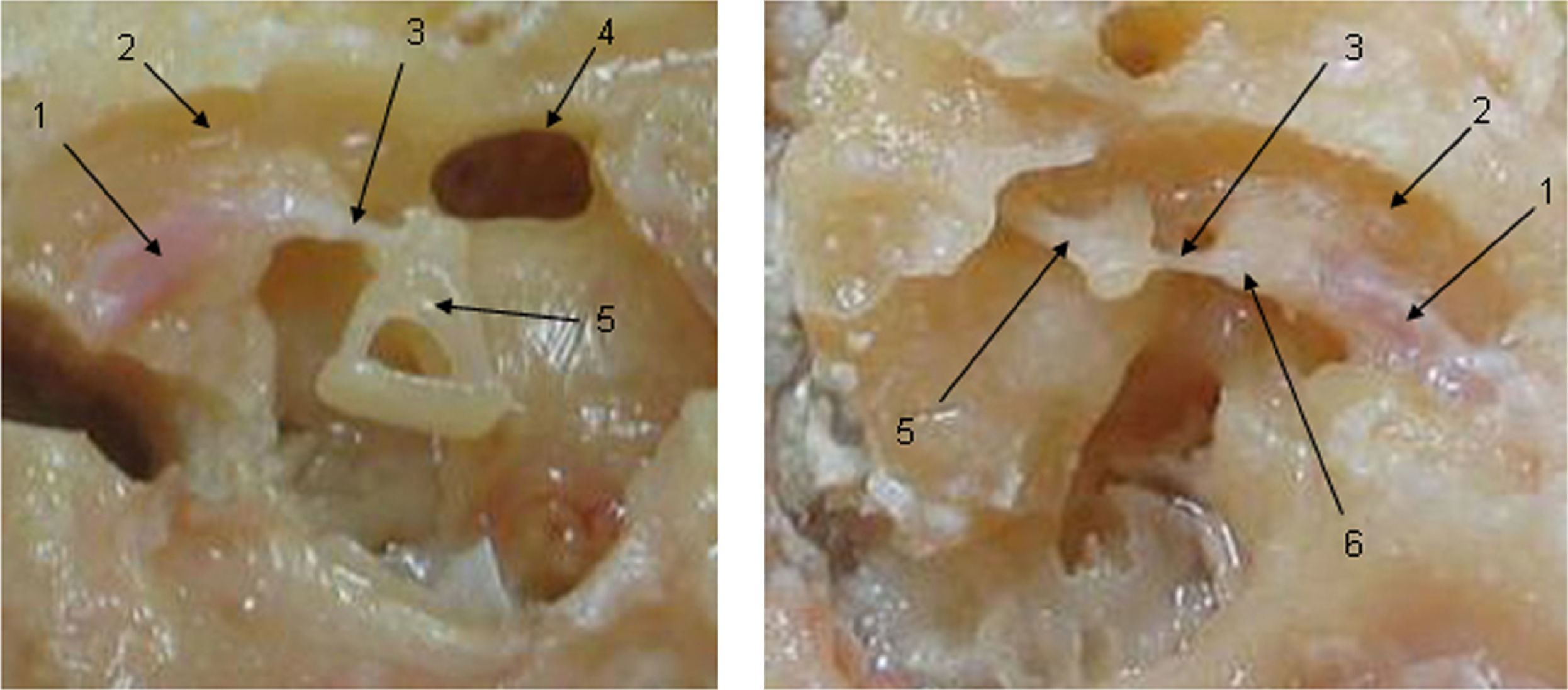
Los desórdenes temporomandibulares están asociados con síntomas como tinnitus, vértigo, sensación de pérdida auditiva, plenitud ótica y otalgia. La conexión y disfunción de los músculos tensor del martillo (TM) y tensor del velo del paladar (TVP) parece estar asociada a esta sintomatología referida. Se busca demostrar y explicar esta conexión a través de la morfometría de las estructuras.
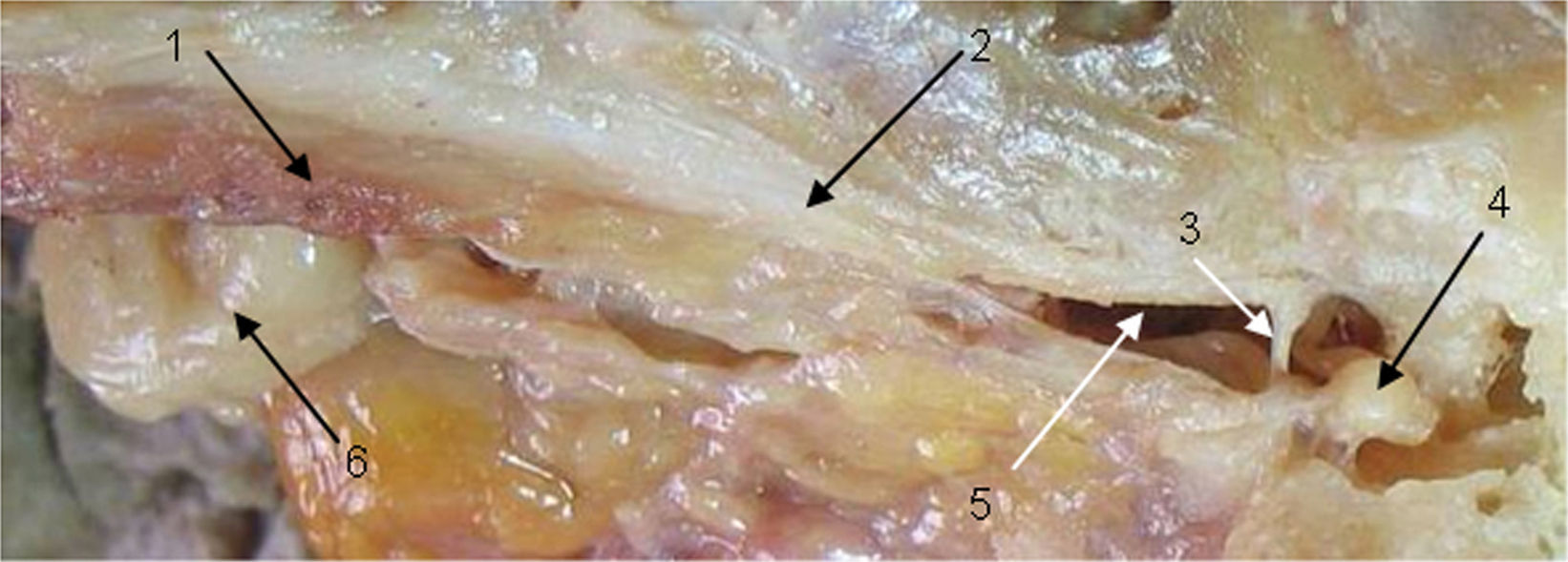
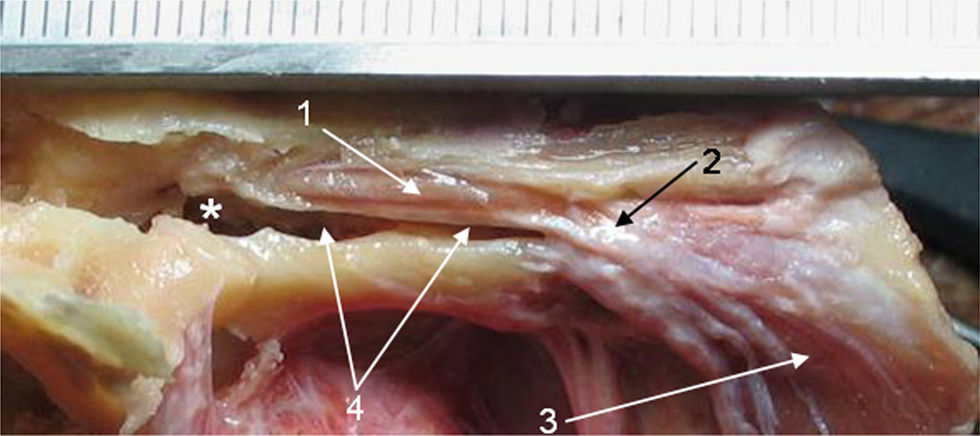
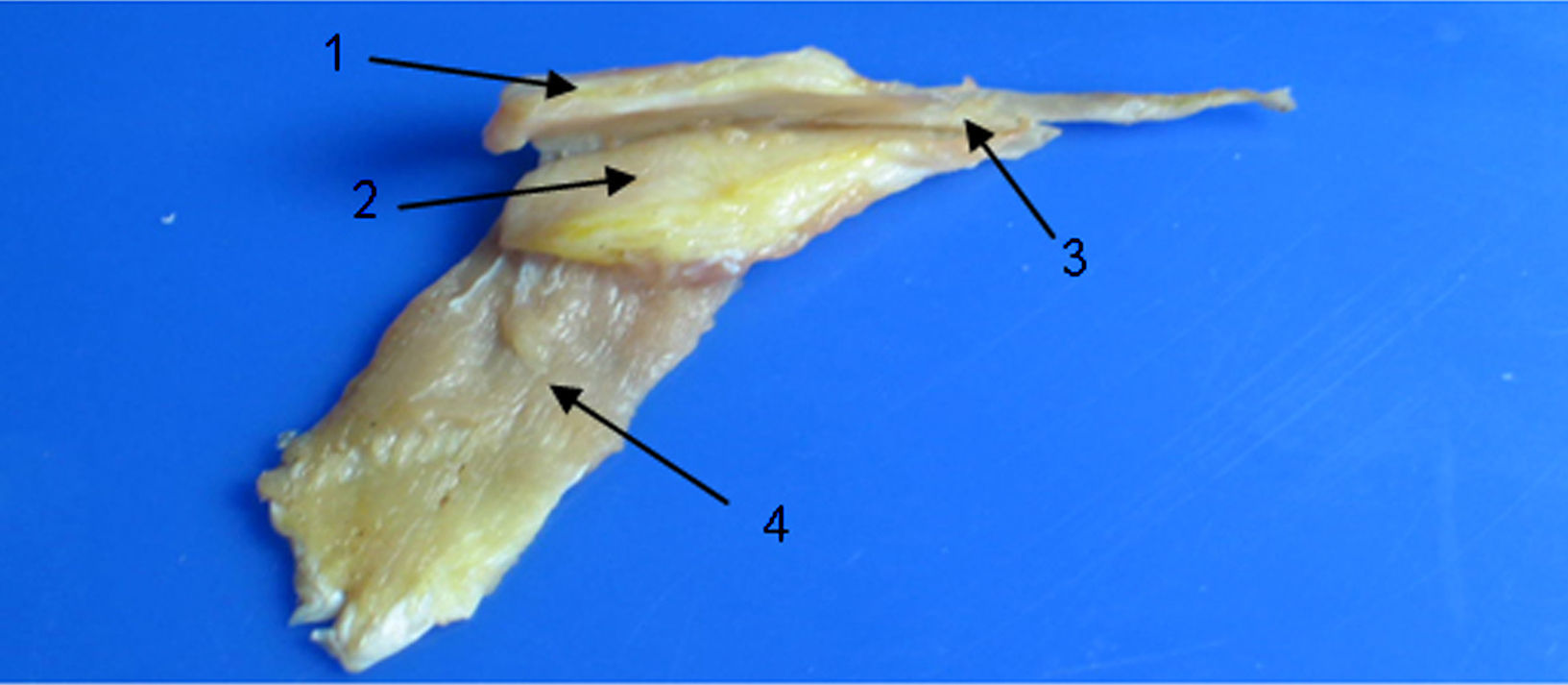
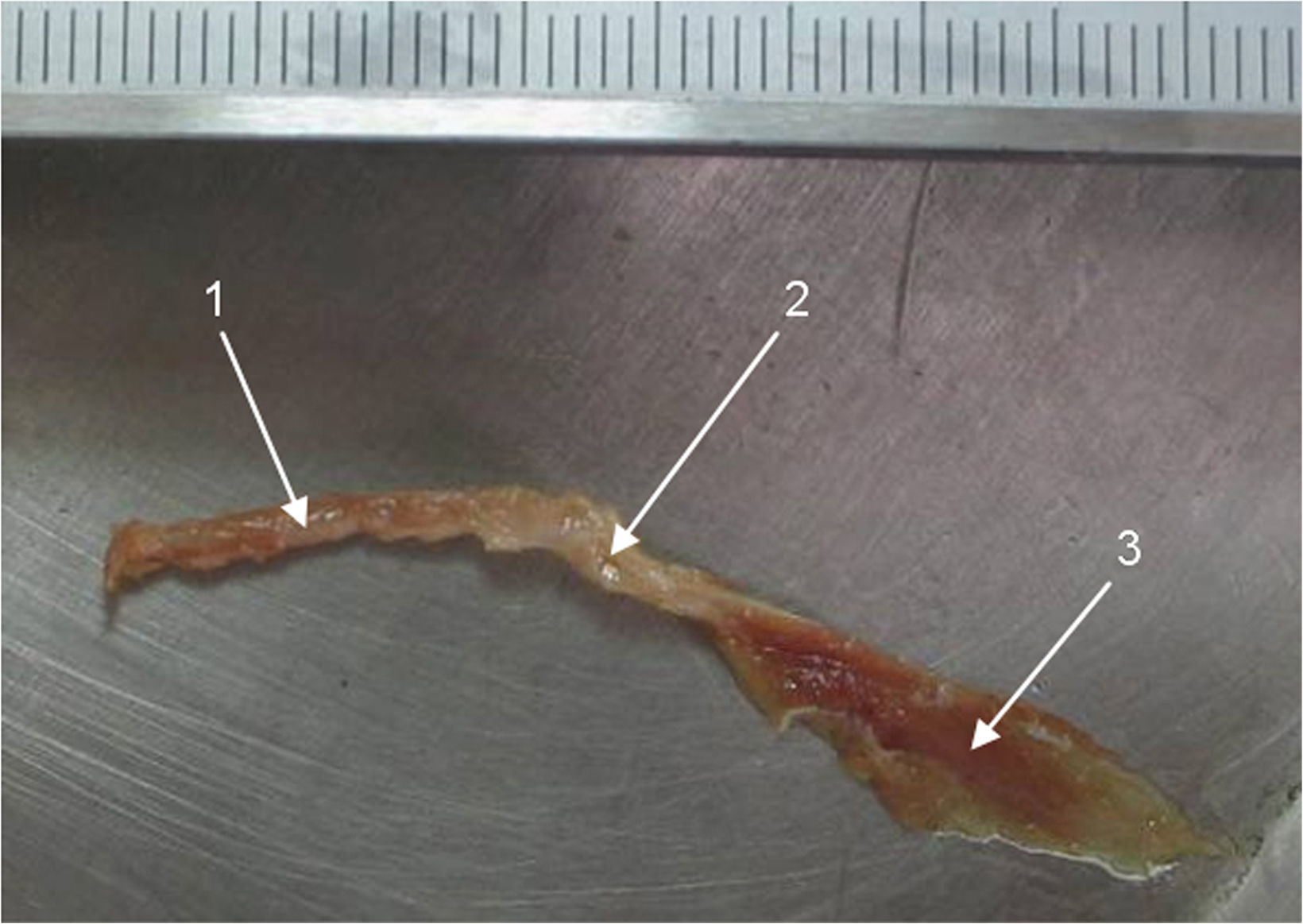
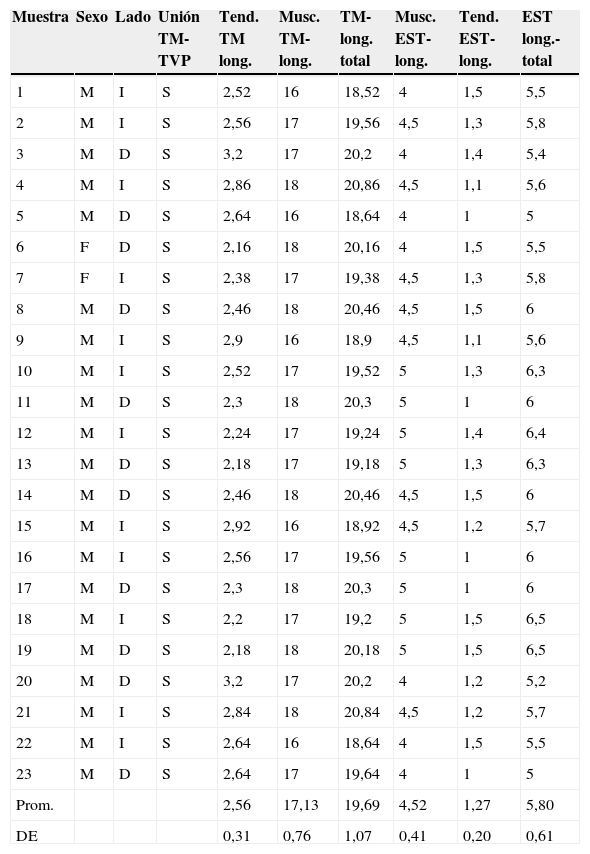
MétodosSe estudiaron 22 bloques pareados y 1 izquierdo de hueso temporal humanos. Se realizaron medidas digitales correspondientes al TM y el músculo del estribo.
ResultadosLa longitud promedio del músculo del estribo fue de 5,8mm (DE: 0,61) y la del TM fue de 19,69mm (DE: 1,07). En la totalidad de las muestras se halló conexión anatómica de los músculos TVP y TM a través de un tendón común.
ConclusionesSe matiza la necesidad de un manejo interdisciplinario entre el médico y el odontólogo especialista en dolor craneofacial.
Temporomandibular disorders are associated with symptoms such as tinnitus, vertigo, sensation of hearing loss, ear fullness and otalgia. The connection and dysfunction of the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini muscles seems to be associated with the aforementioned symptoms. We seek to demonstrate and explain this connection through the morphometry of these structures.
MethodsWe studied 22 paired blocks and 1 left side of human temporal bone. Digital measurements were made of the tensor tympani muscles and stapes.
ResultsThe average length of the stapedial muscle was 5.8mm SD 0.61, and that of the tensor tympani was 19.69mm SD 1.07. Anatomical connections were found in all the samples between the tensor veli palatini muscles through a common tendon.
ConclusionsThere is a need for an interdisciplinary management between physician and specialized dentist in cases of craniofacial pain.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora