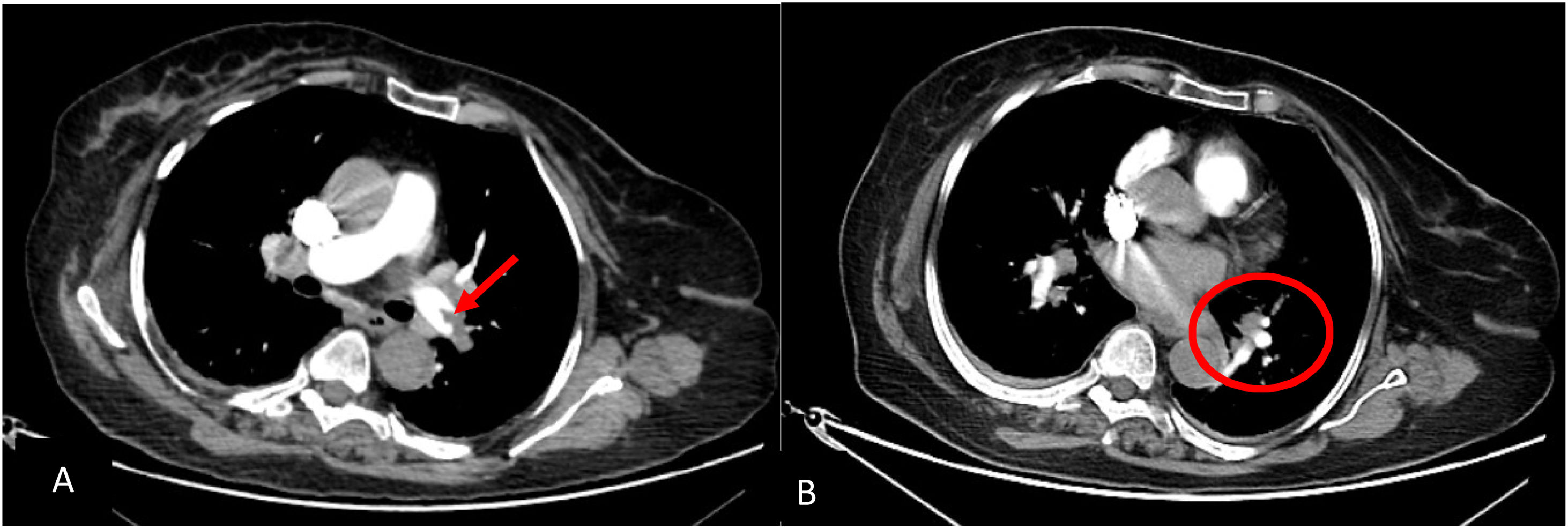
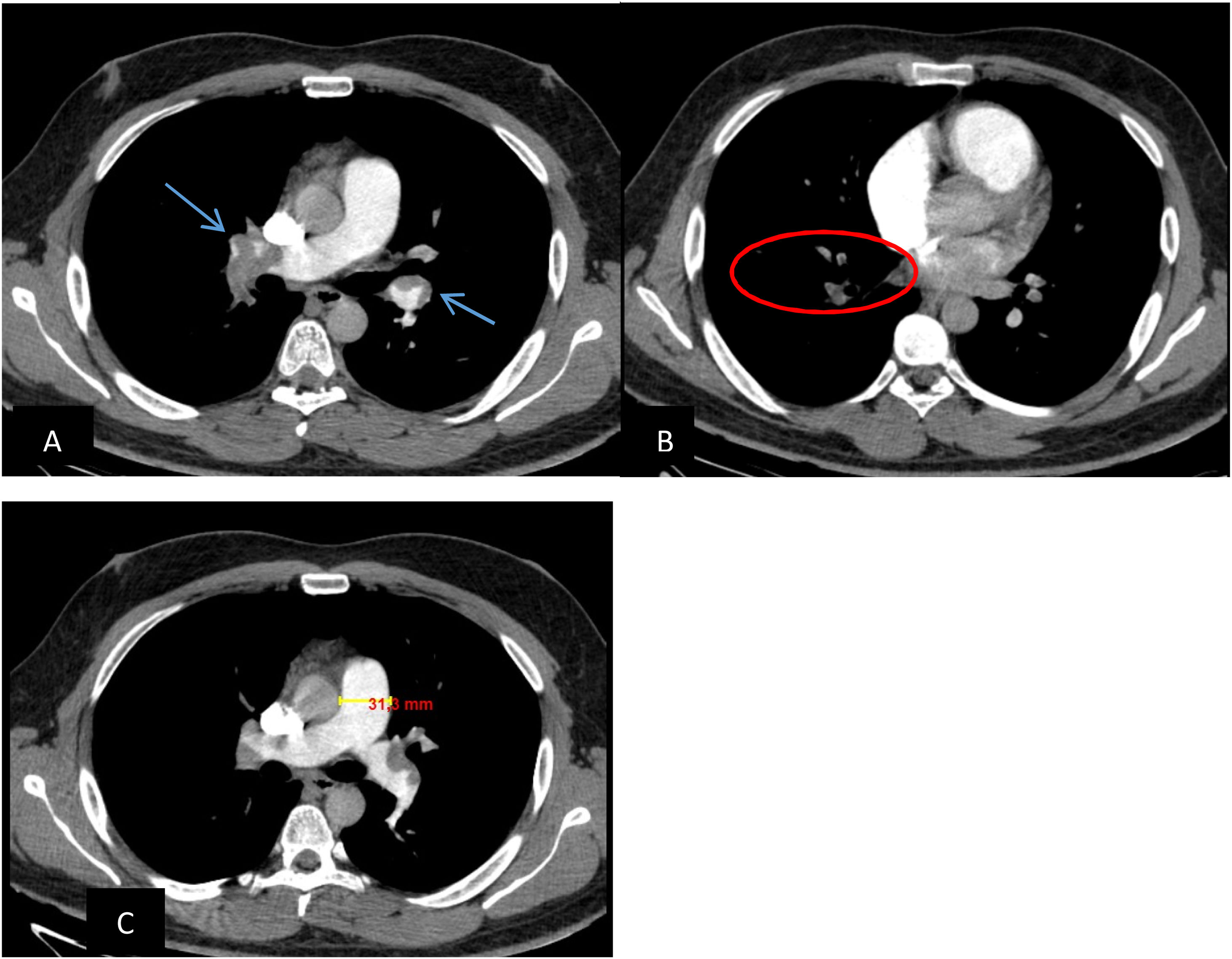
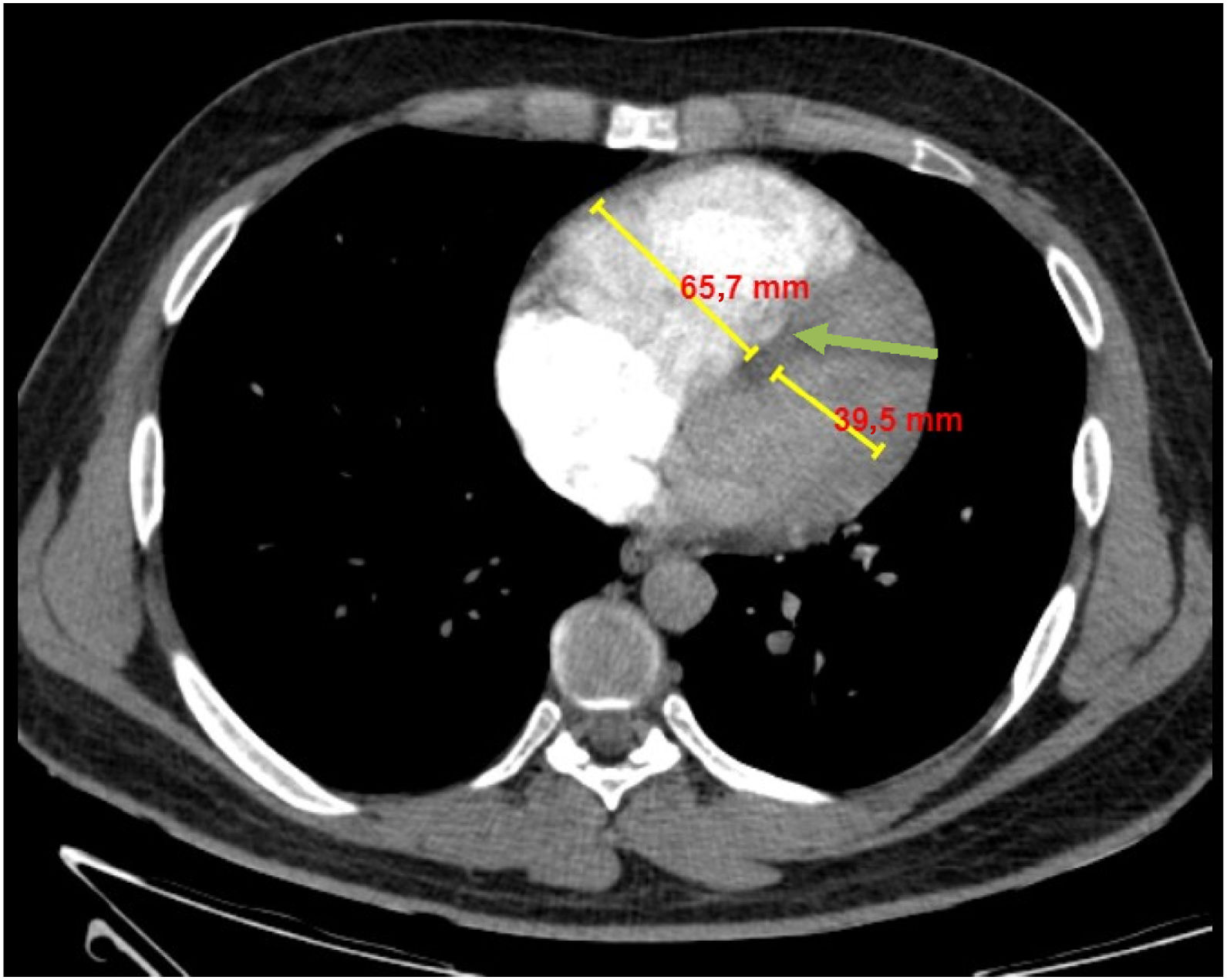
Este estudio fue diseñado para determinar los predictores de la hipertensión pulmonar y los signos de disfunción cardíaca derecha causados por la embolia pulmonar (EP) que pueden conducir a la detección temprana de los pacientes de alto riesgo. Por lo tanto, se evaluó el valor predictivo del índice de obstrucción de la arteria pulmonar (IOAP), medido mediante angiografía pulmonar por TC (APTC) en el contexto agudo, para predecir los pacientes susceptibles de sufrir complicaciones cardíacas por EP. También se investigaron otros dos índices de APTC, el diámetro de la arteria pulmonar (DAP) y el strain del ventrículo derecho (VD), en estos pacientes y se demostró su valor predictivo de las complicaciones cardíacas en la ecocardiografía de seguimiento.
Materiales y métodosEn el estudio fueron incluidos 120 pacientes con diagnóstico definitivo de EP. El IOAP, el DAP y el strain del VD se midieron mediante APTC en el momento del diagnóstico inicial. Se realizó una ecocardiografía transtorácica 6 meses después del diagnóstico de EP y se midieron los índices ecocardiográficos del VD. Se utilizó la correlación de Pearson para investigar la correlación entre IOAP, DAP, strain del VD y los signos de disfunción del hemicardio derecho.
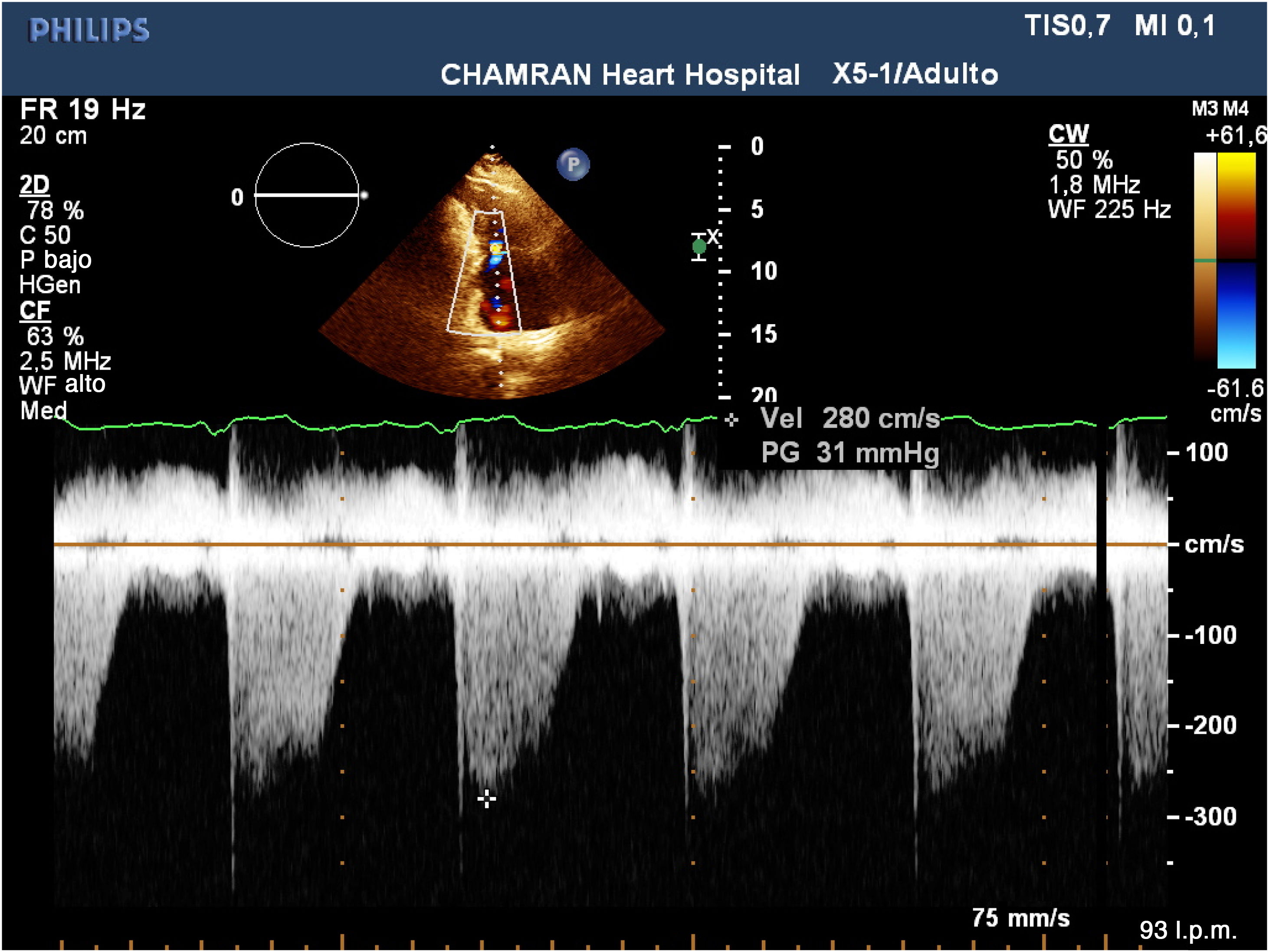
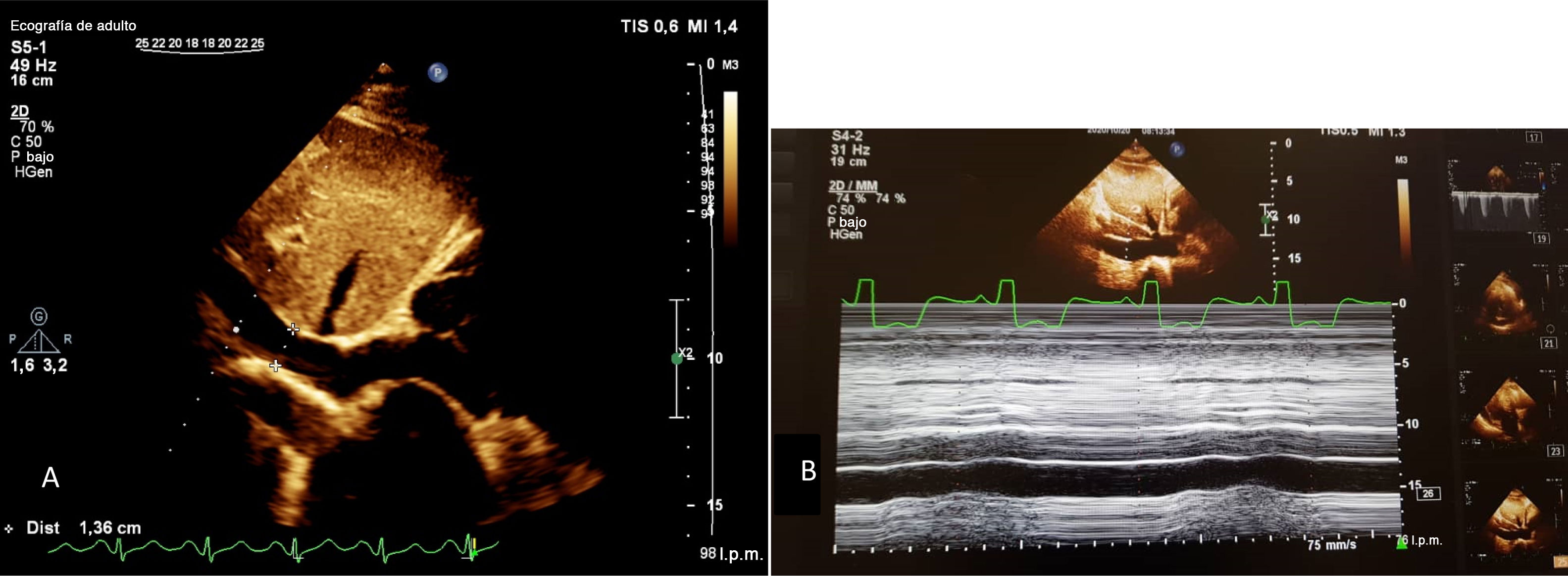
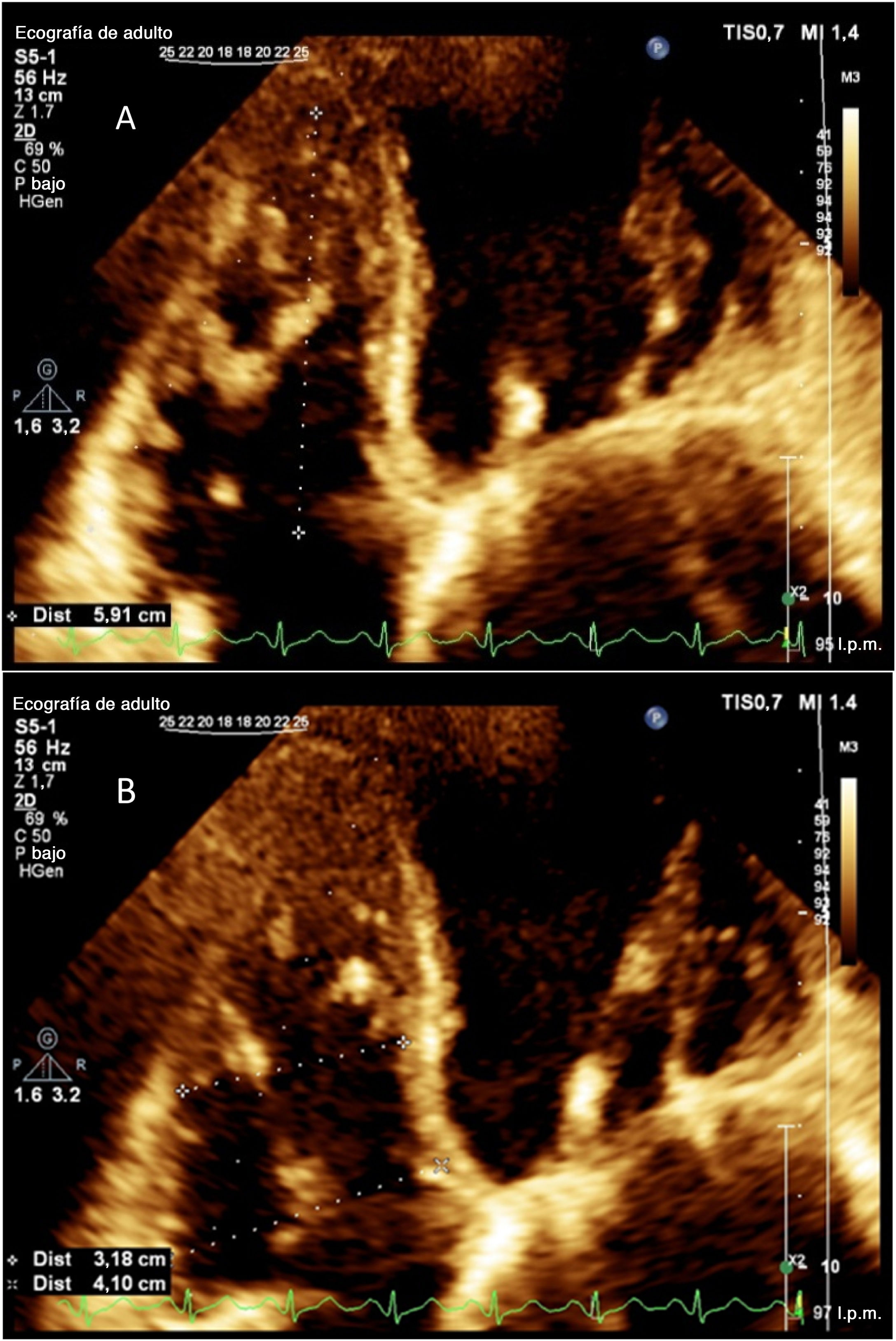
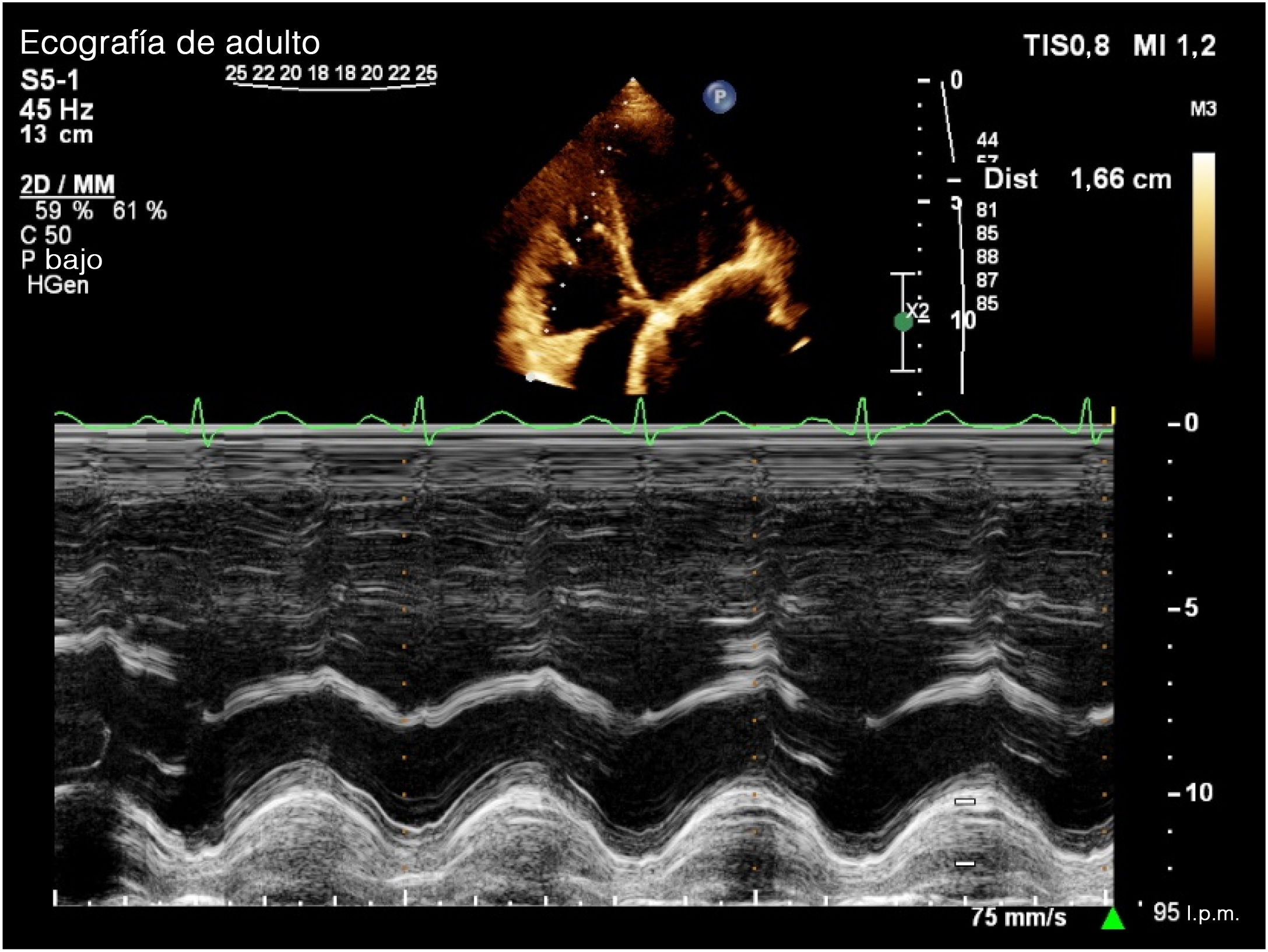
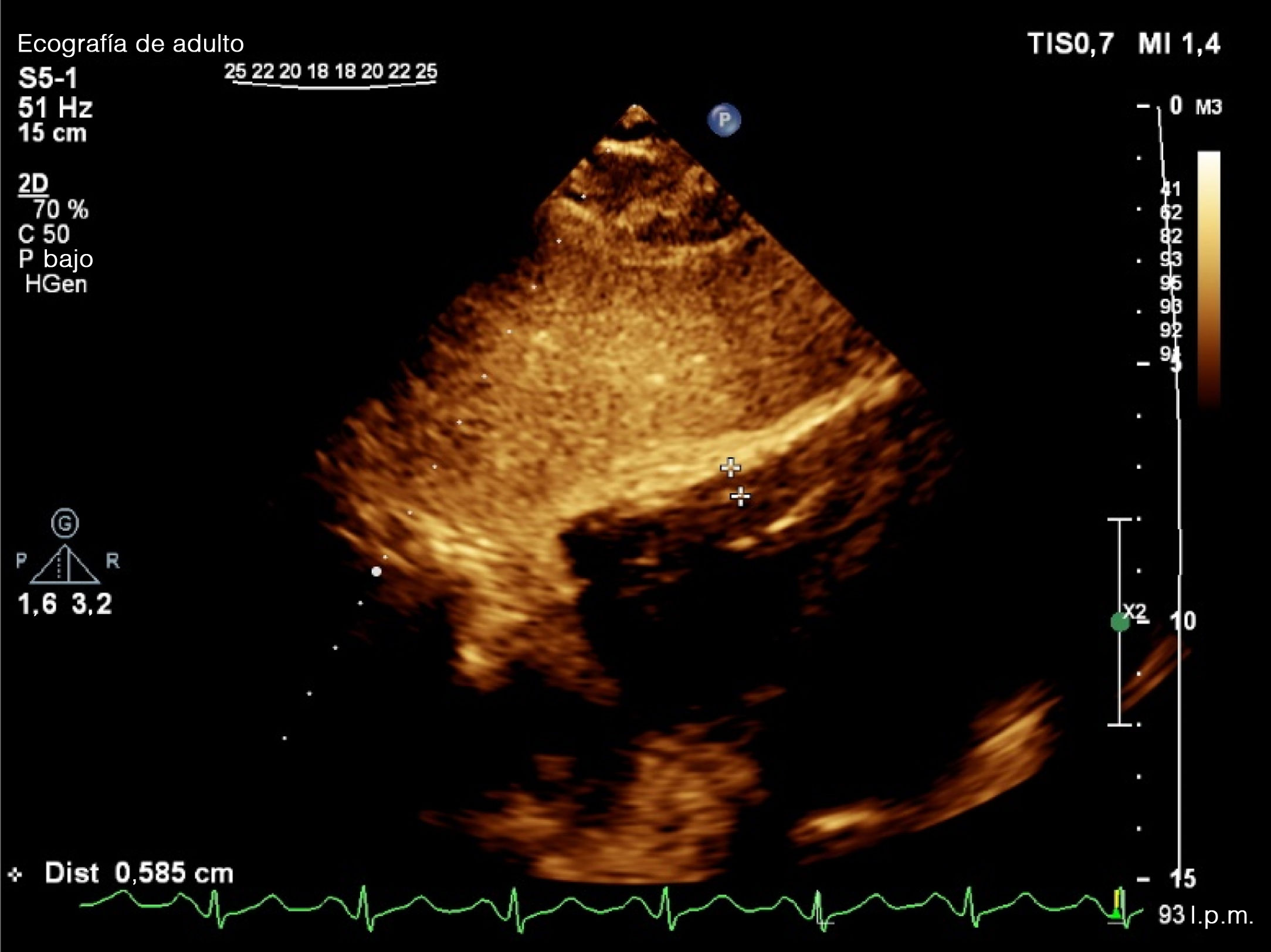
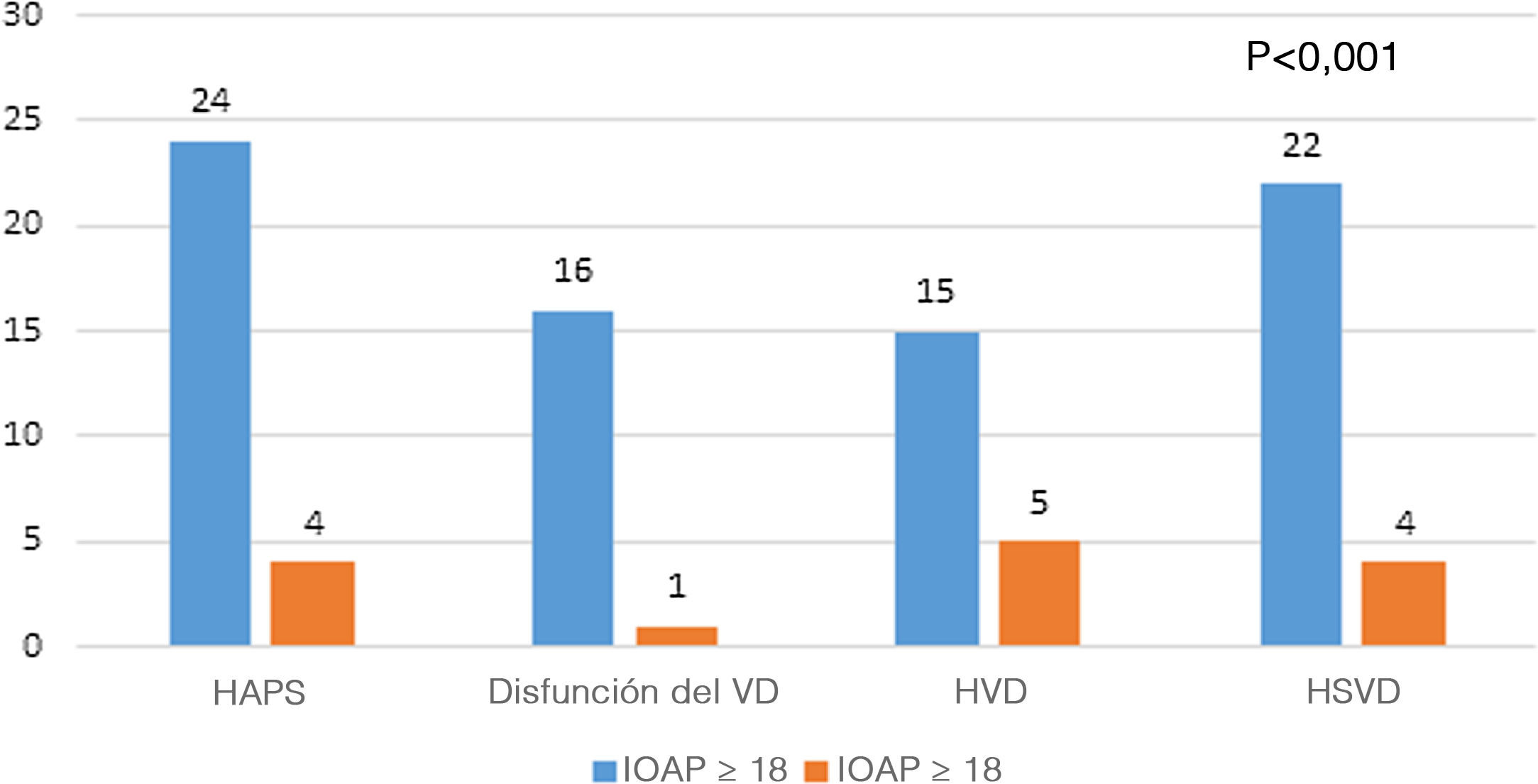
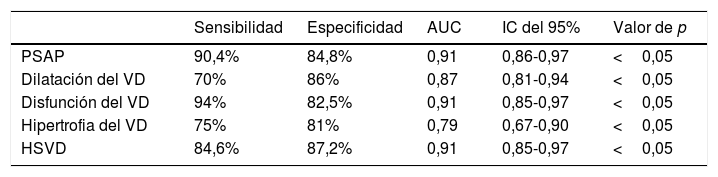
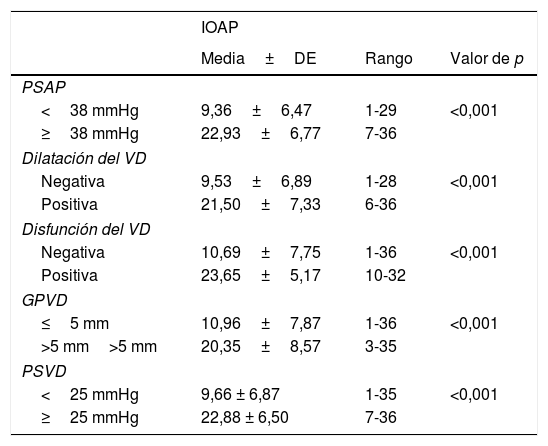
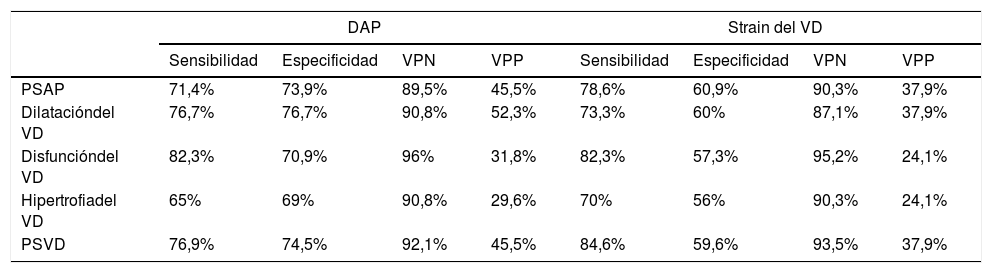
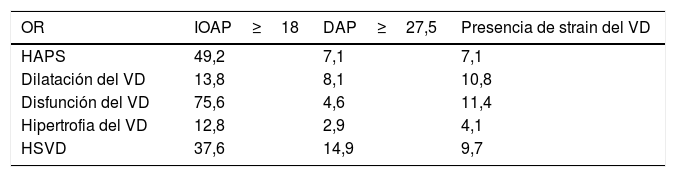
ResultadosEl IOAP estaba fuertemente correlacionado con la presión arterial pulmonar sistólica (PAPS) (r=0,83), la presión sistólica del VD (r=0,78) y el grosor de la pared del VD (r=0,61) en la ecocardiografía de seguimiento a largo plazo. Se detectó una mayor tasa de disfunción del VD y de dilatación del VD entre los pacientes con mayor IOAP (p<0,001). Un IOAP≥18 fue claramente predictivo del desarrollo de la disfunción del VD. También la evolución de la hipertensión pulmonar, la hipertensión sistólica del VD, la dilatación del VD, la disfunción del VD y la hipertrofia del VD fueron significativamente más frecuentes entre los pacientes con mayor DAP y strain del VD (p<0,001).
ConclusionesEl IOAP, el DAP y el strain del VD son índices de APTC sensibles y específicos que pueden predecir el desarrollo de complicaciones a largo plazo, como la hipertensión pulmonar y la disfunción cardíaca derecha, en el momento del diagnóstico inicial de la EP.
This study was designed to determine predictors of pulmonary hypertension and signs of right heart dysfunction caused by pulmonary embolism (PE) that may lead to early detection of high-risk patients. So the predictive value of pulmonary artery obstruction index (PAOI), measured by pulmonary CT angiography (PCTA) in the acute setting, in predicting the patients susceptible to PE cardiac complications was evaluated. Also two other PCTA indices, pulmonary artery diameter (PAD), and right ventricle (RV) strain, in these patients were investigated and their predictive value for cardiac complications on follow up echocardiography were demonstrated.
Materials and methodsIn the study 120 patients with a definite diagnosis of PE were included. The PAOI, PAD and RV strain were measured using PCTA at the time of the initial diagnosis. Transthoracic echocardiography was done 6 months after the diagnosis of PE and RV echocardiographic indices were measured. Pearson correlation was used to investigate correlation between PAOI, PAD, RV strain and signs of right heart dysfunction.
ResultsPAOI was strongly correlated with systolic pulmonary artery pressure (SPAP) (r=0.83), RV systolic pressure (r=0.78) and RV wall thickness (r=0.61) in long-term follow up echocardiography. A higher rate of RV dysfunction and RV dilation was detected among the patients with higher PAOI (P<0.001). PAOI≥18 was strongly predictive for development of RV dysfunction. Also developments of pulmonary hypertension, RV systolic hypertension, RV dilation, RV dysfunction, and RV hypertrophy were significantly more common among patients with higher PAD and RV strain (P<0.001).
ConclusionsPAOI, PAD and RV strain are sensitive and specific PCTA indices that can predict the development of long-term complications such as pulmonary hypertension and right heart dysfunction, at the time of initial PE diagnosis.