The sharon fruit, also know as kaki or persimmon fruit, is the edible fruit of the persimmon tree (Dyospiros kaki) which belongs to the Ebenaceae family. It is native to China and Japan, where it was been cultivated for centuries. Persimmon were introduced into Europe and California (Dyospiros Virginiana or American Persimmon) in the mid 19 th century and are currently produced in the south of France, Italy and Spain, where it is known as kaki.
The sharon fruit can be classified into two general categories: those that bear astringent fruit until they are soft ripe and those that bear nonastringent fruits. Astringent cultivars contain high levels of soluble tannins and cannot be eaten until fully ripe and very soft, unless the astringency has been artificially removed. Non-astringent cultivars contain low levels of soluble tannins and can be eaten at various stages or firmness, from very hard to very soft.
The fruit consist of a berry, as large as an apple, orange in color, with soft, juicy pulp, sweet if ripe, and is usually eaten fresh by itself. The sharon fruit, 5-8 cm or more in diameter, resembles a tomato in appearance and contains vitamin A, with lesser amounts of vitamin C.
CASE REPORT
This report describes a case of a 33-years-old-man who suffered from an anaphylactic reaction after eating a sharon fruit. Previously he presented a history of oral allergy syndrome by nuts and peanuts and occupational asthma due to cereals included in poultry feeding stuffs.
He exhibited urticaria, facial angioedema, asthma, vomit, and loss blood pressure 15 minutes after eating a fresh sharon fruit. The symptoms responded promptly to adrenaline and glucocorticoids. He climed to have never eaten this food before.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Skin prick test (SPT) were performed with standardized extracts of grass pollens, mites, animal danders, moulds and foods, and legumes, vegetables, nuts, fresh fruits, and sharon fruit by prick by prick. The test was considered positive when the average diameter of the wheal was > 3 mm.
Serum-specific IgE was identified with the use of the EIA: solid- phase antigen was obtained by coupling the extract solution (2 mg/ml) to the 6 mm diameter CNB-activated paper disc as described by Ceska and Lundquist (1). This chromogenic immunoassay was considered positive when a value higher than 0.35 KU/L was obtained for the tested serum.
SDS-PAGE was carried out according to the method of Laemli (2). After electrophoresis, gels were stained by diffusion in 0.1 % Coomassie Brillant Blue R-250. The proteins were electrophoretically transferred to Inmobilon-P-membranes (PVDF membranes) essentially as described by Towbin et al (3).
RESULTS
SPT was positive for barley (12 mm), nuts (10 mm), peach (8 mm) and kiwi (8 mm). A prick by prick test with sharon fruit resulted positive (15 mm), but the same test in five controls patients, 2 atopic and 3 non-atopic, were negative.
Serum specific IgE was positive for sharon fruit 0.4 KU/L (class 1), wheat 0.73 KU/L (class 2), rye 0.88 KU/L (class 2), and barley 3.95 KU/L (class 3).
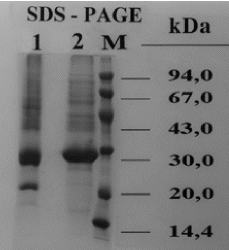
SDS-PAGE of sharon fruit in absence of beta-mercaptoethanol, demonstrated 12 proteins bands with following apparent molecular masses: 93, 83, 77, 74, 66, 56, 47.8, 42, 39, 36, 27.2, and 20.8 KDa.
After beta-mercaptoethanol treatment the 27.2 KDa protein band originated a unique protein with an apparent molecular mass of 28.2 KDa (fig. 1A).
Figure 1A.--Sharon fruit extract electrophoretic results after Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 staining. Lane 1: non reducing-conditions. Lane 2: protein bands wich were electrophoresed after being treated with beta-mercaptoethanol. Lane M: molecular mass marker.
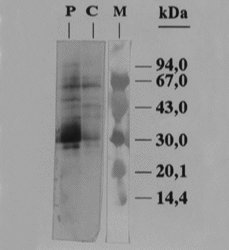
The immunoblot revealed (fig. 1B) showed 7 IgE-binding protein bands with apparent molecular masses of 72- 62- 47.7- 41.7- 37.3- 29.4, and 26.4 KDa; other similars bands also was seen with a nonallergic control serum.
Figure 1B.--Sharon fruit extract IEF after Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 staining and IEF Immunoblotting. Lane P: Immunoblotting incubated with patient serum. Lane C: Immunoblotting incubated with control serum (pool from non atopic subjects'sera). Lane M: molecular mass marker.
DISCUSSION
We have demonstrated by in vivo and in vitro test that a new variety of kaki (sharon fruit) can be cause of anaphylaxis.
Prandini et al described an anaphylactic reaction after eating persimmon (4). In our case, an IgE mediated mechanism was supported by inmediate positive skin reaction, EIA and immunoblotting. However, the results of this methods in vitro might be considered non-specific because we found differents allergic bands. We were not able to perform inhibition immunoassays to investigate cross-reactivity between food allergens and sharon fruit because of the low level of IgE binding to the solid-phase allergen. Further assays must be done in order to characterize and purify the involved major allergens.