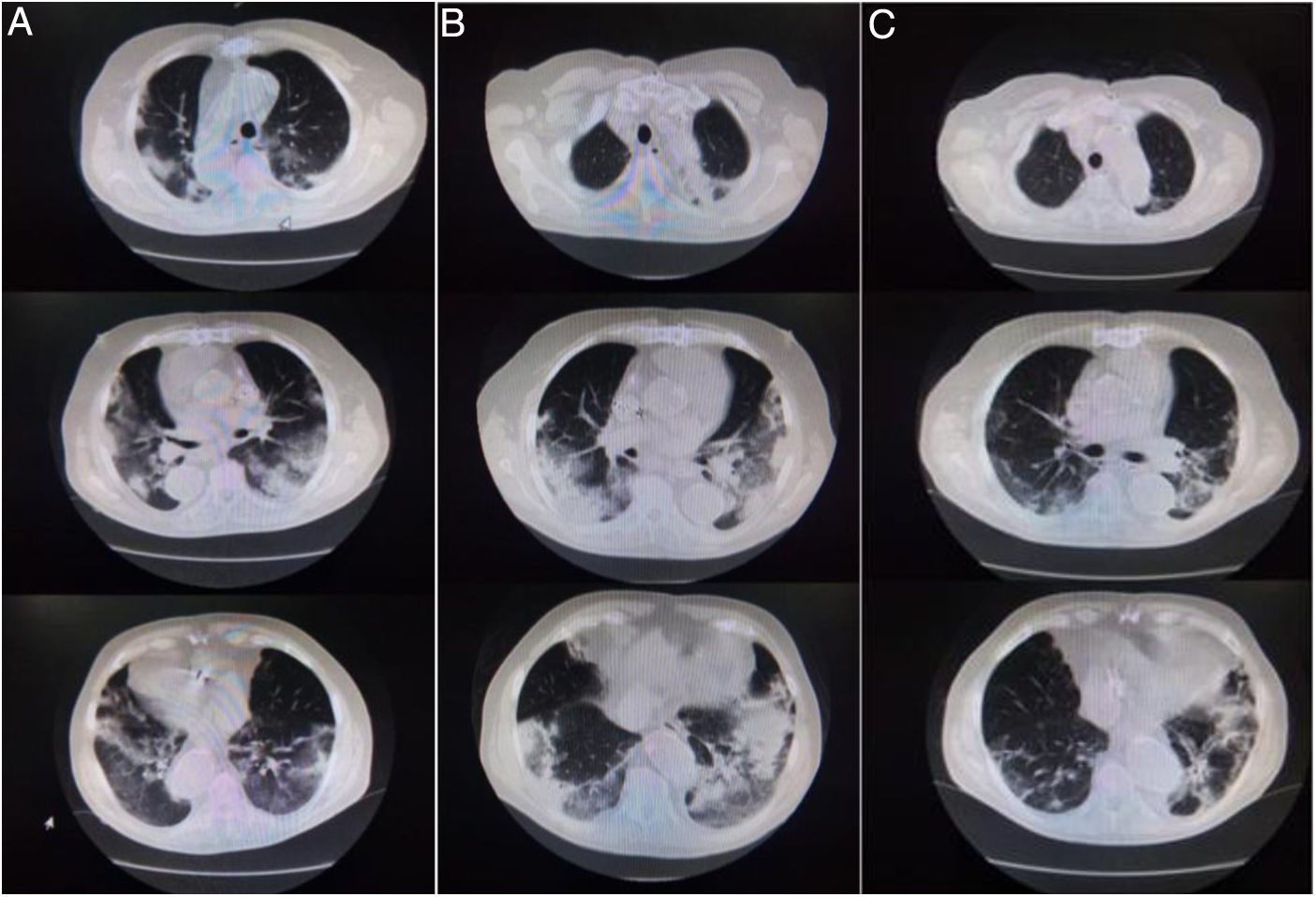
La enfermedad por coronavirus se caracteriza por una fase aguda en la que prevalecen síntomas respiratorios y una fase post aguda en la que los síntomas están relacionados con la inmovilización prolongada, disfunciones respiratorias, trastornos cognitivos y emocionales. Por lo tanto, existe la necesidad de una rehabilitación pulmonar (RP) donde el objetivo es mejorar las condiciones físicas y mentales del paciente. El siguiente reporte de un caso tiene como objetivo describir la evolución de un paciente internado con hipoxemia por secuela de neumonía por COVID-19, que realiza RP para lograr desvincularse del oxígeno y lograr volver a su domicilio.
Paciente masculino, 79 años, con COVID-19 y neumonía bilateral que requiere internación durante 28días. A los 15días de internado se encuentra con debilidad muscular y altos requerimientos de oxígeno, por lo que comienza un programa de RP. A los 28días logra el alta con oxígeno. A la cuarta semana de comenzada la rehabilitación logra desvincularse del oxígeno y puede continuar su rehabilitación ambulatoria.
Los pacientes con COVID-19 con neumonía bilateral con hipoxemia deberían comenzar un programa de RP de forma temprana con la finalidad de evitar o limitar el deterioro físico y emocional del paciente.
Coronavirus disease is characterized by an acute phase in which respiratory symptoms prevail and a post-acute phase in which symptoms are related to prolonged immobilization, respiratory dysfunctions, cognitive and emotional disorders. Therefore, there is a need for pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) where the objective is to improve the physical and mental conditions of the patient. The following case report aims to describe the progression of a patient hospitalized with hypoxaemia due to the sequelae of COVID-19 pneumonia, who underwent PR to achieve weaning from oxygen and to return home.
Male patient, 79 years old, with COVID-19 and bilateral pneumonia who required hospitalization for 28days. After 15days of hospitalization, he had developed muscle weakness and high oxygen requirements, and therefore began a PR programme. At 28days, he was discharged with oxygen. The fourth week after starting rehabilitation, he is able to disconnect from oxygen and continue his outpatient rehabilitation.
Patients with COVID-19 with bilateral pneumonia with hypoxaemia should start a PR programme early to avoid or limit the physical and emotional deterioration of the patient.
Artículo
Socios de la Asociación de Medicina Crítica y Cuidado Intensivo
Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la AMCI, clique aquí
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora