To use imaging and laboratory techniques to evaluate the vascular distribution of magnetofluid in a rat model of liver metastases.
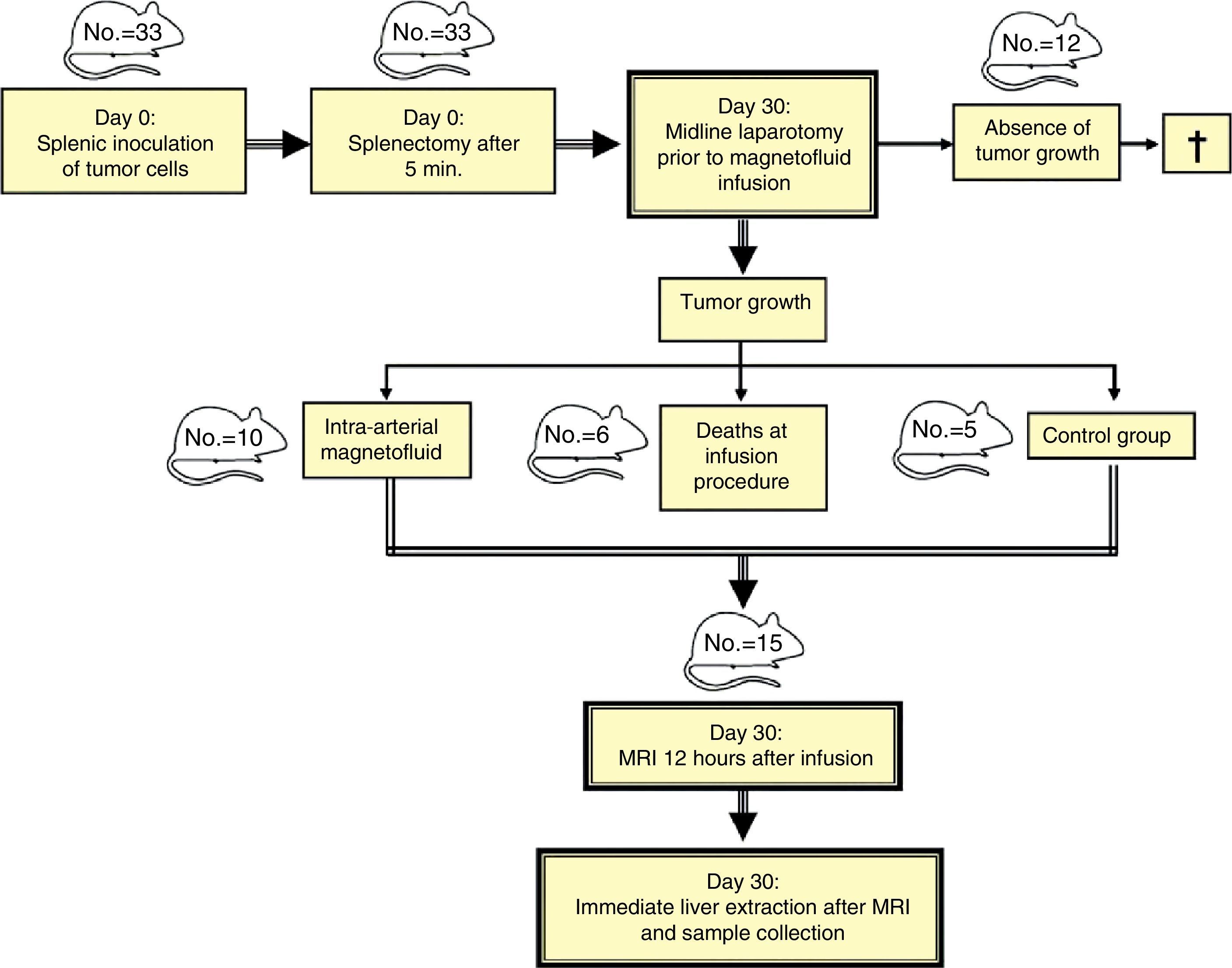
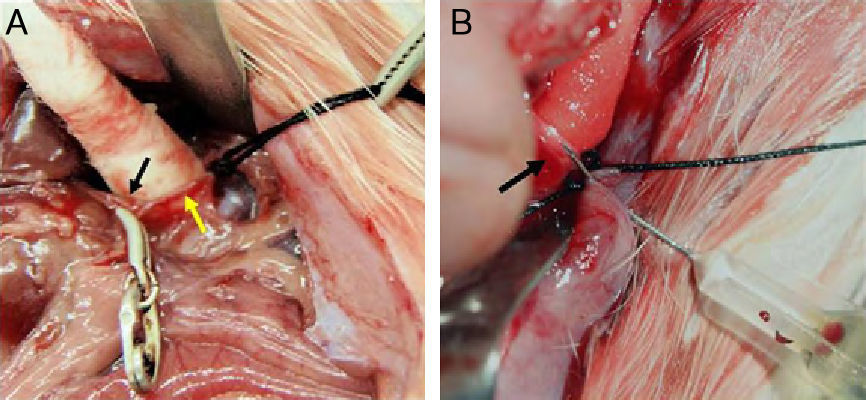
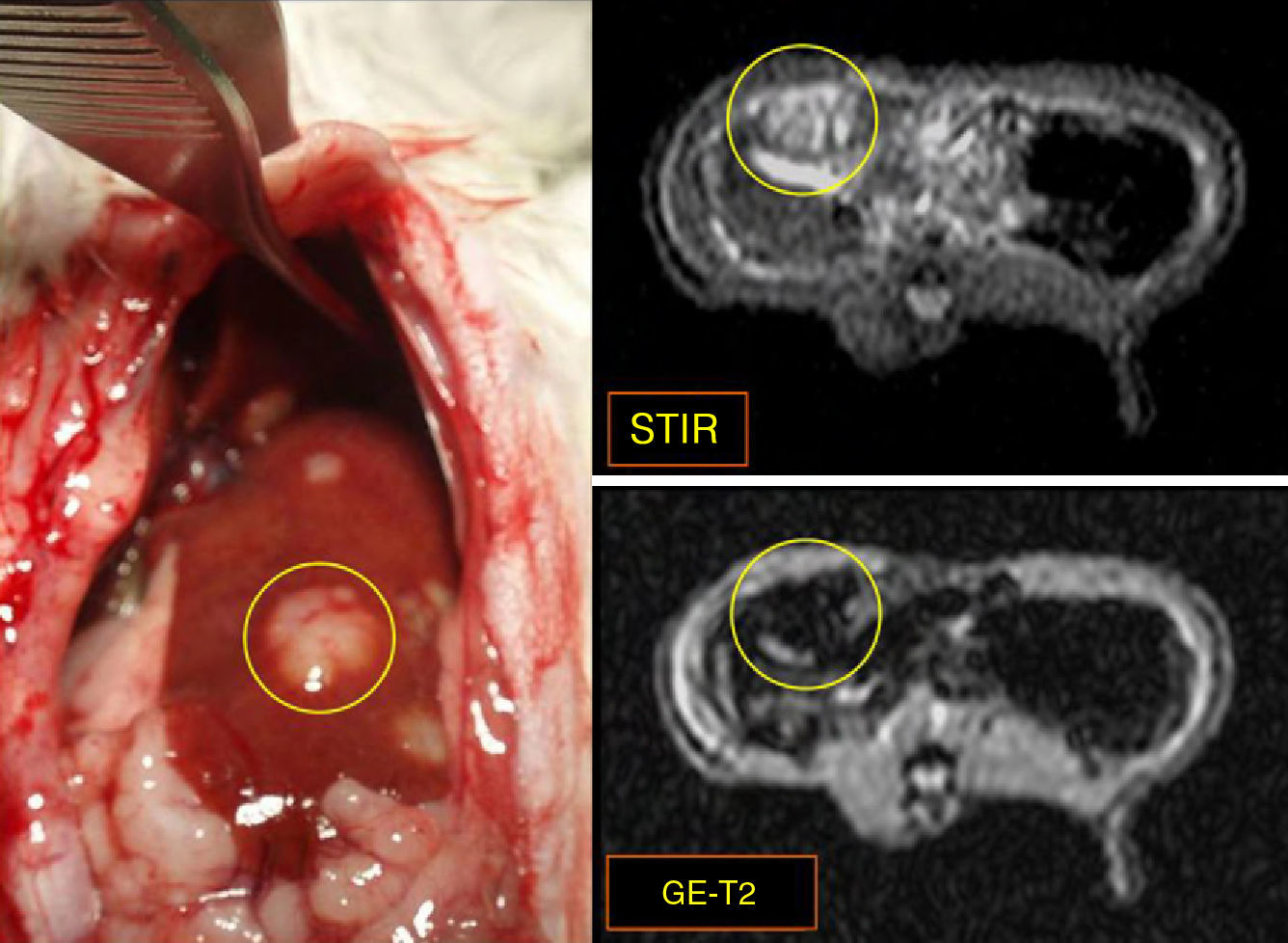
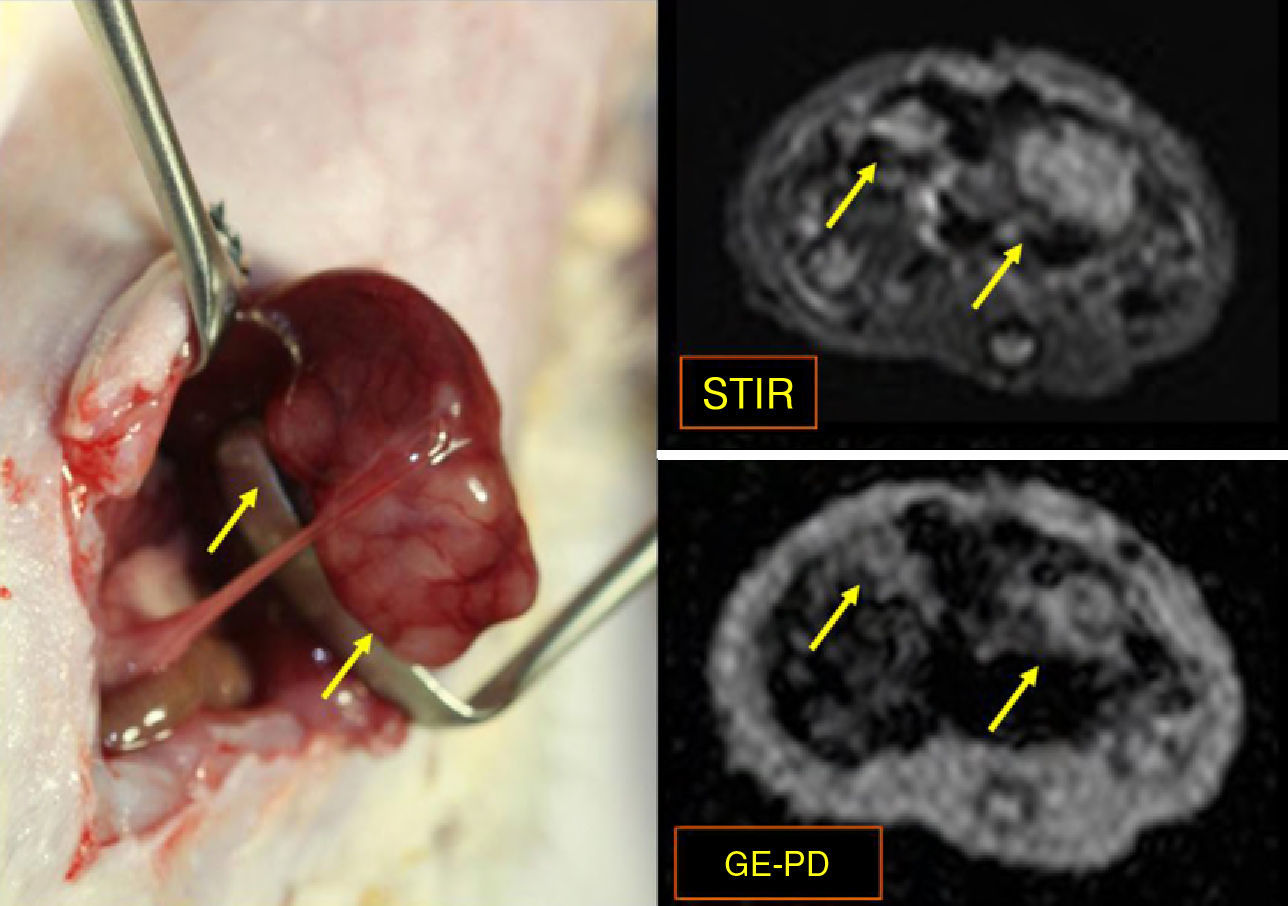
Material and methodsThe livers of 33 WAG/Rij Crl rats were seeded with CC-531 colorectal cancer cells. After we checked tumor development, 10 rats received hepatic intra-arterial infusions of Lipiodol® with nanoparticles of Fe3O4 in suspension, and 5 were reserved as controls. Axial STIR (TR: 3600ms/TE: 29ms/TI: 130ms) and gradient-echo (GE) (120/4 and 120/14) MRI sequences were acquired on a 1.5 T scanner. After necropsy, rats were classified into one of two stages according to tumor development: early (<10 metastases, each <3mm) or advanced (>10 metastases, each >3mm). Samples of liver and of metastases were taken from the 15 animals for quantification of iron concentrations by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS). The data were analyzed using nonparametric tests; values of p<0.05 were considered significant.
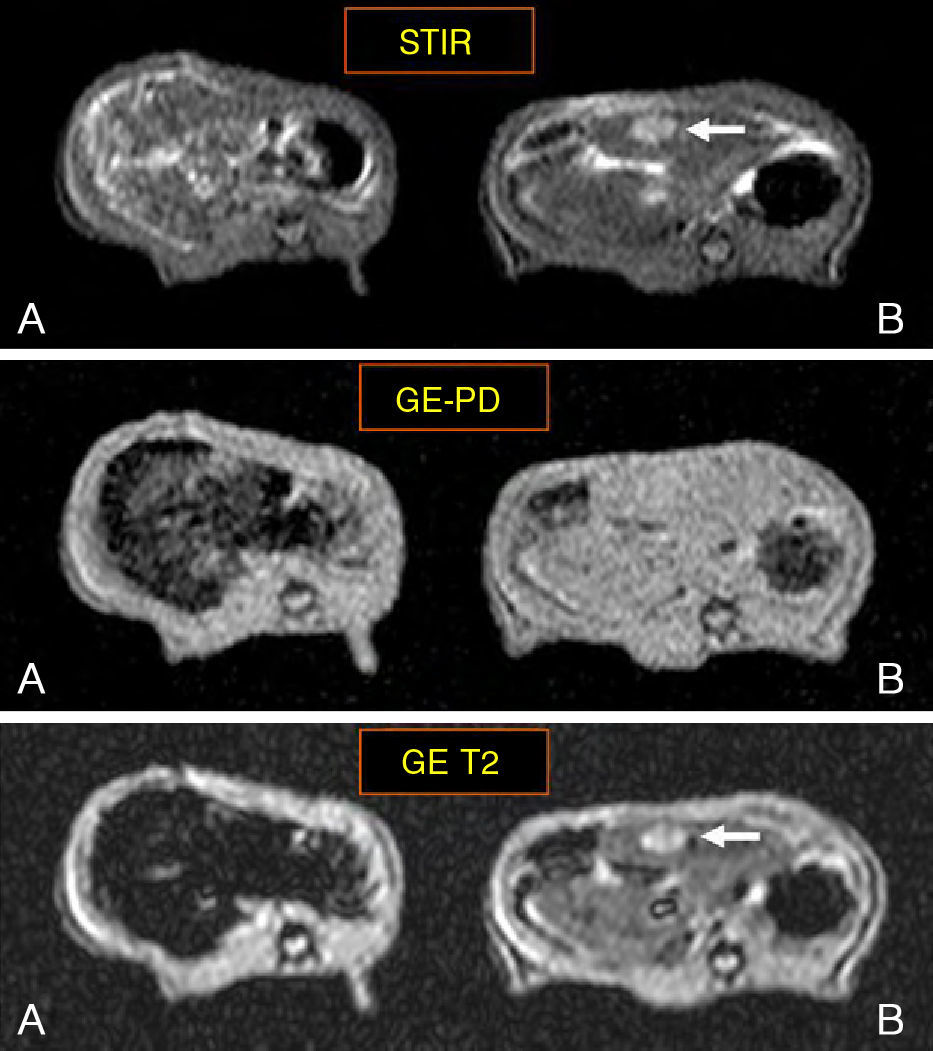
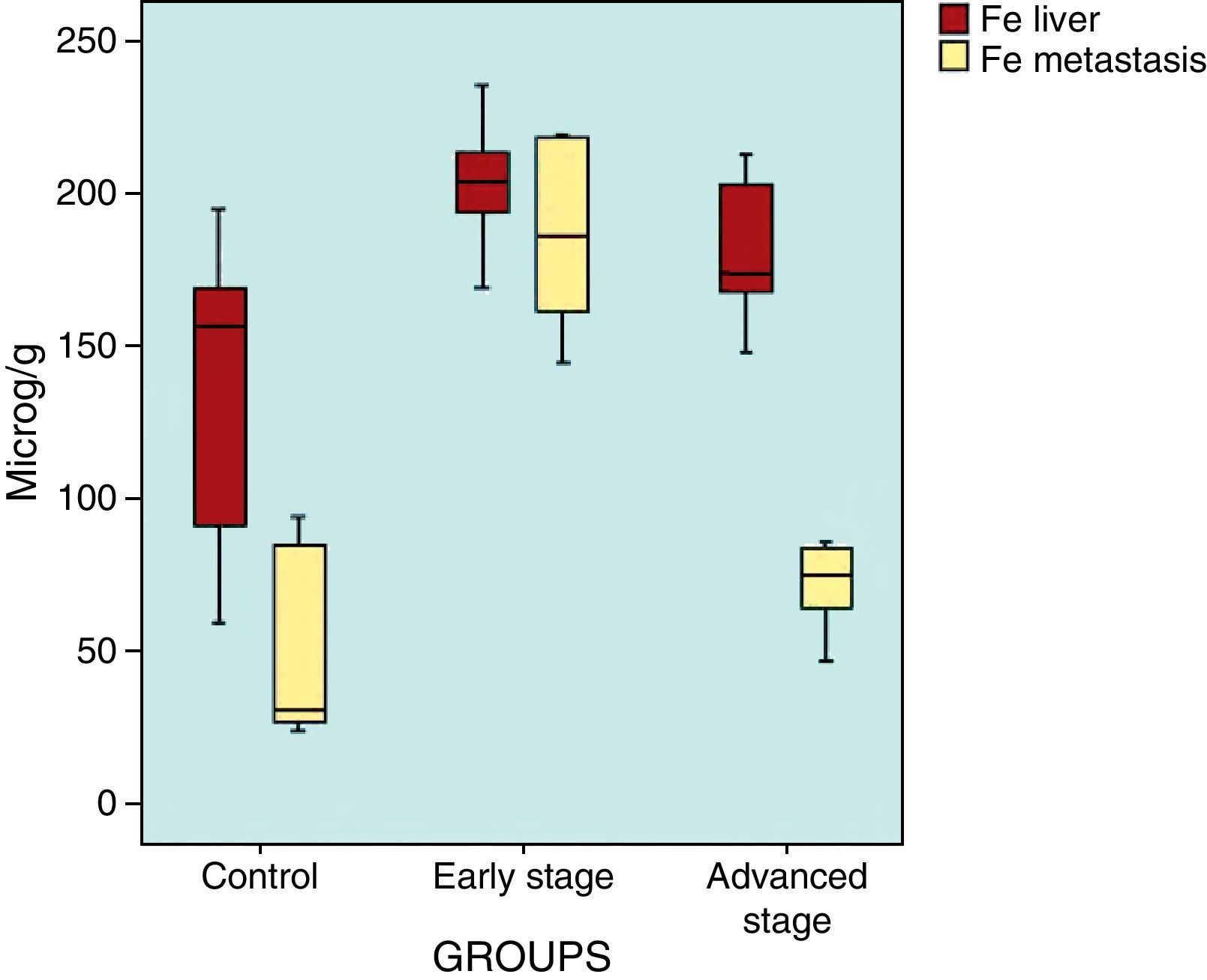
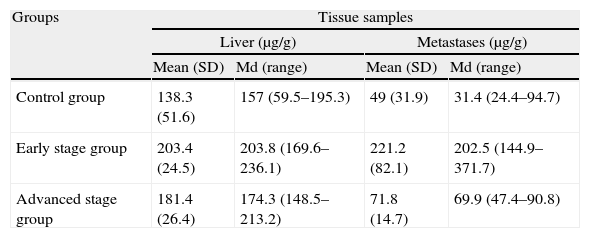
ResultsFive animals had early tumor development and five had advanced tumor development. In the GE sequences, early stage metastases showed homogeneous signal reduction attributable to the presence of magnetofluid. Spectrometry found significant differences between the iron concentration in rats with early stage metastases and controls (p=0.002) as well as between rats with early stage metastases and those with late stage metastases (p=0.001). The ratio of exogenous iron in metastases and in liver in early stage rats was 2.6:1. The concentration of exogenous iron in the liver was significantly different from that in tumors only in early stage animals (p=0.043).
ConclusionsMRI and spectrometry made it possible to evaluate the vascular distribution of magnetofluid in the liver and revealed the differences in its affinity for metastases in different stages of disease.
Valorar la distribución vascular de un magnetofluido por técnicas de imagen y laboratorio, en un modelo de metástasis hepáticas.
Material y métodosEl hígado de 33 ratas WAG/RijCrl fue diseminado con células de carcinoma colorrectal CC-531. Tras comprobar desarrollo tumoral, diez ratas recibieron infusionesintrarteriales hepáticas de Lipiodol® con nanopartículas de Fe3O4 en suspensión, y cinco se reservaron como controles. Posteriormente, en RM de 1,5 T se practicaron secuencias axiales STIR (TR: 3.600 ms/TE: 29 ms/TI: 130 ms) y eco de gradiente (EG) (120/4 y 120/14). Tras necropsia, según desarrollo tumoral, las ratas se clasificaron en dos estadios: precoz (< 10 metástasis, de < 3 mm), avanzado (> 10 metástasis, de > 3 mm). De los 15 animales se tomaron muestras de hígado y metástasis, para cuantificar mediante espectrometría (ICP-MS) las concentraciones de hierro. En el análisis estadístico se emplearon pruebas no paramétricas. Se consideraron significativos valores de p < 0,05.
ResultadosCinco animales presentaron afectación precoz y cinco, avanzada. En secuencias EG, las metástasis en estadio precoz mostraron disminución homogénea de se¿nal atribuible a presencia de magnetofluido. La espectrometría demostró diferencias significativas entre la concentración de hierro determinado en metástasis de ratas en estadio precoz y control (p = 0,002), y entre animales en estadio precoz y avanzado (p = 0,001). La razón entre hierro exógeno metastásico y hepático en ratas en estadio precoz fue 2,6:1. La concentración de hierro exógeno hepático y tumoral mostró diferencias significativas sólo en animales en estadio precoz (p = 0,043).
ConclusionesRM y Espectrometría permitieron evaluar la distribución vascular hepática del magnetofluido, y revelaron su desigual afinidad por metástasis en diferentes estadios.