV) was assessed by 2D-echocardiography. BODE index was calculated using body mass index (BMI); forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1, %); modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) and distance walked during 6-minute walk test (6MWD).
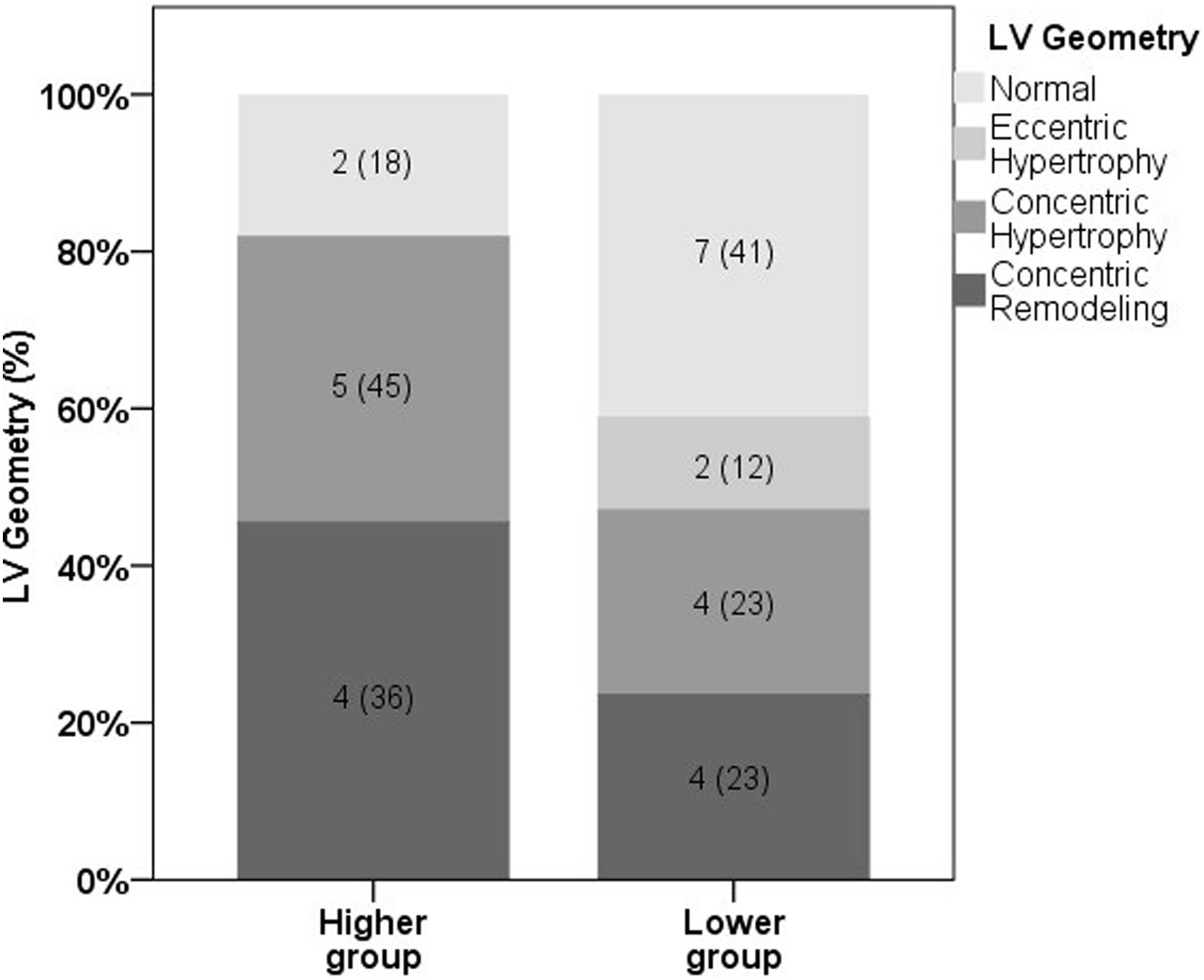
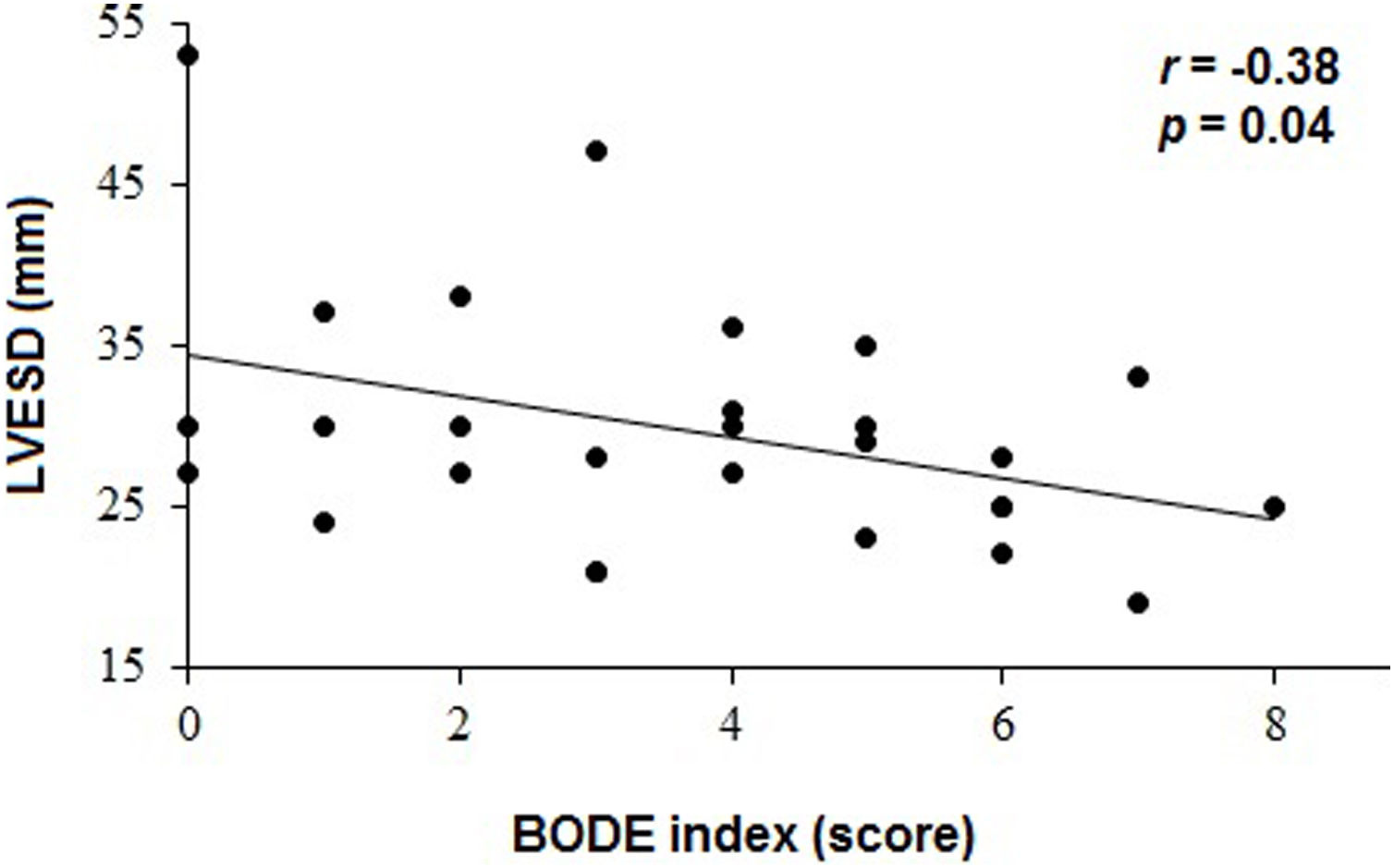
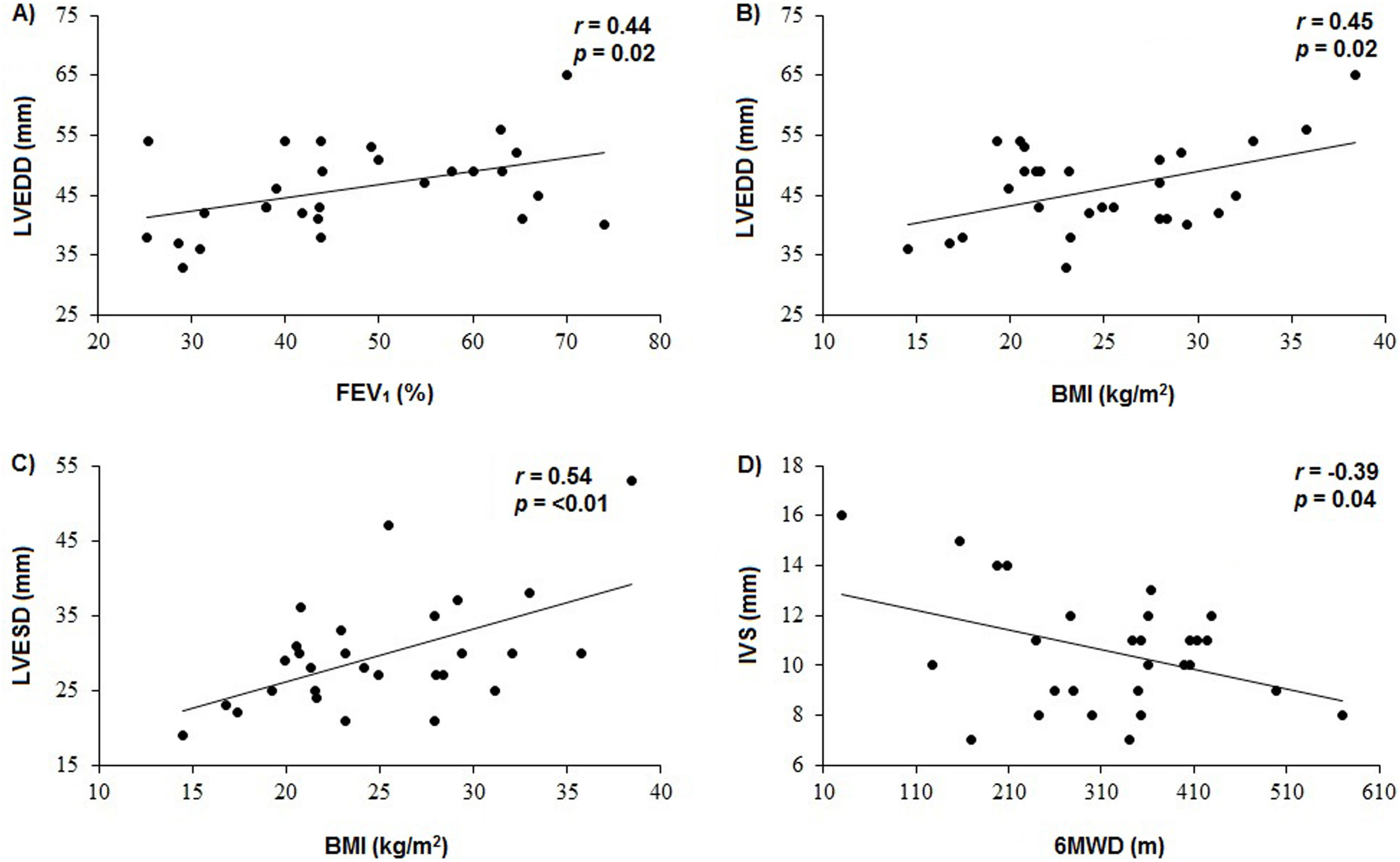
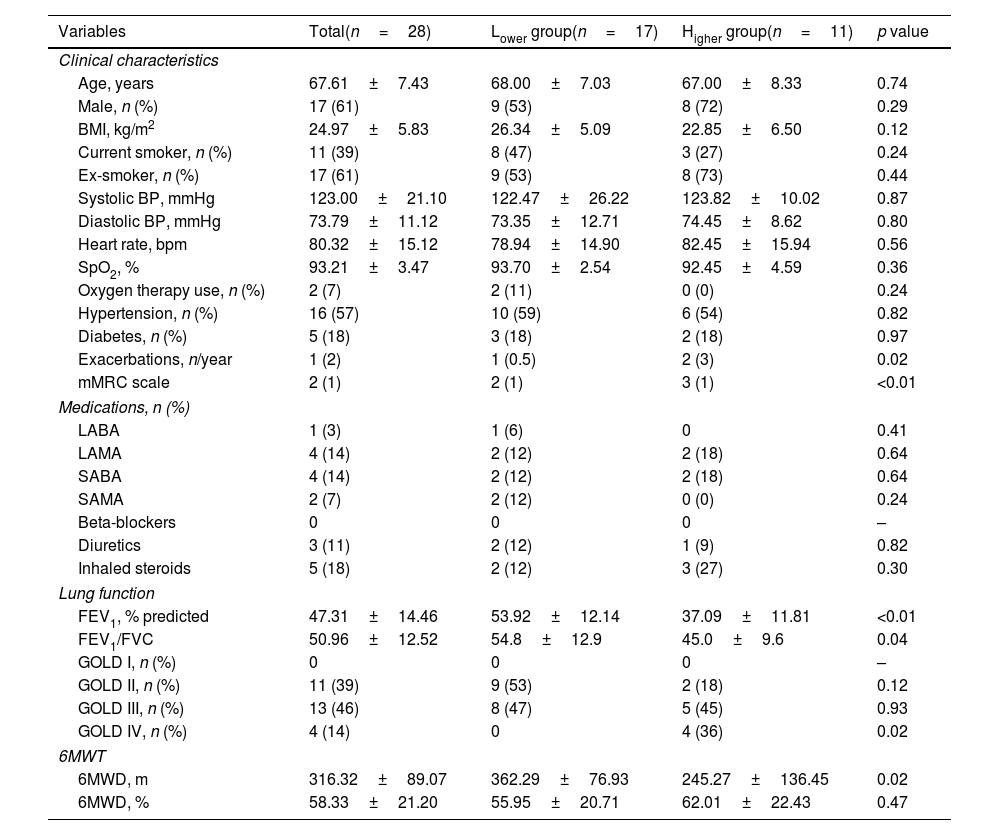
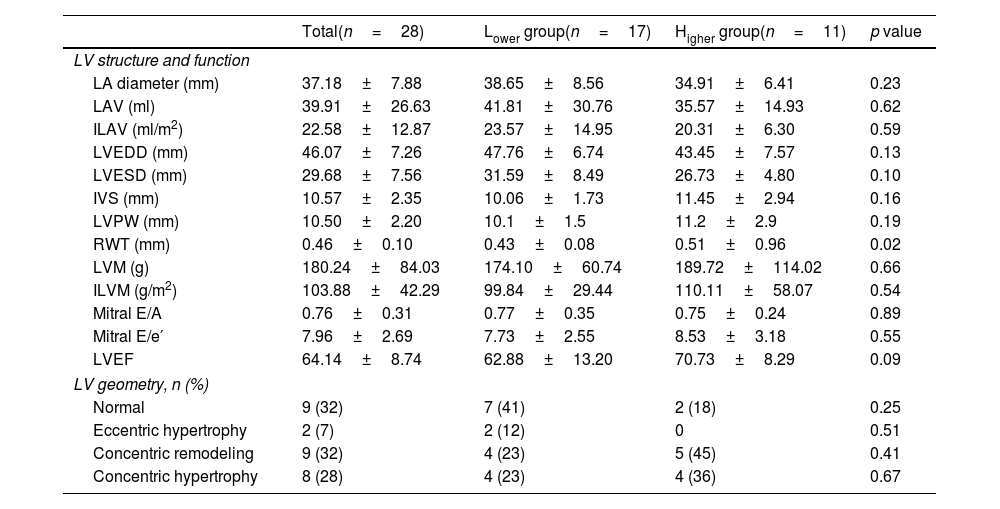
ResultsPatients in the Higher group showed lower oxygen arterial saturation (p=0.02), FEV1 (p<0.01) and 6MWD (p=0.02) and higher value of relative posterior wall thickness (RWT) compared to Lower group (p=0.02). There were significant associations between LV end-systolic diameter (LVESD) and BODE index (r=−0.38, p=0.04), LV end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD) and FEV1 (r=0.44, p=0.02), LVEDD and BMI (r=0.45, p=0.02), LVESD and BMI (r=0.54, p=0.003) and interventricular septal thickness and 6MWD (r=−0.39, p=0.04).
ConclusionsMore severe COPD patients, BODE score ≥5, may have higher RWT, featuring a possible higher concentric remodeling of LV in this group. Besides that, a greater disease severity may be related to LV chamber size reduction.
Investigar la asociación entre la estructura del ventrículo izquierdo y la gravedad de la enfermedad en pacientes con EPOC.
Métodos28 pacientes con EPOC fueron estratificados según la gravedad de la enfermedad, utilizando el índice BODE, en grupos Inferior (n=17) y Superior (n=11), compuestos por pacientes con menor gravedad (BODE<5) y mayor gravedad (BODE≥5), respectivamente. El ventrículo izquierdo (VI) se evaluó mediante ecocardiografía 2D. El índice BODE se calculó utilizando el índice de masa corporal (IMC), el volumen espiratorio forzado en el primer segundo (VEF1, %) el modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) y la distancia recorrida en la prueba de caminata de 6minutos (PC6M).
ResultadosLos pacientes del grupo Superior mostraron menor saturación arterial de oxígeno (p=0,02), VEF1 (p<0,01) y PC6M (p=0,02) y mayor valor de espesor relativo de la pared posterior (RWT) en comparación con el grupo Inferior (p=0,02). Hubo asociaciones significativas entre el diámetro telesistólico del VI (DSVI) y el índice BODE (r=−0,38, p=0,04), el diámetro telediastólico del VI (DDVI) y el VEF1 (r=0,44, p=0,02), el DVI y el IMC (r=0,45, p=0,02), el DSVI y el IMC (r=0,54, p=0,003) y el espesor del tabique interventricular y la PC6M (r=−0,39, p=0,04).
ConclusionesLos pacientes con EPOC más grave, puntuación BODE ≥5, pueden tener un RWT más alto, presentando una posible remodelación concéntrica del VI en este grupo. Además de eso, una mayor gravedad de la enfermedad puede estar relacionada con la reducción del tamaño de la cámara del VI.