To evaluate the appropriateness of medication prescribing and to analyze interventions carried out in polymedicated elderly patients in nursing homes (NHs).
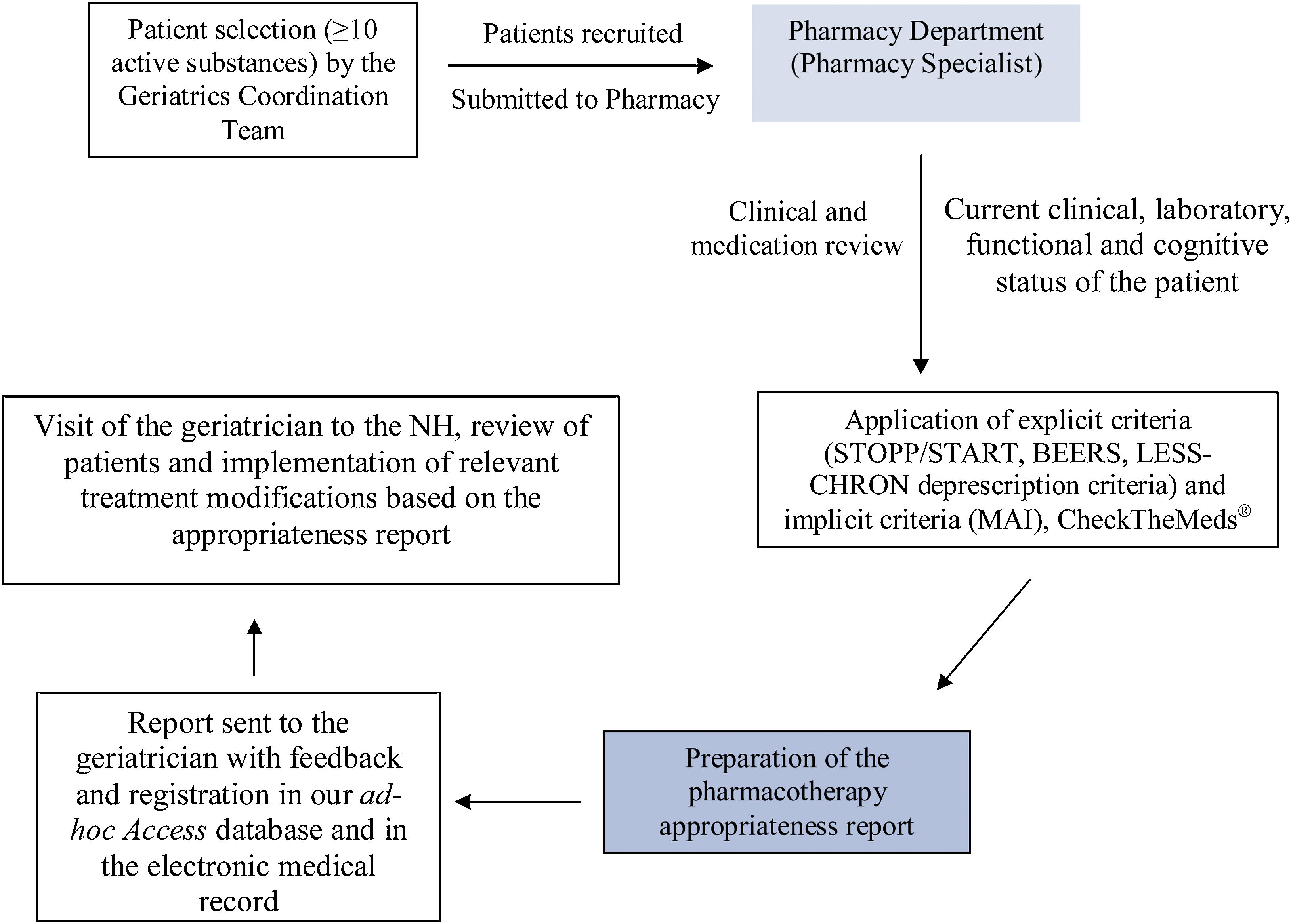
MethodsProspective study of potentially inappropriate medication prescribing in polymedicated older adults living in NHs, implemented via a collaborative project between NHs and the geriatric and pharmacy departments of a university hospital. The pharmacist reviewed patients’ active medical prescriptions and prepared an individualized report with proposals aimed at therapeutic optimization that was sent for evaluation to the geriatrician in charge of the NH. The drug-related problems (DRPs) were classified according to the Third Consensus of Granada and the potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) were identified by explicit criteria (STOPP/START, BEERS, LESS-CHRON), implicit criteria (MAI) and CheckTheMeds® software. It was measured the degree of acceptance of the interventions carried out, and the economic impact was calculated from the direct costs of the discontinued drugs.
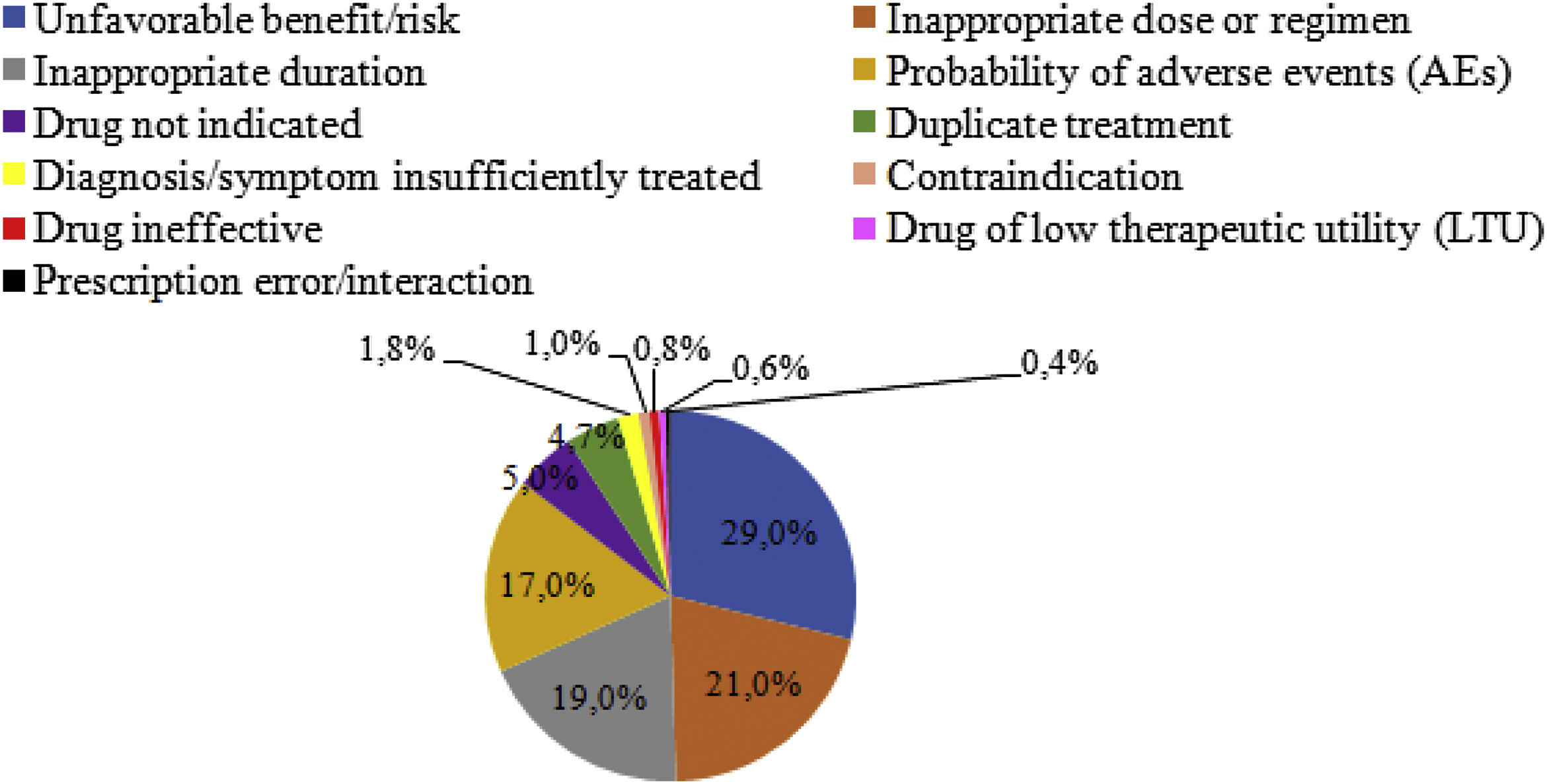
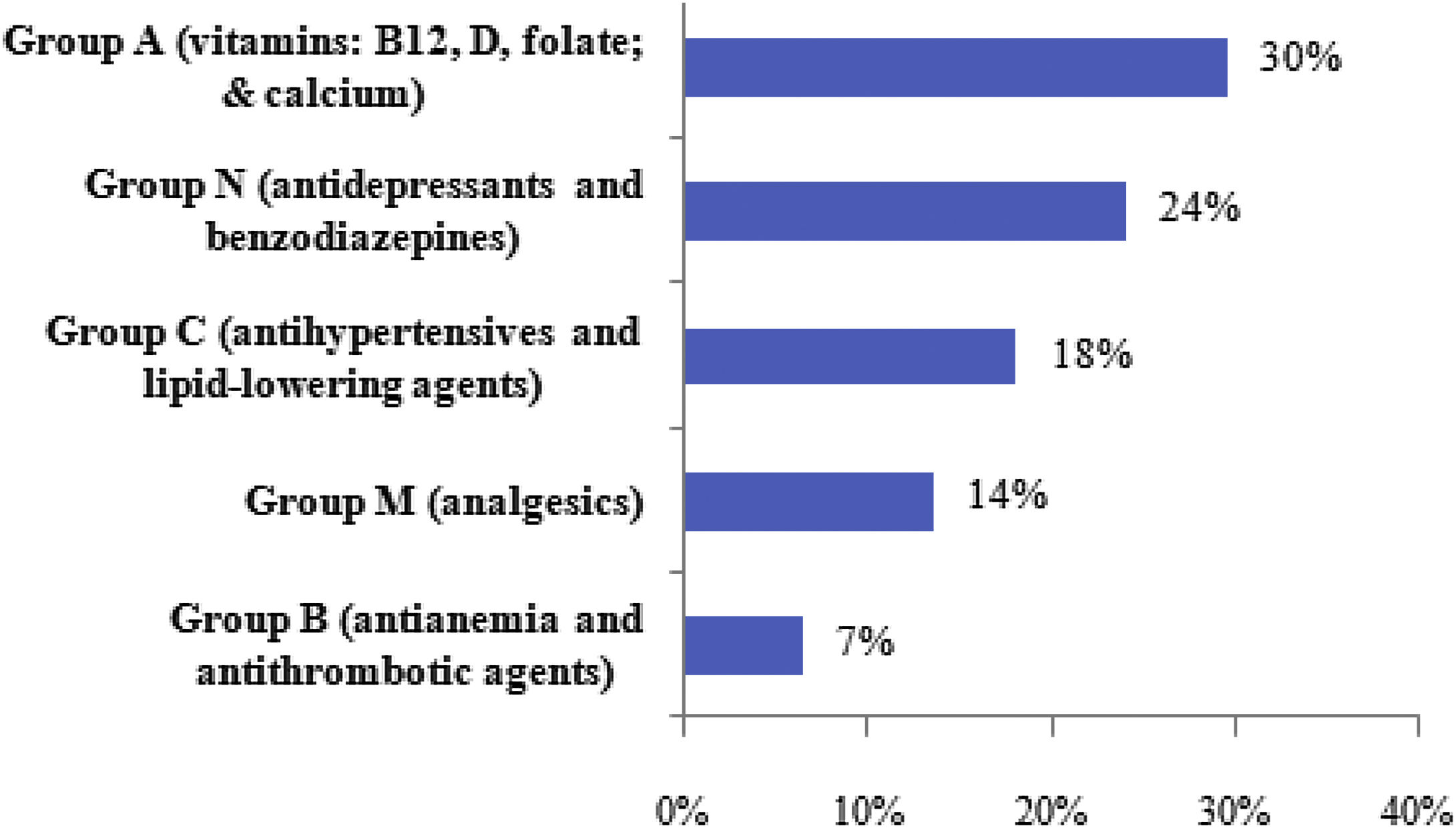
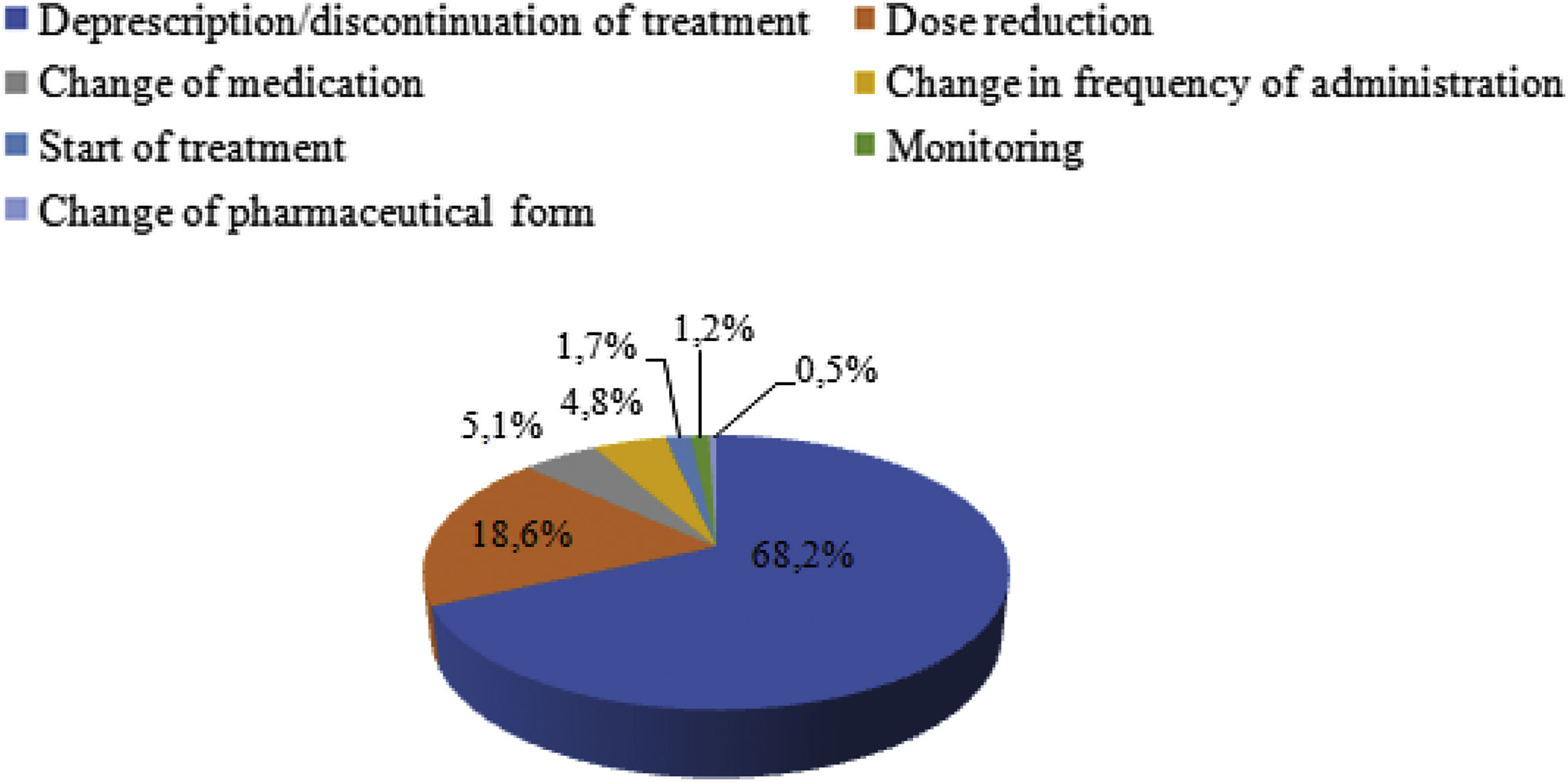
ResultsOf the 210 patients reviewed by the pharmacy department, 105 patients from 10 NHs were analyzed. A total of 510 prescriptions with possible DRPs were identified (38.5% of all prescribed drugs). According to STOPP/START/BEERS or LESS-CHRON criteria, 41.2% were PIPs. The main DRPs identified were: unfavorable risk-benefit ratio, inappropriate dose/regimen, inappropriate treatment duration, probability of adverse events, medication not indicated, and duplicate therapy. Interventions were proposed for 81.5% of the DRPs detected, of which 73.3% were accepted. This resulted in a 23.1% reduction in the number of drugs prescribed per patient and an economic saving of €16,218 per 6-month period.
ConclusionThe appropriateness of medication prescribing in polymedicated older adults living in NHs by the pharmacist has made it possible to reduce DRPs and PIPs and to save costs thanks to the high degree of acceptance by geriatricians.
Adecuar la farmacoterapia y analizar las intervenciones realizadas en pacientes ancianos institucionalizados en centros sociosanitarios (CSS) con polifarmacia.
MétodosEstudio prospectivo de un programa de adecuación farmacoterapéutica en pacientes ancianos polimedicados de CSS mediante la puesta en marcha de un proyecto de coordinación de geriatría, farmacia hospitalaria y CSS desde el área de atención especializada. El farmacéutico realizó una revisión farmacoterapéutica de las prescripciones activas de los pacientes, elaborándose un informe individualizado con propuestas dirigidas a la optimización terapéutica. Los problemas relacionados con la medicación (PRM) encontrados se clasificaron según el Tercer Consenso de Granada, y las prescripciones potencialmente inapropiadas (PPI) se identificaron mediante criterios explícitos (STOPP/START, BEERS, criterios de deprescripción LESS-CHRON), criterios implícitos (MAI) y el programa informático CheckTheMeds®. Se midió el grado de aceptación de las intervenciones realizadas, y la repercusión económica se calculó a partir de los costes directos de los fármacos desprescritos.
ResultadosDe los 210 pacientes revisados por el servicio de farmacia se analizaron 105 pacientes evaluados por geriatría pertenecientes a 10 CSS. Se detectaron 510 prescripciones con posibles PRM (38,5% del total de fármacos prescritos). El 41,2% se correspondían a PPI según criterios STOPP/START/BEERS o LESS-CHRON. Los principales PRM identificados fueron: fármacos de beneficio/riesgo desfavorable, dosis o pauta no adecuada, duración no adecuada, mayor probabilidad de efectos adversos, medicamento no indicado y duplicidad. Se intervino en el 81,5% de los PRM detectados, con un grado de aceptación del 73,3% y una reducción del 23,1% en el número de medicamentos prescritos por paciente, con un ahorro económico de 16.218€/6 meses.
ConclusiónLa adecuación farmacoterapéutica en pacientes mayores polimedicados ingresados en CSS por parte del farmacéutico ha permitido disminuir los PRM y las PPI y ahorrar costes gracias al alto grado de aceptación por parte de los geriatras.