Vitamin D status may be related to allergen sensitizations, but the evidence is inconsistent. The objective of this study was to assess whether serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels were associated with allergic sensitizations in early childhood.
MethodsData were collected from 2642 children who visited the Guangdong Women and Children’s Hospital from January 2016 to May 2017 for routine health check-ups. Serum 25(OH)D levels were tested by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay. Allergic sensitizations including food and inhalant allergens were tested for specific IgE antibodies at one year (12 months 0 days through 12 months 30 days) and two years (24 months 0 days through 24 months 30 days) of age.
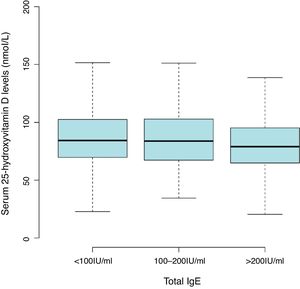
ResultsThe mean level of serum 25(OH)D was 86.47±27.55nmol/L, with a high prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency (<75nmol/L) in children aged 0–2 years (36.8%). Lower 25(OH)D levels with serum total IgE of more than 200IU/mL (81.54±25.53nmol/L) compared with less than 100IU/mL (87.92±28.05nmol/L). The common sensitization to allergens in children aged one and two years were milk (44.2%), cat epithelium (26.4%), egg (13.1%), dog epithelium (12.7%) and Dermatophagoides farinae (6.7%). After multivariate adjustment, data in 25(OH)D treated as a continuous variable or categories, no consistent associations were found between 25(OH)D levels and allergen-specific IgEs.
ConclusionsSerum 25(OH)D level showed an inverse relationship with total IgE level in early childhood. However, there is lack of evidence to support associations between low 25(OH)D levels and allergic sensitization to various allergens.
The prevalence of allergic diseases among children has been increasing rapidly worldwide in the past few decades.1,2 The immune system plays an important role in the development of allergies, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) with immunomodulatory effects, the main circulating form of vitamin D in serum, may influence the pathogenesis of allergic susceptibility.3 Observational studies identified conflicting relationships between vitamin D deficiency and the risk of asthma, atopic dermatitis, and elevated serum IgE levels.4 Results from the US population found a link between low vitamin D status and higher prevalence of allergens in children and adolescents, suggesting vitamin D deficiency might be an adverse factor for development of allergy.5 Similarly, children with insufficient vitamin D (25(OH)D≤50nmol/L) in Australia showed increased risk of peanut and egg allergy compared to those with adequate vitamin D levels.6 Peroni et al. demonstrated that average 25(OH)D concentrations were lower in children with moderate and severe atopic dermatitis.7 Furthermore, Mullins et al.8 and Vassallo et al.9 found that children born in autumn or winter had a higher incidence of food allergy, speculating vitamin D status (ultraviolet exposure) may be the potential factors leading to the pathogenesis of food allergy in children. However, several recent studies have been unable to demonstrate a consistently protective effect of vitamin D on allergies. Heimbeck et al.10 showed that average 25(OH)D concentration was relative higher in those with eczema compared with those without. Data from a cohort study in Norway showed 25(OH)D levels were not related to the severity of atopic eczema.11
The role of vitamin D in allergic diseases remains controversial. The objective of this study was to assess the relationship between serum 25(OH)D insufficiency (<75nmol/L) and allergic sensitization measured by serum specific IgE antibodies among children aged 0–2 years in southern China.
Materials and methodsStudy design and participantsFrom January 2016 to May 2017, children aged one year (12 months 0 days through 12 months 30 days) and two years (24 months 0 days through 24 months 30 days) who visited the Department of Children’s Health Care at Guangdong Women and Children’s Hospital for routine health check-ups were recruited in this study. If the parents were willing to allow their children’s blood to be tested for the vitamin D concentration and allergic sensitizations, the children were enrolled. Children with a history of medical problems (such as skeletal disease, genetic syndromes, or malabsorptive disorders) and with incomplete data (including 25(OH)D levels, total serum IgE and antigen-specific IgE levels) were excluded. Data on demographics including age, sex, weight and date of visit were collected from medical records. The Medical Research Ethics Board of Guangdong Women and Children’s Hospital approved this study, and parents of eligible children provided written informed consent.
Vitamin D measurementThe vitamin D status was assessed by measuring the serum 25(OH)D values using the Abbott ARCHITECT i4000 instrument (Abbott Laboratories, Lake Bluff, IL, USA). The detailed biochemical analysis of the laboratory procedures has been reported elsewhere.12 According to updated clinical practice guidelines released by the Endocrine Society,13 vitamin D level was divided into two categories in this analysis: deficiency or insufficiency (25(OH)D<75nmol/L) and sufficiency (25(OH)D≥75nmol/L).
Serum total and allergen-specific IgESerum total IgE and specific IgE were quantified in all subjects with the AllergyScreen system (Mediwiss Analytic GmbH, Moers, Germany) which was used to detect 10 kinds of food allergens (Egg, Milk, Shrimp, Beef, Shellfish, Crab, Amaranth, Mango, Cashew nut, Pineapple) and nine kinds of inhalant allergens (Dermatophagoides farinae, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Mulberry, Cat, Dog, Cockroach, Aspergillus species, Ragweed, Birch). The specific IgE levels were divided into seven categories from zero to six: grade zero (<0.35IU/mL); grade one (0.35–0.70IU/mL); grade two (0.70–3.50IU/mL); grade three (3.5–17.5IU/mL); grade four (17.5–50IU/ml); grade five (50–100IU/mL); and grade six (>100IU/mL). The IgE level >0.35IU/mL was considered as positive allergic sensitization.
Statistical analysisThe continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviations (SD). Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and proportions (%). 25(OH)D level was used as a continuous variable to evaluate relationships with specific IgE levels by linear model. In addition, logistic regression analysis was used to identify the odds ratio (OR) of each 25(OH)D category. P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. All statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS statistical software package (V20, IBM Statistics, Chicago, IL, USA) and R software (V3.1.2, http://www.R-project.org).
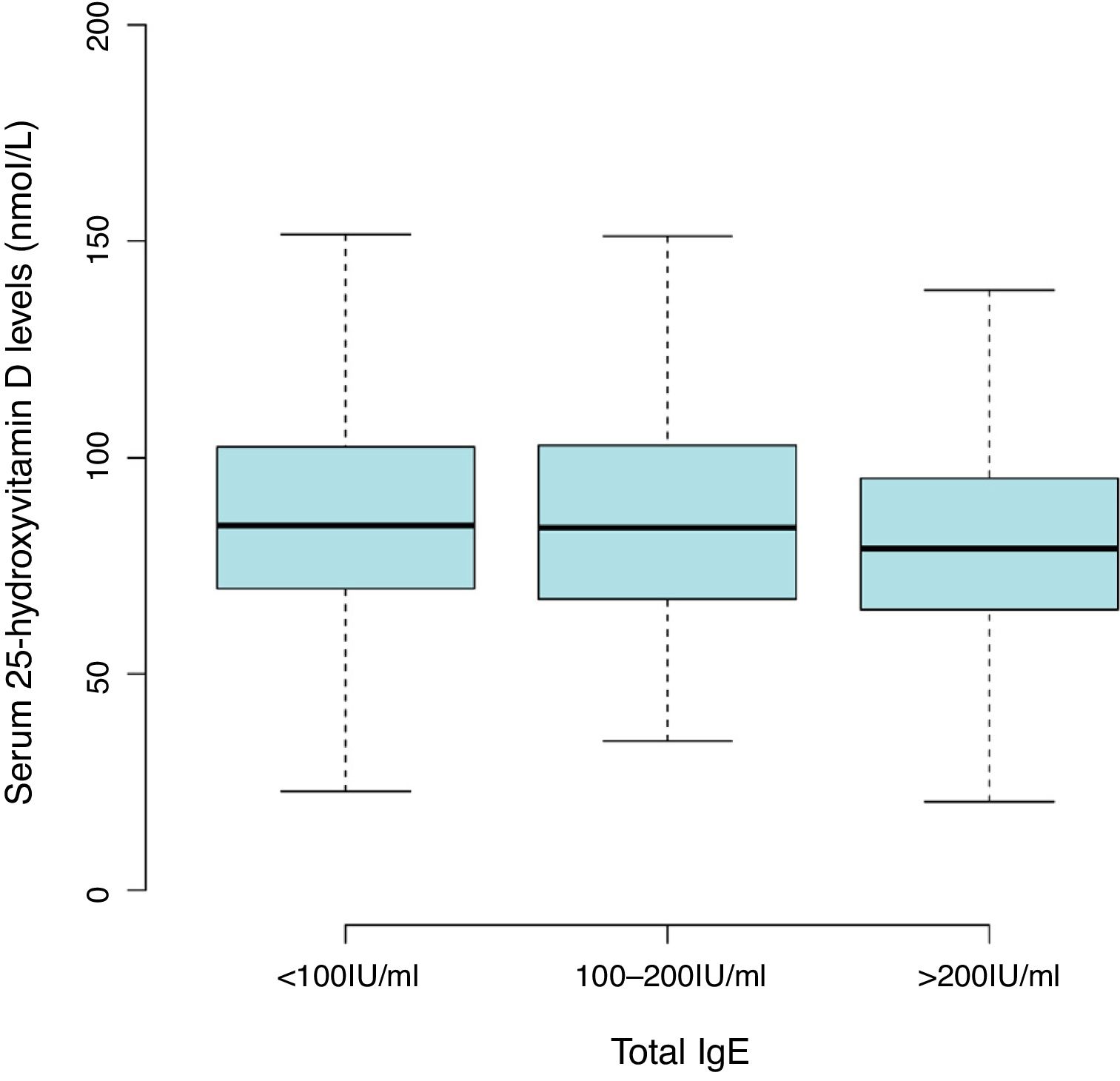
Results2642 children aged one and two years were included in the final analyses. The mean level of serum 25(OH)D was 86.47±27.55nmol/L with a high prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency (<75nmol/L) in the children (36.8%). There was a trend toward lower 25(OH)D levels with serum total IgE of more than 200IU/mL (81.54±25.53nmol/L) compared with less than 100 IU/mL (87.92±28.05nmol/L) (Fig. 1 and Table S1). The overall positive rate of total IgE was 34.0%. Participants’ characteristics by 25(OH)D levels in children aged 0–2 years were shown in Table 1.
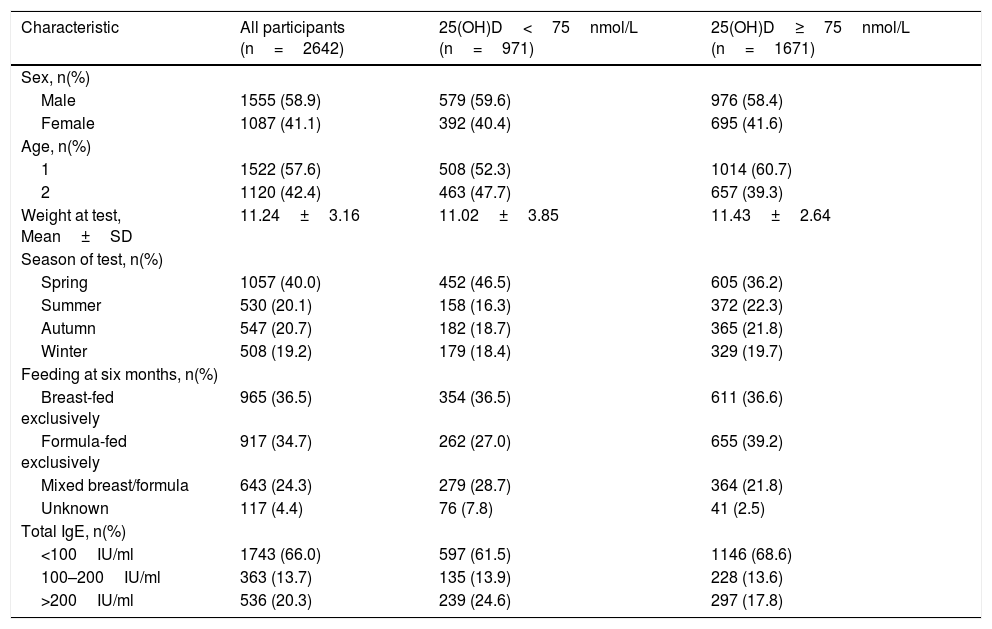
Participants’ characteristics by 25(OH)D levels in children aged 1 and 2 years.
| Characteristic | All participants (n=2642) | 25(OH)D<75nmol/L (n=971) | 25(OH)D≥75nmol/L (n=1671) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n(%) | |||
| Male | 1555 (58.9) | 579 (59.6) | 976 (58.4) |
| Female | 1087 (41.1) | 392 (40.4) | 695 (41.6) |
| Age, n(%) | |||
| 1 | 1522 (57.6) | 508 (52.3) | 1014 (60.7) |
| 2 | 1120 (42.4) | 463 (47.7) | 657 (39.3) |
| Weight at test, Mean±SD | 11.24±3.16 | 11.02±3.85 | 11.43±2.64 |
| Season of test, n(%) | |||
| Spring | 1057 (40.0) | 452 (46.5) | 605 (36.2) |
| Summer | 530 (20.1) | 158 (16.3) | 372 (22.3) |
| Autumn | 547 (20.7) | 182 (18.7) | 365 (21.8) |
| Winter | 508 (19.2) | 179 (18.4) | 329 (19.7) |
| Feeding at six months, n(%) | |||
| Breast-fed exclusively | 965 (36.5) | 354 (36.5) | 611 (36.6) |
| Formula-fed exclusively | 917 (34.7) | 262 (27.0) | 655 (39.2) |
| Mixed breast/formula | 643 (24.3) | 279 (28.7) | 364 (21.8) |
| Unknown | 117 (4.4) | 76 (7.8) | 41 (2.5) |
| Total IgE, n(%) | |||
| <100IU/ml | 1743 (66.0) | 597 (61.5) | 1146 (68.6) |
| 100–200IU/ml | 363 (13.7) | 135 (13.9) | 228 (13.6) |
| >200IU/ml | 536 (20.3) | 239 (24.6) | 297 (17.8) |
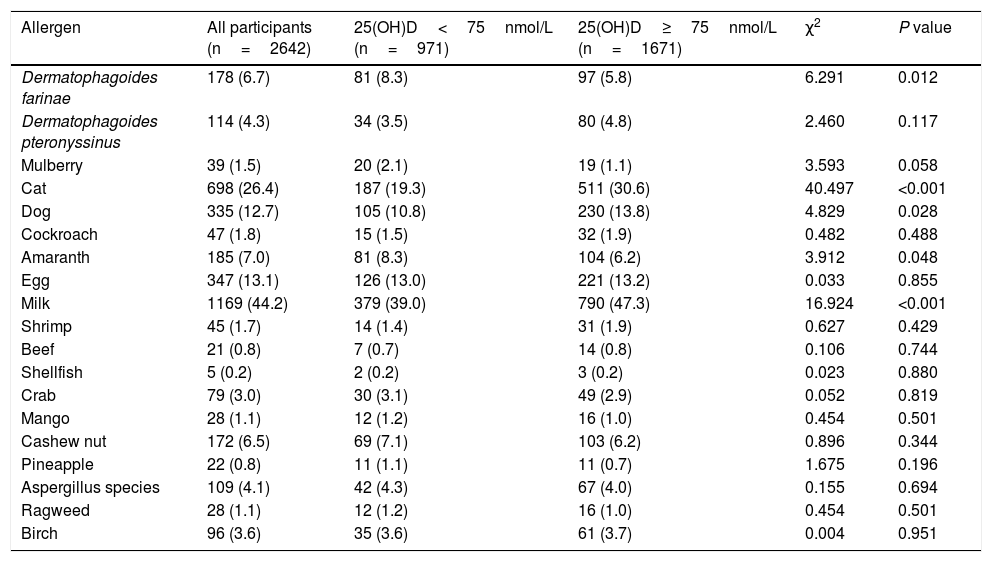
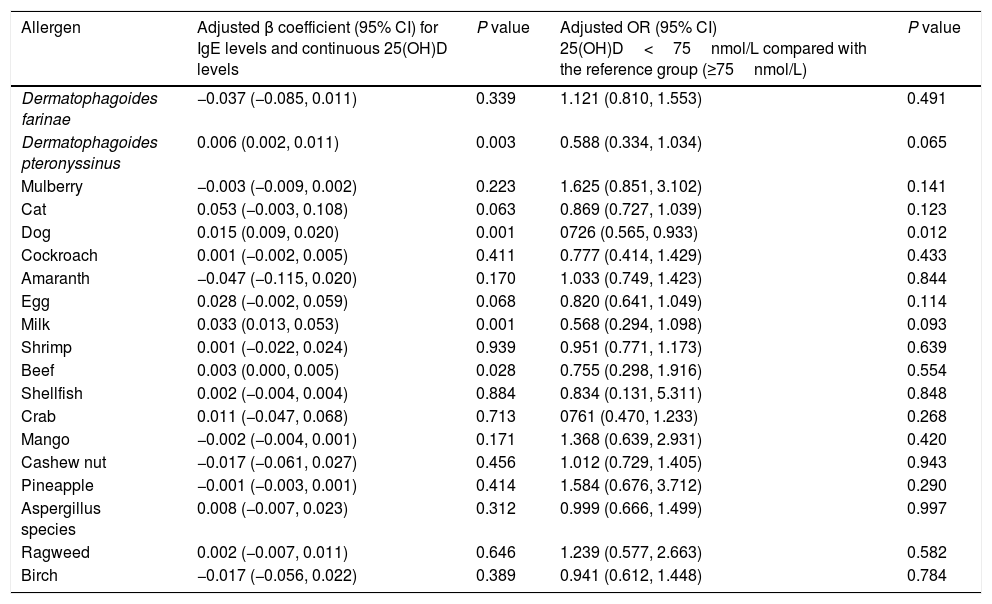
Table 2 shows the common sensitization to allergens in the children aged 0–2 years were milk (44.2%), cat epithelium (26.4%), egg (13.1%), dog epithelium (12.7%) and Dermatophagoides farinae (6.7%). A significantly higher prevalence of Dermatophagoides farinae sensitization was found in children with low 25(OH)D level (<75nmol/L). The prevalence of sensitization to cat, dog and milk was higher in children with sufficient 25(OH)D level (≥75nmol/L). After multivariate adjustment using linear and logistic regression, there were fewer associations present between 25(OH)D and positive allergen-specific IgE levels when analyzing the data in 25(OH)D categories or as continuous variables (Table 3). To determine whether the standard vitamin D cut-off point of 75nmol/L used in this analysis masked a graded association between vitamin D levels and allergen-specific IgEs, we subsequently analyzed the ORs for positive allergens associated with 25(OH)D levels of less than 50nmol/L compared with a level of 75nmol/L or greater. Fewer significant associations were observed between 25(OH)D levels and allergen-specific IgEs (Table S2). The 25(OH)D levels of less than 50nmol/L showed protective associations with dog allergens (OR, 0.541; 95% CI, 0.307–0.955) and milk allergens (OR, 0.627; 95% CI, 0.430–0.914).
Prevalence of positive serum antigen-specific IgE tests by serum 25(OH)D levels in children aged 1 and 2 years.
| Allergen | All participants (n=2642) | 25(OH)D<75nmol/L (n=971) | 25(OH)D≥75nmol/L (n=1671) | χ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermatophagoides farinae | 178 (6.7) | 81 (8.3) | 97 (5.8) | 6.291 | 0.012 |
| Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus | 114 (4.3) | 34 (3.5) | 80 (4.8) | 2.460 | 0.117 |
| Mulberry | 39 (1.5) | 20 (2.1) | 19 (1.1) | 3.593 | 0.058 |
| Cat | 698 (26.4) | 187 (19.3) | 511 (30.6) | 40.497 | <0.001 |
| Dog | 335 (12.7) | 105 (10.8) | 230 (13.8) | 4.829 | 0.028 |
| Cockroach | 47 (1.8) | 15 (1.5) | 32 (1.9) | 0.482 | 0.488 |
| Amaranth | 185 (7.0) | 81 (8.3) | 104 (6.2) | 3.912 | 0.048 |
| Egg | 347 (13.1) | 126 (13.0) | 221 (13.2) | 0.033 | 0.855 |
| Milk | 1169 (44.2) | 379 (39.0) | 790 (47.3) | 16.924 | <0.001 |
| Shrimp | 45 (1.7) | 14 (1.4) | 31 (1.9) | 0.627 | 0.429 |
| Beef | 21 (0.8) | 7 (0.7) | 14 (0.8) | 0.106 | 0.744 |
| Shellfish | 5 (0.2) | 2 (0.2) | 3 (0.2) | 0.023 | 0.880 |
| Crab | 79 (3.0) | 30 (3.1) | 49 (2.9) | 0.052 | 0.819 |
| Mango | 28 (1.1) | 12 (1.2) | 16 (1.0) | 0.454 | 0.501 |
| Cashew nut | 172 (6.5) | 69 (7.1) | 103 (6.2) | 0.896 | 0.344 |
| Pineapple | 22 (0.8) | 11 (1.1) | 11 (0.7) | 1.675 | 0.196 |
| Aspergillus species | 109 (4.1) | 42 (4.3) | 67 (4.0) | 0.155 | 0.694 |
| Ragweed | 28 (1.1) | 12 (1.2) | 16 (1.0) | 0.454 | 0.501 |
| Birch | 96 (3.6) | 35 (3.6) | 61 (3.7) | 0.004 | 0.951 |
Associations between antigen-specific IgE levels and 25(OH)D levels in children aged 1 and 2 years.
| Allergen | Adjusted β coefficient (95% CI) for IgE levels and continuous 25(OH)D levels | P value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) 25(OH)D<75nmol/L compared with the reference group (≥75nmol/L) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermatophagoides farinae | −0.037 (−0.085, 0.011) | 0.339 | 1.121 (0.810, 1.553) | 0.491 |
| Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus | 0.006 (0.002, 0.011) | 0.003 | 0.588 (0.334, 1.034) | 0.065 |
| Mulberry | −0.003 (−0.009, 0.002) | 0.223 | 1.625 (0.851, 3.102) | 0.141 |
| Cat | 0.053 (−0.003, 0.108) | 0.063 | 0.869 (0.727, 1.039) | 0.123 |
| Dog | 0.015 (0.009, 0.020) | 0.001 | 0726 (0.565, 0.933) | 0.012 |
| Cockroach | 0.001 (−0.002, 0.005) | 0.411 | 0.777 (0.414, 1.429) | 0.433 |
| Amaranth | −0.047 (−0.115, 0.020) | 0.170 | 1.033 (0.749, 1.423) | 0.844 |
| Egg | 0.028 (−0.002, 0.059) | 0.068 | 0.820 (0.641, 1.049) | 0.114 |
| Milk | 0.033 (0.013, 0.053) | 0.001 | 0.568 (0.294, 1.098) | 0.093 |
| Shrimp | 0.001 (−0.022, 0.024) | 0.939 | 0.951 (0.771, 1.173) | 0.639 |
| Beef | 0.003 (0.000, 0.005) | 0.028 | 0.755 (0.298, 1.916) | 0.554 |
| Shellfish | 0.002 (−0.004, 0.004) | 0.884 | 0.834 (0.131, 5.311) | 0.848 |
| Crab | 0.011 (−0.047, 0.068) | 0.713 | 0761 (0.470, 1.233) | 0.268 |
| Mango | −0.002 (−0.004, 0.001) | 0.171 | 1.368 (0.639, 2.931) | 0.420 |
| Cashew nut | −0.017 (−0.061, 0.027) | 0.456 | 1.012 (0.729, 1.405) | 0.943 |
| Pineapple | −0.001 (−0.003, 0.001) | 0.414 | 1.584 (0.676, 3.712) | 0.290 |
| Aspergillus species | 0.008 (−0.007, 0.023) | 0.312 | 0.999 (0.666, 1.499) | 0.997 |
| Ragweed | 0.002 (−0.007, 0.011) | 0.646 | 1.239 (0.577, 2.663) | 0.582 |
| Birch | −0.017 (−0.056, 0.022) | 0.389 | 0.941 (0.612, 1.448) | 0.784 |
β coefficient represents an increase in IgE level per 10nmol/L increase in 25(OH)D level.
Adjusted for age, sex, weight, season, and feeding at six months.
The relationship between 25(OH)D levels and allergen sensitization is controversy. This study demonstrated that low serum 25(OH)D level is associated with higher total IgE level in early childhood. However, our study did not permit conclusions regarding associations between lower levels of 25(OH)D and allergic sensitization to various allergens. Similar to our results, Searing et al.14 and Sharief et al.5 showed inadequate level of serum 25(OH)D had higher total IgE levels, supporting a possible link between low 25(OH)D levels and allergic sensitization. As previous reports have revealed,15 25(OH)D was associated with total serum IgE level, but not with sensitization to antigen-specific IgE. The biological mechanisms causing the difference were unclear, speculating that vitamin D was associated with total serum IgE level and specific allergen in a different manner.
The aspect of the vitamin D immunomodulatory effect plays a role in the regulation of allergen-induced inflammatory pathways.16 Vitamin D and its immunologic functions were related to developing allergic disease. There is a variety of literature describing the biological mechanisms, including the effects on immune cells,17,18 improved handling or prevention of predisposing infections,16,19–21 or decreased inflammatory responses.22 Many studies have investigated the relationship between vitamin D deficiency and allergic diseases.23–25 However, another theory is consistent with several observational studies linking increased 25(OH)D levels with higher IgE levels and risk of allergic disease, as studied by Back et al.26 and Kang et al.27 The reasons for these conflicting results regarding the relationship between vitamin D and allergies might be influenced by different ethnicity and methods of determining allergy. The association between allergic sensitization and vitamin D deficiency might be influenced by individual genetic polymorphism.28 Moreover, most of the studies were conducted in Western populations with a lack of studies in Asian populations. Our findings help to add information on the relationship between serum 25(OH)D levels and allergic sensitization in Chinese children. However, fewer significant associations were observed between 25(OH)D levels and allergen-specific IgEs (such as protective associations with dog allergens and milk allergens). These results were in contrast to hypotheses suggesting observed inverse associations between vitamin D deficiency and allergic sensitizations. The possible mechanisms why such associations were seen remains unclear. Vitamin D deficiency in children was more likely to occur when they spent much time indoors. If these children were living with a dog in the home, it might influence the risk of allergic sensitization to dog. Higher 25(OH)D level was associated with milk allergens, which might be a concomitant exposure to formula feeding with fortified vitamin D. Previous studies have determined that formula feeding was associated with an increased risk of milk allergy in children.29
The study had several potential limitations. First, the subjects were recruited from a single-center and the sample is not representative of the general population. Second, the information were mainly collected from medical records, and that this may limit to analyze some important potential confounders such as vitamin D supplement, outdoor activities, and keeping pets. Therefore, the associations between vitamin D levels and allergic sensitizations might be underestimated. We also lacked information on maternal vitamin D status, which could influence total or specific IgE concentration in early children. Future studies should examine the impact of maternal vitamin D concentration during pregnancy on IgE concentration in children. Furthermore, owing to the cross-sectional nature of the study, we are unable to draw inferences regarding the causality between the observed IgE level differences and vitamin D.
ConclusionsIn conclusion, there was an inverse relationship between serum 25(OH)D and total IgE level in early childhood. However, there is a lack of evidence to support associations between low 25(OH)D levels and allergic sensitization to various allergens.
Conflict of interestNone declared.
Consent for publicationAll the authors have approved the manuscript.
Funding sourceThis work was supported by the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China [A2018255] and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Women and Children Hospital [YN2017G11]. The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.