The aim of this study was to study whether FDG was uniformly distributed throughout the skeleton and whether age and gender affected this biodistribution.
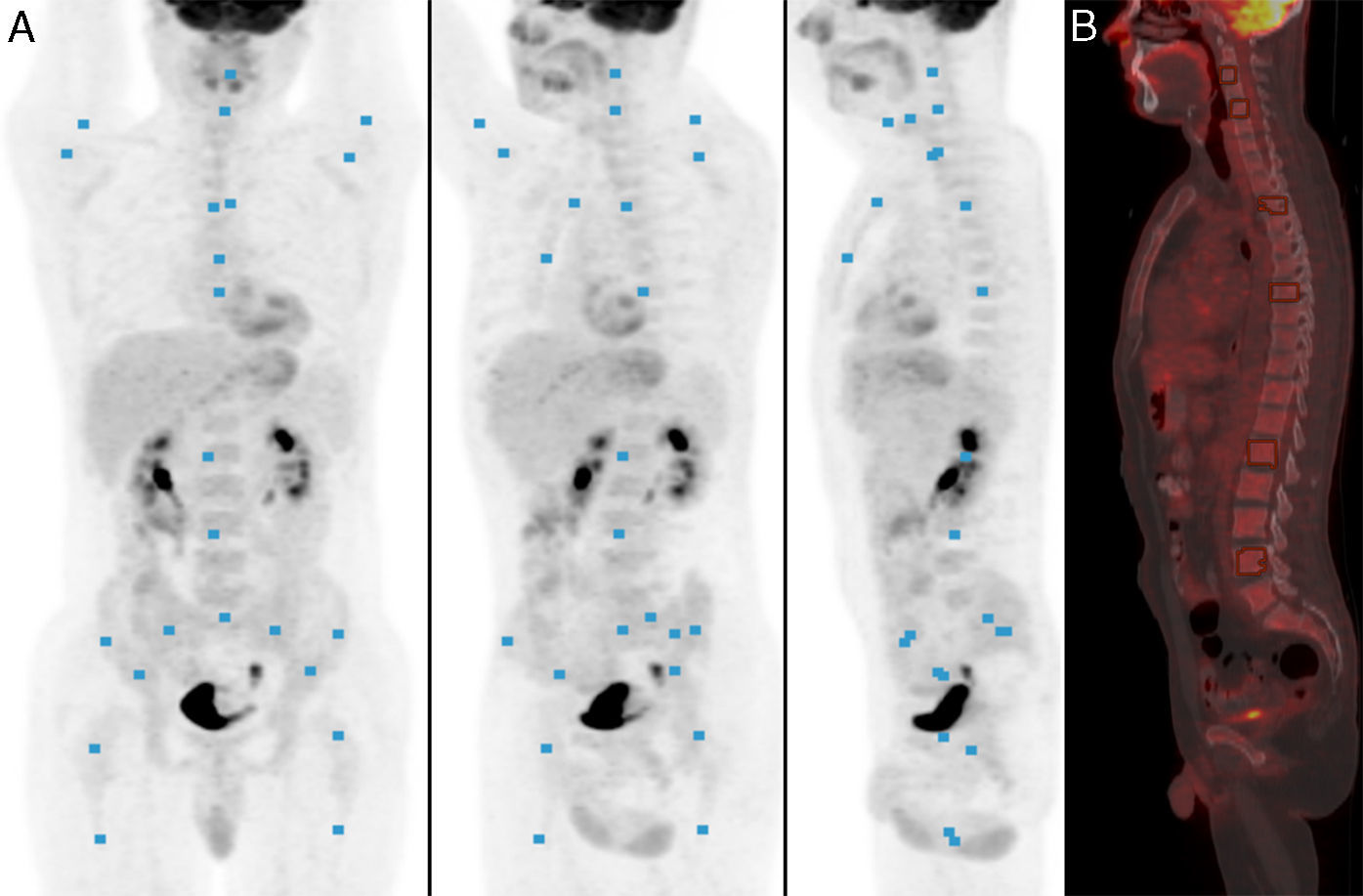
Material and MethodsA total of 158 patients were included in this retrospective study. None of the patients had received prior treatment that had affected the bone marrow and patients with bone metastases, trauma, benign and/or malignant hematologic disorders were excluded from the study. The SUVmax from the 24 different locations in the skeleton was obtained and all the values were compared with each other.
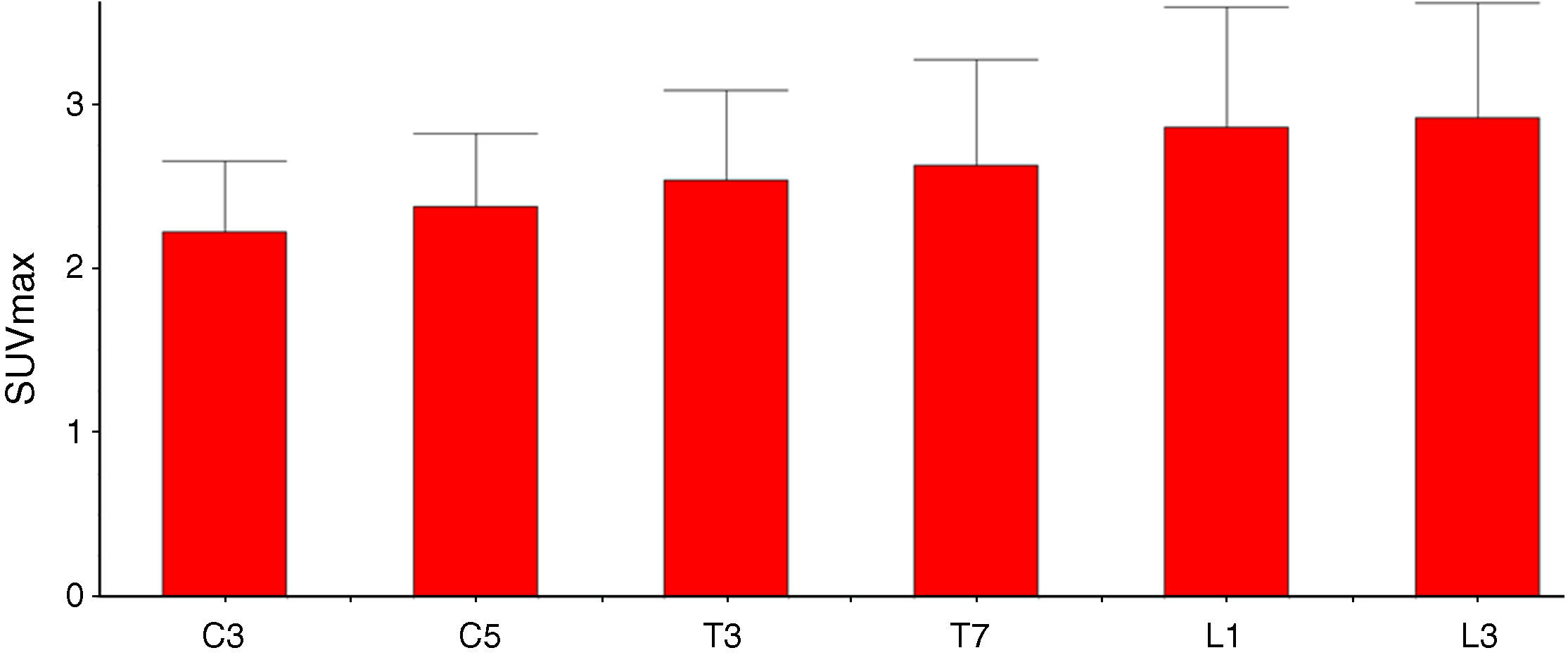
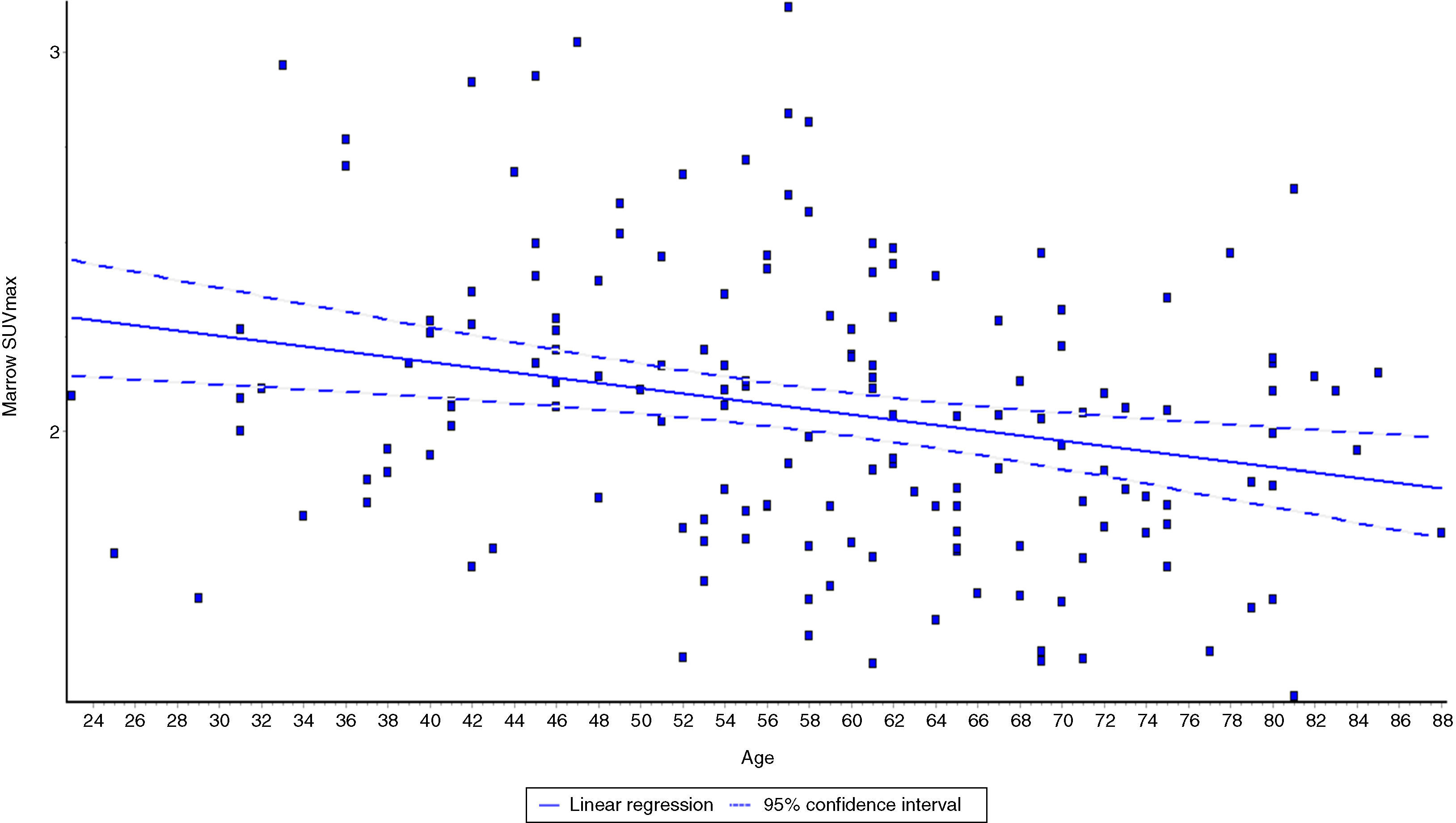
ResultsFDG uptake in the skeleton was not uniform in both sexes. While the highest FDG uptake was seen in the L3 vertebra, the lowest glucose metabolism was observed in the diaphysis of the femur. Concerning the vertebral column, FDG uptakes were also non-uniform and the SUVmax gradually increased from the cervix to the lumbar spine. The mean skeletal SUVmax was decreased in accordance with age in both genders.
ConclusionFDG was not uniformly distributed throughout the skeleton in both sexes. It had a tendency to increase from the appendicular to axial skeleton and from cervical to lumbar spine in the vertebral column that may be related with the normal distribution of the red bone marrow. Additionally, the glycolytic metabolism of the whole skeleton was gradually decreased in accordance with the age in both sexes.
El objetivo de este estudio fue investigar si la FDG se distribuye uniformemente por todo el esqueleto y si la edad y el género afectan la biodistribución.
Material y MétodosUn total de 158 pacientes fueron incluidos en este estudio retrospectivo. Ningún paciente había recibido tratamiento previo que afectara a la médula ósea y los pacientes con metástasis óseas, trauma, trastornos hematológicos benignos y/o malignos fueron excluidos del estudio. Se obtuvieron las SUVmáx de las 24 ubicaciones diferentes en el esqueleto y todos los valores se compararon entre sí.
ResultadosLa captación de FDG en el esqueleto no fue uniforme en ambos sexos. Mientras que la captación de FDG más alta se observó en la vértebra L3, el metabolismo de la glucosa más bajo se observó en la diáfisis de los fémures. Con respecto a la columna vertebral, la FDG captación tampoco fue uniforme y la SUVmáx aumentó gradualmente desde la columna cervical a la columna lumbar. La SUVmax media esquelética se redujo según la edad en ambos sexos.
ConclusiónLa FDG no se distribuyó de manera uniforme en todo el esqueleto en ambos sexos. Tuvo una tendencia a aumentar desde las extremidades al esqueleto axial y desde la columna cervical a la columna lumbar lo que puede estar relacionado con la distribución normal de la médula ósea roja. Además, el metabolismo glicolítico de todo el esqueleto se redujo gradualmente a medida que avanzaba la edad en ambos sexos.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)