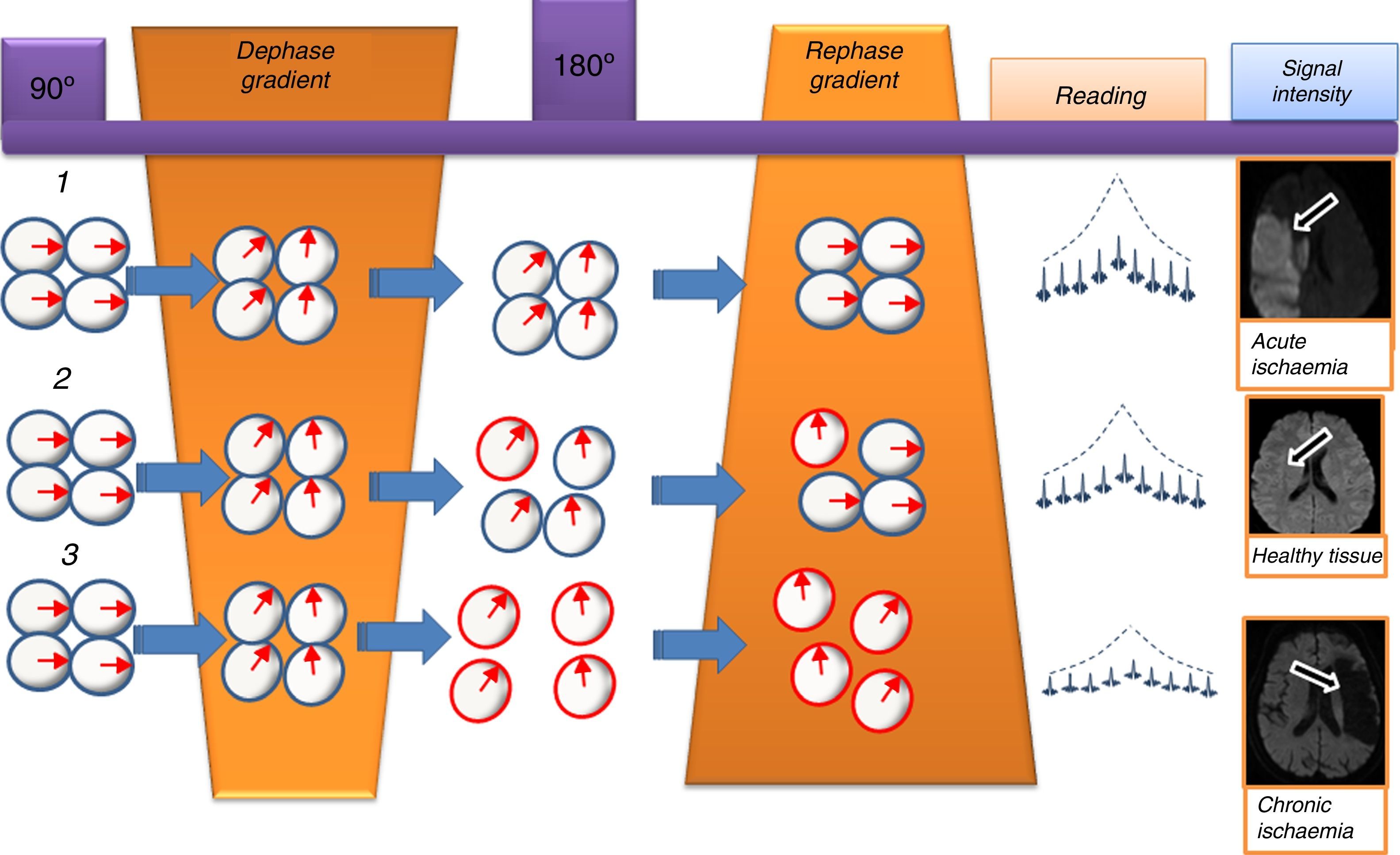
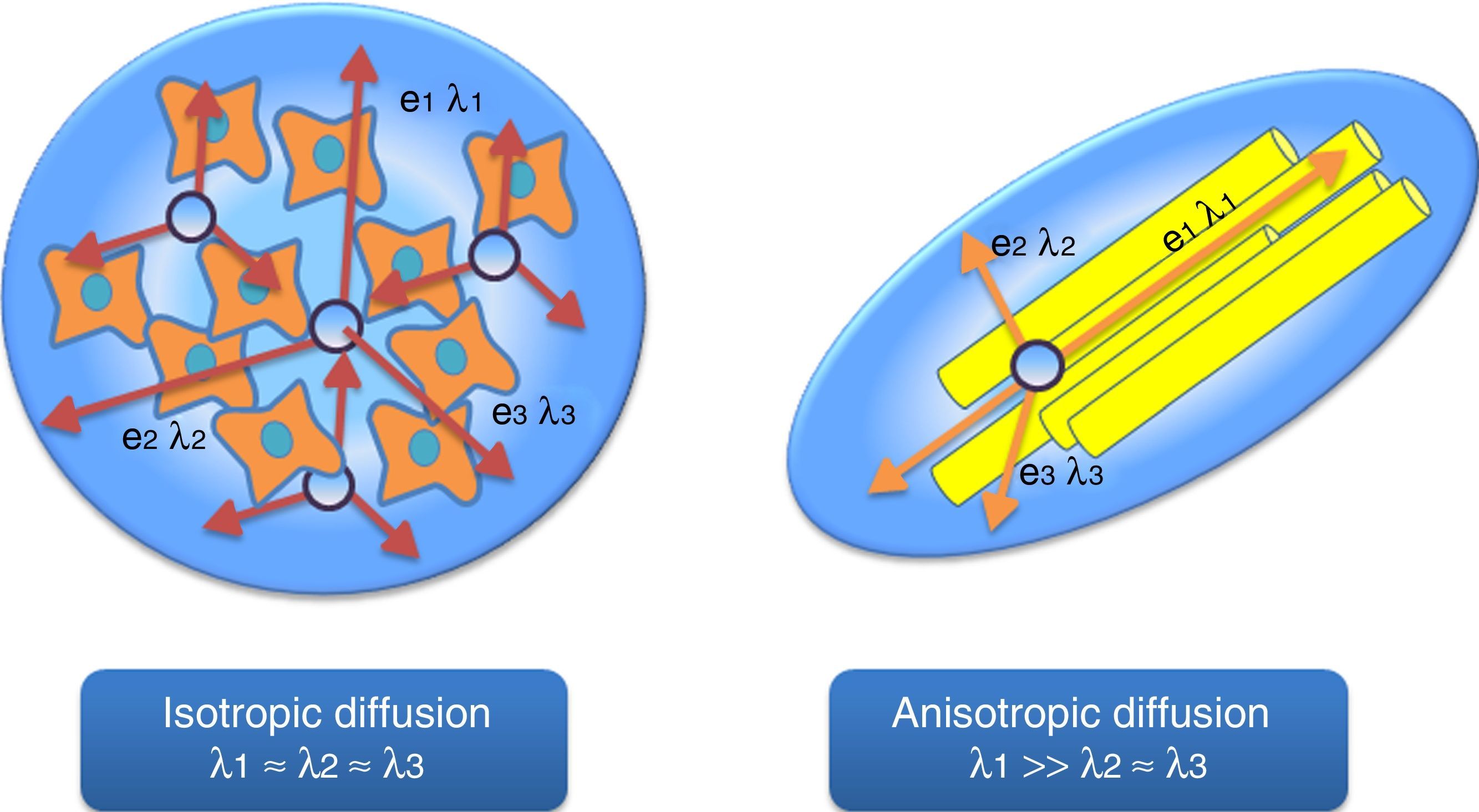
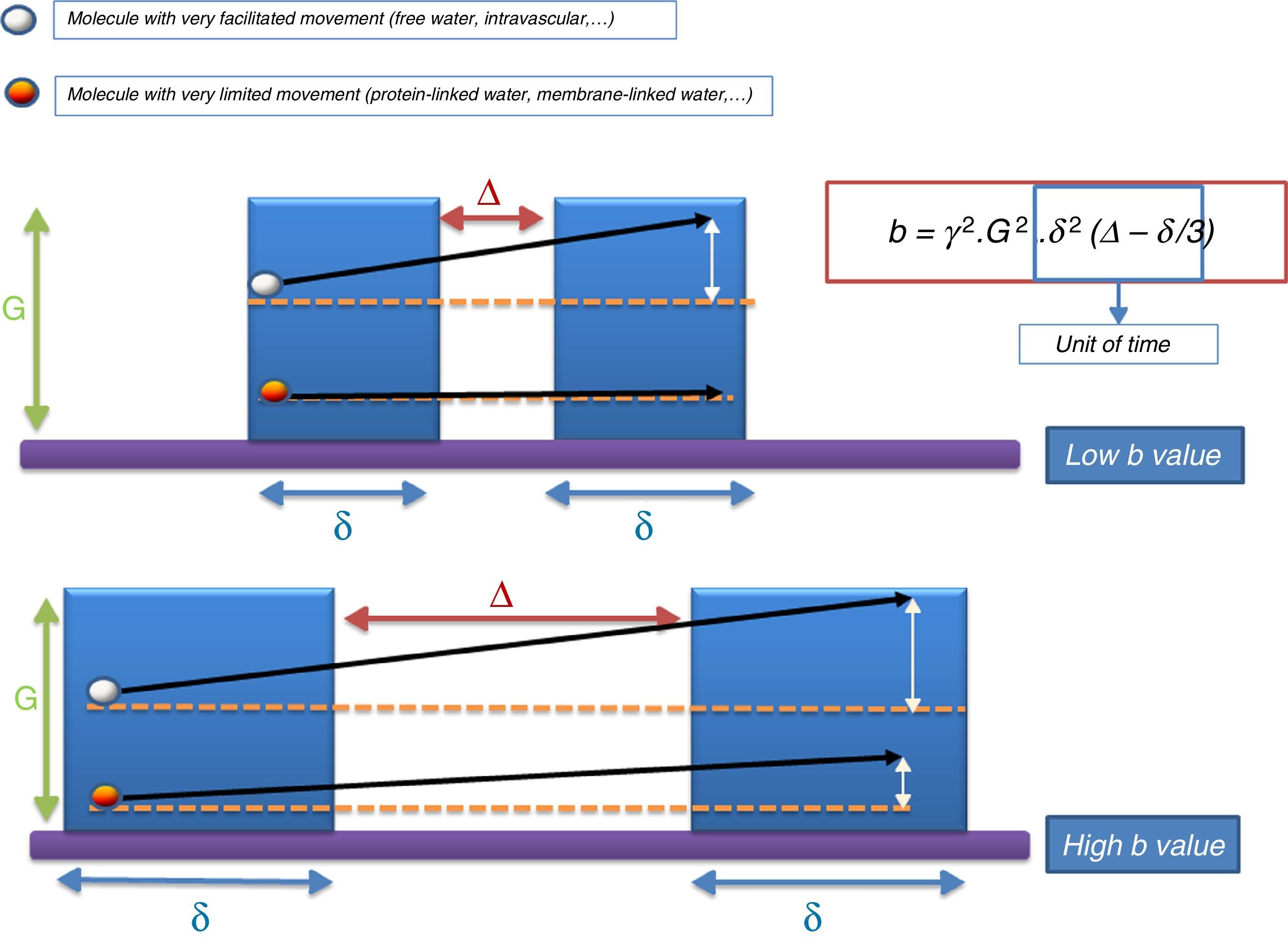
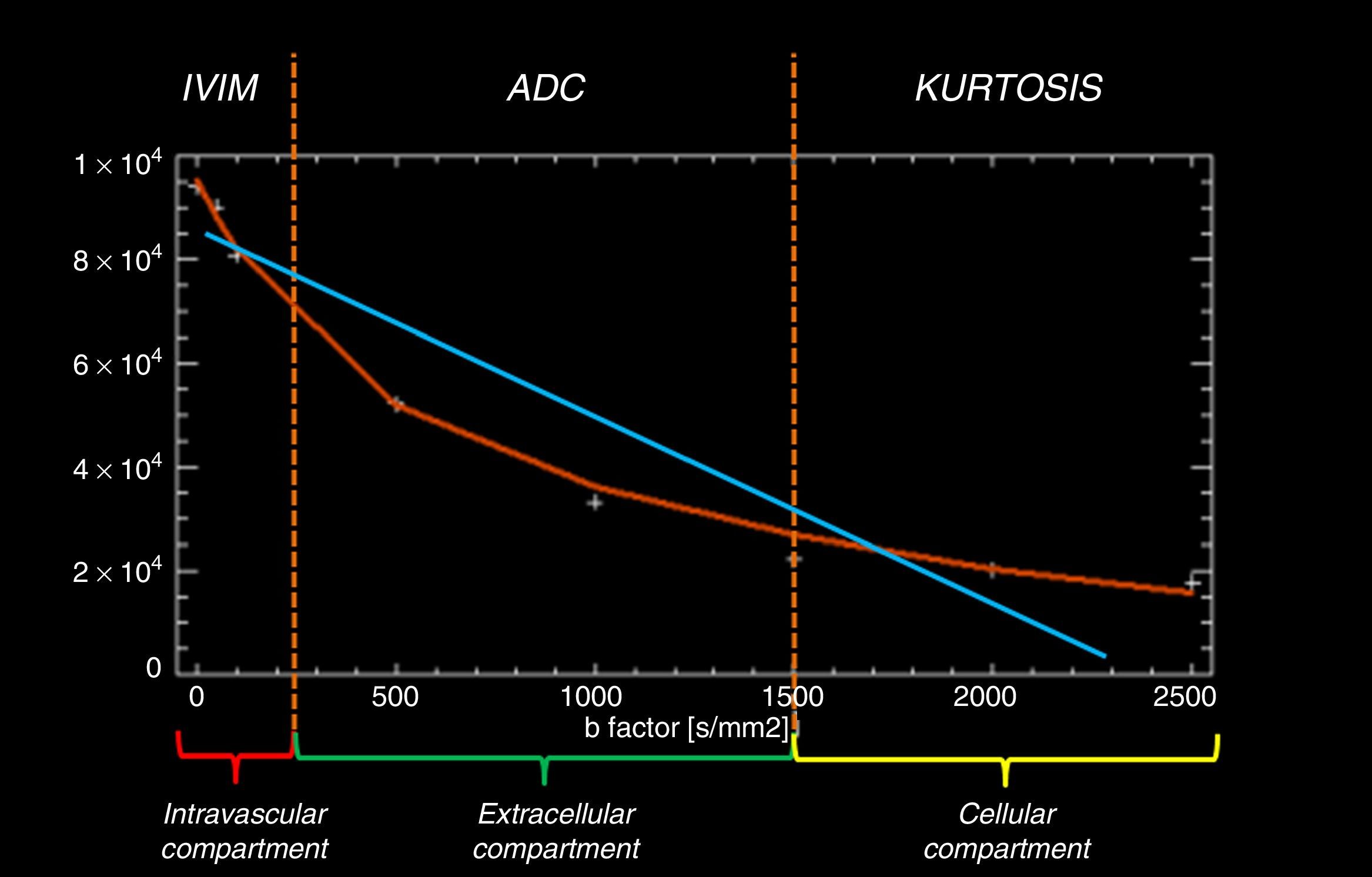
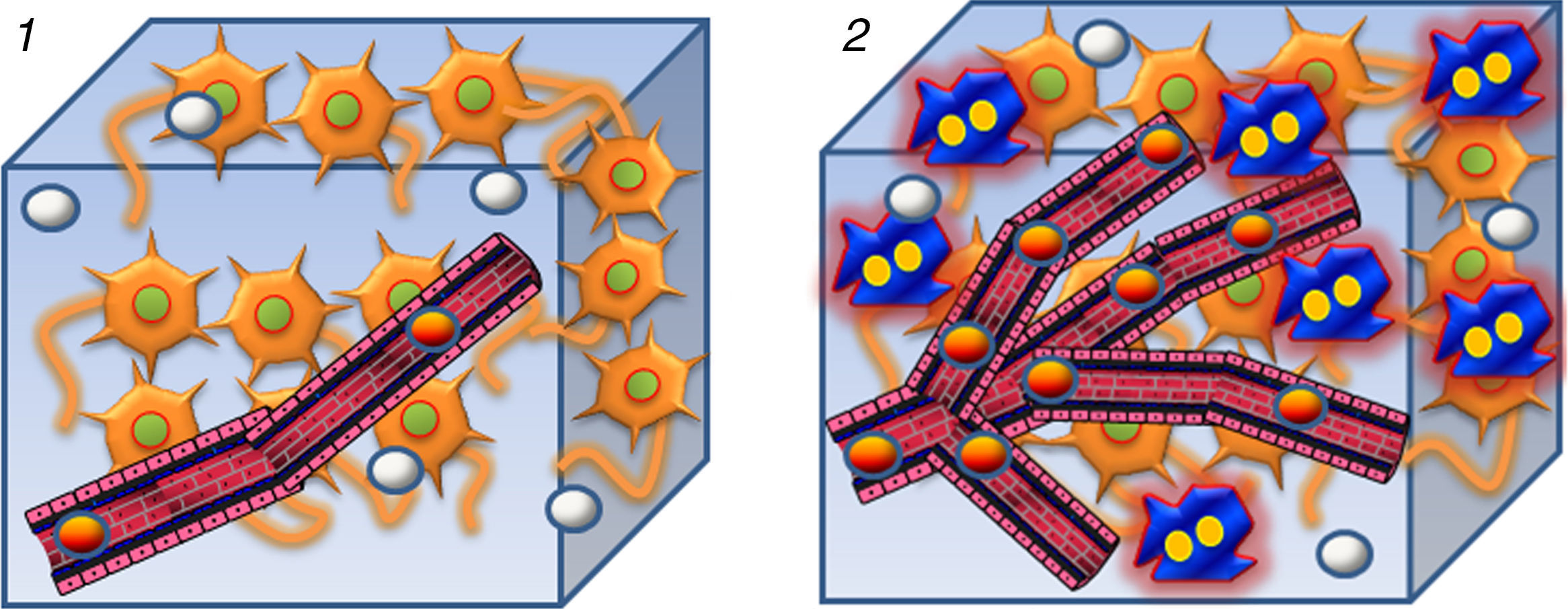
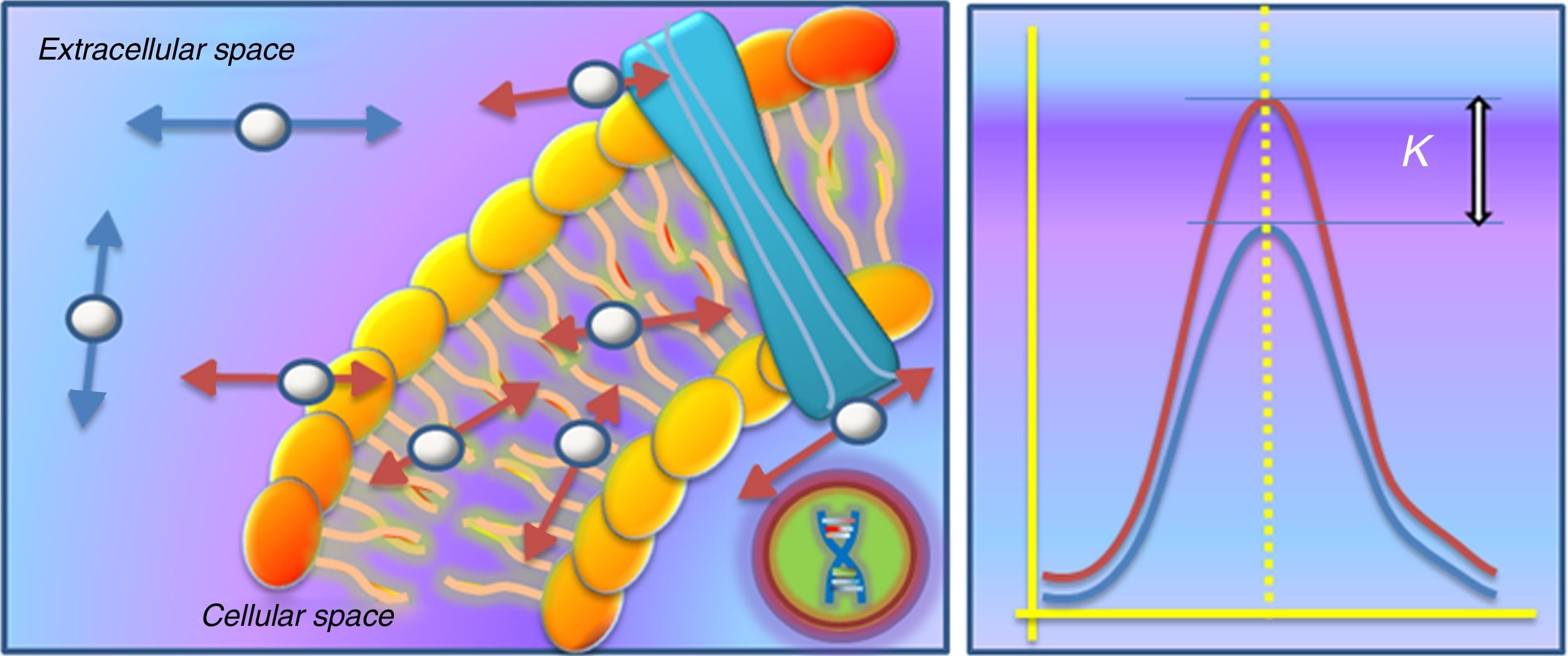
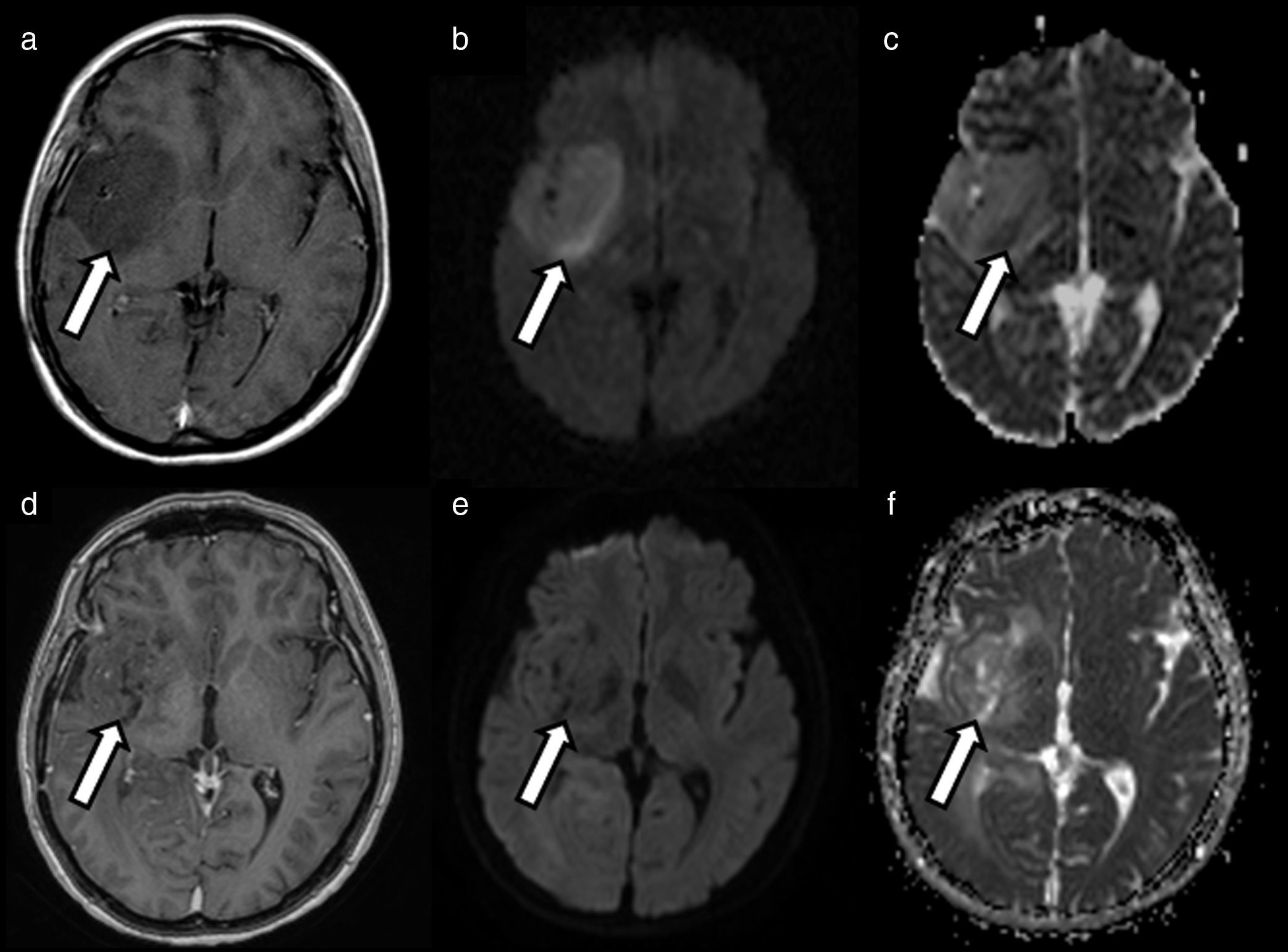
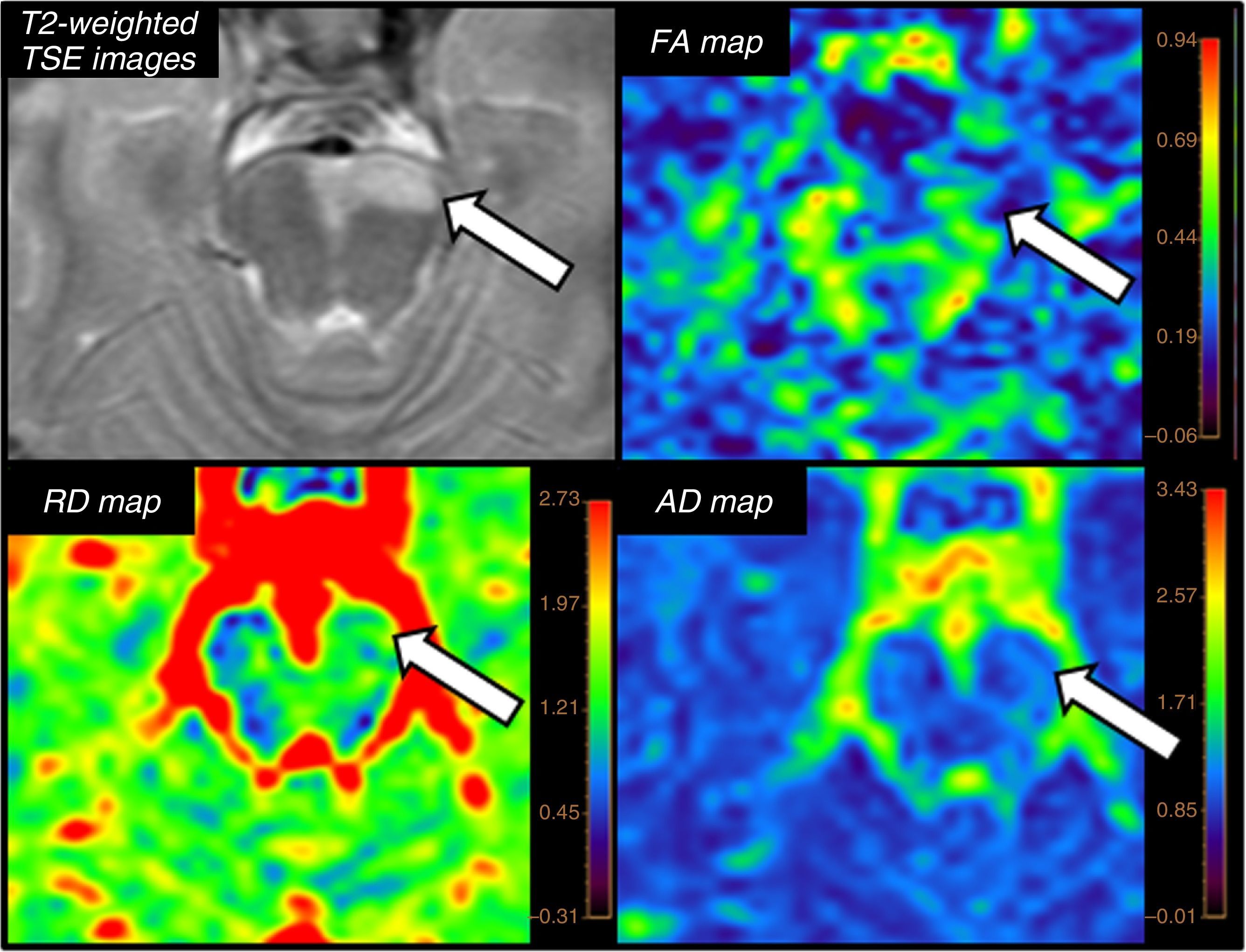
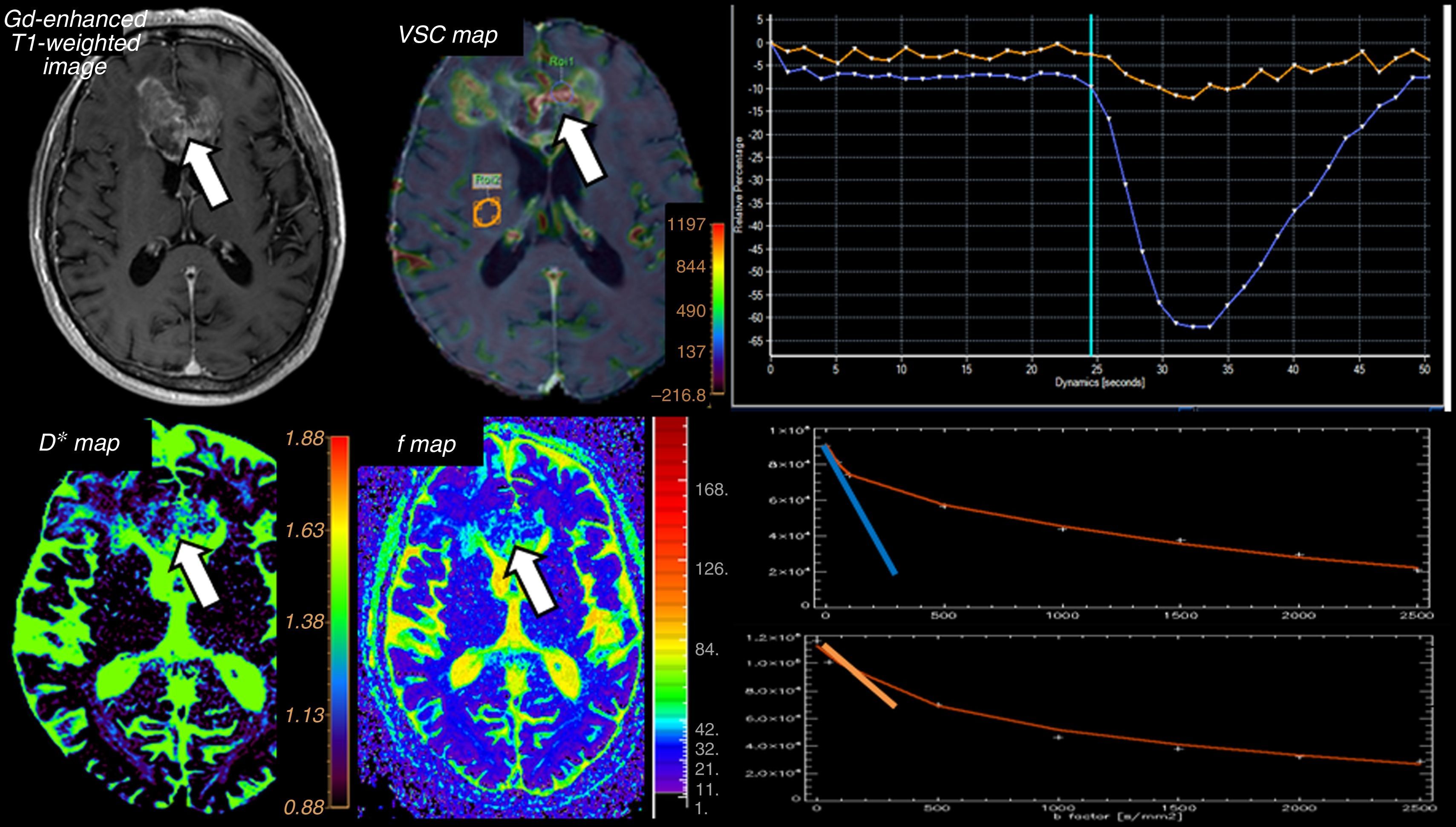
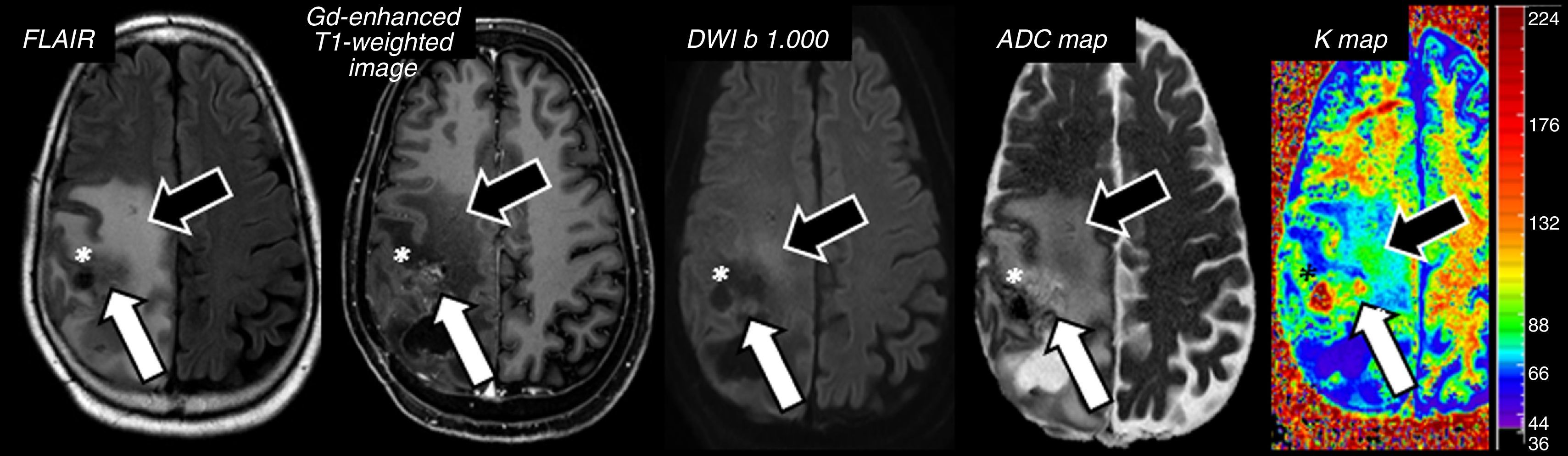
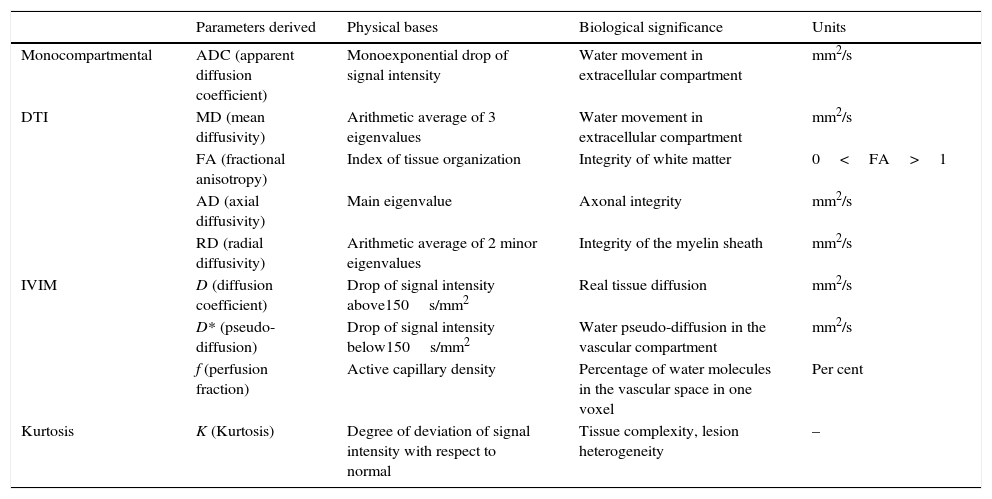
The introduction of diffusion-weighted sequences has revolutionized the detection and characterization of central nervous system (CNS) disease. Nevertheless, the assessment of diffusion studies of the CNS is often limited to qualitative estimation. Moreover, the pathophysiological complexity of the different entities that affect the CNS cannot always be correctly explained through classical models. The development of new models for the analysis of diffusion sequences provides numerous parameters that enable a quantitative approach to both diagnosis and prognosis as well as to monitoring the response to treatment; these parameters can be considered potential biomarkers of health and disease. In this update, we review the physical bases underlying diffusion studies and diffusion tensor imaging, advanced models for their analysis (intravoxel coherent motion and kurtosis), and the biological significance of the parameters derived.
La introducción de las secuencias potenciadas en difusión ha supuesto una revolución para la detección y caracterización de la patología del sistema nervioso central. Sin embargo, en numerosas ocasiones, la valoración de dichos estudios se limita a una estimación cualitativa. Además, la complejidad fisiopatológica de las distintas entidades que afectan al sistema nervioso central no siempre puede ser correctamente explicada por los modelos clásicos. El desarrollo de nuevo modelos para el análisis de las secuencias de difusión aporta numerosos parámetros que podrían permitir un abordaje cuantitativo tanto desde el punto de vista del diagnóstico como pronóstico, así como para llevar a cabo la monitorización terapéutica, y podrían ser considerados como potenciales biomarcadores de salud y enfermedad. Realizamos por este motivo una actualización que incluye las bases físicas de los estudios de difusión y tensor de difusión, sus modelos de análisis avanzado (IVIM y Kurtosis) y la significación biológica de los parámetros derivados.