Hay muchas causas de hipoacusia neurosensorial, entre las que tiene especial interés la patología autoinmune del oído interno por su posible reversibilidad con tratamiento esteroideo, a veces asociada a enfermedades sistémicas autoinmunes. La tiroiditis crónica autoinmune o de Hashimoto (TA) presenta anticuerpos que podrían afectar al oído interno independientemente del hipotiroidismo, efecto que no ha sido suficientemente estudiado y nunca mediante audiometría con extensión en altas frecuencias.
El objetivo de este trabajo es estudiar si existe afectación de los umbrales auditivos en pacientes de TA, sin hipotiroidismo, en la totalidad del espectro auditivo humano (128 Hz – 20 kHz) distribuido por grupos de edad.
Materiales y métodosSe han seleccionado 128 pacientes divididos en dos grupos. El primer grupo de pacientes presenta anticuerpos antitiroideos elevados sin necesitar tratamiento sustitutivo con tiroxina. El segundo grupo con tratamiento sustitutivo con tiroxina, bien controlados. Se comparan con el grupo control (GC) de 209 pacientes. En todos se realizó historia clínica, exploración otológica, estudio de niveles de anticuerpos antitiroideos, TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T3 y T4 libres, timpanograma, estudio audiométrico convencional y con extensión en altas frecuencias.
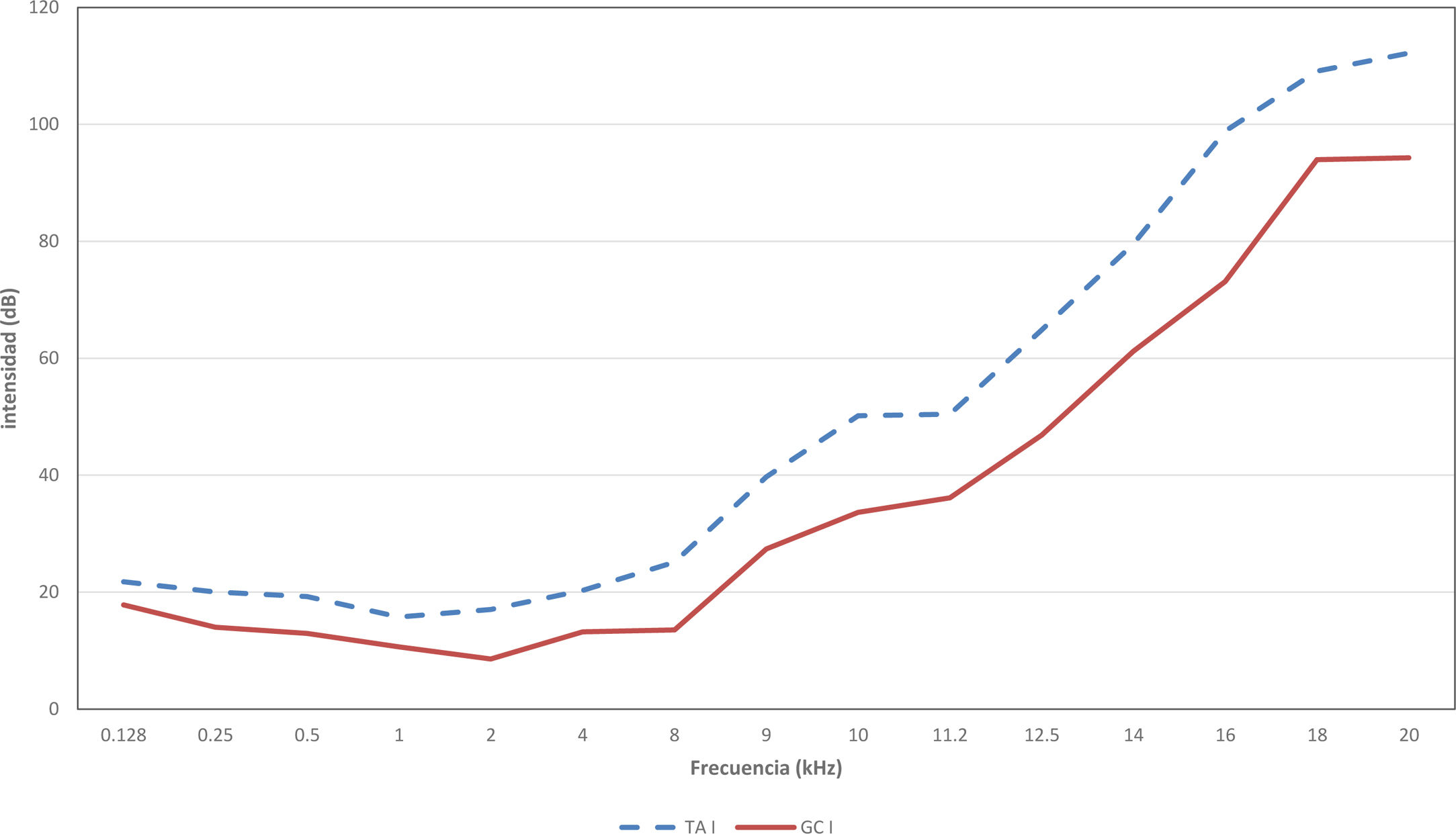
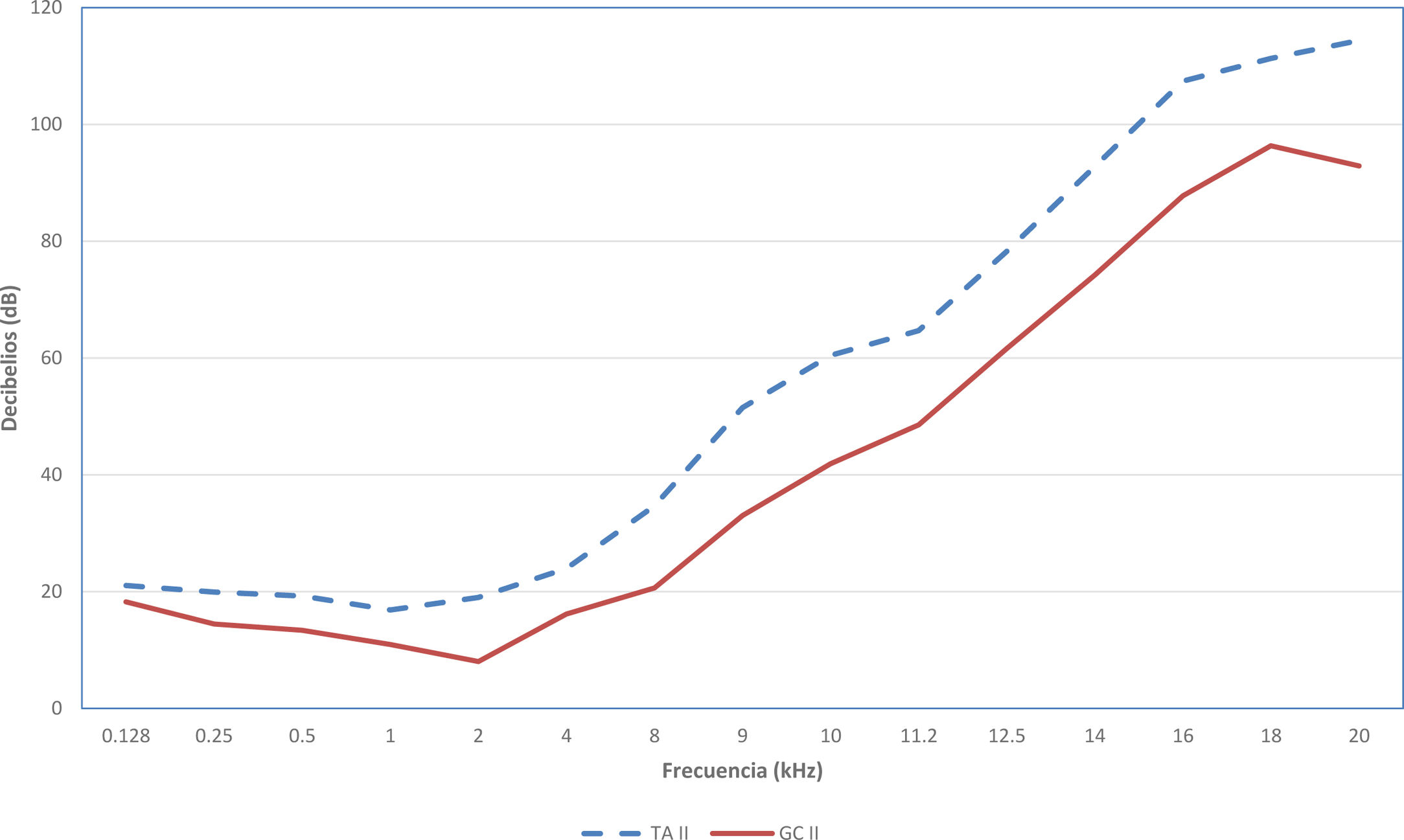
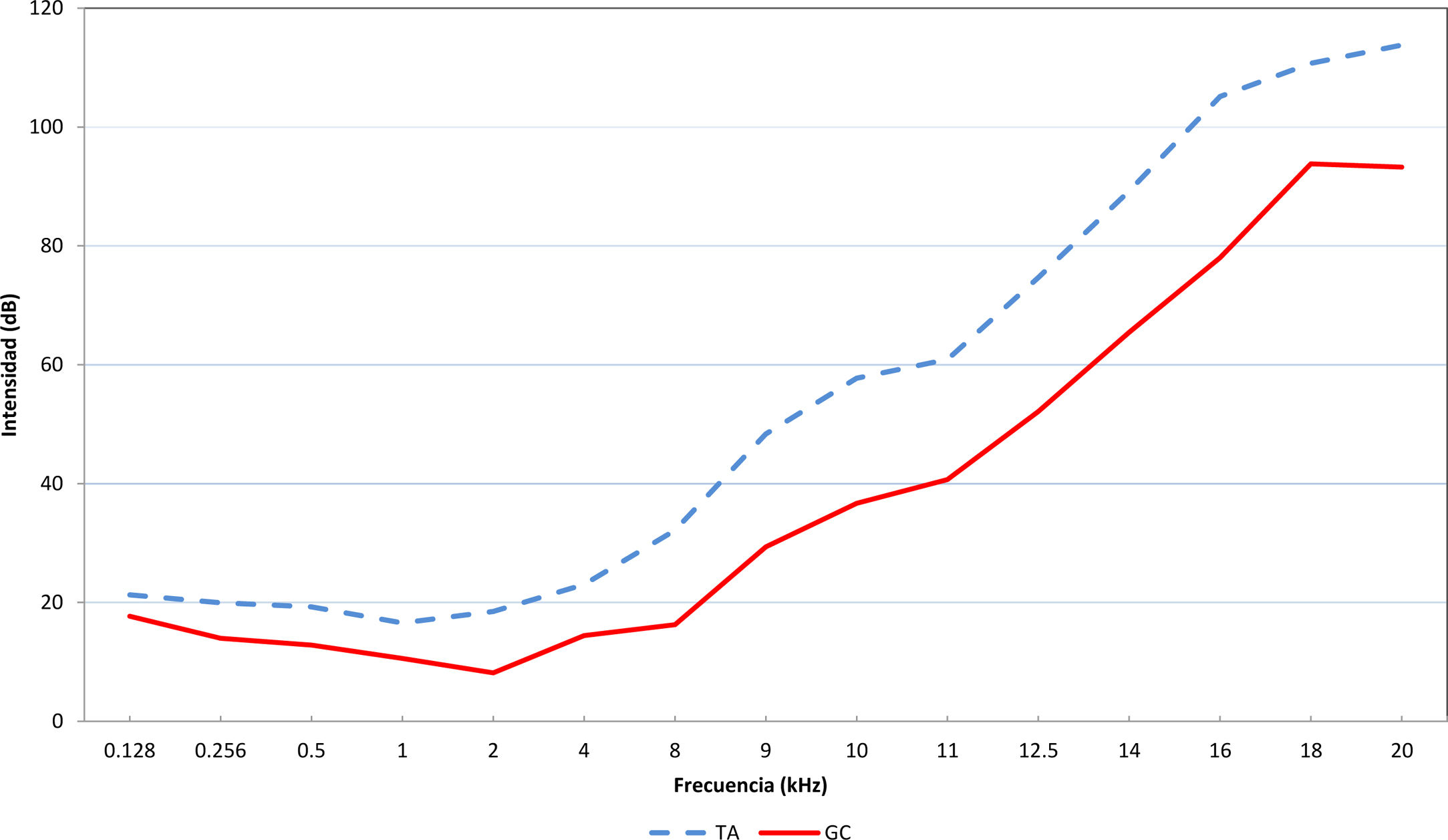
ResultadosTodos los pacientes fueron mujeres. Ambos grupos mostraron peor audición que los controles, siendo la diferencia estadísticamente significativa en todas las frecuencias; en el rango de frecuencias de 8 – 20 kHz con una diferencia de más de 10 dB, y en los rangos de 9-16 kHz y de 20 kHz de más de 20 dB.
Cuando se clasifican por grupos de edad, en los sujetos más jóvenes (20-29 años) estas diferencias se encuentran en todas las frecuencias, exceptuando las conversacionales (500 – 4.000 Hz), entre 30 y 49 años la diferencia es estadísticamente significativa en todas las frecuencias, y de 50 a 69 años las diferencias las encontramos especialmente en las frecuencias conversacionales.
ConclusionesEste primer trabajo estudiando la totalidad del espectro auditivo en la tiroiditis de Hashimoto confirma que la hipoacusia, en relación con el trastorno autoinmune, predomina su afectación inicialmente en extensión en altas frecuencias y que posiblemente esa hipoacusia se prolonga hasta afectar a las frecuencias convencionales, que es el momento en el que se detecta en la clínica habitual. Estos resultados destacan el papel de la audiometría con extensión en altas frecuencias para diagnosticar la hipoacusia subclínica en pacientes con TA.
Although sensorineural hearing loss may have different aetiologies, we focused on autoimmune hearing loss since it may be reversible with corticosteroid therapy; this entity is sometimes associated with systemic autoimmune diseases. Hashimoto's thyroiditis or chronic autoimmune thyroiditis shows antibodies and may be harmful to hearing thresholds regardless of hypothyroidism effect. To date this effect has not been sufficiently studied and never with extended high frequencies. The aim of this work is to study by age groups whether hearing thresholds in the human auditory range (128 to 20,000 Hz) are affected in Hashimoto's disease.
Materials and methodsTwo groups of 128 patients affected by Hashimoto's thyroiditis were included. First group: patients with pathological antithyroid antibodies who do not need L-thyroxine treatment. Second group: patients controlled with L-thyroxine substitutive treatment. Audiometric threshold study comparing between the groups of patients and a group of 209 controls was performed. All patients underwent complete otorhinolaryngological examination, antithyroid antibodies, TSH, T3 and T4 blood levels, tympanometry, conventional pure-tone audiometry, and extended-high-frequency audiometry.
ResultsAll patients were women. Both groups showed worst audiometric thresholds than the control group; both study groups showed worse hearing than controls, this difference was statistically significant in all frequencies. In the 8-20 kHz frequency range this difference was more than 10 dB, and in the 9-16 kHz and 20 kHz range this difference was more than 20 dB. When separated by age groups, in younger subjects (20-29 years) these differences were found in all frequencies, except for conversational frequencies (500 - 4,000 Hz); between 30 and 49 years the difference is statistically significant in all frequencies; and from 50 to 69 years differences are found, especially in the conversational frequencies.
ConclusionsThis first work studying the human auditory range in the chronic autoimmune thyroiditis or Hashimoto's thyroiditis confirms that hearing loss related to the autoimmune disorder predominates at extended-high-frequencies initially. But ends up involving all frequencies in pure-tone conventional audiometry, then it may be detected in routine clinical tests. These results support the role of extended-high-frequencies audiometry to diagnose subclinical hearing loss in patients affected by Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora