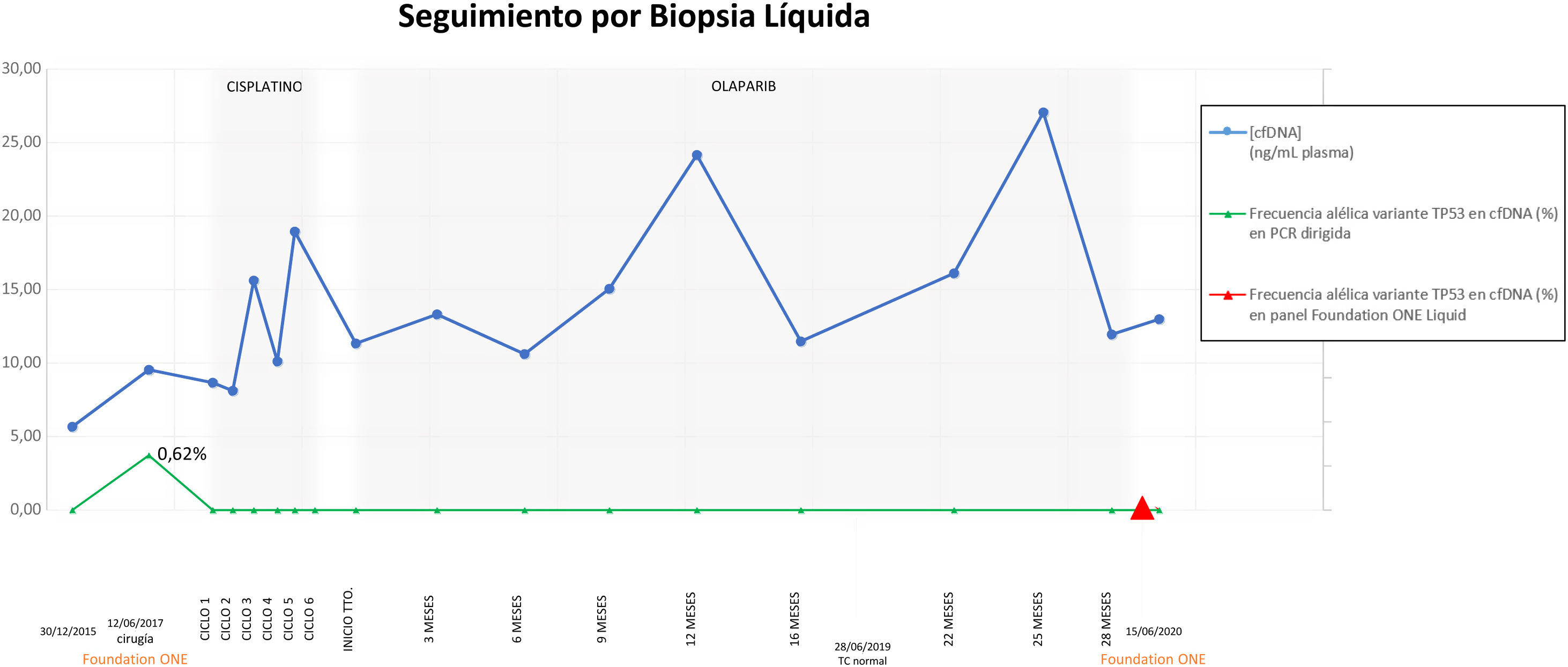
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2387020621006562" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2021.01.022" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-01-07" "aid" => "5633" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U.. All rights reserved" "copyrightAnyo" => "2021" "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2022;158:36-7" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S0025775321001834" "issn" => "00257753" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2021.01.021" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-01-07" "aid" => "5633" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2022;158:36-7" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Carta científica</span>" "titulo" => "Biopsia líquida en la detección de recidiva tumoral en el carcinoma papilar seroso primario de peritoneo" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "36" "paginaFinal" => "37" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Liquid biopsy in the detection of tumor relapse in primary peritoneal serous papillary carcinoma" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figura 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1244 "Ancho" => 2925 "Tamanyo" => 195087 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Parametrización de niveles de cfDNA (ng/ml, plasma) (círculos grandes) y frecuencia alélica variante TP53 en cfDNA (%) en PCR dirigida (círculos pequeños) y en panel FoundationOne® Liquid (triángulo).</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Tamara Díaz Vico, Estrella O. Turienzo Santos, María Luisa Ruiz Fernández" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Tamara" "apellidos" => "Díaz Vico" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Estrella O." "apellidos" => "Turienzo Santos" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "María Luisa" "apellidos" => "Ruiz Fernández" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2387020621006562" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2021.01.022" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020621006562?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775321001834?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/00257753/0000015800000001/v2_202201010646/S0025775321001834/v2_202201010646/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020621006677" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2021.03.023" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-01-07" "aid" => "5665" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2022;158:38-9" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Trigeminal trophic syndrome after ischaemic stroke" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "38" "paginaFinal" => "39" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Síndrome trófico del trigémino tras ictus isquémico" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 605 "Ancho" => 905 "Tamanyo" => 71051 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Fig. " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Clinical presentation: round ulcer with regular borders affecting the right nasal ala with early involvement of the proximal portion of the nasolabial fold.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Noelia Moreiras Arias, Bernardo Sopeña, Laura Sainz Gaspar" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Noelia" "apellidos" => "Moreiras Arias" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Bernardo" "apellidos" => "Sopeña" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Laura" "apellidos" => "Sainz Gaspar" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775321002293" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2021.03.016" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775321002293?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020621006677?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000015800000001/v2_202201200752/S2387020621006677/v2_202201200752/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S238702062100663X" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2021.01.023" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2022-01-07" "aid" => "5634" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2022;158:35-6" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Scientific letter</span>" "titulo" => "Discrepancies between erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in non-infectious inflammatory diseases" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "35" "paginaFinal" => "36" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Discrepancias entre la velocidad de sedimentación globular y la proteína C reactiva en enfermedades inflamatorias no infecciosas" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Joaquim Torné Cachot, Javier García Pont, Helena Camell Ilari" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Joaquim" "apellidos" => "Torné Cachot" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Javier" "apellidos" => "García Pont" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Helena" "apellidos" => "Camell Ilari" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775321001846" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2021.01.022" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775321001846?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S238702062100663X?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000015800000001/v2_202201200752/S238702062100663X/v2_202201200752/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:16 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Scientific letter</span>" "titulo" => "Liquid biopsy in the detection of tumor relapse in primary peritoneal serous papillary carcinoma" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "saludo" => "Dear Editor:" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "36" "paginaFinal" => "37" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Tamara Díaz Vico, Estrella O. Turienzo Santos, María Luisa Ruiz Fernández" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Tamara" "apellidos" => "Díaz Vico" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "tamara.diaz.vico@gmail.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "*" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Estrella O." "apellidos" => "Turienzo Santos" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "María Luisa" "apellidos" => "Ruiz Fernández" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:2 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Unidad de Cirugía Oncológica Peritoneal (UCOP), Servicio de Cirugía General y del Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias (HUCA), Oviedo, Asturias, Spain" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Centro Médico de Asturias, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Biopsia líquida en la detección de recidiva tumoral en el carcinoma papilar seroso primario de peritoneo" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1244 "Ancho" => 2925 "Tamanyo" => 195087 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Parameterization of cfDNA levels (ng/mL, plasma) (large circles) and TP53 variant allele frequency in cfDNA (%) in targeted PCR (small circles) and FoundationOne® Liquid panel (triangle).</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Primary peritoneal serous papillary carcinoma (PPSPC) is a rare tumour that affects the peritoneal surface diffusely.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0005"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> It has similar clinical and histological features to ovarian serous papillary carcinoma in the absence of a detectable primary ovarian tumor.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0010"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a> Following the latest update of the FIGO classification for the staging of ovarian tumours, the concept of mesothelial surface as the origin of ovarian epithelial tumours is discarded and the discussion of tubal carcinogenesis is introduced.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0015"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a></p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The patient is a 52-year-old female who presents with a 4-month history of diffuse abdominal pain. A chest-abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan was performed, which described multiple pericapsular hepatic lesions indicative of tumour deposits, nodular lesions in the greater omentum, right diaphragmatic and supravesical pelvic peritoneum, and capsular thickening of the right ovary, compatible with peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC). Exploratory laparoscopy was performed along with biopsy and right adnexectomy. The pathological study showed a high-grade PPSPC with absence of malignancy in the right adnexa. The patient was referred to the Peritoneal Cancer Surgery Unit of our centre in May 2015, undergoing complementary studies that showed elevated levels of CA 125: 1,145.2 U/mL. Debulking surgery was scheduled, with removal of tumour deposits in hepatic segments 6–8, cholecystectomy, omentectomy, hysterectomy and left adnexectomy, pelvic peritonectomy, appendectomy, and peritonectomy of the right hemidiaphragm, with an initial PC index of 11, final of 0 and complete debulking of 0. <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy</span> (HIPEC) was combined with paclitaxel 90 mg. The pathological analysis revealed PPSPC involvement in all samples submitted. He subsequently received 6 cycles of adjuvant carboplatin and paclitaxel-based chemotherapy.</p><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">After a disease-free interval of 2 years, the patient presented with peritoneal recurrence confirmed by CT scan in the form of tumour deposits in the left diaphragm with spleen infiltration. Debulking surgery was scheduled again, completing peritonectomy of the remaining areas: left hemidiaphragm, mesocolon, and both leaves of the small bowel mesentery, as well as splenectomy, atypical gastrectomy of the greater gastric curvature, and removal of tumour deposits on the body and tail of the pancreas (initial PC index of 10, final of 0; complete debulking of 0). i-HIPEC (<span class="elsevierStyleItalic">second-look surgery</span> or <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">repeat HIPEC</span>) was performed, combined with adjuvant treatment, repeating the previous regimen. The pathological findings showed tumour involvement not only in the specimens with known tumour deposits, but also in the macroscopically seemingly healthy peritoneal specimens. After completing chemotherapy, Olaparib was prescribed as maintenance treatment.</p><p id="par0020" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Throughout the entire cancer process, tumour marker monitoring and thoracoabdominal CT scan was carried out every 3–4 months, incorporating serial plasma liquid biopsies (LB) with bio-TM parametrisation for the early detection of tumour recurrence. At the time of diagnosis, the patient had elevated levels of CA 125 and <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">circulating tumour DNA</span> (ctDNA) (p.Cys242fs * 5 <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">TP53</span>). PCys242fs*5 levels <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">TP53</span> remained high after the first debulking surgery, becoming negative only after i-HIPEC was performed, once the peritonectomy was completed (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>). To date, no tumour relapse or elevation of tumour markers has been observed, neither in serum nor in LB, with a disease-free interval of 30 months.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0025" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Patients with early-stage disease or at risk of developing PC may benefit from increasing diagnostic alternatives. The concept of LB has evolved into a highly active field of research in search of plasma bio-TMs and is recommended as an alternative to tumour tissue analysis in some malignancies.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0020"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">4</span></a> It encompasses the analysis of ctDNA, <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">circulating free DNA</span> (cfDNA), circulating tumour cells, circulating miRNAs, and exosomes. In general, cfDNA can be identified in plasma, detecting genetic and dynamic changes. Regarding PPSPC, mutation in the <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">TP53</span> gene, whether or not associated with mutations in <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">BRCA1/BRCA2</span>, is believed to be driving the carcinogenic process.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0025"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5</span></a> Accordingly, we established a parameterisation by serial LB of cfDNA and ctDNA levels. Interestingly, ctDNA levels, elevated at baseline and after surgery, decreased to undetectable levels after complete peritonectomy and HIPEC, performed after confirmation of tumour relapse. The fact that plasma levels of ctDNA remained elevated after the initial surgery, despite the removal of all macroscopically visible tumour burden, leads us to consider complete peritonectomy and HIPEC as the optimal therapeutic approach for PPSPC with peritoneal extension.</p><span id="sec0005" class="elsevierStyleSection elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSectionTitle" id="sect0005">Authorship</span><p id="par0030" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Tamara Díaz Vico and Estrella O. Turienzo Santos: design and writing of the article. María Luisa Ruiz Fernández: critical review and final approval of the article. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.</p></span></span>" "textoCompletoSecciones" => array:1 [ "secciones" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "sec0005" "titulo" => "Authorship" ] 1 => array:1 [ "titulo" => "References" ] ] ] "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: Díaz Vico T, Turienzo Santos EO, Ruiz Fernández ML. Biopsia líquida en la detección de recidiva tumoral en el carcinoma papilar seroso primario de peritoneo. Med Clin (Barc). 2022;158:36–37.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figure 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1244 "Ancho" => 2925 "Tamanyo" => 195087 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Parameterization of cfDNA levels (ng/mL, plasma) (large circles) and TP53 variant allele frequency in cfDNA (%) in targeted PCR (small circles) and FoundationOne® Liquid panel (triangle).</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0005" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:5 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0005" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Mesothelioma of the pelvic peritoneum resembling papillary cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary; case report" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => "M. Swerdlow" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/0002-9378(59)90287-x" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Am J Obstet Gynecol" "fecha" => "1959" "volumen" => "77" "paginaInicial" => "197" "paginaFinal" => "200" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13606191" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0010" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Serous ovarian and primary peritoneal cancers: a comparative analysis of clinico-pathological features, molecular subtypes and treatment outcome" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "B. Gao" 1 => "K. Lindemann" 2 => "L. Anderson" 3 => "S. Fereday" 4 => "J. Hung" 5 => "K. Alsop" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.06.023" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Gynecol Oncol" "fecha" => "2016" "volumen" => "142" "paginaInicial" => "458" "paginaFinal" => "464" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27444035" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0015" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "The new FIGO staging for system for ovarian, fallopian tube and primary peritoneal cancer" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "F. Zeppernick" 1 => "I. Meinhold-Heerlein" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1007/s00404-014-3364-8" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Arch Gynecol Obstet" "fecha" => "2014" "volumen" => "290" "paginaInicial" => "839" "paginaFinal" => "842" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25082067" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0020" "etiqueta" => "4" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Colorectal cancer diagnostics: biomarkers, cell-free DNA, circulating tumor cells and defining heterogeneous populations by single-cells analysis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "C. Kin" 1 => "E. Kidess" 2 => "G.A. Poultsides" 3 => "B.C. Visser" 4 => "S.S. Jeffrey" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1586/14737159.2013.811896" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Expert Rev Mol Diagn" "fecha" => "2013" "volumen" => "13" "paginaInicial" => "581" "paginaFinal" => "599" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23895128" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0025" "etiqueta" => "5" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Are all pelvic (nonuterine) serous carcinomas of tubal origin?" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "C.G. Przybycin" 1 => "R.J. Kurman" 2 => "B.M. Ronnett" 3 => "I.M. Shih" 4 => "R. Vang" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181ef7b16" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Am J Surg Pathol" "fecha" => "2010" "volumen" => "34" "paginaInicial" => "1407" "paginaFinal" => "1416" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20861711" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/23870206/0000015800000001/v2_202201200752/S2387020621006562/v2_202201200752/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "43311" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Scientific letters" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/23870206/0000015800000001/v2_202201200752/S2387020621006562/v2_202201200752/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020621006562?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Journal Information
Vol. 158. Issue 1.
Pages 36-37 (January 2022)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 158. Issue 1.
Pages 36-37 (January 2022)
Scientific letter
Liquid biopsy in the detection of tumor relapse in primary peritoneal serous papillary carcinoma
Biopsia líquida en la detección de recidiva tumoral en el carcinoma papilar seroso primario de peritoneo
Visits
3
This item has received
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail