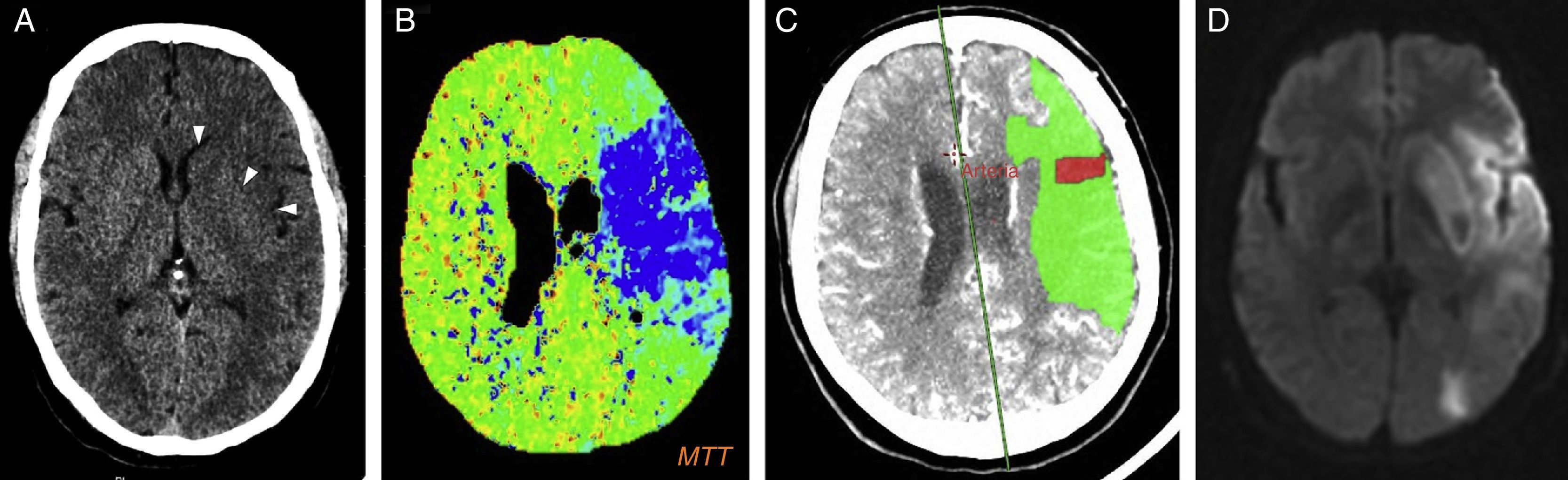
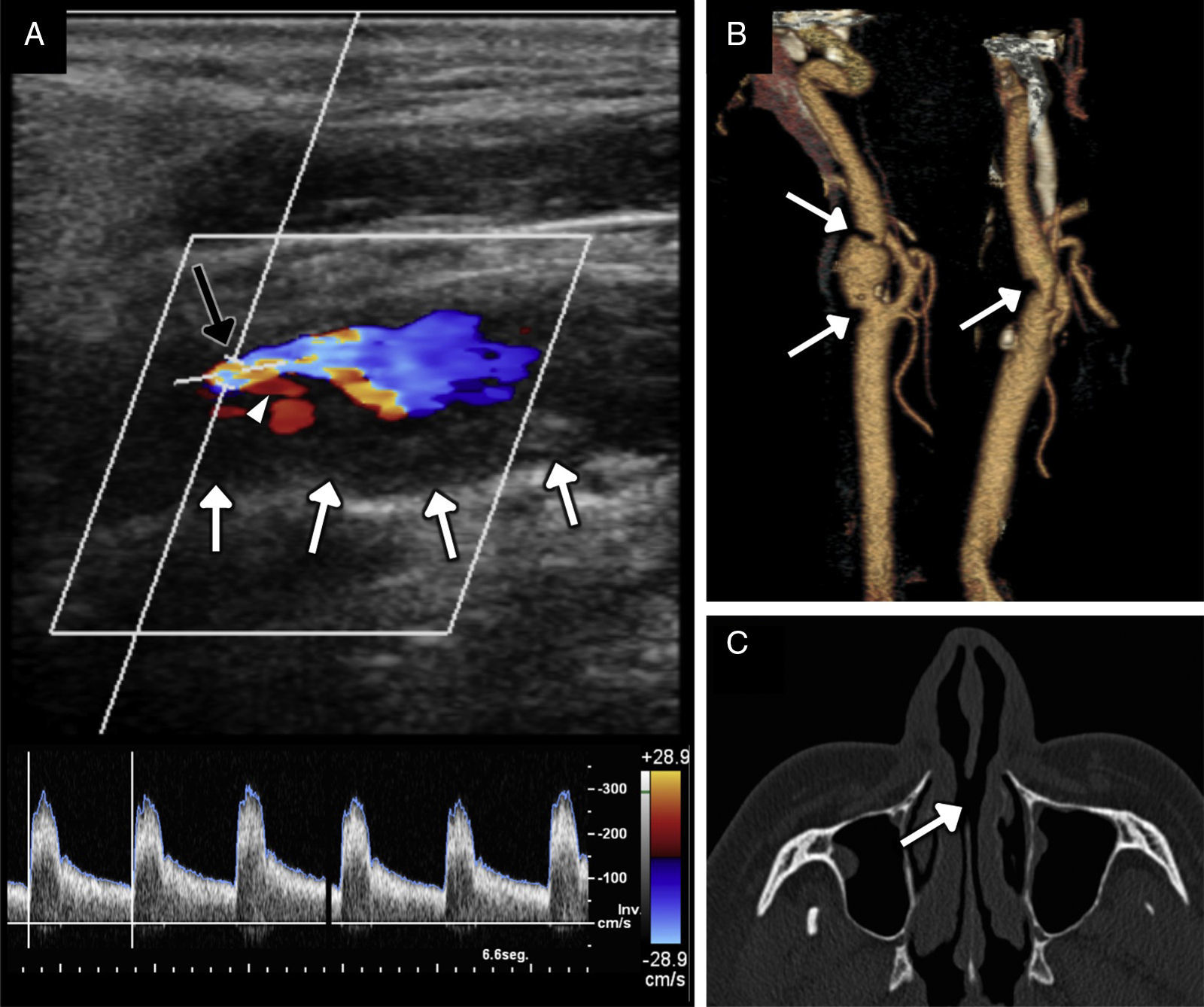
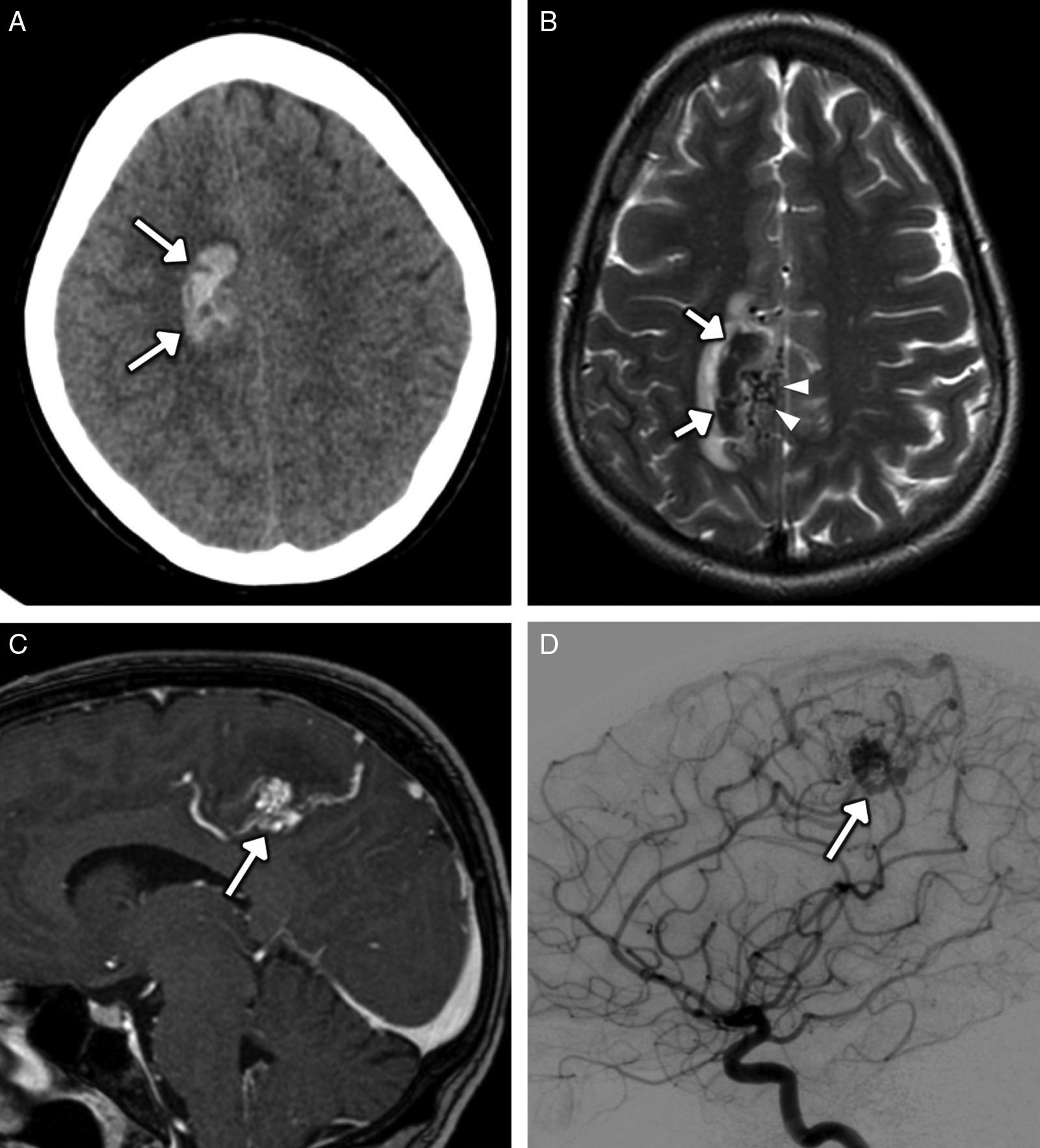
Recreational drug abuse represents a serious public health problem. Neuroimaging traditionally played a secondary role in this scenario, where it was limited to detecting acute vascular events. However, thanks to advances in knowledge about disease and in morphological and functional imaging techniques, radiologists have now become very important in the diagnosis of acute and chronic neurological complications of recreational drug abuse.
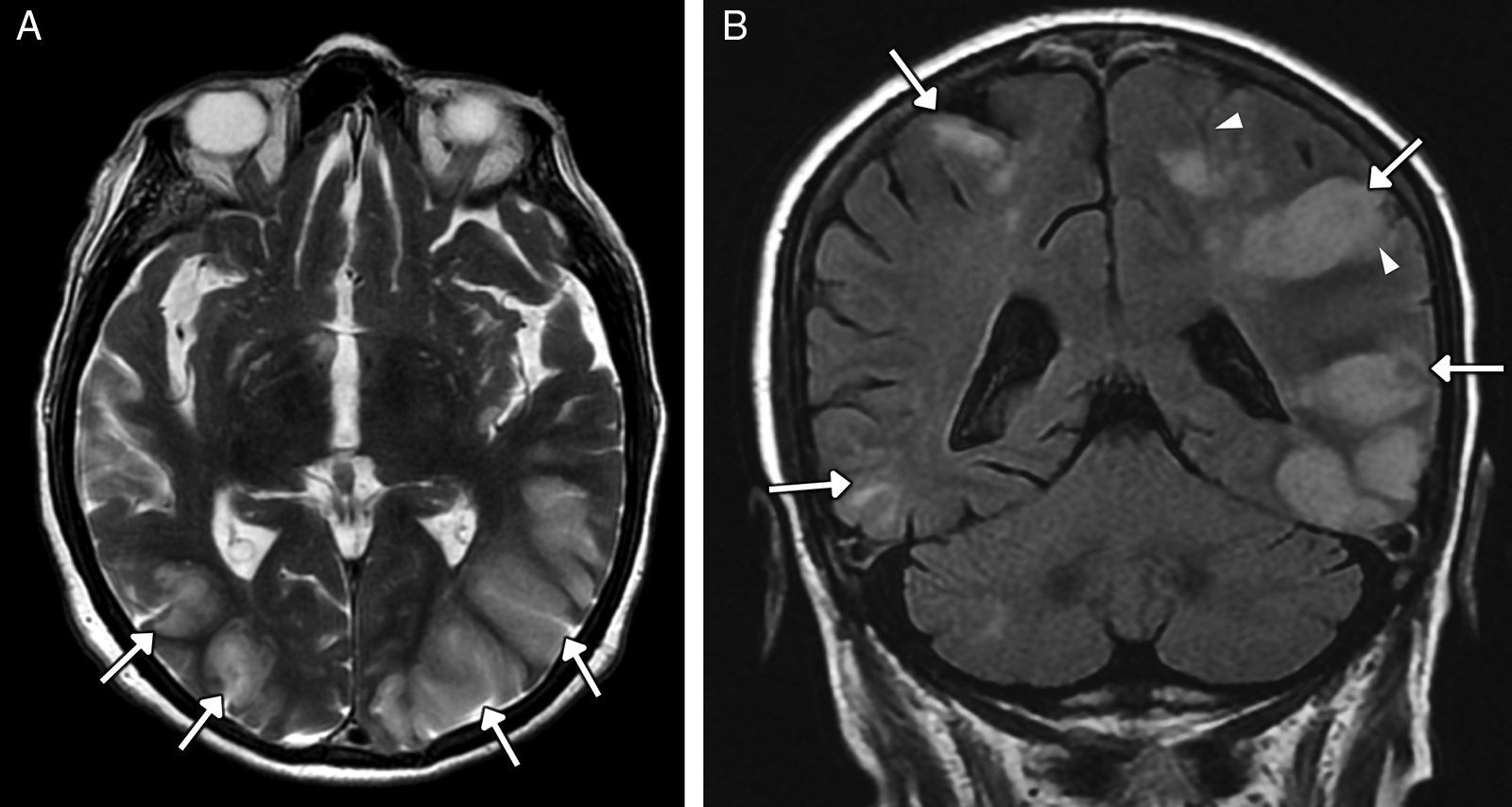
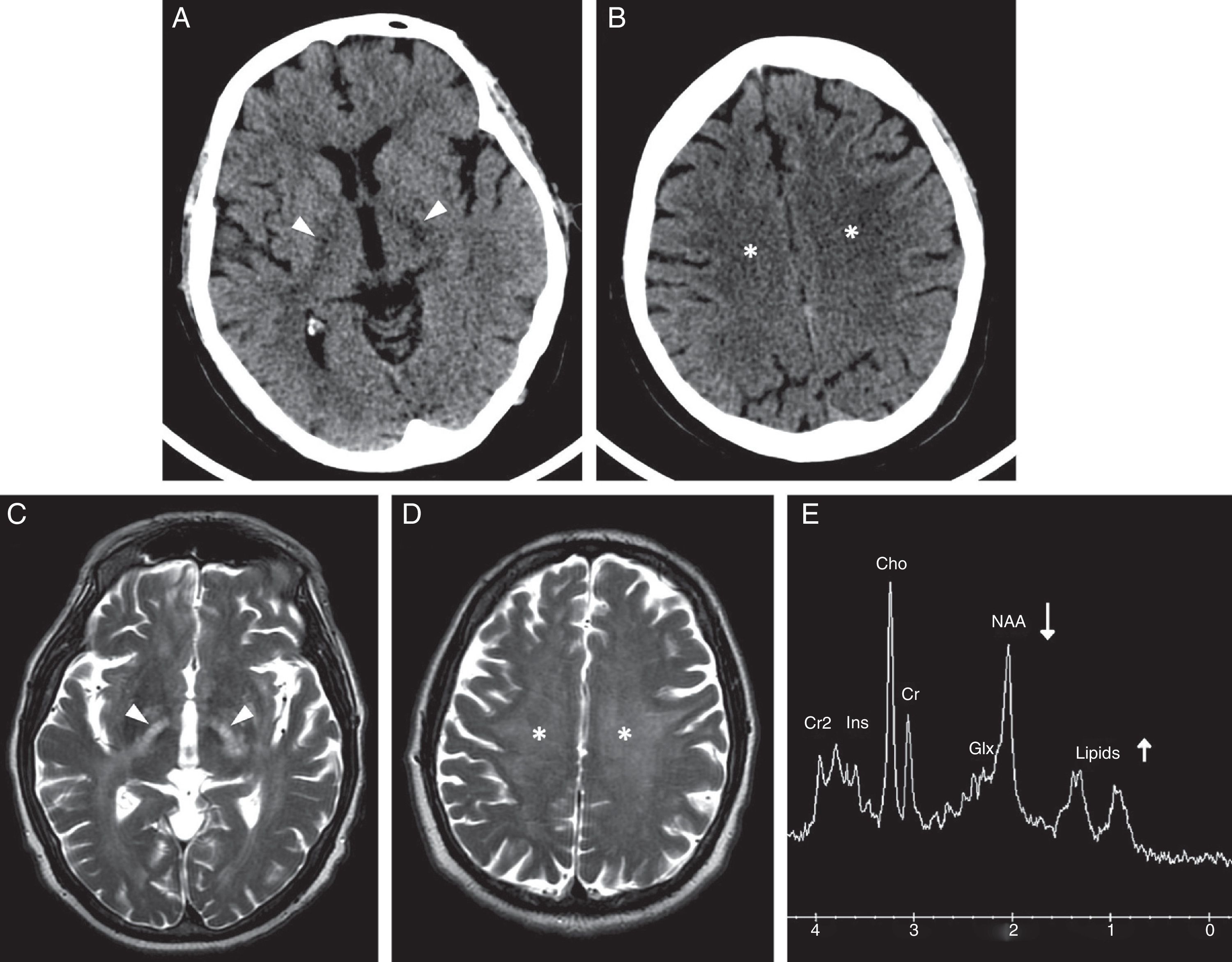
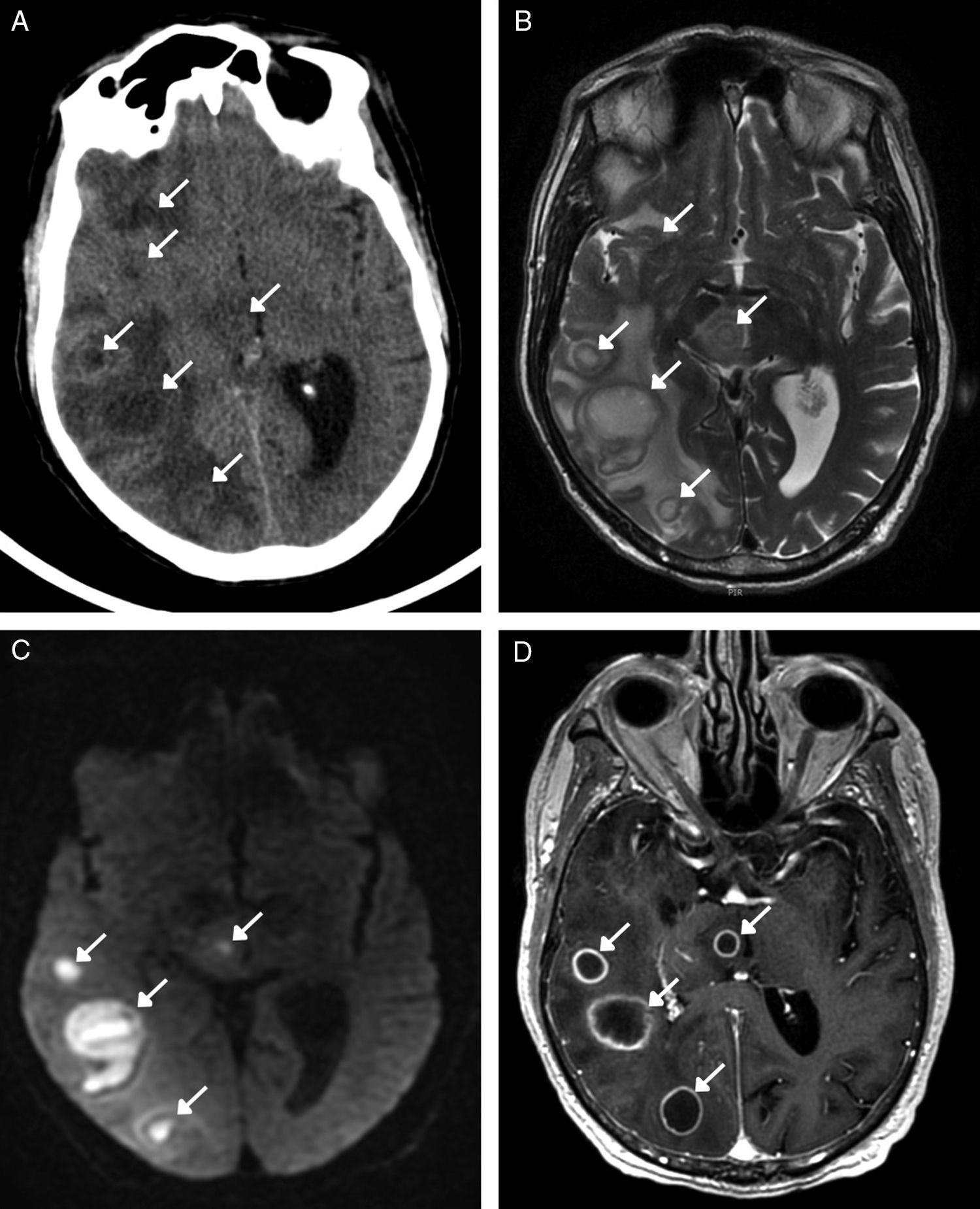
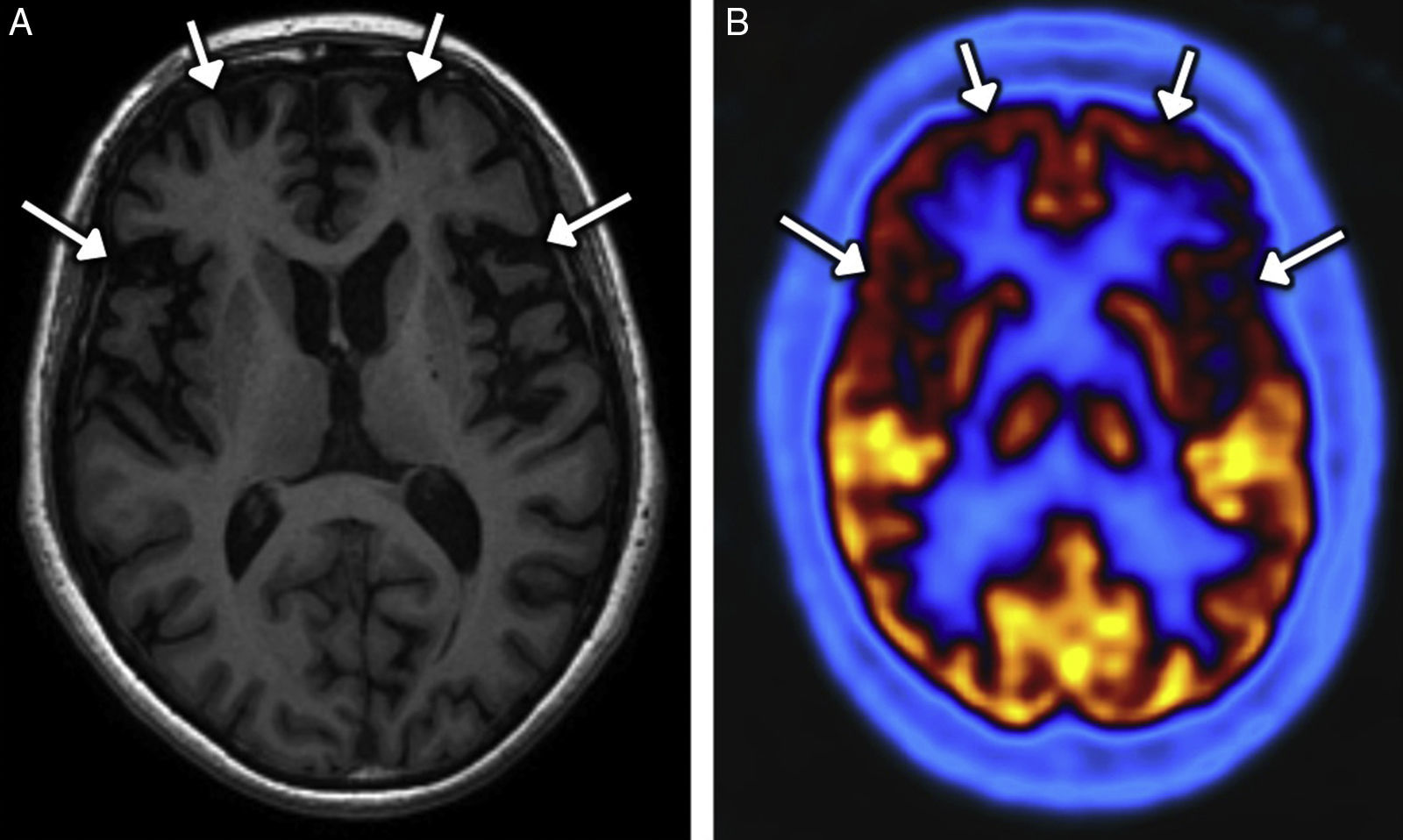
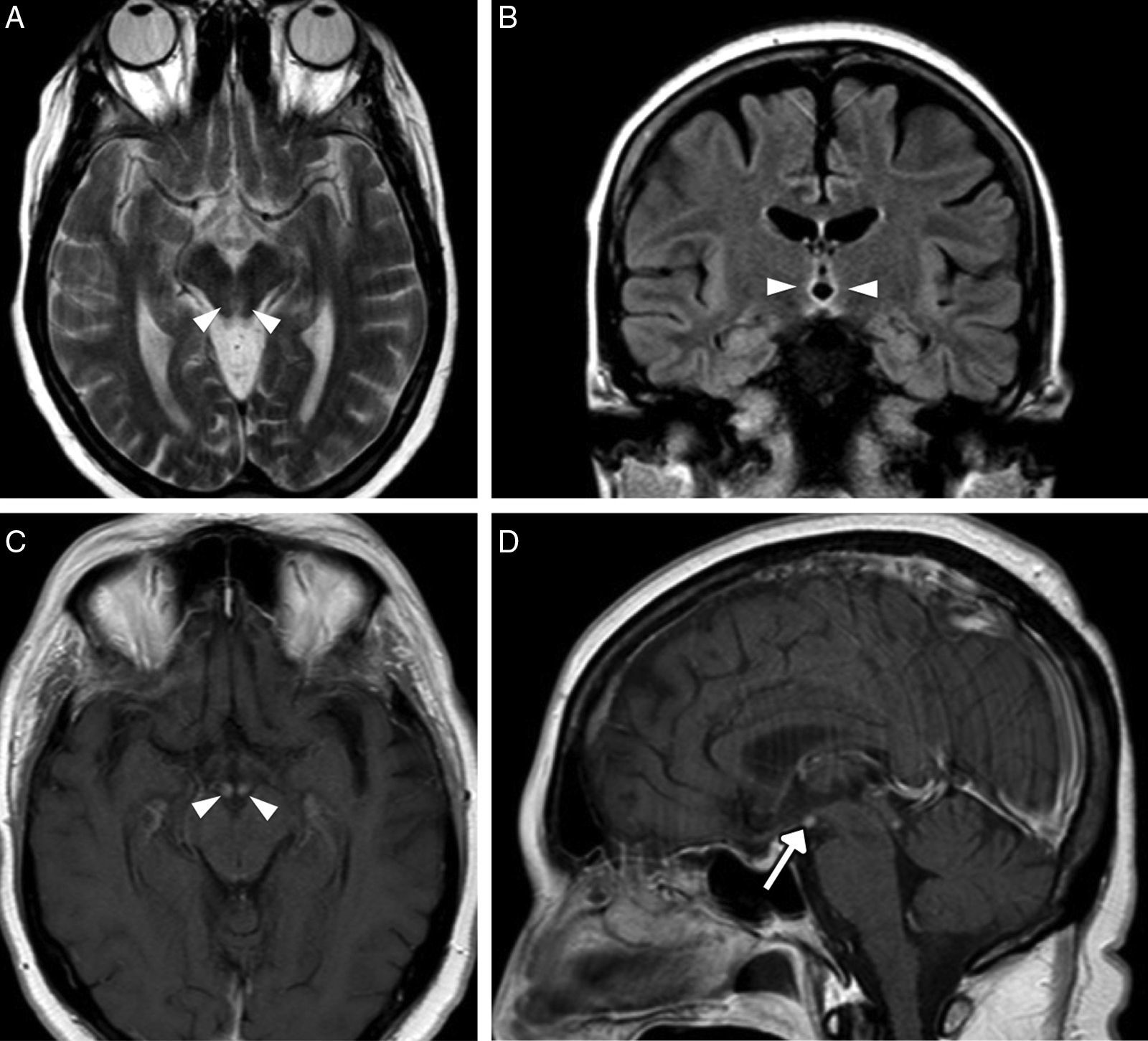
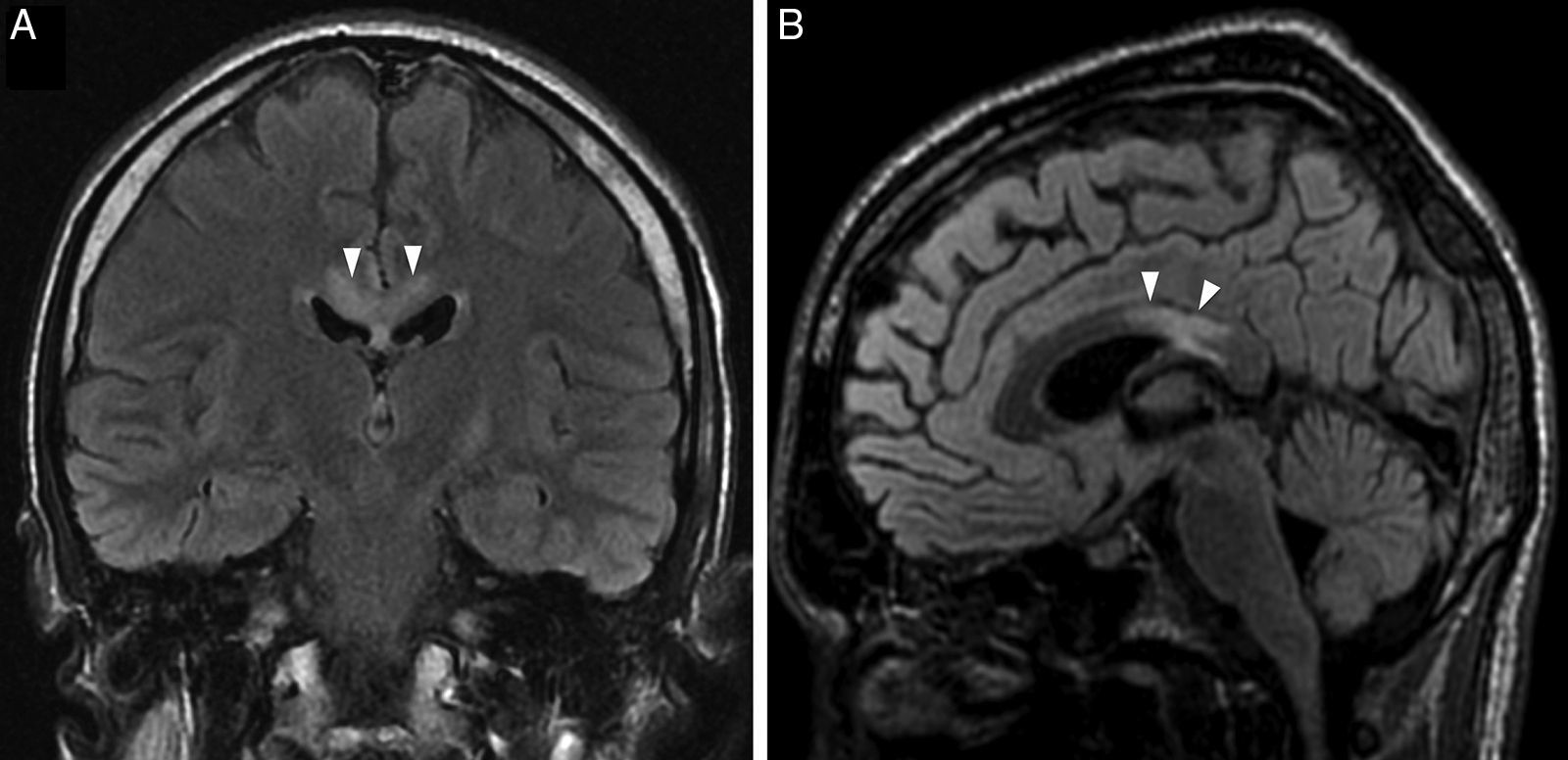
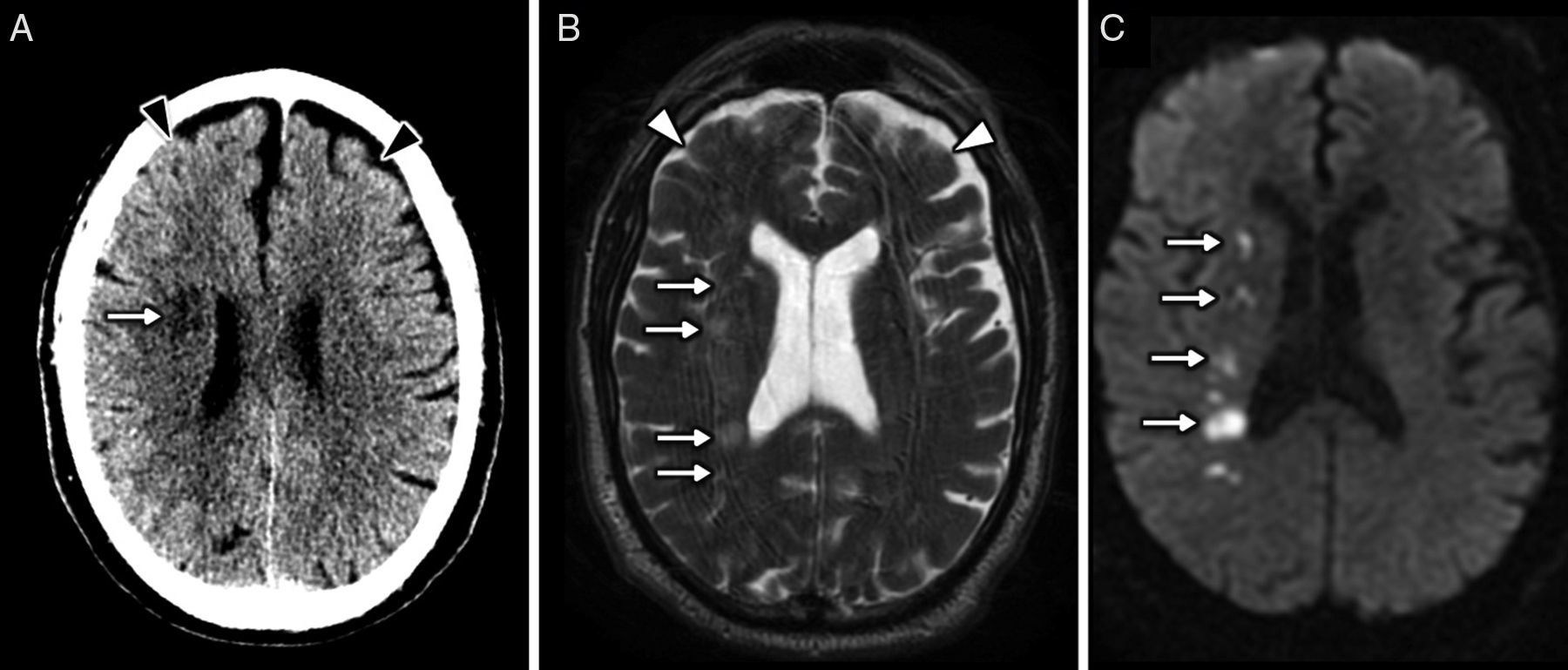
The main complications are neurovascular disease, infection, toxicometabolic disorders, and brain atrophy. The nonspecific symptoms and denial of abuse make the radiologist's involvement fundamental in the management of these patients. Neuroimaging makes it possible to detect early changes and to suggest an etiological diagnosis in cases with specific patterns of involvement.
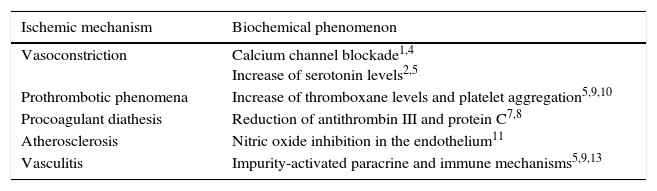
We aim to describe the pattern of abuse and the pathophysiological mechanisms of the drugs with the greatest neurological repercussions as well as to illustrate the depiction of the acute and chronic cerebral complications on conventional and functional imaging techniques.
Las drogas constituyen un gran problema sociosanitario. Tradicionalmente, la neuroimagen ha tenido un papel secundario limitado a la detección de eventos vasculares agudos. En la actualidad, el radiólogo ha adquirido gran relevancia en el diagnóstico de las complicaciones neurológicas agudas y crónicas, debido al avance en el conocimiento de la enfermedad y al desarrollo de las técnicas de imagen morfológicas y funcionales. Las principales complicaciones son la patología neurovascular, la infección, los trastornos tóxico-metabólicos y la atrofia cerebral. La sintomatología inespecífica y la negación del consumo hacen que la implicación del radiólogo pueda resultar fundamental en la atención de estos pacientes. La neuroimagen permite detectar alteraciones precoces y plantear el diagnóstico etiológico ante patrones de afectación específicos. Nuestro objetivo es describir el patrón de consumo y el mecanismo fisiopatológico de las drogas con mayor repercusión neurológica, así como ilustrar las complicaciones cerebrales agudas y crónicas mediante técnicas de imagen convencional y funcional.