The healthcare sector emits 5% of greenhouse gases worldwide, inhaled anaesthetic agents have contributed to this effect for years. Other countries measured and limited their use, leading to positive environmental changes. There is a lack of data on Colombia. This project aims to evaluate the environmental impact of desflurane, isoflurane, and sevoflurane between 2019 and 2022 in a hospital in Bogota.
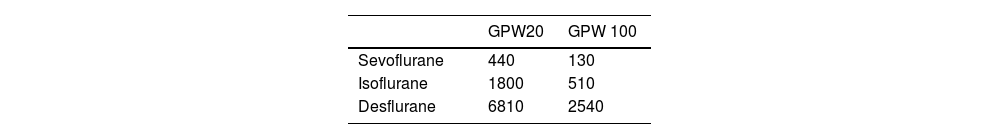
MethodsA retrospective exploration of inhaled anaesthetic agents use was conducted using our hospital's pharmacy inventory between 2019 and 2022. ORACLE software tools were used, along with the amount of anaesthetics dispensed by the pharmacy. The CO2 equivalent was calculated in kilograms using the global warming potential at 20 and 100 years.
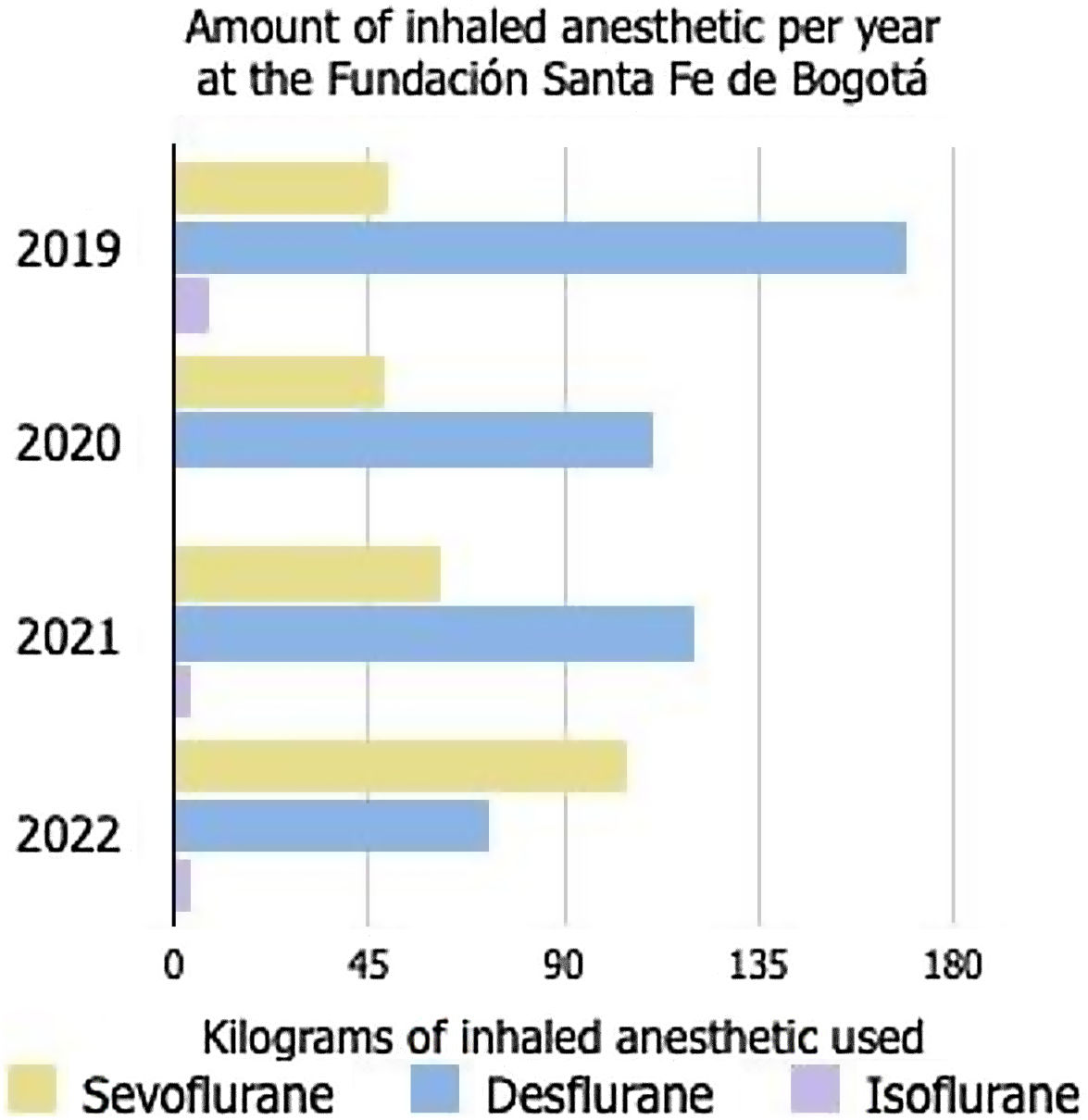
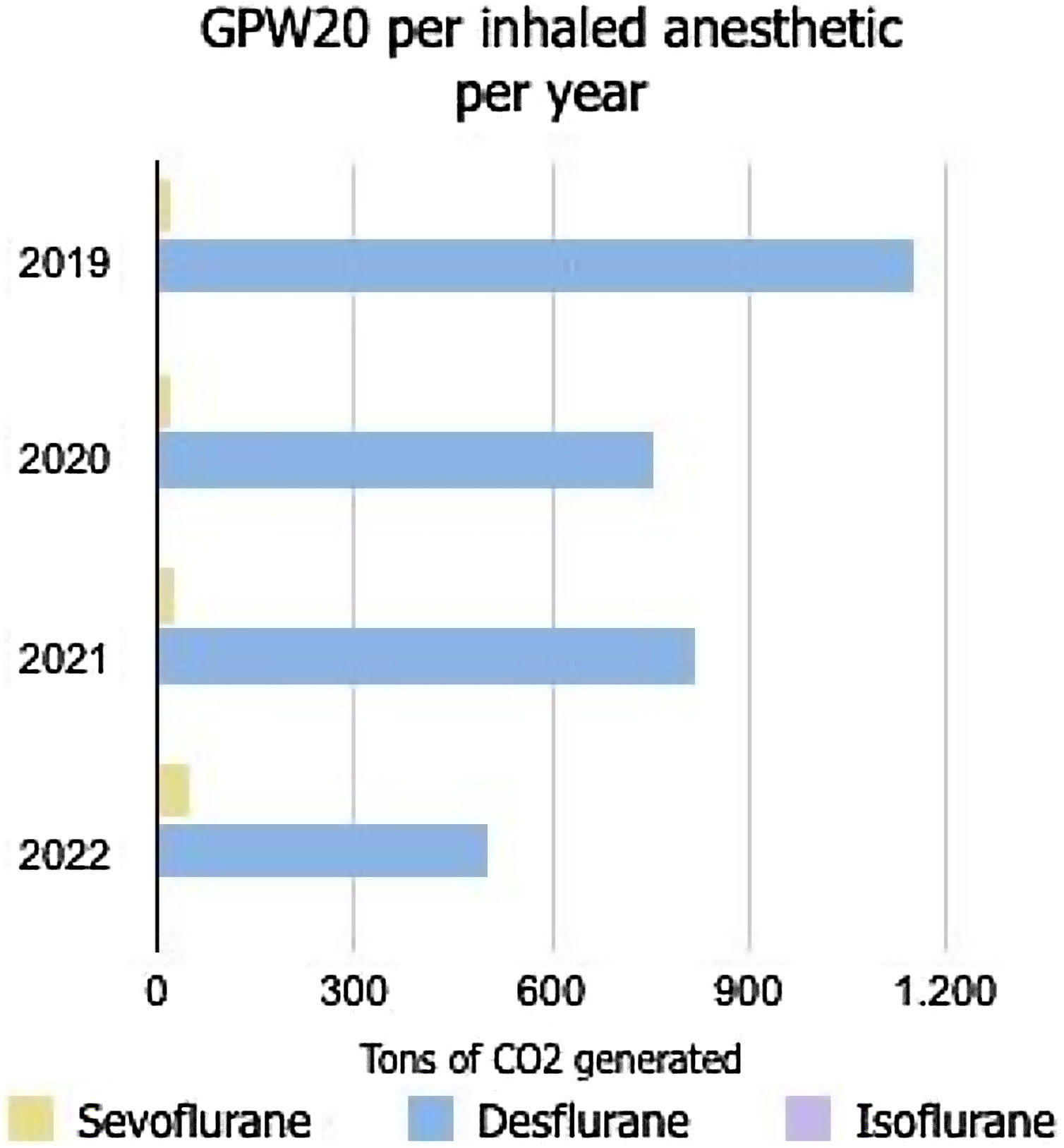
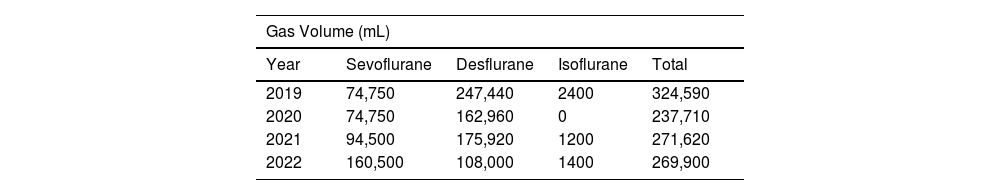
ResultsA total of 743&#¿;kg of inhaled anaesthetic agents was administered between 2019 and 2022. Sevoflurane accounted for 265.7&#¿;kg, Desflurane for 473.9&#¿;kg, while isoflurane was used in smaller quantities. There was a change in the trend between 2019/2020 and 2021/2022, with an increase of 69.3&#¿;kg in sevoflurane use and a decrease of 86.2&#¿;kg in desflurane use. The CO2 emissions from desflurane decreased from 190.7 to 131.9&#¿;t over 20 years and from 711 to 492&#¿;t over 100 years.
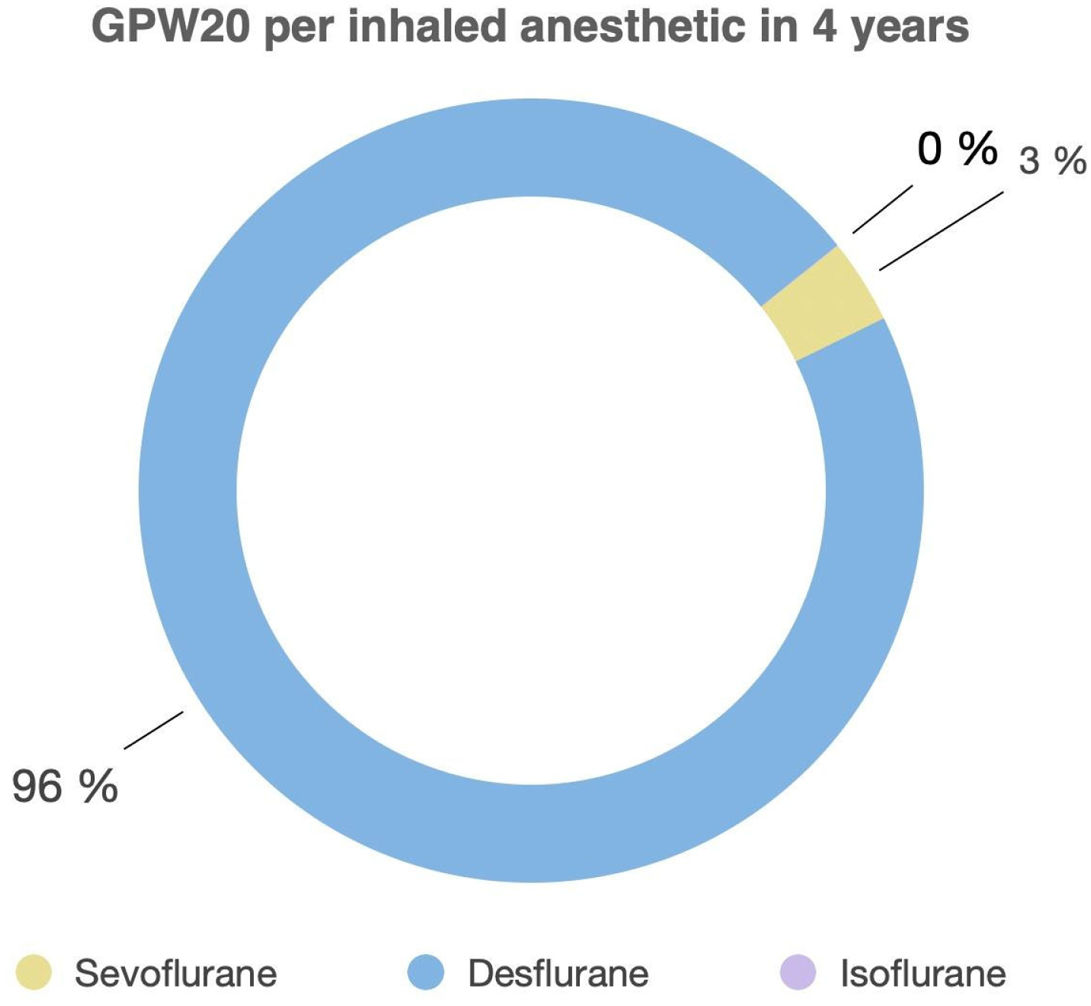
ConclusionsThe use of sevoflurane increased by 70%, whereas that of desflurane decreased by 31%. CO2 emissions were reduced by 557&#¿;t in 20 years and 210&#¿;t in 100 years. The environmental impact of sevoflurane is 97% lower than desflurane in our OR’s.
El sector salud genera el 5% de las emisiones de gases de efecto invernadero (GEI) a nivel global, siendo los anestésicos inhalados un contribuyente importante. Estudios en otros países han demostrado que la medición y limitación de su uso generan cambios ambientales positivos. En Colombia, la información sobre este tema es escasa. Este estudio evalúa el impacto ambiental del desflurano, isoflurano y sevoflurano entre 2019 y 2022 en un hospital de Bogotá.
MetodologíaSe realizó una evaluación retrospectiva del uso de anestésicos inhalados entre 2019 y 2022, utilizando el inventario de farmacia del hospital. Se emplearon herramientas de software ORACLE y la cantidad de anestésicos dispensados. El equivalente de CO2 se calculó en kilogramos utilizando el potencial de calentamiento global (PCA) a 20 y 100 años.
ResultadosSe administraron 743&#¿;kg de anestésicos inhalados entre 2019 y 2022. El sevoflurano representó 265,7&#¿;kg, el desflurano 473,9&#¿;kg y el isoflurano se utilizó en menor medida. Se observó un cambio en la tendencia entre 2019/2020 y 2021/2022: el uso de sevoflurano aumentó en 69,3&#¿;kg mientras que el desflurano disminuyó en 86,2&#¿;kg. Las emisiones de CO2 del desflurano se redujeron de 190,7 a 131,9 toneladas en 20 años, y de 711 a 492 toneladas en 100 años.
ConclusionesEl uso de sevoflurano aumentó un 70% mientras que el de desflurano disminuyó un 31%. Las emisiones de CO2 se redujeron en 557 toneladas en 20 años y 210 toneladas en 100 años. El impacto ambiental del sevoflurano es un 97% menor que el del desflurano en el quirófano.