La valoración de los parámetros hemodinámicos índice de resistencia renal (IR), velocidad pico sistólica (PSV), velocidad mínima diastólica (EDV) y flujo de la arteria renal (FR) mediante ecografía Doppler para el diagnóstico y monitorización posquirúrgica de la uropatía obstructiva parcial crónica.
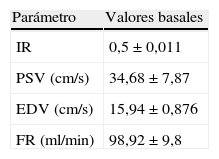
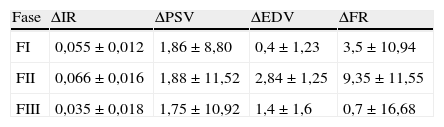
Material y métodosSe emplean 50 animales de la especie porcina. El estudio se divide en 3 fases. La fase I consta de la valoración ecográfica dúplex-Doppler de ambos riñones, determinando los parámetros objeto de estudio. La ratio de cada índice se calcula como la diferencia entre el valor del riñón en estudio y su contralateral. El examen termina con la realización de cistografía de compresión, urografía excretora y ureteropielografía retrógrada. Seguidamente, se procede a la creación de un modelo de obstrucción parcial del uréter derecho. Transcurridas 6 semanas, comienza la fase II mediante la realización de las pruebas descritas anteriormente y posterior resolución endourológica de la obstrucción. La fase III consiste en un seguimiento a los 6 meses del tratamiento mediante las pruebas realizadas en las fases previas.
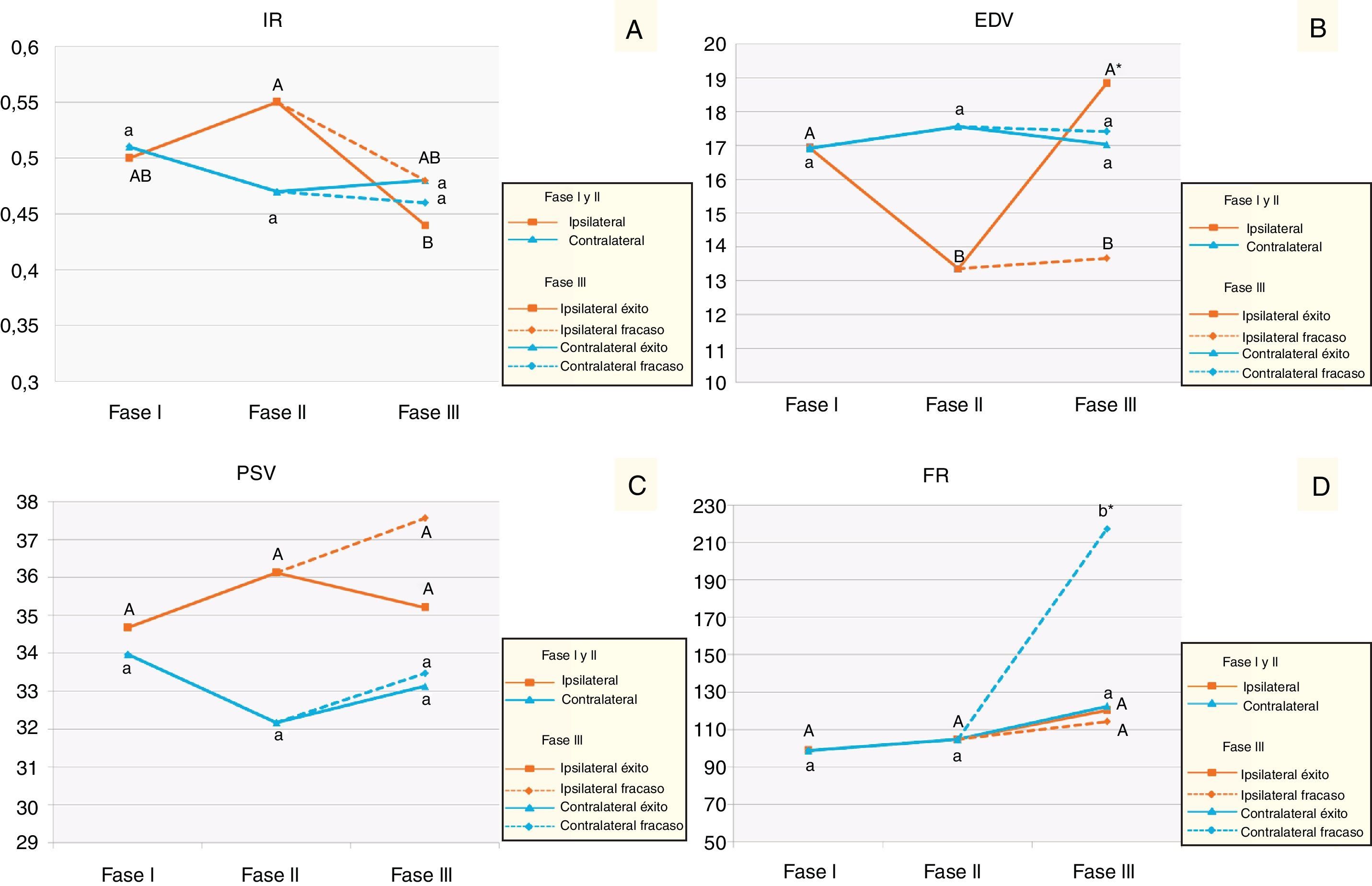
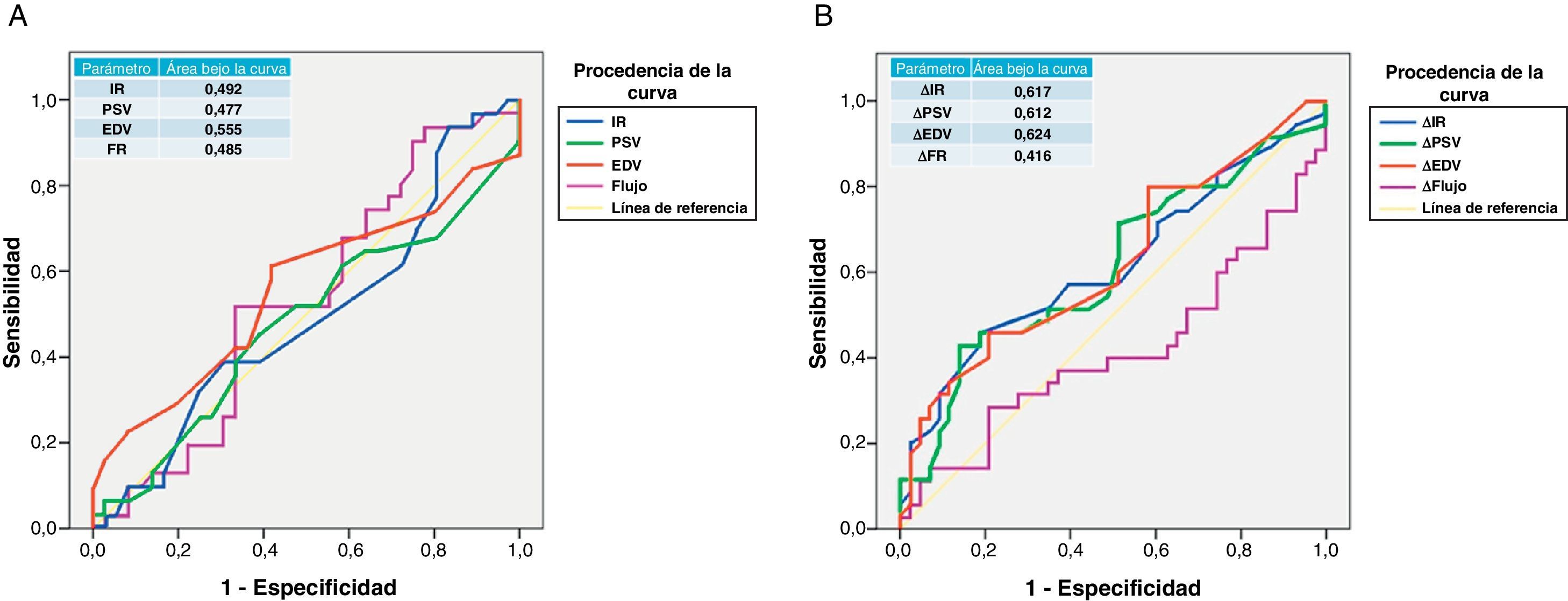
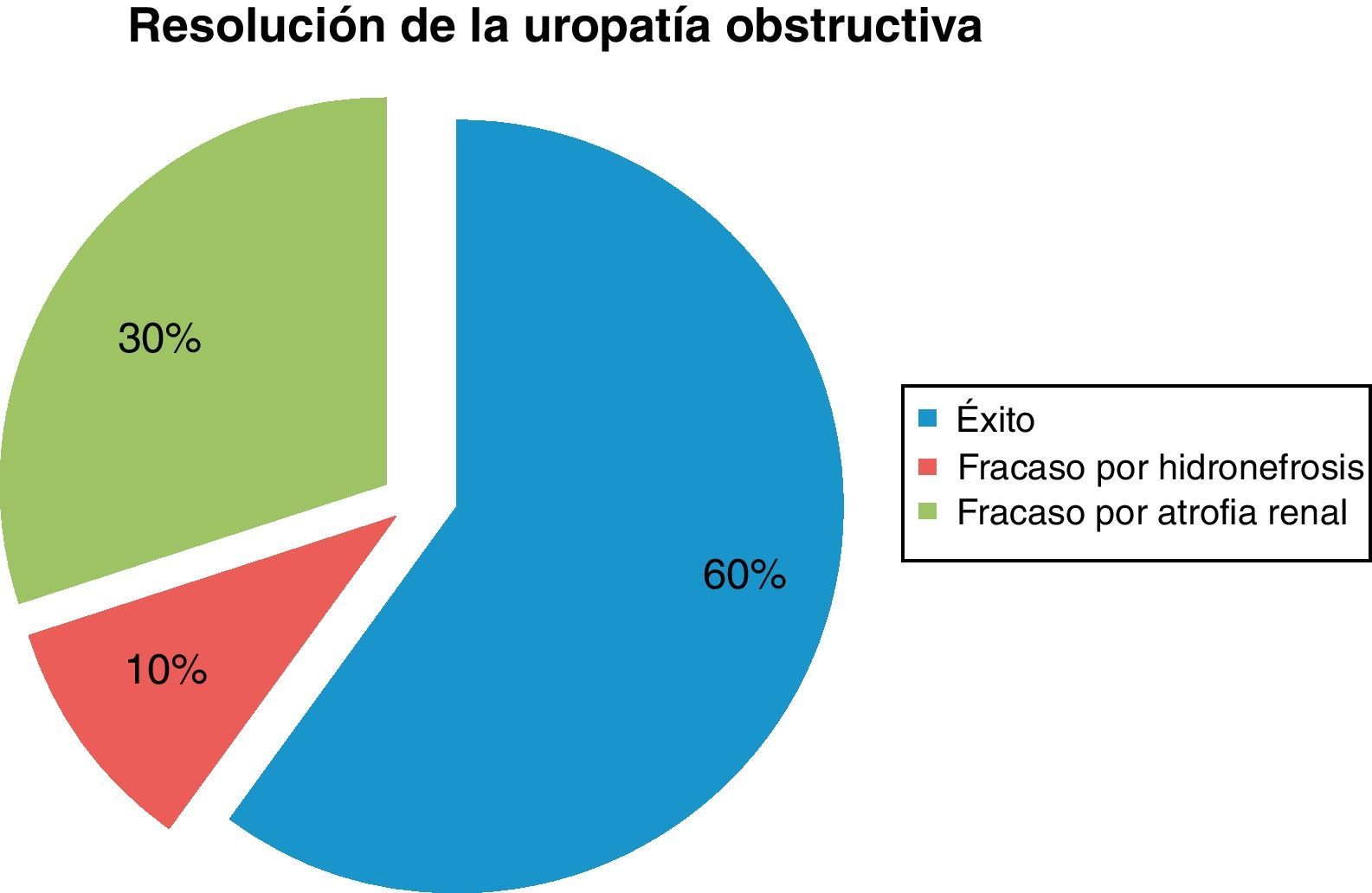
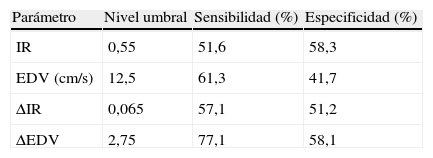
ResultadosDe los parámetros estudiados la EDV y su ratio son los que mayor sensibilidad y especificidad muestran como marcador diagnóstico de uropatía obstructiva. En el seguimiento posquirúrgico se observa como el IR y principalmente la EDV retornan a los valores basales.
ConclusionesLa ΔEDV es el parámetro que mayor eficacia muestra para el diagnóstico de uropatía obstructiva parcial crónica; pero esta es insuficiente para relegar las técnicas de diagnóstico convencionales. Todos los parámetros, principalmente la EDV, han mostrado ser útiles como pruebas complementarias de monitorización y pronóstico tras la resolución endourológica de la uropatía obstructiva.
This study has aimed to assess the hemodynamic parameters, Renal Resistive Index (RI), Peak Systolic Velocity (PSV), End-Diastolic Velocity (EDV) and Blood Flow of the Renal Artery (FR) by Doppler Ultrasound for diagnosis and monitoring postsurgical partial chronic obstructive uropathy.
Material and methodsFifty pigs were used. The experiment was divided into three phases. Phase I consisted of a duplex-Doppler evaluation of the both kidneys to determine the parameters under study. The ratio of each index is calculated as the difference between the value of study kidney and the contralateral. After, a fluoroscopic examination was performed by compressive cystography, excretory urography and retrograde ureteropyelography. Finally, a model of partial right ureteral obstruction was created. After six weeks of the obstructive model, Phase II was begun with the diagnosis of the uropathy, by means of the aforementioned diagnostic methods and the endourological treatment was completed. Phase III is a follow-up performed at 6 months of treatment using the same methods as in the previous phases.
ResultsOf the parameters studied, the EDV and its ratio showed greater sensitivity and specificity as a diagnostic marker of obstructive uropathy. In the postoperative monitoring, it was observed that the RI and the EDV returned to baseline levels, with the baseline values.
ConclusionsThe ΔEDV and its ratio is the parameter that shows the greater efficacy for the diagnosis of chronic partial obstructive uropathy, however, it is insufficient to avoid conventional diagnostic techniques. All the parameters, mainly the EDV, have proven useful as complementary tests for monitoring after endourologic resolution of obstructive uropathy.