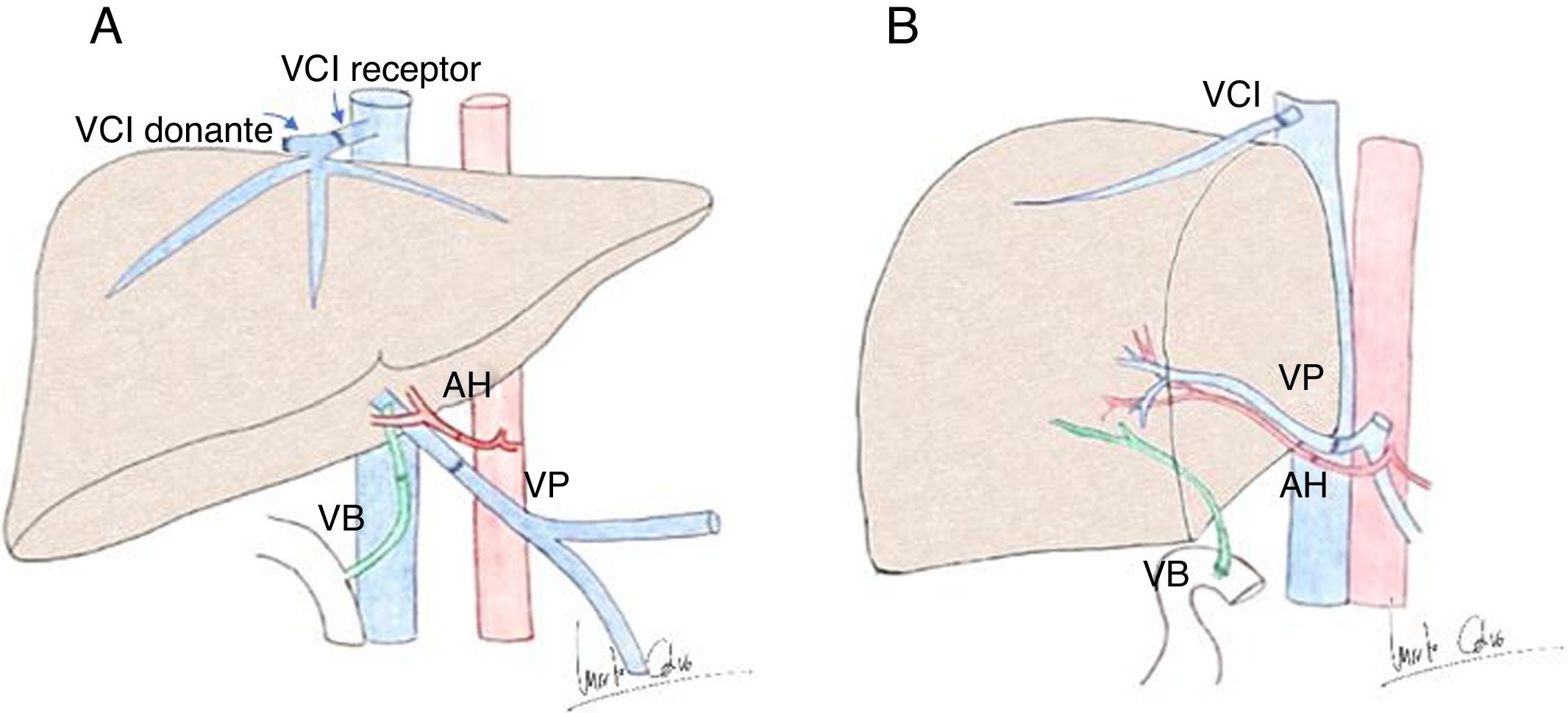
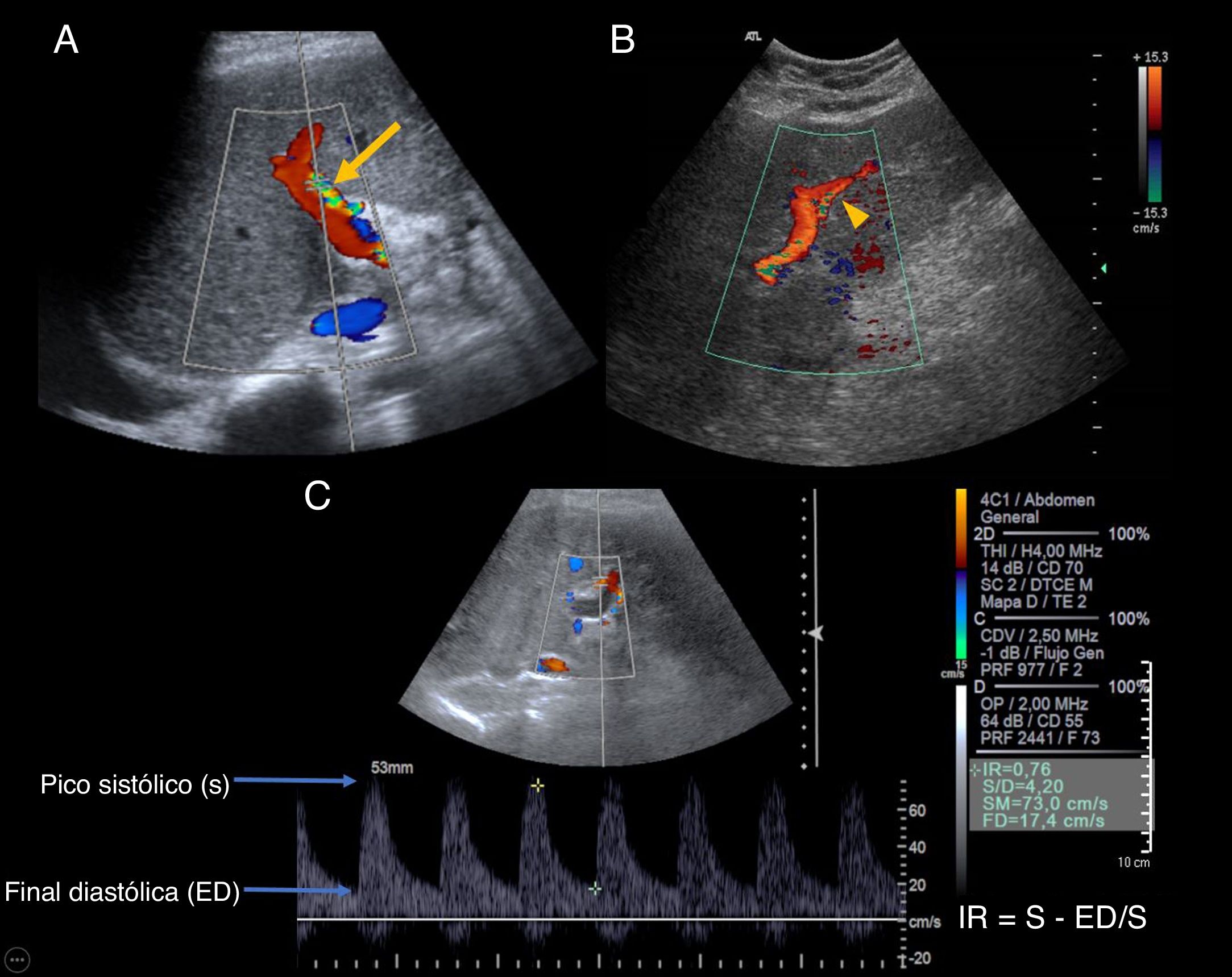
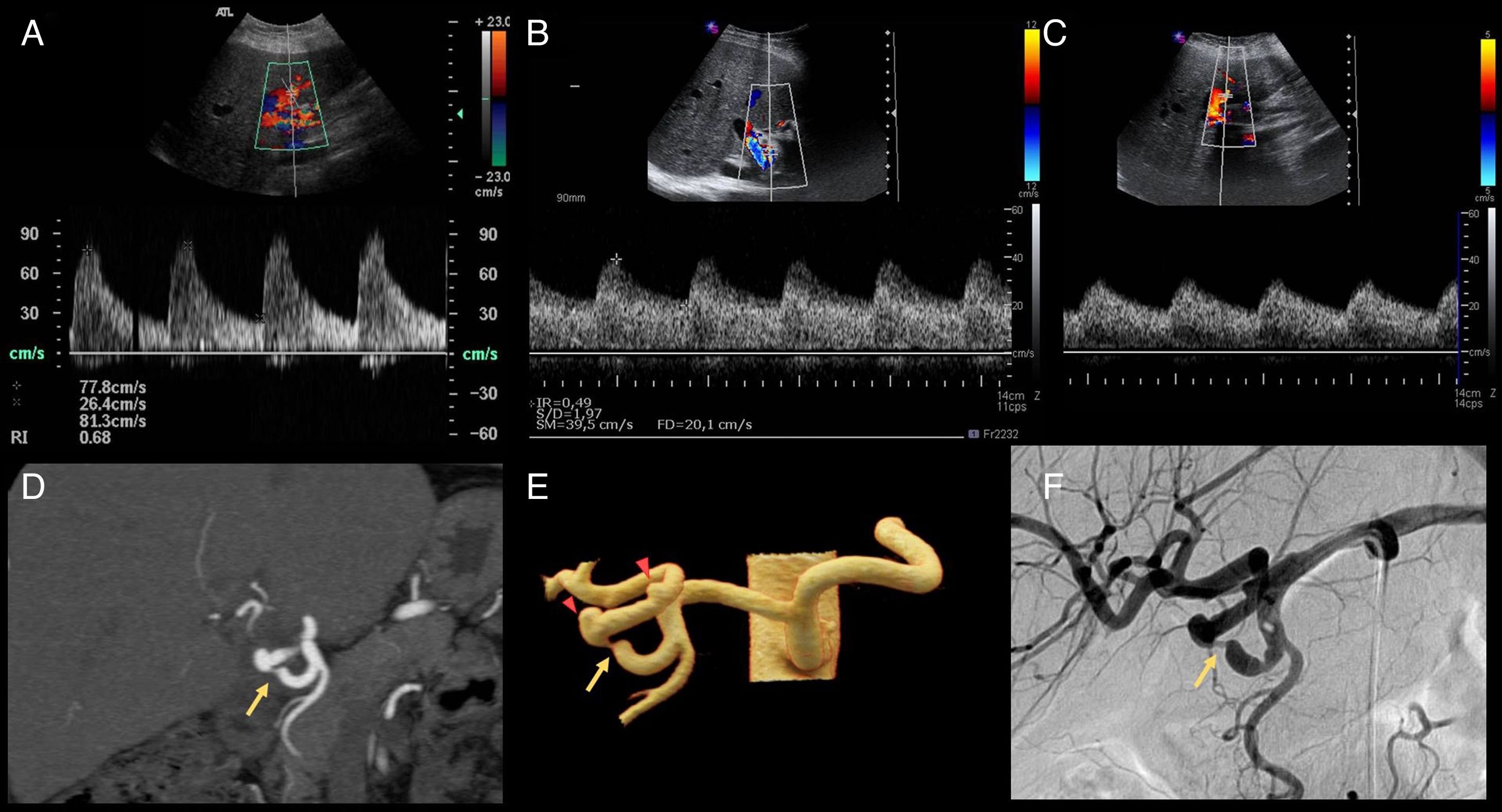
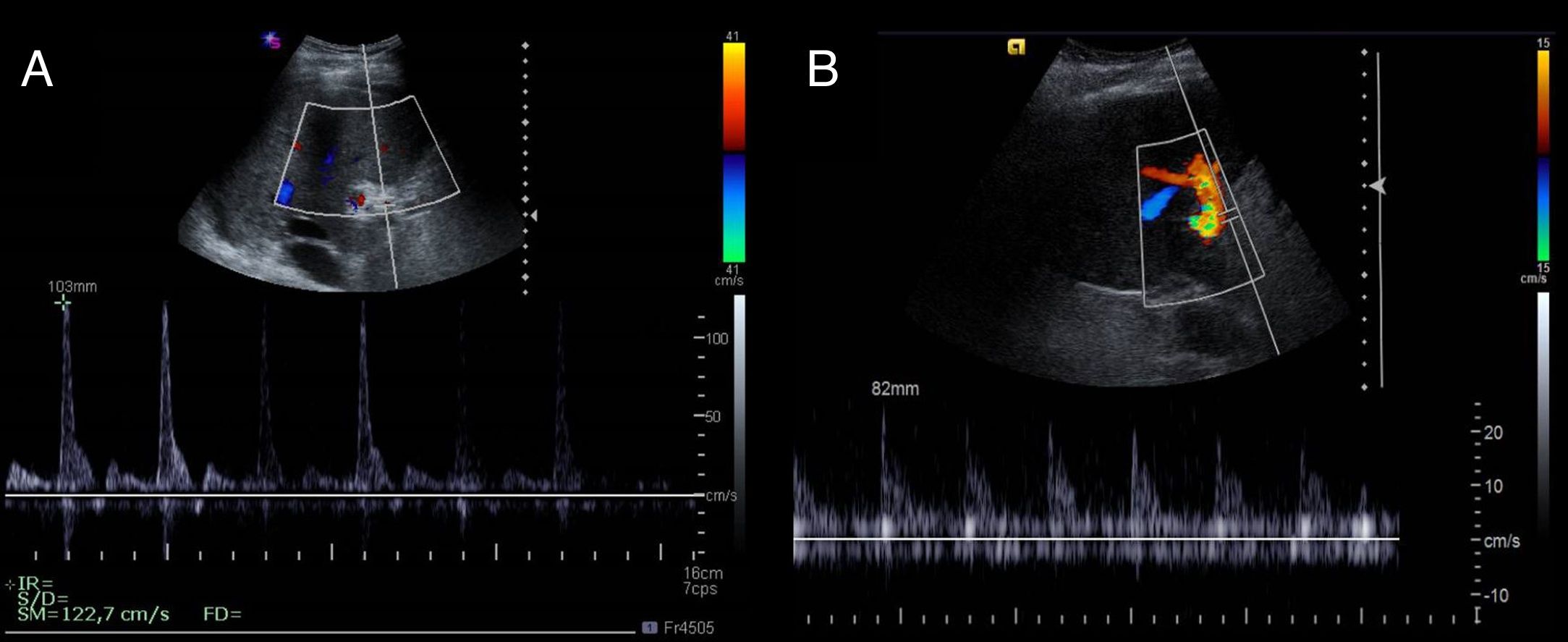
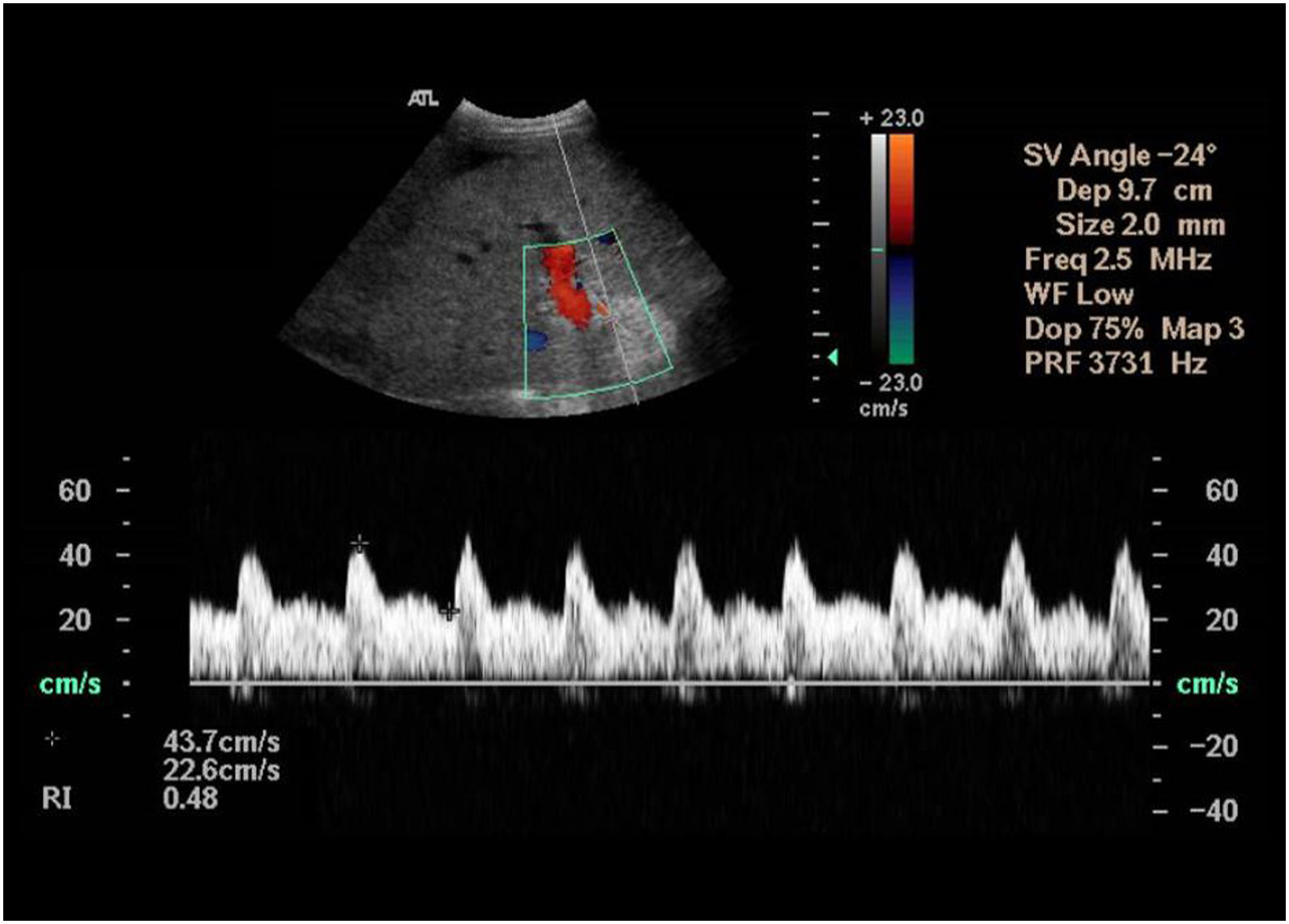
El trasplante hepático es uno de los tratamientos de la hepatopatía crónica en estadios avanzados y pacientes seleccionados con tumores hepáticos. La ecografía es la técnica de imagen de elección para su evaluación. En este trabajo se revisan la técnica quirúrgica, la anatomía del trasplante hepático y los hallazgos ecográficos normales en el postoperatorio inmediato, que servirán de referencia para evaluaciones posteriores.
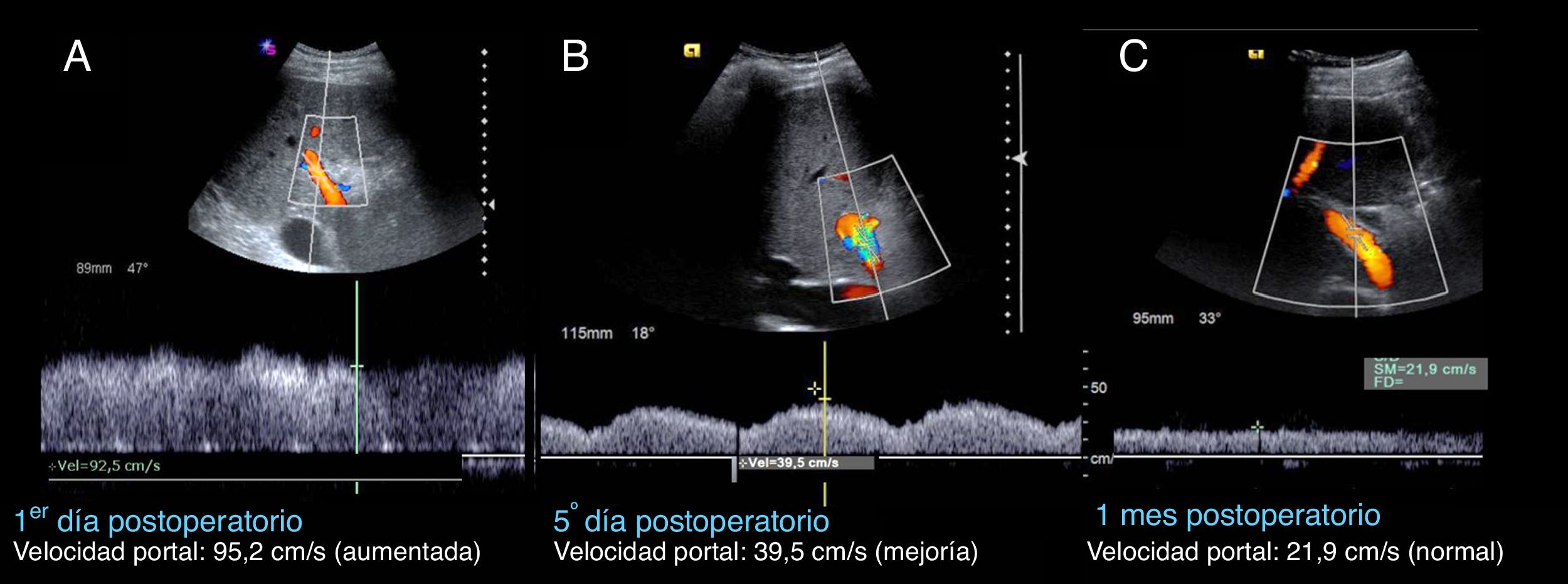
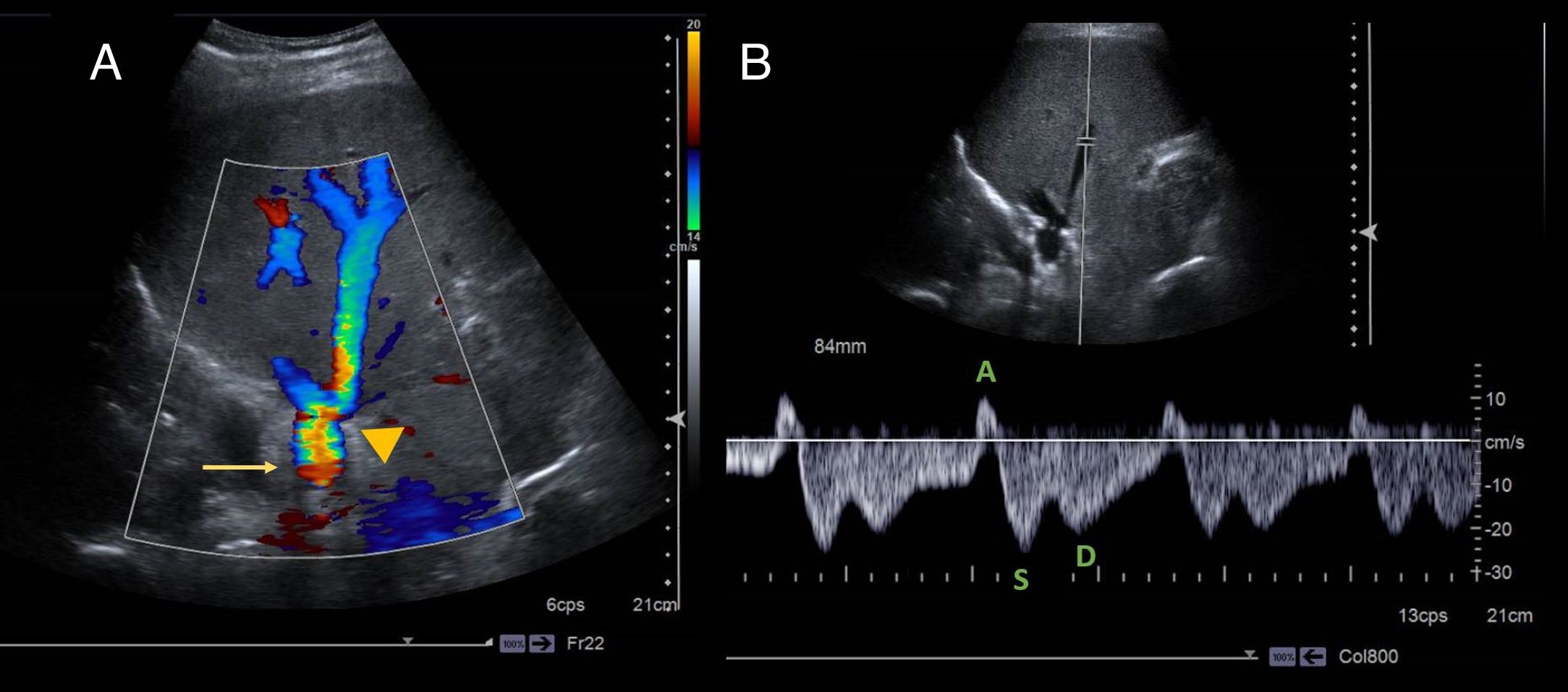
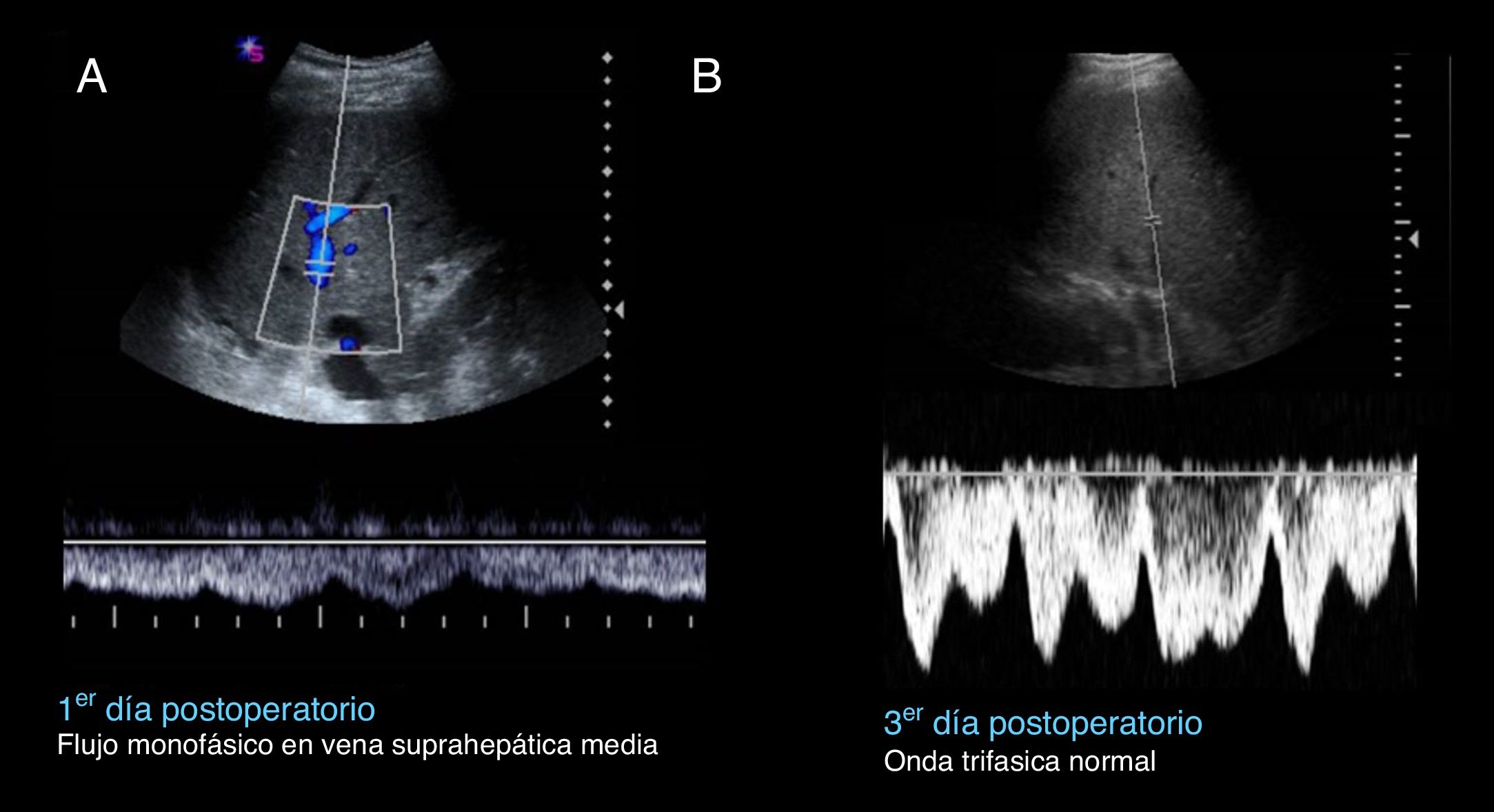
ConclusiónLas complicaciones vasculares tempranas (arteriales y portales) pueden suponer una amenaza para el injerto o el paciente. Tras el trasplante hepático existe un periodo de adaptación del injerto al nuevo medio y de recuperación posquirúrgica en el que podemos observar alteraciones parenquimatosas o hallazgos en el estudio Doppler que difieren de los habituales y se pueden considerar como normales en esta situación; generalmente son transitorios. Su conocimiento e interpretación es clave para detectar o excluir complicaciones.
Liver transplantation is one of the treatments for patients with advanced stage chronic liver disease and for selected patients with hepatic tumors. Ultrasonography is the first-choice imaging technique to evaluate liver transplants. This article reviews the surgical technique, anatomy, and normal findings on ultrasonography in the immediate postoperative period in patients who have undergone liver transplantation, which will be used as a reference in follow-up studies.
ConclusionEarly vascular (arterial and portal) complications can represent a threat for the graft or the patient. During the period after liver transplantation, the patient is recovering from surgery and the transplanted organ is adapting to its new environment. In this period, ultrasonography can show alterations in the parenchyma or Doppler findings that would be considered abnormal in other situations; these findings are usually transitory. Knowing how to interpret them is key to detecting or ruling out complications.