Individual genetic variability favors the capacity of response and toxicity to the drugs is different in each person. Rheumatoid arthritis reported rates of response to the drugs etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab and methotrexate is close to 60%. This variability can be explained by genetic polymorphisms characteristic of each patient.
ObjectiveTo identify genetic polymorphisms reported in scientific articles that may affect the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, and methotrexate, and their response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
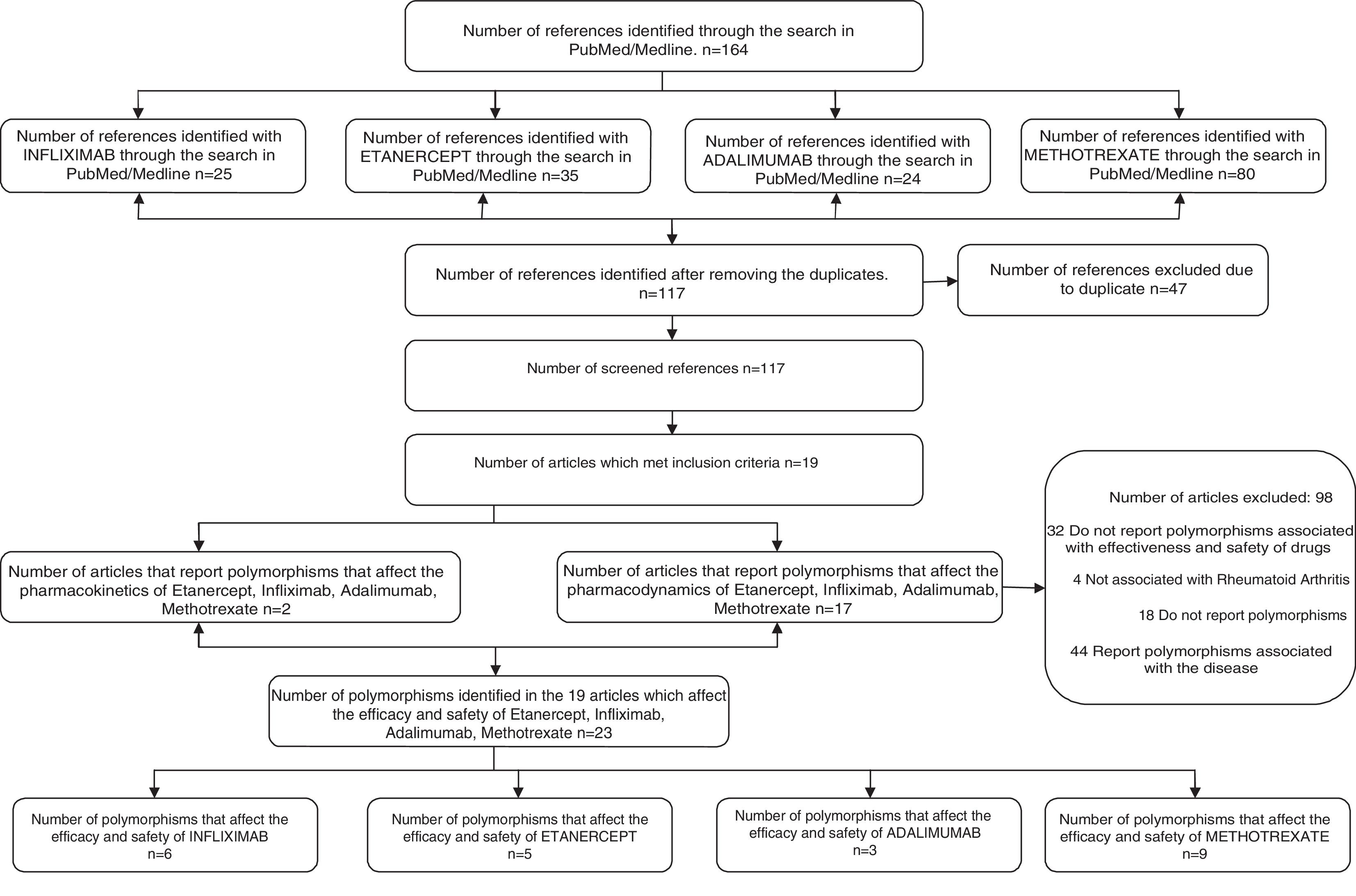
Materials and methodA systematic search was performed in PubMed and Medline, with the key terms: “rheumatoid arthritis” and “pharmacogenomic” and “polymorphisms” and “methotrexate” and “infliximab” and “adalimumab” and “etanercept”, obtaining 164 articles, 117 non-duplicates, and 19 articles that met the inclusion criteria.
ResultsOf the 19 articles, 2 reported polymorphisms affecting the pharmacokinetics of infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, methotrexate, and 17, pharmacodynamics. In the 19 articles, 23 polymorphisms of clinical relevance were identified in European, Japanese, Jordanian, and Indian populations.
ConclusionsA total of 23 polymorphisms with clinical relevance were identified, which could be the basis for the design of a specific test sequencing in rheumatoid arthritis patients being considered for treatment with infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, or methotrexate. The practical usefulness of this strategy requires evidence in specific clinical studies, associated with a targeted and personalized genetic test, and its effect on the effectiveness and safety of drug therapy with these drugs prescription.
La variabilidad genética individual favorece que la capacidad de respuesta y toxicidad a los fármacos sea diferente en cada persona. En la artritis reumatoide se reportan índices de respuesta a los medicamentos etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab y metotrexato cercanos al 60%. Esta variabilidad puede explicarse por polimorfismos genéticos característicos de cada paciente.
ObjetivoIdentificar polimorfismos genéticos reportados en artículos científicos que pueden afectar la farmacocinética y la farmacodinámica de etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab y metotrexato, y su respuesta en pacientes con artritis reumatoide.
Materiales y métodoSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática en PubMed/Medline, con los términos clave: «rheumatoid arthritis» and «pharmacogenomic» and «polymorphisms» and «metotrexato» and «infliximab» and «adalimumab» and «etanercept» obteniendo 164 artículos, 117 no duplicados y 19 artículos que cumplieron los criterios de inclusión.
ResultadosDe los 19 artículos, 2 reportaron polimorfismos que afectan la farmacocinética de infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept y metotrexato, y 17, la farmacodinámica. En los 19 artículos se identificaron 23 polimorfismos de relevancia clínica en población europea, japonesa, jordana e india.
ConclusionesSe identifican 23 polimorfismos de relevancia clínica, los cuales podrían ser el soporte para el diseño de un test de secuenciación específica en pacientes con artritis reumatoide, en los que se considere la utilización de infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept o metotrexato. La utilidad práctica de este tipo de estrategia requiere ser evidencia en estudios clínicos específicos, relacionados con una prescripción orientada por test genéticos y personalizada, y su efecto sobre la efectividad y seguridad de la farmacoterapia con estos medicamentos.
Human beings exhibit genetic variation associated with differences in their DNA sequences, which entails that the capacity to respond to the therapeutic and toxic effects of the drugs may be different in each individual.1,2 The discipline that studies this genetic variability in the response to a drug, at an individual level, is pharmacogenetics; meanwhile, pharmacogenomics also includes the environmental variables thereof.3–5 These disciplines are useful in clinical practice to predict the individual response of patients to different drugs, especially for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.6 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic heterogeneous autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the synovial membrane, the cartilage and the bone; and over time it generates deformity, disability and deterioration in the quality of life.7,8 Among the drugs used in its treatment are the inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, which report a response rate of 40%, and methotrexate (MTX) with 50%.8 This variability can occur due to genetic single-nucleotide polymorphisms that affect the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of these drugs.
A systematic review of the International Journal of Rheumatology in 2013 reports that approximately 50% of patients with RA in Europe interrupt their TNF-α inhibitor during the first 5 years due to problems of effectiveness or safety of the respective medication.9 Similarly, the Brigham and Women's Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study (BRASS), conducted in Boston, reports that 42% of patients with RA informed the withdrawal of their anti-TNF-α treatment.10 In this context of a large number of patients who discontinue the treatment with anti-TNF-α, the generation of information that improves the ability to predict which patients will respond to specific therapies would be a significant contribution in the proper management of RA.
The mentioned problems of effectiveness and safety could be associated with the genetic variability of each patient, including the environmental variables, which are expressed by genetic polymorphisms. In general, a genetic polymorphism is a variation in a determined DNA sequence present in more than 1% of the individuals of a population.11 According to the Canary Institute for Cancer Research “they are classified into: variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism (VNTR), restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP)”.12 In this context, the genetic variability is associated in 90% with SNPs, due to the activity of the genes dependent on enzymes involved in the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of the drugs used in the treatment of RA, thus affecting their efficacy and safety.13
RA is a major public health problem; in the last years, better health outcomes have been achieved with the incorporation of synthetic and biological disease modifying drugs. However, problems of variability in response are reported, which lead to ineffectiveness and adverse reactions in 30%–40% of patients.14 In this sense, pharmacogenomics, through the study of genetic variants of proteins involved in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drugs, becomes a way to maximize the efficacy and safety of the pharmacotherapy. In this aspect, pharmacogenomics favors a better understanding of the biological mechanisms and thus, the development of clinical models that predict the antirheumatic drug with greater benefit for each patient.
It is estimated that at 10 years of evolution of the RA, almost 80% of patients have some degree of limitation. The prognosis is uncertain and the lesions, which appear in the first years of disease, may continue despite clinical improvement, since the pathogenesis of these lesions may differ from a simple acute joint inflammation.15
Common risk factors regarding the development of RA, such as smoking, female sex, the presence of HLA DRB1 and the educational level, have been found in Colombia.16
Epidemiological dataIn Canada and the United States the prevalence ranges between 0.8% and 1.1%.17,18 Similarly, the data of prevalence in Europe range between 0.5% and 1%.19,20 In Latin America, it has been reported between 0.45% and 0.9%.21–23 On the other hand, different studies show that the incidence of RA tends to decrease; thus, between 1955 and 1994 the incidence would have been reduced by 50%.24 In Europe, the reported incidence rates of RA range between 0.009%–0.045%; in North America they vary between 0.024%–0.075% in Caucasian population and between 0.09%–0.89% in American Indian population. Although it is not clear, several factors have been proposed to explain the differences in incidence, among which are genetic, environmental and cultural factors.25
Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritisRA is characterized by the presence of rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies. It is observed in the initial phase of RA and involves the activation of both T and B cells. Proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF, IL-1 and IL-17, stimulate the inflammation and degradation of bone and cartilage. However, there is no decrease in the number of Treg cells, which could contribute to the pathophysiology of the disease.26
Genetic susceptibilityIt is estimated that up to 66% of patients with RA have genetic risk, which has been associated with the presence of certain alleles of the major histocompatibility complex, especially with the HLA-DR4 type. In this sense, it is accepted that the disease is associated with a given genetic load that generates a greater susceptibility to the immune response against an antigen (Ag) and thus, inflammation of the synovial membrane and osteoarticular destruction is generated.27
Globally, individuals respond to pharmacotherapy in a different way and no medication is 100% effective in all patients,28 which may be due to an alteration in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drugs associated with genetic-environmental conditions.29 In this context, the study of pharmacogenomic candidate genes has been more successful than the study of the candidate genes of the disease in identifying and explaining the variation of the pharmacological response,30 which has favored personalized prescription.31 Within this framework, it is necessary to have systematic information on the pharmacogenomics of RA, identifying polymorphisms of clinical relevance in the response and toxicity of TNF-α inhibitors and methotrexate. This type of information could contribute to the development of genetic tools to support the pharmacotherapeutic decision and improve the response to the treatment of this disease. Therefore, the objective of this work was to identify the polymorphisms to be used in the design of the specific sequencing test in patients with RA before the prescription of infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept and methotrexate.
MethodsSystematic review in PubMed/Medline. To identify the studies, a search in PubMed/Medline was conducted from September 2011 to September 2016, without limits in language and type of study, using the terms: “rheumatoid arthritis” and “pharmacogenomic” and “polymorphisms” and “methotrexate” and “infliximab” and “adalimumab” and “etanercept”. Specifically, it was contemplated the combination of keywords and filters: “rheumatoid arthritis” [MeSH Terms] AND “pharmacogenomic” [MeSH Terms] AND “polymorphisms” [MeSH Terms] AND “methotrexate” [MeSH Terms] AND “infliximab” [MeSH Terms] AND “adalimumab” [MeSH Terms] and “etanercept” [MeSH Terms]. Studies that reported polymorphisms of a single nucleotide and that affected the efficacy and safety of infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept and methotrexate were defined as inclusion criteria.
Data extractionThe articles that met the inclusion criteria were analyzed for data extraction. It was created a data collection form that included: the author and reference of the article reporting the polymorphism, the medication(s) studied, the type of study, the year of publication, the population, the polymorphism of interest, its manifestation and the report or not of pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic variability. Finally, each identified polymorphism was searched in Hap Map, in order to identify the gene to which it belongs, together with its alias, the organism, lineage, location and exon.
ResultsApplying the defined search criteria, 164 articles were found (25 related to infliximab, 24 to adalimumab, 35 to etanercept and 80 to methotrexate), of which 47 were repeated, remaining 117. Of this group of 117 articles, 19 met the inclusion criteria (Fig. 1). Of the 19 articles, two reported polymorphisms that affect the pharmacokinetics of infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept and methotrexate, which are associated with increased plasma concentrations, while 17 articles identified polymorphisms that affect their pharmacodynamics, which is associated with blockade of receptors and is manifested by ineffectiveness of the drugs (Table 1).
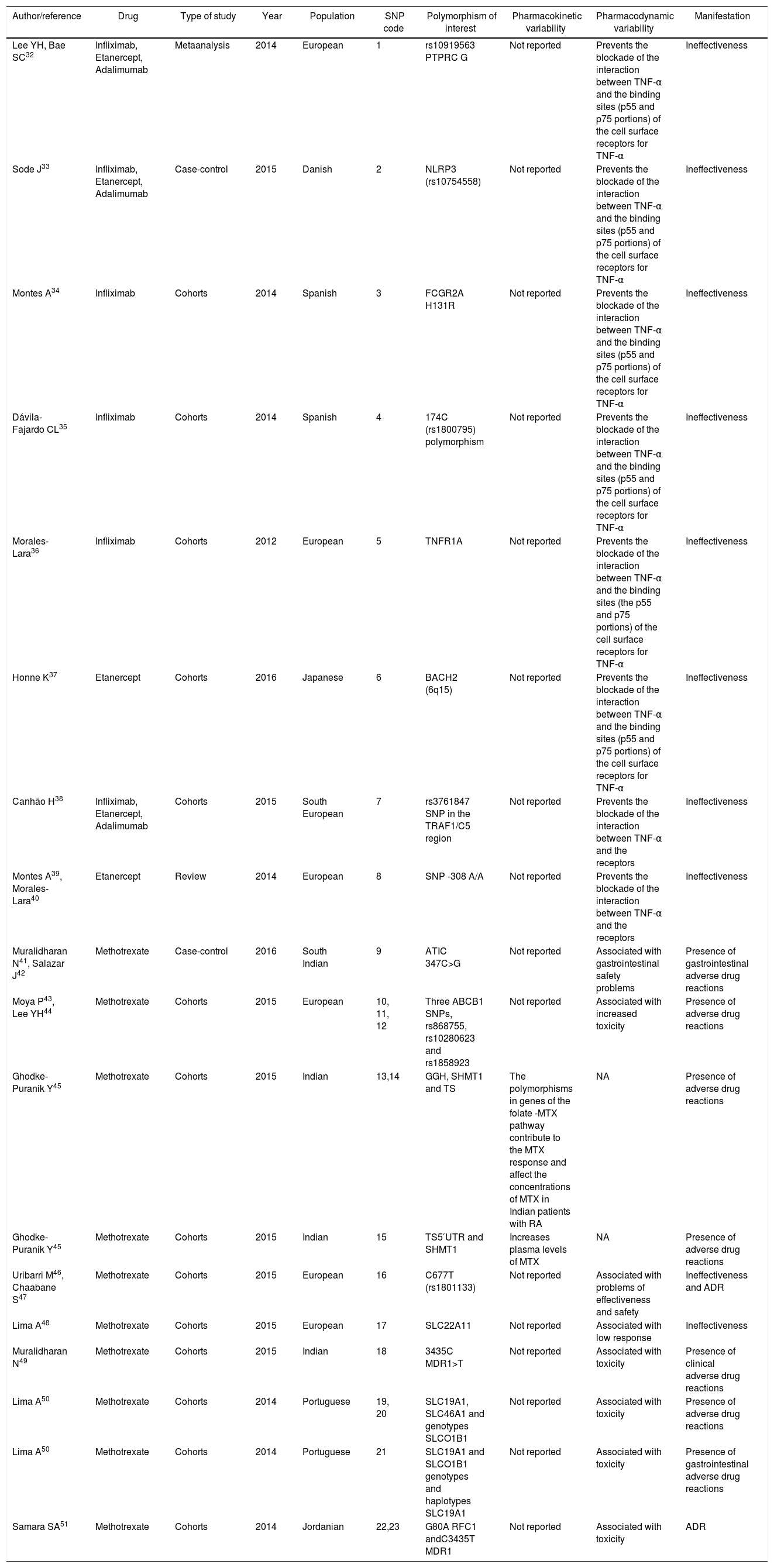
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with variability in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab.
| Author/reference | Drug | Type of study | Year | Population | SNP code | Polymorphism of interest | Pharmacokinetic variability | Pharmacodynamic variability | Manifestation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee YH, Bae SC32 | Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab | Metaanalysis | 2014 | European | 1 | rs10919563 PTPRC G | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the binding sites (p55 and p75 portions) of the cell surface receptors for TNF-α | Ineffectiveness |
| Sode J33 | Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab | Case-control | 2015 | Danish | 2 | NLRP3 (rs10754558) | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the binding sites (p55 and p75 portions) of the cell surface receptors for TNF-α | Ineffectiveness |
| Montes A34 | Infliximab | Cohorts | 2014 | Spanish | 3 | FCGR2A H131R | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the binding sites (p55 and p75 portions) of the cell surface receptors for TNF-α | Ineffectiveness |
| Dávila-Fajardo CL35 | Infliximab | Cohorts | 2014 | Spanish | 4 | 174C (rs1800795) polymorphism | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the binding sites (p55 and p75 portions) of the cell surface receptors for TNF-α | Ineffectiveness |
| Morales-Lara36 | Infliximab | Cohorts | 2012 | European | 5 | TNFR1A | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the binding sites (the p55 and p75 portions) of the cell surface receptors for TNF-α | Ineffectiveness |
| Honne K37 | Etanercept | Cohorts | 2016 | Japanese | 6 | BACH2 (6q15) | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the binding sites (p55 and p75 portions) of the cell surface receptors for TNF-α | Ineffectiveness |
| Canhão H38 | Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab | Cohorts | 2015 | South European | 7 | rs3761847 SNP in the TRAF1/C5 region | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the receptors | Ineffectiveness |
| Montes A39, Morales-Lara40 | Etanercept | Review | 2014 | European | 8 | SNP -308 A/A | Not reported | Prevents the blockade of the interaction between TNF-α and the receptors | Ineffectiveness |
| Muralidharan N41, Salazar J42 | Methotrexate | Case-control | 2016 | South Indian | 9 | ATIC 347C>G | Not reported | Associated with gastrointestinal safety problems | Presence of gastrointestinal adverse drug reactions |
| Moya P43, Lee YH44 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2015 | European | 10, 11, 12 | Three ABCB1 SNPs, rs868755, rs10280623 and rs1858923 | Not reported | Associated with increased toxicity | Presence of adverse drug reactions |
| Ghodke-Puranik Y45 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2015 | Indian | 13,14 | GGH, SHMT1 and TS | The polymorphisms in genes of the folate -MTX pathway contribute to the MTX response and affect the concentrations of MTX in Indian patients with RA | NA | Presence of adverse drug reactions |
| Ghodke-Puranik Y45 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2015 | Indian | 15 | TS5′UTR and SHMT1 | Increases plasma levels of MTX | NA | Presence of adverse drug reactions |
| Uribarri M46, Chaabane S47 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2015 | European | 16 | C677T (rs1801133) | Not reported | Associated with problems of effectiveness and safety | Ineffectiveness and ADR |
| Lima A48 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2015 | European | 17 | SLC22A11 | Not reported | Associated with low response | Ineffectiveness |
| Muralidharan N49 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2015 | Indian | 18 | 3435C MDR1>T | Not reported | Associated with toxicity | Presence of clinical adverse drug reactions |
| Lima A50 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2014 | Portuguese | 19, 20 | SLC19A1, SLC46A1 and genotypes SLCO1B1 | Not reported | Associated with toxicity | Presence of adverse drug reactions |
| Lima A50 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2014 | Portuguese | 21 | SLC19A1 and SLCO1B1 genotypes and haplotypes SLC19A1 | Not reported | Associated with toxicity | Presence of gastrointestinal adverse drug reactions |
| Samara SA51 | Methotrexate | Cohorts | 2014 | Jordanian | 22,23 | G80A RFC1 andC3435T MDR1 | Not reported | Associated with toxicity | ADR |
The 19 selected articles correspond to European, Japanese, Jordanian and Indian populations and they report the following 23 single nucleotide polymorphisms: rs10919563 PTPRC G, NLRP3 (rs10754558), FCGR2A H131R, 174C (rs1800795), TNFR1A, BACH2 (6q15), rs3761847 SNP in the TRAF1/C5 region, SNP -308 A/A, ATIC 347C>G, ABCB1 rs868755, rs10280623, rs1858923, GGH, SHMT1 and TS, TS5′UTR, C677T (rs1801133), SLC22A11, 3435C MDR1>T, SLC19A1, SLC46A1 and SLCO1B1, G80A RFC1 and C3435T MDR1 genotypes (Table 1). Specifically, of these 23 polymorphisms, 6 were associated with infliximab, 5 with etanercept, 3 with adalimumab and 9 with methotrexate (Fig. 1).
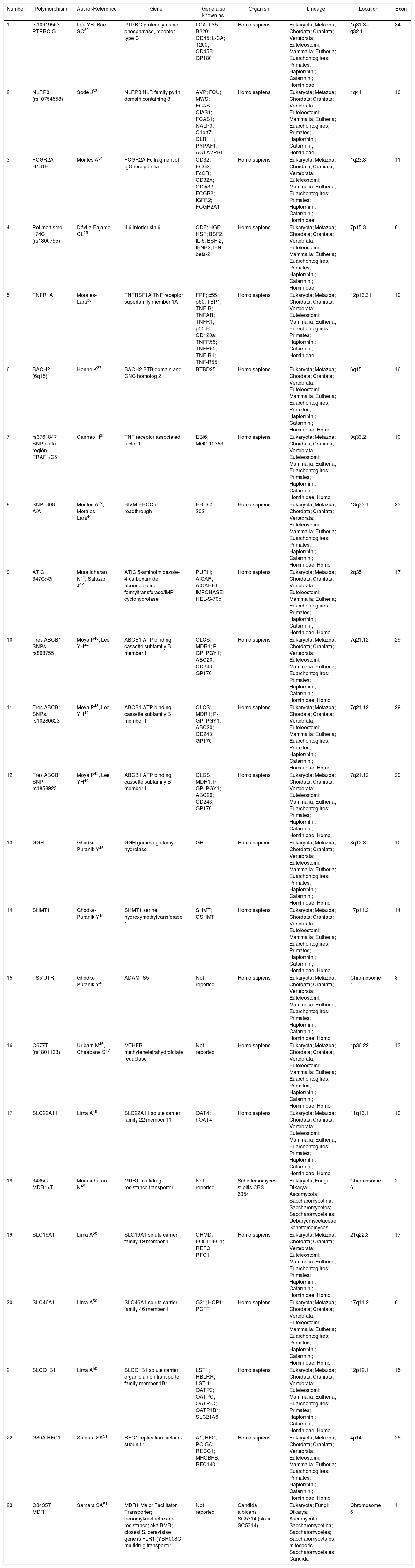
The search of the 23 identified polymorphisms in the HapMap database allowed to register, for each of them, the gene that encodes it, the organism in which it is manifested, its lineage, its location or locus and the exon. In this sense, of the 23 identified polymorphisms stood out (Table 2):
- •
Nineteen (82.6%) correspond to the Homo sapiens species.
- •
In the polypeptide sequence, the regions that are translated into amino acids come mainly from exon 10 (5 polymorphisms), from exon 29 (3 polymorphisms) and from exon 17 (2 polymorphisms).
- •
The SLC gene (of different genetic families) was found associated with 4 polymorphisms, while the ABCB1 (ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1) was found associated with 3 of the 23 polymorphisms and the MDR1 gene with 2 polymorphisms.
Location and exons of genes identified with single nucleotide polymorphism that affect the effectiveness and safety of infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab and methotrexate.
| Number | Polymorphism | Author/Reference | Gene | Gene also known as | Organism | Lineage | Location | Exon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rs10919563 PTPRC G | Lee YH, Bae SC32 | PTPRC protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type C | LCA; LY5; B220; CD45; L-CA; T200; CD45R; GP180 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae | 1q31.3–q32.1 | 34 |
| 2 | NLRP3 (rs10754558) | Sode J33 | NLRP3 NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 | AVP; FCU; MWS; FCAS; CIAS1; FCAS1; NALP3; C1orf7; CLR1.1; PYPAF1; AGTAVPRL | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae | 1q44 | 10 |
| 3 | FCGR2A H131R | Montes A34 | FCGR2A Fc fragment of IgG receptor Iia | CD32; FCG2; FcGR; CD32A; CDw32; FCGR2; IGFR2; FCGR2A1 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae | 1q23.3 | 11 |
| 4 | Polimorfismo-174C (rs1800795) | Dávila-Fajardo CL35 | IL6 interleukin 6 | CDF; HGF; HSF; BSF2; IL-6; BSF-2; IFNB2; IFN-beta-2 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae | 7p15.3 | 6 |
| 5 | TNFR1A | Morales-Lara36 | TNFRSF1A TNF receptor superfamily member 1A | FPF; p55; p60; TBP1; TNF-R; TNFAR; TNFR1; p55-R; CD120a; TNFR55; TNFR60; TNF-R-I; TNF-R55 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae | 12p13.31 | 10 |
| 6 | BACH2 (6q15) | Honne K37 | BACH2 BTB domain and CNC homolog 2 | BTBD25 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 6q15 | 16 |
| 7 | rs3761847 SNP en la región TRAF1/C5 | Canhão H38 | TNF receptor associated factor 1 | EBI6; MGC:10353 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 9q33.2 | 10 |
| 8 | SNP -308 A/A | Montes A39, Morales-Lara40 | BIVM-ERCC5 readthrough | ERCC5-202 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 13q33.1 | 23 |
| 9 | ATIC 347C>G | Muralidharan N41, Salazar J42 | ATIC 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase | PURH; AICAR; AICARFT; IMPCHASE; HEL-S-70p | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 2q35 | 17 |
| 10 | Tres ABCB1 SNPs, rs868755 | Moya P43, Lee YH44 | ABCB1 ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1 | CLCS; MDR1; P-GP; PGY1; ABC20; CD243; GP170 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 7q21.12 | 29 |
| 11 | Tres ABCB1 SNPs, rs10280623 | Moya P43, Lee YH44 | ABCB1 ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1 | CLCS; MDR1; P-GP; PGY1; ABC20; CD243; GP170 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 7q21.12 | 29 |
| 12 | Tres ABCB1 SNP rs1858923 | Moya P43, Lee YH44 | ABCB1 ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1 | CLCS; MDR1; P-GP; PGY1; ABC20; CD243; GP170 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 7q21.12 | 29 |
| 13 | GGH | Ghodke-Puranik Y45 | GGH gamma-glutamyl hydrolase | GH | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 8q12.3 | 10 |
| 14 | SHMT1 | Ghodke-Puranik Y45 | SHMT1 serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 | SHMT; CSHMT | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 17p11.2 | 14 |
| 15 | TS5′UTR | Ghodke-Puranik Y45 | ADAMTS5 | Not reported | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | Chromosome 1 | 8 |
| 16 | C677T (rs1801133) | Uribarri M46, Chaabane S47 | MTHFR methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase | Not reported | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 1p36.22 | 13 |
| 17 | SLC22A11 | Lima A48 | SLC22A11 solute carrier family 22 member 11 | OAT4; hOAT4 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 11q13.1 | 10 |
| 18 | 3435C MDR1>T | Muralidharan N49 | MDR1 multidrug-resistance transporter | Not reported | Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS 6054 | Eukaryota; Fungi; Dikarya; Ascomycota; Saccharomycotina; Saccharomycetes; Saccharomycetales; Debaryomycetaceae; Scheffersomyces | Chromosome: 6 | 2 |
| 19 | SLC19A1 | Lima A50 | SLC19A1 solute carrier family 19 member 1 | CHMD; FOLT; IFC1; REFC; RFC1 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 21q22.3 | 17 |
| 20 | SLC46A1 | Lima A50 | SLC46A1 solute carrier family 46 member 1 | G21; HCP1; PCFT | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 17q11.2 | 6 |
| 21 | SLCO1B1 | Lima A50 | SLCO1B1 solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 | LST1; HBLRR; LST-1; OATP2; OATPC; OATP-C; OATP1B1; SLC21A6 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 12p12.1 | 15 |
| 22 | G80A RFC1 | Samara SA51 | RFC1 replication factor C subunit 1 | A1; RFC; PO-GA; RECC1; MHCBFB; RFC140 | Homo sapiens | Eukaryota; Metazoa; Chordata; Craniata; Vertebrata; Euteleostomi; Mammalia; Eutheria; Euarchontoglires; Primates; Haplorrhini; Catarrhini; Hominidae; Homo | 4p14 | 25 |
| 23 | C3435T MDR1 | Samara SA51 | MDR1 Major Facilitator Transporter; benomyl/methotrexate resistance; aka BMR; closest S. cerevisiae gene is FLR1 (YBR008C) multidrug transporter | Not reported | Candida albicans SC5314 (strain: SC5314) | Eukaryota; Fungi; Dikarya; Ascomycota; Saccharomycotina; Saccharomycetes; Saccharomycetales; mitosporic Saccharomycetales; Candida | Chromosome 6 | 1 |
In RA, drugs such as methotrexate and TNF-α inhibitors like infliximab, adalimumab and etanercept are very important to achieve remission in patients; however, the genetic variability of the individuals implies that the capacity of response and toxicity to these medicines is different and that the reported rates are lower than 60%.8 Pharmacogenomics deals with the possible associations of genetic polymorphisms with responses to drugs, it is a branch of medical science that is still in its initial phase and requires more time to demonstrate positive results, so it depends on a good articulation between the research sector, legislation, pharmaceuticals companies and healthcare institutions that in the future, medicines can be developed for the benefit of improving health conditions and cost of treatments in small target groups; likewise, the value of non-genetic variables in the progression of a disease, such as age, gender, diet and lifestyle, which are also key in the response to a therapy, should not be left aside.
The relevance of this study consists in providing the possibility of applying the research of candidate genes selected for their biological importance, either in the kinetics or because of their relationship in the pharmacological action, in the identification of individuals at risk of experiencing adverse effects or with probability of being resistant to treatment. Therefore, it is expected that the information generated would be susceptible to be used in the design of specific sequencing tests, contributing to identify the best therapeutic option (greater effectiveness and safety) in patients with RA.18
In the treatment of RA, the possibility of associating certain polymorphisms with the efficiency of the treatment, reducing the adverse effects of the use of a drug, can be of great value both for the patient and for the medical practice and its economic aspect.1 The results obtained with this systematic review are a basis for the design of the specific sequencing test in patients with RA before the prescription of infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept and methotrexate; hence the importance of designing and validating with multicenter studies specific genomic tests that contribute to a personalized prescription to improve the effectiveness and safety of treatments with these drugs and achieve lower healthcare costs. The identification of the 23 polymorphisms of clinical relevance obtained with the review is very important for the design of genomic tests; however, it is necessary to include other genes in the multicentre studies, during exome sequencing, before validating and standardizing a test for use in clinical practice.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare they do not have any conflict of interest.
University of Antioquia, Colciencias, University Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe.
Please cite this article as: Puentes Osorio Y, Amariles Muñoz P, Aristizábal Bernal BH, Pinto Peñaranda LF, Calleja Hernández MÁ. Farmacogenómica de etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab y metotrexato en artritis reumatoide. Revisión estructurada. Rev Colomb Reumatol. 2018;25:22–37.