La presepsina (PSEP) subtipo soluble de CD14 o sCD14-ST es un producto complejo del clivaje de CD14 que se libera en la circulación general y actualmente está disponible una cuantificación rápida automatizada. Los niveles circulantes de PSEP pueden ser percibidos como un testigo de monocitos-macrófagos activados en respuesta a patógenos. Así, la PSEP representa un biomarcador de la fase inicial de la infección sistémica. El objetivo del estudio es evaluar el diagnóstico y pronóstico de PSEP en sujetos con sepsis y choque séptico en un servicio de urgencias.
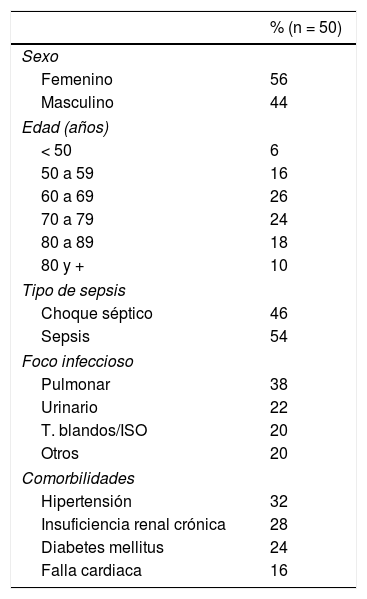
Materiales y métodosEstudio piloto, observacional, prospectivo en el que se incluyó a 50 sujetos que cumplieron los criterios de selección, ingresados por el servicio de urgencias durante el periodo de julio del 2016 a enero del 2017. Se analizaron variables demográficas, diagnóstico de sepsis o choque séptico y mortalidad. Se realizaron y compararon los biomarcadores para el diagnóstico precoz de infección, tales como: PSEP, procalcitonina y proteína C reactiva al ingreso, a las 48 h y al séptimo día. NT-proBNP se realizó en la hora 0.
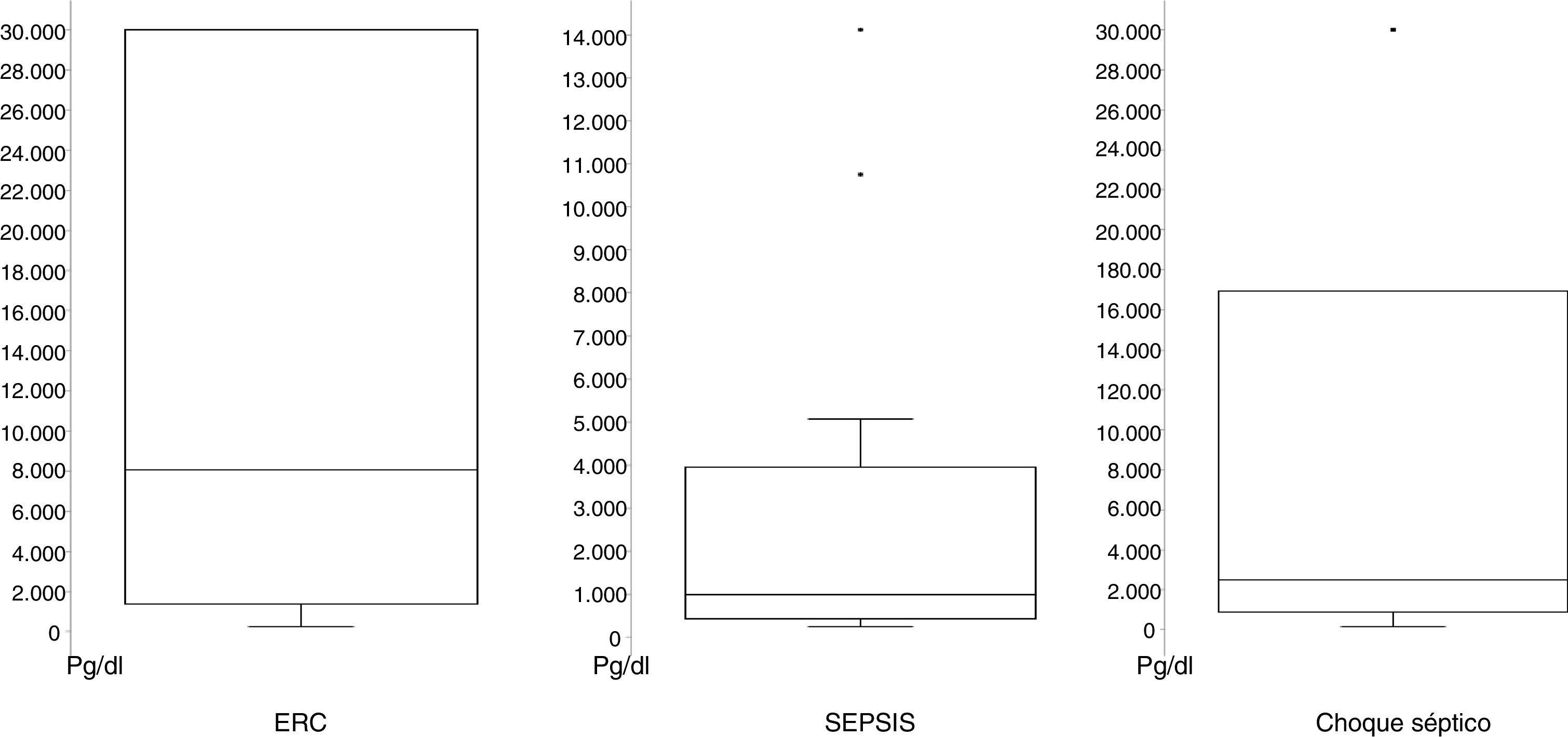
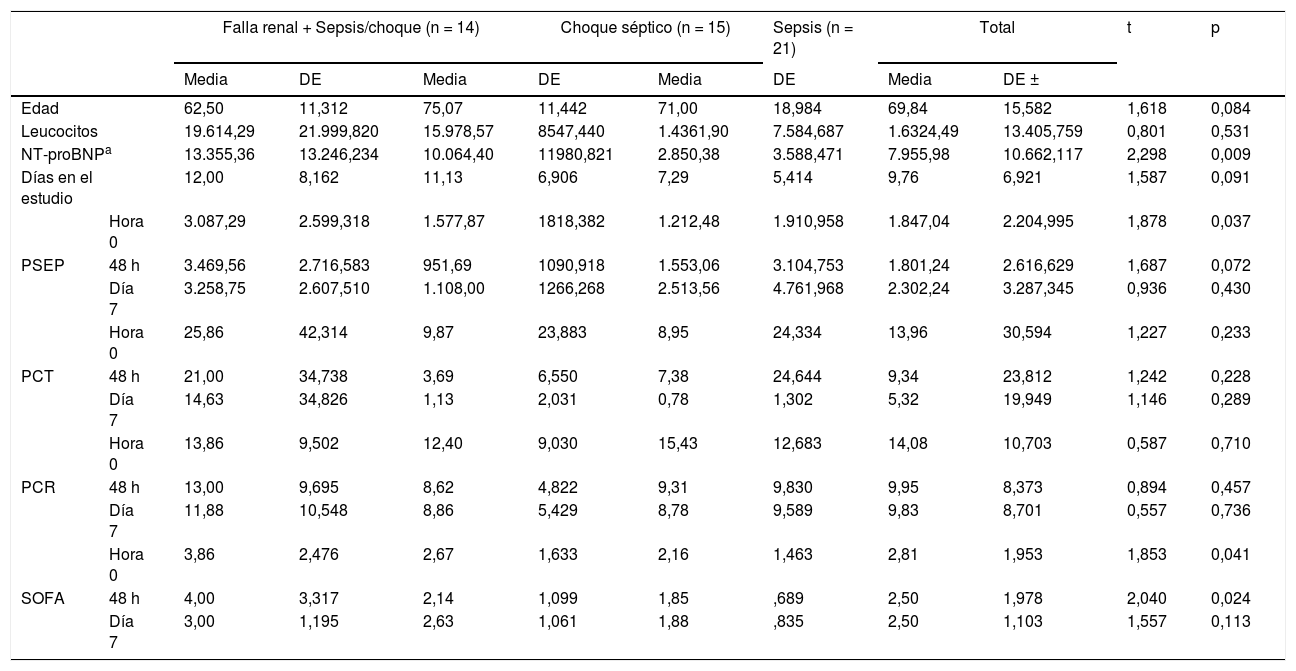
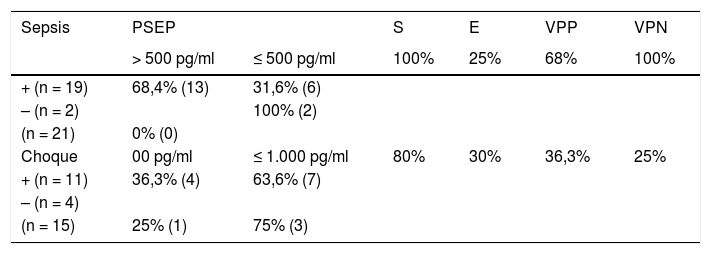
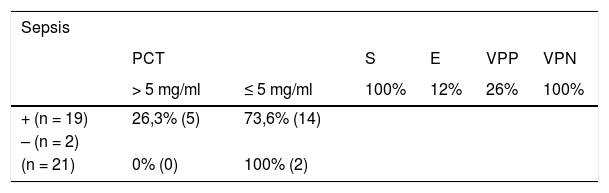
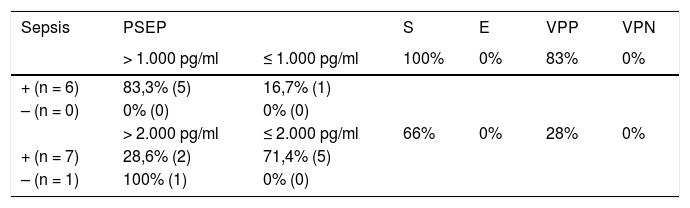
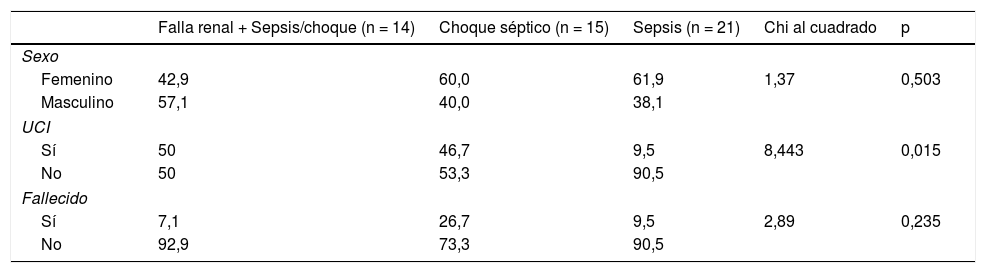
ResultadosEl 46% de los participantes fueron h o m b r e s. El promedio de edad fue de 69,8 años (DE ± 15,6); los sujetos fueron estratificados en 3grupos: ERC con sepsis/choque (n = 14), sepsis (n = 21) y choque séptico (n = 15). Al comparar los promedios de las variables cuantitativas, según pertenecer a uno de los 3grupos de observación, se encontró que el valor de PSEP a la hora cero presentó diferencias significativas (p < 0,05), siendo notable en los participantes con enfermedad renal y aquellos en choque séptico. De igual manera se encontró que el valor de NT-proBNP en la hora 0, y el SOFA a la hora 0 y a las 48h h presentaron diferencias significativas (p < 0,05).
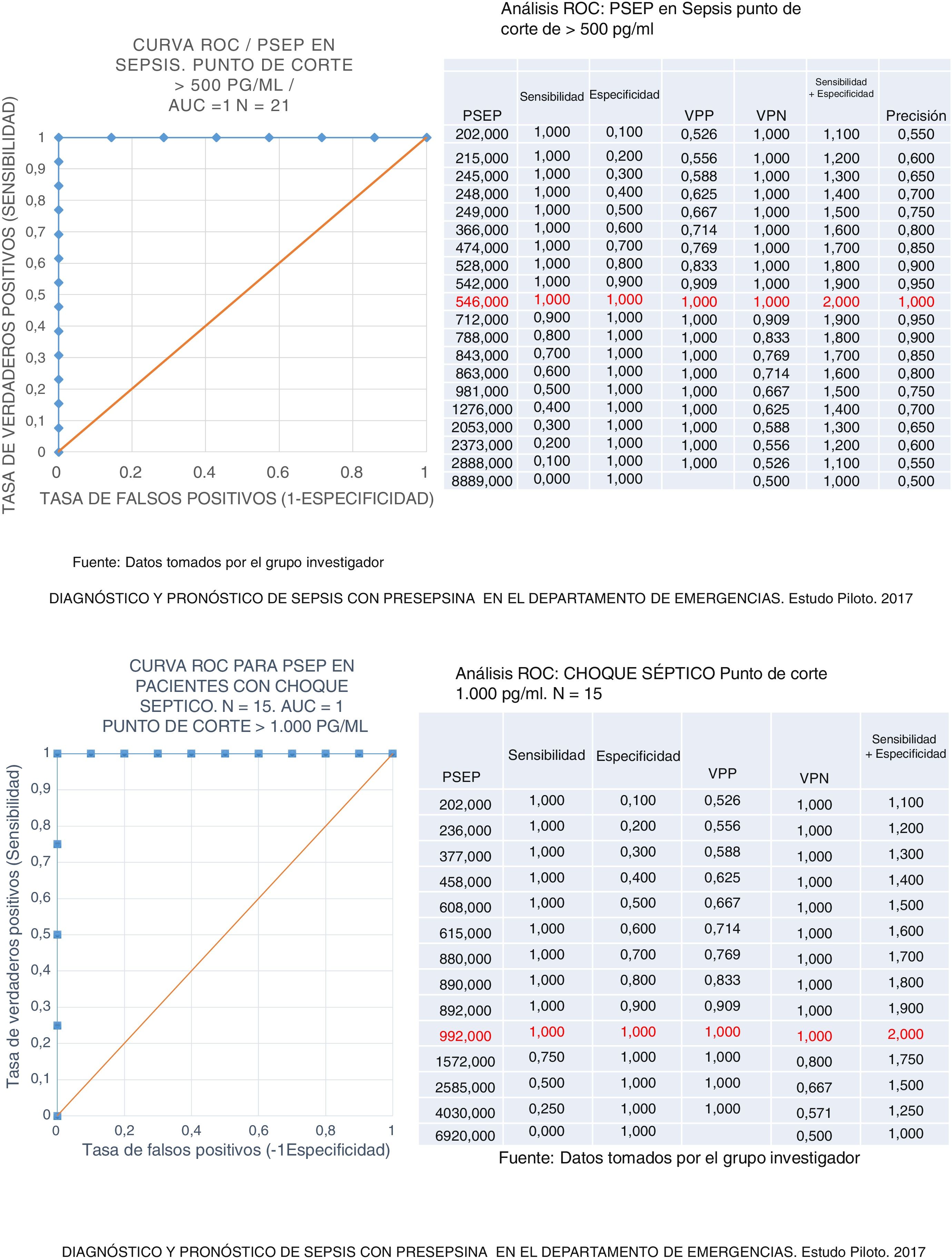
Análisis estadísticoEl análisis de la información se realizó a partir de medidas de tendencia central y de dispersión. Los puntos de corte establecidos para sepsis, choque séptico y pacientes con ERC se aplicaron a la muestra en la tabla de contingencia para evaluar la prueba diagnóstica; se analizaron sensibilidad, especificidad, VPP, VPN y curva ROC.
ComentarioLa PSEP demuestra en este estudio piloto su valor diagnóstico y pronóstico en sepsis. Un estudio multicéntrico nacional permitirá validar la prueba en nuestro medio y demostrar su eficacia diagnóstica.
Soluble presepsin (PSEP) a subtype of CD14 or sCD14-ST is a complex product of CD14 cleavage that is released into the general circulation and can now be quantified by a rapid automated method. The circulating levels of PSEP can be perceived as a control of activated monocytes-macrophages in response to pathogens. Thus, PSEP represents a biomarker of the initial phase of the systemic infection. The objective of the study is to evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic value of PSEP in subjects with sepsis and septic shock in an emergency department.
Materials and methodsPilot, observational, prospective study was conducted on 50 subjects who fulfilled the selection criteria, and admitted to the Emergency Department during the period July 2016 to January 2017. The demographic variables, diagnosis of sepsis or septic shock, and mortality were collected. Biomarker analyses were performed, and compared for the early diagnosis of infection, such as: presepsin (PSEP), procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, on admission, at 48hours, and on the seventh day. NT-proBNP was performed at hour 0.
ResultsThe mean age of the subjects in the study was 69.8 years (SD ± 15,6), and 46% of the participants were men. The subjects were stratified into 3groups: chronic kidney disease (CKD) with sepsis/shock (n = 14), sepsis (n = 21), and septic shock (n = 15). When comparing the means of the quantitative variables, and depending on which of the 3observation groups they belonged, it was found that the PSEP value at zero hour was significantly different (P<.05), being notable in the participants with kidney disease, and in those with septic shock. Similarly, it was found that the value of NT-proBNP at hour 0, and the Sepsis-related organ failure assessment (SOFA) score at zero hour, and at 48hours had significant differences (P<.05).
Statistical analysisThe analysis of the information was performed using measurement of central tendency and dispersion. The cut-off points established for sepsis, septic shock, and patients with CKD were applied to the sample in the contingency table to evaluate the diagnostic test, its sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV, and ROC curve.
CommentPSEP demonstrated its diagnostic and prognostic value in sepsis in this pilot study. A national Multicentre study will be used to validate the test in Colombia and demonstrate its diagnostic efficacy.
Artículo
Socios de la Asociación de Medicina Crítica y Cuidado Intensivo
Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la AMCI, clique aquí
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora