Muchos pacientes con enfermedad por coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) han sido diagnosticados mediante tomografía computarizada (TC). Una herramienta de pronóstico obtenida de esta podría ser un predictor útil de mortalidad.
ObjetivosEvaluar los hallazgos de la TC de tórax entre los pacientes sobrevivientes y no sobrevivientes con COVID-19 y la utilidad clínica de una puntuación de TC.
MétodosDel 1 de abril al 25 de julio de 2020 se incluyeron 124 pacientes hospitalizados con infección confirmada por SARS-CoV-2.
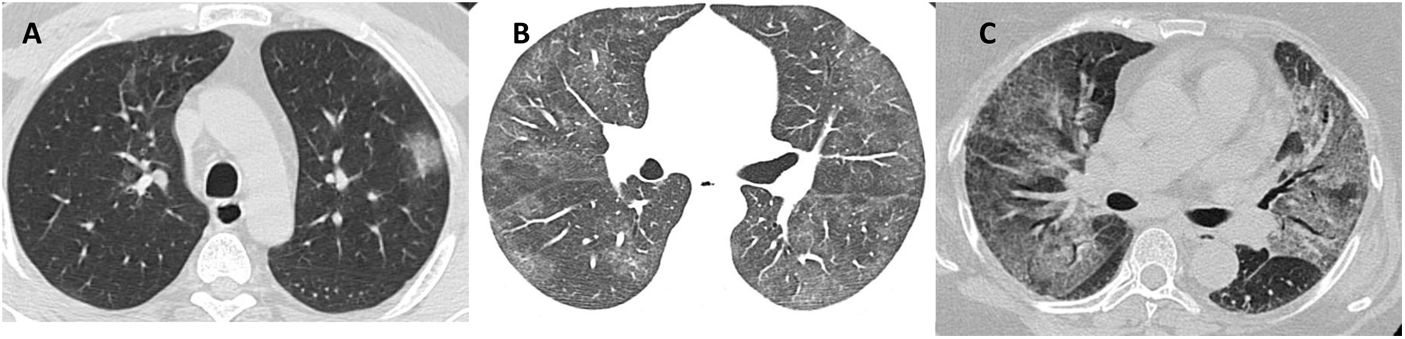
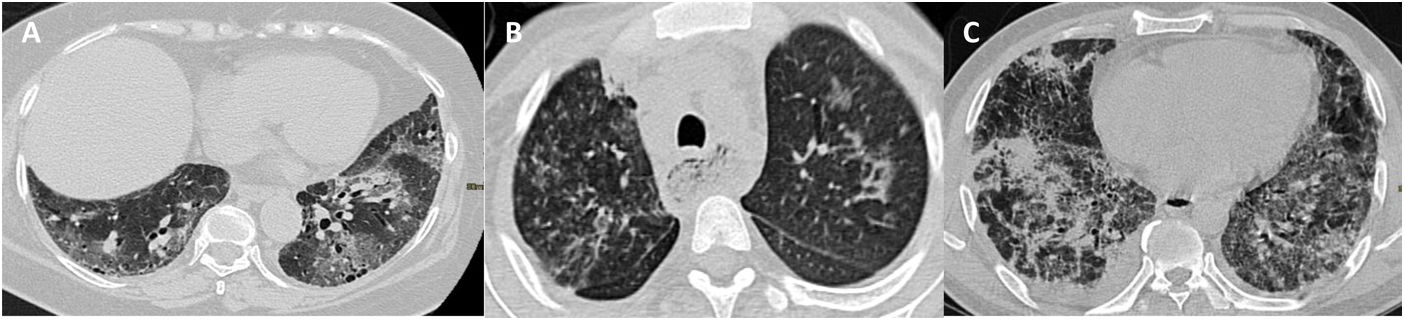
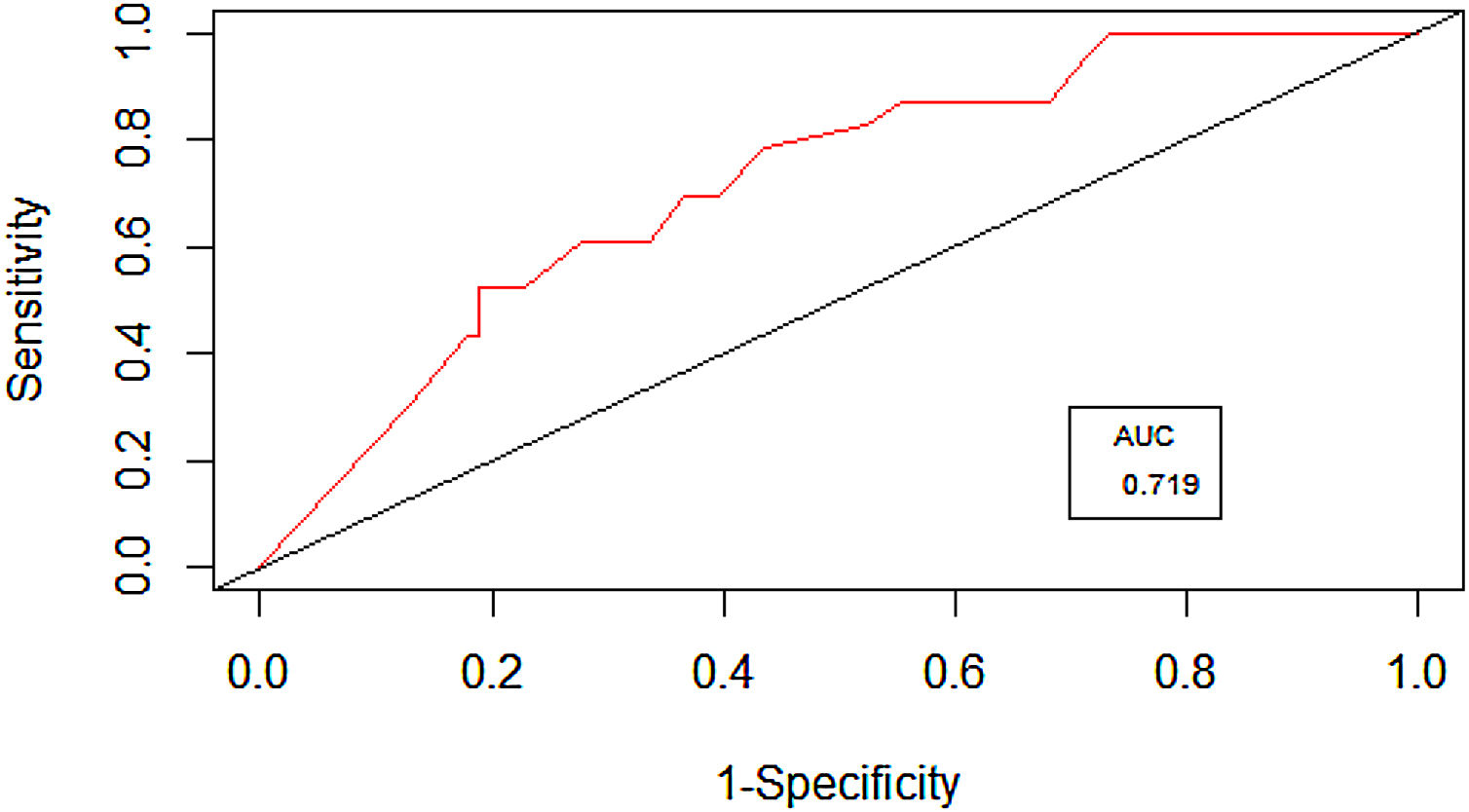
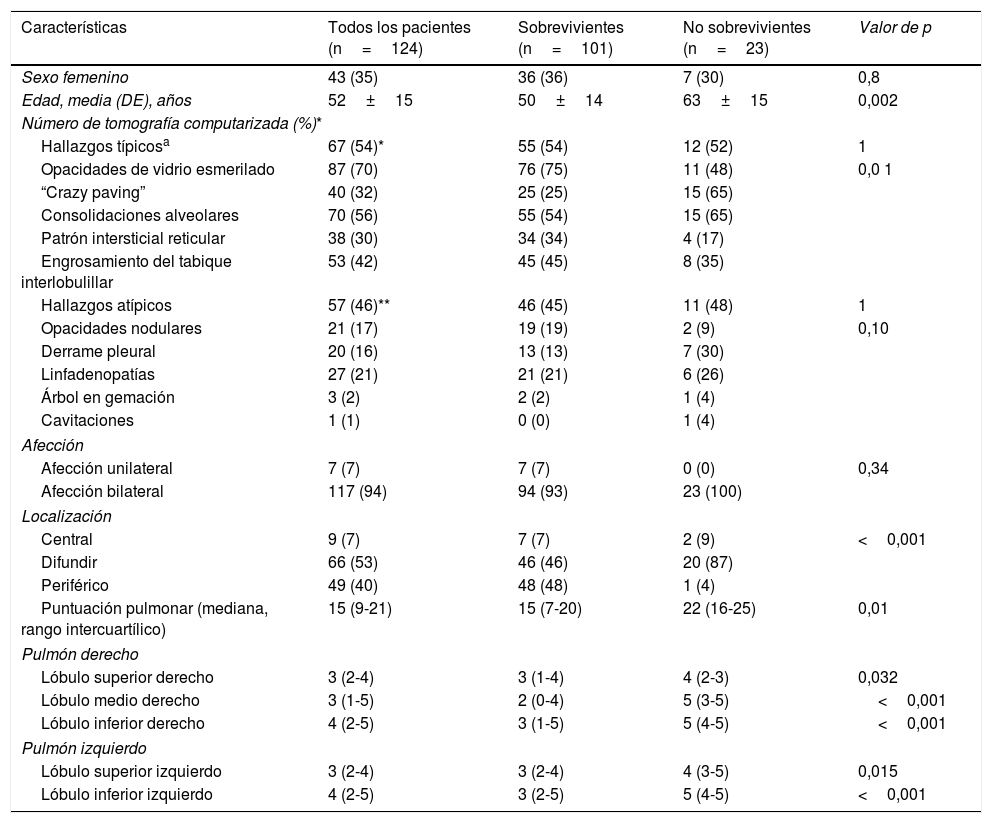
ResultadosLas opacidades en vidrio deslustrado fueron el principal hallazgo típico en los sobrevivientes (75%), mientras que el patrón de “crazy paving” o empedrado fue el principal hallazgo típico en los no sobrevivientes (65%). Los hallazgos atípicos estuvieron presentes hasta en el 46% de los pacientes. Hubo una relación directamente proporcional entre la puntuación de la TC de tórax y la mortalidad, teniendo en cuenta un punto de corte óptimo de la puntuación de la TC de 18 para predecir la muerte con una sensibilidad del 70% [intervalo de confianza (IC) del 95%: 47%-87%].
ConclusionesNuestros datos sugieren una mayor prevalencia de lesiones atípicas en esta cohorte. La puntuación de la TC de tórax tuvo una alta sensibilidad para predecir la mortalidad hospitalaria.
Many patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been diagnosed with computed tomography (CT). A prognostic tool based on CT findings could be useful for predicting death from COVID-19.
ObjectivesTo compare the chest CT findings of patients who survived COVID-19 versus those of patients who died of COVID-19 and to determine the usefulness the clinical usefulness of a CT scoring system for COVID-19.
MethodsWe included 124 patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections who were hospitalized between April 1, 2020 and July 25, 2020.
ResultsWhereas ground-glass opacities were the most common characteristic finding in survivors (75%), crazy paving was the most characteristic finding in non-survivors (65%). Atypical findings were present in 46% of patients. The chest CT score was directly proportional to mortality; a score≥18 was the best cutoff for predicting death, yielding 70% sensitivity (95%CI: 47%-87%).
ConclusionsOur results suggest that atypical lesions are more prevalent in this cohort. The chest CT score had high sensitivity for predicting hospital mortality