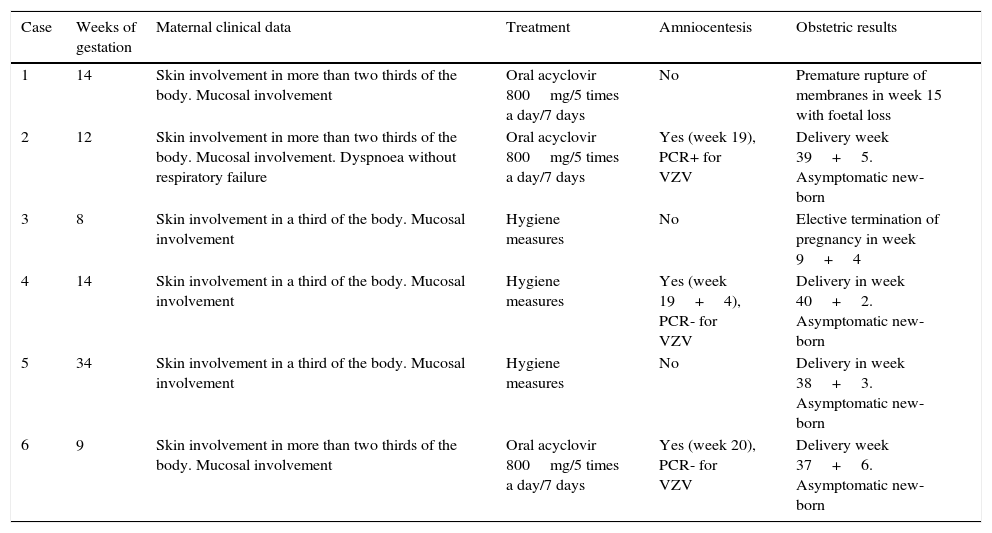
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2387020616300614" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.04.036" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2016-01-01" "aid" => "3280" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U.. All rights reserved" "copyrightAnyo" => "2015" "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2016;146:40-1" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S0025775315001864" "issn" => "00257753" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2015.03.007" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2016-01-01" "aid" => "3280" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2016;146:40-1" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 55 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 27 "PDF" => 28 ] ] "es" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Carta científica</span>" "titulo" => "Varicela en la gestación" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "40" "paginaFinal" => "41" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Varicella infection in pregnancy" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Maria de la Calle, Felix Omeñaca, Jose Luis Bartha" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Maria" "apellidos" => "de la Calle" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Felix" "apellidos" => "Omeñaca" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Jose Luis" "apellidos" => "Bartha" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2387020616300614" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.04.036" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616300614?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775315001864?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/00257753/0000014600000001/v1_201512260043/S0025775315001864/v1_201512260043/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020616300717" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.04.046" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2016-01-01" "aid" => "3318" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2016;146:41-2" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Scientific letter</span>" "titulo" => "Importance of appropriate clinical management of direct oral anticoagulants" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "41" "paginaFinal" => "42" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Importancia del empleo adecuado de los anticoagulantes orales directos" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Juan Antonio Millón Caño, Noelia Vilalta Setó, José Mateo Arranz, Juan Carlos Souto Andrés" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Juan Antonio" "apellidos" => "Millón Caño" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Noelia" "apellidos" => "Vilalta Setó" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "José" "apellidos" => "Mateo Arranz" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Juan Carlos" "apellidos" => "Souto Andrés" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775315002717" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2015.04.025" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775315002717?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616300717?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000014600000001/v3_201605230108/S2387020616300717/v3_201605230108/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020616300894" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.04.048" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2016-01-01" "aid" => "3369" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "crp" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2016;146:35-9" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Diagnosis and treatment</span>" "titulo" => "Migraine" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "35" "paginaFinal" => "39" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Migraña" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1759 "Ancho" => 1470 "Tamanyo" => 159802 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Options for the symptomatic treatment of migraine. NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; IV: intravenous.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Nuria Riesco, Carmen García-Cabo, Julio Pascual" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Nuria" "apellidos" => "Riesco" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Carmen" "apellidos" => "García-Cabo" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Julio" "apellidos" => "Pascual" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775315004492" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2015.07.003" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775315004492?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616300894?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000014600000001/v3_201605230108/S2387020616300894/v3_201605230108/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:14 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Scientific letter</span>" "titulo" => "Varicella infection in pregnancy" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "saludo" => "Dear Editor:" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "40" "paginaFinal" => "41" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Maria de la Calle, Felix Omeñaca, Jose Luis Bartha" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Maria" "apellidos" => "de la Calle" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "maria.delacalle@uam.es" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Felix" "apellidos" => "Omeñaca" "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">c</span>" "identificador" => "aff0015" ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Jose Luis" "apellidos" => "Bartha" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:3 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Unidad de Medicina Materno-Fetal, Servicio de Obstetricia, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio de Neonatología, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] 2 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio de Pediatría, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain" "etiqueta" => "c" "identificador" => "aff0015" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Varicela en la gestación" ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Varicella during pregnancy is a rare disease, with an incidence of one in 10,000 pregnancies.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0045"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> Although it is a benign disease, its onset during pregnancy can carry maternal and foetal risks. In pregnant women it increases the risk of complications such as pneumonia and viral encephalitis.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0050"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2,3</span></a> In the foetus, the risk of vertical transmission through the placenta is low, so most new-borns of mothers with varicella in pregnancy are asymptomatic. This risk is higher in the third trimester of pregnancy.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0060"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">4</span></a> However, the risk of foetal infection with the development of congenital varicella syndrome is higher if maternal infection occurs in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, with an incidence of 1–2%.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0065"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5</span></a> Typical manifestations of congenital varicella syndrome include skin lesions (70%), neurological disorders (62%), eye abnormalities (52%), limb hypoplasia (46%) and low birth weight (23%).<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0070"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">6</span></a> If a varicella infection in pregnancy is suspected, serological confirmation is recommended with IgM+ and/or PCR+ of a vesicle for varicella zoster virus (VZV). The diagnosis of foetal infection should be done by amniocentesis from week 19 to confirm DNA positivity for VZV in the amniotic fluid. Confirmation of foetal infection does not always indicate that the foetus is anomalous, but these foetuses should be closely monitored with ultrasounds, as sometimes late ultrasound abnormalities may appear. The foetal neurological study should include performing an MRI in the third trimester.</p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">We treated six cases of varicella infection in pregnant women in 2014, among 5600 deliveries in the same year at our institution (0.11%). In all cases, the diagnosis was confirmed by IgM+ serology and/or PCR+ of a dermal vesicle. In 5 patients, varicella was diagnosed before week 20 of gestation, and one of them, who was in the eighth week, decided to terminate the pregnancy. In all cases there was both dermal and mucosal involvement, without other clinical manifestations, except for one patient who had respiratory failure or dyspnoea without anomalies in chest radiology. Rupture of membranes occurred in one case, resulting in foetal loss a week after the diagnosis. Three patients with skin involvement in more than two thirds of the body were treated with oral acyclovir for 7 days. Amniocentesis was performed in 3 cases, and the PCR for VZV was positive in one of them, although this case and the remaining 3 who completed gestation had normal deliveries with asymptomatic new-borns. The clinical characteristics for the 6 patients are shown in <a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#tbl0005">Table 1</a>.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="tbl0005"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Treatment of mild cases of varicella during pregnancy mainly includes hygienic measures. In highly symptomatic cases, oral antivirals, such as acyclovir, will be administered at doses of 800<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg, 5 times a day, between 24 and 72<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h of the rash onset, for 7 days. In cases of progression to varicella pneumonia, the patient must be admitted and administered intravenous acyclovir at a dose of 10–15<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/kg/8<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h between 5 and 10 days.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0075"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">7</span></a> When varicella occurs within 5 days before delivery or within 2 days the same 2, the risk of vertical transmission is high (>50%) and the neonate may not have protective antibodies of maternal origin, so the risk of severe neonatal varicella is high. For this reason, postponing the delivery with tocolytic drugs for 7 days after the onset of skin rash is recommended. If labour is triggered during that period, neonatologists should be informed so that they can administer the neonate specific immunoglobulin against VZV.</p><p id="par0020" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">If there is a case of varicella contact during pregnancy, IgG serology to VZV should be performed. If the mother is not immunized, she should be administered prophylactically gamma globulin against VZV in the first 72–96<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h after contact.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0075"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">7</span></a></p><p id="par0025" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">IgG serology to VZV should also be carried out in women with a fertility desire whose medical history of varicella is unknown, and receive the vaccine if negative. Special emphasis will have to be placed on women whose work activity poses a high risk of infection, although a high rate of immunity to VZV has been recently described in this group.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0080"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">8</span></a> The varicella vaccine should never be administered during pregnancy.</p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: de la Calle M, Omeñaca F, Bartha JL. Varicela en la gestación. Med Clin (Barc). 2016;146:40–41.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:8 [ "identificador" => "tbl0005" "etiqueta" => "Table 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIATABLA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at1" "detalle" => "Table " "rol" => "short" ] ] "tabla" => array:2 [ "leyenda" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">PCR, polymerase chain reaction; VZV, varicella zoster virus.</p>" "tablatextoimagen" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "tabla" => array:1 [ 0 => """ <table border="0" frame="\n \t\t\t\t\tvoid\n \t\t\t\t" class=""><thead title="thead"><tr title="table-row"><th class="td" title="table-head " align="left" valign="top" scope="col" style="border-bottom: 2px solid black">Case \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</th><th class="td" title="table-head " align="left" valign="top" scope="col" style="border-bottom: 2px solid black">Weeks of gestation \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</th><th class="td" title="table-head " align="left" valign="top" scope="col" style="border-bottom: 2px solid black">Maternal clinical data \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</th><th class="td" title="table-head " align="left" valign="top" scope="col" style="border-bottom: 2px solid black">Treatment \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</th><th class="td" title="table-head " align="left" valign="top" scope="col" style="border-bottom: 2px solid black">Amniocentesis \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</th><th class="td" title="table-head " align="left" valign="top" scope="col" style="border-bottom: 2px solid black">Obstetric results \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</th></tr></thead><tbody title="tbody"><tr title="table-row"><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">1 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">14 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Skin involvement in more than two thirds of the body. Mucosal involvement \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Oral acyclovir 800<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/5 times a day/7 days \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">No \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Premature rupture of membranes in week 15 with foetal loss \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">2 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">12 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Skin involvement in more than two thirds of the body. Mucosal involvement. Dyspnoea without respiratory failure \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Oral acyclovir 800<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/5 times a day/7 days \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Yes (week 19), PCR+ for VZV \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Delivery week 39<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>+<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>5.<br>Asymptomatic new-born \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">3 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">8 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Skin involvement in a third of the body. Mucosal involvement \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Hygiene measures \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">No \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Elective termination of pregnancy in week 9<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>+<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>4 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">4 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">14 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Skin involvement in a third of the body. Mucosal involvement \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Hygiene measures \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Yes (week 19<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>+<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>4), PCR- for VZV \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Delivery in week 40<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>+<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>2.<br>Asymptomatic new-born \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">5 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">34 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Skin involvement in a third of the body. Mucosal involvement \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Hygiene measures \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">No \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Delivery in week 38<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>+<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>3. Asymptomatic new-born \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">6 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="char" valign="top">9 \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Skin involvement in more than two thirds of the body. Mucosal involvement \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Oral acyclovir 800<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/5 times a day/7 days \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Yes (week 20), PCR- for VZV \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td><td class="td" title="table-entry " align="left" valign="top">Delivery week 37<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>+<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>6.<br>Asymptomatic new-born \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr></tbody></table> """ ] "imagenFichero" => array:1 [ 0 => "xTab1053355.png" ] ] ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Clinical characteristics of patients.</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0005" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:8 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0045" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Chickenpox during pregnancy" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "V. Mirlesse" 1 => "P. Lebon" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Arch Pediatr" "fecha" => "2003" "volumen" => "10" "paginaInicial" => "1113" "paginaFinal" => "1118" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14643554" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0050" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Varicella infection in pregnancy" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => "D.E. McCarter-Spaulding" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Obstet Gynecol Neonatol Nurs" "fecha" => "2001" "volumen" => "30" "paginaInicial" => "667" "paginaFinal" => "673" ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0055" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Risk factors and outcome of varicella-zoster virus pneumonia in pregnant women" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "J.H. Harger" 1 => "J.M. Ernest" 2 => "G.R. Thurnau" 3 => "A. Moawad" 4 => "V. Momirova" 5 => "M.B. Landon" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1086/338832" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Infect Dis" "fecha" => "2002" "volumen" => "185" "paginaInicial" => "422" "paginaFinal" => "427" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11865393" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0060" "etiqueta" => "4" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of congenital varicella syndrome" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "T. Tongsong" 1 => "K. Srisupundit" 2 => "K. Traisrisilp" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1002/jcu.21891" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Clin Ultrasound" "fecha" => "2012" "volumen" => "40" "paginaInicial" => "176" "paginaFinal" => "178" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22323269" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0065" "etiqueta" => "5" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Varicella in the fetus and newborn" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "C.K. Smith" 1 => "A.M. Arvin" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.siny.2008.11.008" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Semin Fetal Neonatal Med" "fecha" => "2009" "volumen" => "14" "paginaInicial" => "209" "paginaFinal" => "217" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19097954" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 5 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0070" "etiqueta" => "6" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Congenital varicella syndrome: still a problem?" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "C. Auriti" 1 => "F. Piersigilli" 2 => "M.R. de Gasperis" 3 => "G. Seganti" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1159/000220602" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Fetal Diagn Ther" "fecha" => "2009" "volumen" => "25" "paginaInicial" => "224" "paginaFinal" => "229" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19478488" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 6 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0075" "etiqueta" => "7" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Management of varicella infection (chicken pox) in pregnancy" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "colaboracion" => "Maternal Fetal Medicine Committee" "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "A. Shrim" 1 => "G. Koren" 2 => "M.H. Yudin" 3 => "D. Farine" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Obstet Gynaecol Can" "fecha" => "2012" "volumen" => "34" "paginaInicial" => "287" "paginaFinal" => "292" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22385673" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 7 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0080" "etiqueta" => "8" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Susceptibilidad a la varicela en personal sanitario. Aceptación y respuesta a la vacunación" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "A.L. García-Basteiro" 1 => "J.M. Bayas" 2 => "M. Campins" 3 => "M. Torres" 4 => "C. Serra" 5 => "P. Varela" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Med Clin (Barc)" "fecha" => "2011" "volumen" => "137" "paginaInicial" => "340" "paginaFinal" => "345" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/23870206/0000014600000001/v3_201605230108/S2387020616300614/v3_201605230108/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "43311" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Scientific letters" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/23870206/0000014600000001/v3_201605230108/S2387020616300614/v3_201605230108/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616300614?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Journal Information
Vol. 146. Issue 1.
Pages 40-41 (January 2016)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 146. Issue 1.
Pages 40-41 (January 2016)
Scientific letter
Varicella infection in pregnancy
Varicela en la gestación
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail