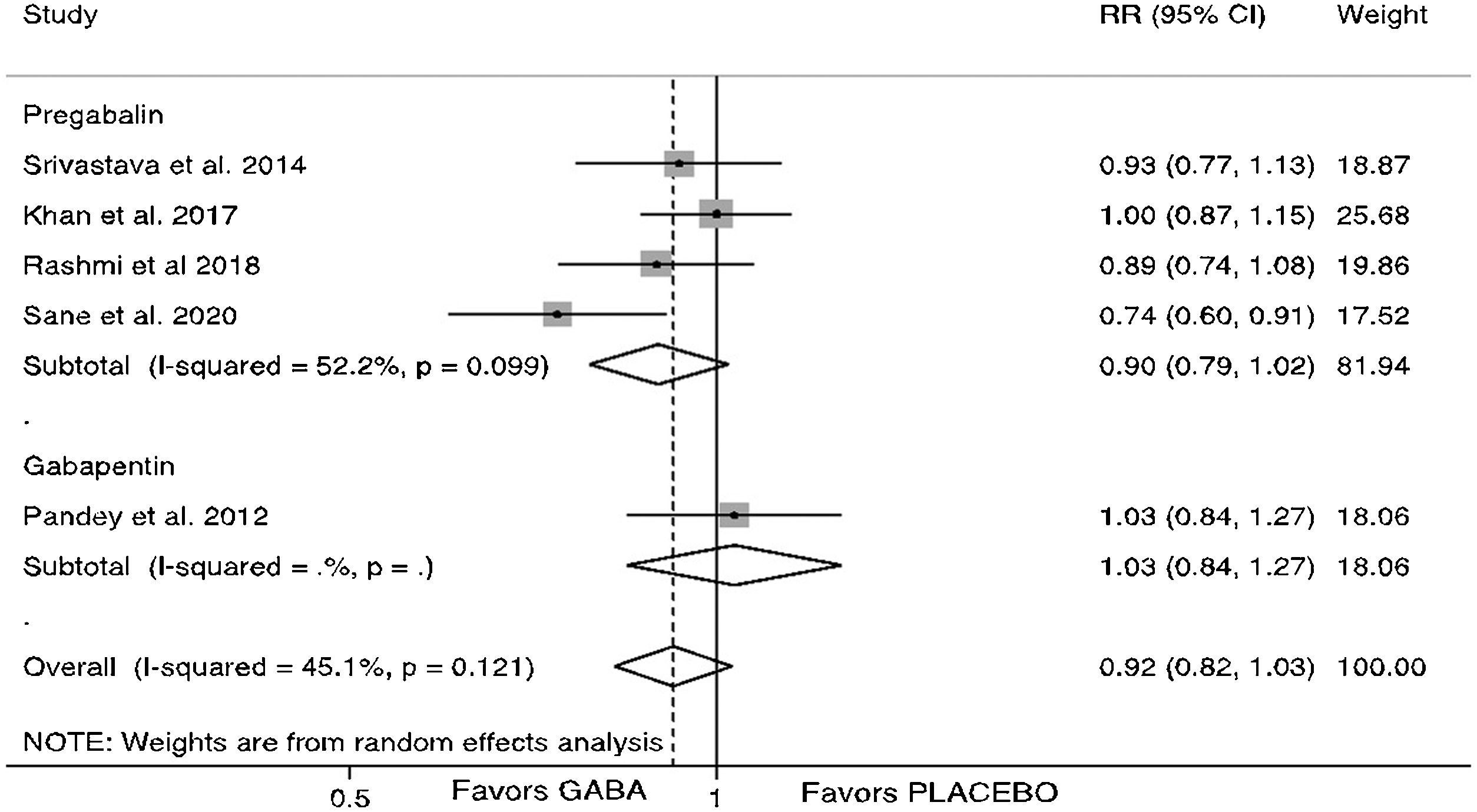
Succinylcholine is the gold standard neuromuscular blocker for rapid sequence induction; however, its use is associated with fasciculation and myalgia. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials comparing gabapentinoids versus placebo for the prevention of fasciculations and succinylcholine-induced myalgias. Six randomized clinical studies were included with a total of 481 patients - 241 in the intervention group and 240 in the placebo group. Gabapentinoids reduced the incidence of succinylcholine-induced myalgia (RR=0.69, 95% CI 0.56−0.84, P<.001), which remained statistically significant for pregabalin (RR=0.71, 95% CI 0.54−0.93, P=.013) and gabapentin (RR=0.61, 95% CI 0.45−0.82, P=.001) separately. There was no difference in fasciculations between the groups (RR=0.92, 95% CI 0.82–1.03, P=.148). Preoperative use of gabapentinoids is associated with lower incidence of succinylcholine-induced myalgias within the first 24h of surgery.
La succinilcolina es el bloqueador neuromuscular de referencia para la inducción de secuencia rápida, sin embargo, su uso se asocia a fasciculaciones y mialgias. Se realizó una revisión sistemática y un metanálisis. Se incluyeron ensayos clínicos controlados aleatorios comparando gabapentinoides versus placebo, para la prevención de fasciculaciones y mialgias inducidas por succinilcolina. Se incluyeron seis estudios clínicos aleatorizados. El número total de pacientes fue de 481, de los cuales 241 estaban en el grupo de intervención y 240 en el grupo de placebo. Los gabapentinoides redujeron la incidencia de mialgia inducida por succinilcolina (RR=0,69, IC del 95% 0,56–0,84, P<,001), que siguió siendo estadísticamente significativa para la pregabalina (RR=0,71, IC del 95% 0,54-0,93, P=,013) y la gabapentina (RR=0,61, IC del 95%: 0,45 a 0,82, P=,001) por separado. No hubo diferencia entre el grupo en las fasciculaciones (RR=0,92, IC del 95%: 0,82 a 1,03, P=,148). El uso preoperatorio de gabapentinoides se asocia con una menor incidencia de mialgias inducidas por succinilcolina dentro de las primeras 24 horas posteriores al procedimiento.