INTRODUCTION
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) have proved to be very effective in the treatment of asthma (1). It is well accepted that the inhaled administration of steroids is efficacious and has fewer side effects than the systemic use. Higher doses of ICS are associated with systemic effects such as a decrease in morning cortisol (2), the biochemical markers of bone formation (3, 4) and increase indices of bone resorption (5).
Fluticasone propionate (FP) is a new ICS with a higher topical antiinflammatory effect. In clinical studies the systemic potency ratio for FP: budesonide (BUD) is ranged from 1.7 to 2.9 (6, 7). In healthy volunteers, it has been shown that both BUD and FP may provoke a short-term reduction in bone resorption (8).
The aim of this study was to compare the effects of FP 400 μg/daily and BUD 800 μg/daily as a pressurized metered dose inhaler (pMDI) for 6 months on clinical indices determined by FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in one second), diurnal variation of PEFR (peak expiratory flow rate) and by PC20 (provocative concentration of histamine causing 20 % fall in FEV1) and on the markers of bone metabolism, calcium, parathyroid hormone and cortisol in adult patients with asthma.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Patients
A total of 20 nonsmoking subjects (6 males) aged 24 to 55 years (mean, 40.6 ± 2.0) entered the study. The patients were selected on the basis of symptoms and lung function parameters compatible with the diagnosis of asthma according to the American Thoracic Society (9). All women were premenopausal. No patient had any other pulmonary disease or serious concomitant disease. Patients had been receiving regular treatment with FP or BDP for an average of 15.2 ± 5.1 months (range, 0 to 60 months).
No patient had a history of chronic systemic steroid use (defined as any dose taken for more than 1 month continuously) more than 4 booster courses of systemic steroids in the past, or in systemic steroid use in the previous 6 months. All subjects gave informed consent for entering to the study. Patients were not receiving drugs affecting bone metabolism, or having concomitant bone disease.
Protocol
After a two-week run-in period 10 patients were given 400 μg/daily FP and 10 patients 800 μg/daily BUD by pressurized metered dose inhaler (pMDI) divided by two doses. They used salbutamol 100 μg pMDI as rescue medication. Patients were instructed how to use their pMDI correctly. Three patients were given long acting β2 agonist to control the symptoms. No other pulmonary medication was allowed.
During run in period patients were recorded their peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) in the morning (7:00 to 8:00 AM) and in the evening (7:00 to 8:00 PM) using a mini wright peak flow meter, preferably not within 4 hours after rescue bronchodilator use. On each occasion they made three readings and entered the highest one on a diary card. The diary cards were filled in during the run-in period and 15 day before the end of treatment period of 6 months and during these periods symptom scores of patients were determined using American Thoracic Society shortness of breath scale (10).
Patients were followed up monthly. Three measurements of FEV1 were made and the best one was recorded. FEV1 measurements were made with dry-bellows spirometry (Model S; Vitalograph, Ltd. Buckingham, UK).
Histamine challenge
Bronchial reactivity to histamine was measured in accordance with a method described by Cockroft and coworkers (11) using a Pari bronchoprovocateur. Histamine dihydrochloride was inhaled in doubling concentrations from 0.03 to 8 mg/ml. The results were expressed as PC20 histamine, which was obtained from the log dose-response curve. All challenge tests and FEV1 measurements were done between 8:30-10:30 AM to avoid the diurnal effects.
Laboratory measurements
Venous blood samples on the mornings of the first and last visits from patients by antecubital venipuncture and morning urine samples were collected at the same time. Blood samples were centrifuged at 4 °C, 2,500 rpm, then serum and urine samples were stored at -20 °C until assayed. The samples were thawed just before the assay. Total alkaline phosphatase activity and total calcium, phosphate levels in sera and creatinin levels in urine were measured by BM- Hitachi 911 automated analyser using its original kits.
Bone formation markers, namely bone isoenzyme of alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcine and collagen type I c-terminal propeptide levels were measured commercially available ELISA kits (Metra Biosystems, Inc. California, USA). Bone resorption marker, deoxypyridinoline (Dpd) concentrations in urine samples were analysed by a competitive enzyme immunoassay (Pyrilinks-DTM Kit; Metra Biosystems, lnc. California, USA).
Urinary Dpd and calcium levels were corrected by the creatinin concentration of the urine sample and expressed as a ratio nMDpd/mM creatinin and mg/dl Ca/mg/dl Cr respectively.
PTH and cortisol levels were determined with IMMULITE PTH and IMMULITE cortisol chemiluminescent enzyme immunometric assay for use with the IMMULITE automated analyser (Immulite, Diagnostic Products Corporation, Los Angeles, California, USA).
Statistical analysis
The first and second measurements were compared between the FP and BUD treatment groups. Wilcoxon signed rank test or the Mann Whitney-U tests were used for analysis when appropriate; p values less than 0,05 were considered as significant. Results are reported as means ± SEM. The personal computer program SPSS-WlN was used for all calculations.
RESULTS
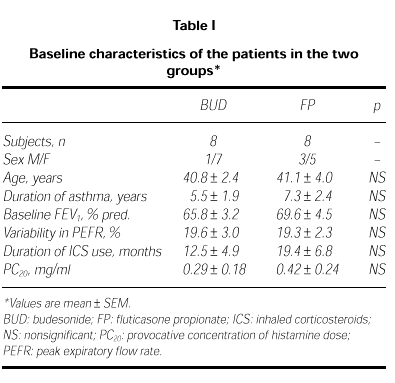
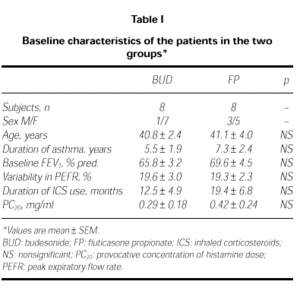
Two patients from FP group and 2 from BUD group were discharged from the study because of uncompliance in three and acute attack in one. The remaining sixteen patients completed the study. Their characteristics are summarized in Table I. The baseline characteristics of the two groups were not different (ie; age, variability of PEFR, FEV1 and PC20 valves; p > 0.05).
Clinical effects
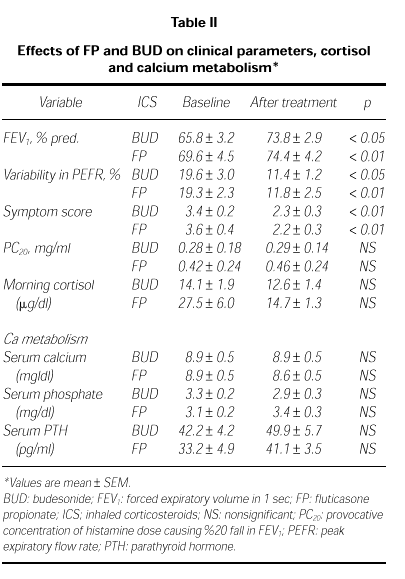
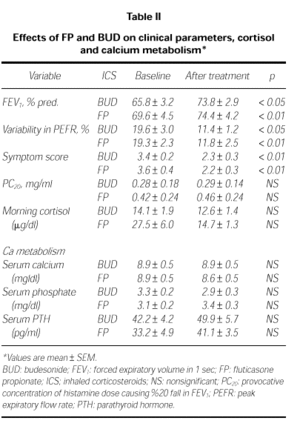
Clinical parameters in both group are before and after the treatment in Table II. Mean values of FEV1 were increased significantly in both treatment groups. In BUD group, FEV1 was increased from 65.8 ± 3.2 % to 73.8 ± 2.9 %, p < 0.05; in FP group, from 69.6 ± 4.5 % to 74.4 ± 4.2 %, p < 0.01. The diurnal variation in PEFR decreased significantly in both treatment groups, from 19.3 ± 2.3 % to 11.8 ± 2.5 % in FP group (p < 0.01) and from 19.6 ± 3.0 % to 11.4 ± 1.2 % (p < 0.05) in BUD group. However mean PC20 values changed from 0.28 ± 0.14 mg/ml to 0.29 ± 0.18 mg/ml after BUD (p > 0.05) and from 0.42 ± 0.24 mg/ml to 0.46 ± 0.24 mg/ml after FP (p = 0.06). There were no significant differences between PC20 values before and after the treatment of both drugs.
Adrenal function
The mean values of morning cortisol changed from 14.1 ± 1.9 μg/dl to 12.6 ± 1.4 μg/dl after BUD (p > 0.05) and from 27.5 ± 6.0 to 14.7 ± 1.3 μg/dl after FP (p > 0.05). There were no significant differences in both of treatment groups (Table II).
Effects on calcium and phosphate metabolism
There were no differences in serum Ca, P and PTH levels of both group before and after the treatment (p > 0.05; Table II).
Bone formation
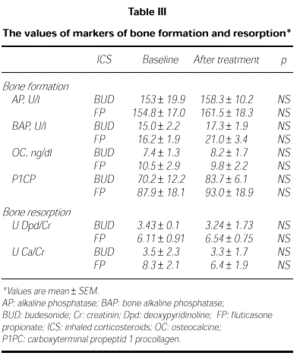
Markers of bone formation AP, BAP, OC, and P1CP did not changed after FP and BUD (p > 0.05; Table III). There were no differences between baseline and posttreatment values of these markers in FP and BUD group (p > 0.05).
Bone resorption
Markers of bone resorption urinary Dpd/Cr and Ca/Cr did not change after both of the treatments (Table III). There were differences between the baseline and posttreatment values of these markers in the groups of FP and BUD (p > 0.05).
DISCUSSION
The present study shows that BUD 800 μg/daily and FP 400 μg/daily by metered dose inhaler for 6 months would result in similar clinical effects without effecting any markers of bone, calcium metabolism and cortisol levels. After 6 months treatment the diurnal variation of PEFR and FEV1 were improved significantly in both BUD and FP group. But the improvement of these clinical markers more prominent in FP. Our findings are consistent with the previous clinical studies that reveal FP results in a similar antiasthma effect at half the dose of BDP (3, 12) or BUD (13).
Although there was a slight increase in the mean PC20 values in the FP group, there was no statistically significant improvement in bronchial hyperreactivity after the both treatment groups. That unchangement in PC20 values after ICS has been shown previously with improvement in respiratory functions (14, 15). This lack of improvement in PC20 values perhaps resulted from our small number of groups studied.
All mean morning cortisol levels for both ICS remained unchanged within normal upper and lower limits. No differences were found between both treatments in morning cortisol. Although the single morning measurements of serum cortisol is not a sensitive method of detecting changes in HPA axis, in the clinical studies it has been widely used to measure the effects of ICS on HPA axis. And as a marker of adrenal suppression, morning cortisol has been shown to be unchanged in some studies as in our study (3, 12).
Osteoporosis is a well known side effect of systemic steroids which is mainly caused by depression of bone formation. High dosages of ICS may decrease bone formation (4) and increase of bone resorption (5). We measured the effects of 400 μg/daily FP and 800 μg/daily BUD on biochemical markers of bone metabolism. The serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (AP) and bone specific alkaline phosphatase (BAP) are higher at times of high osteoblastic activity. It is rather insensitive measure of acute changes in bone formation. The other marker of bone formation is procollagen type 1 synthesis and mainly produced by osteoblasts. In addition, osteocalcin (OC) is a very sensitive marker of osteoblast activity. We found no significant change in serum markers of bone formation AP, BAP, P1CP and OC in either group.
After 12 hr fast, urinary calcium excretion is a measure of the calcium coming mainly from bone. CS inhibit the intestinal absorption of Ca, and P, and they may increase urinary Ca excretion and decrease in serum Ca which may cause secondary hyperparathyroidism, reflected in an increased serum PTH. We found no significant change in serum or urinary calcium, serum P and PTH levels in both FP and BUD.
Desoxypyridinoline (Dpd) a marker of bone resorption, is released by the osteoclast during bone resorption. There were not significant differences in serum Dpd levels after both FP and BUD in our patients.
There are several studies in which BUD and FP have shown to affect the markers of bone metabolism (8, 16). But this effect was said to be dose dependent (16). However, there has not been any agreement about which bone markers effected by the ICS. 800 μg/daily BUD has significantly reduced P1CP (16) suggesting a reduction in bone formation but in another study BUD and FP showed a short term reduction in bone resorption (8). The net effect of bone formation and resorption is clinically important. If, for instance, formation and resorption decrease to the same extent, the changes may not be important, since the net effect may be zero. In contrast to these findings BUD 800 μg/daily for 2.5 yr did not effect bone formation and resorption in patients with asthma (17). And in long term studies FP, at half dose of BDP, results in a similar antiasthma effect but a more safety profile with respect to bone metabolism (3, 12). Only a few studies have directly compared the effects of inhaled FP and BUD on bone markers. In two studies, both BUD and FP did not affect the baseline markers of bone metabolism as in our study (18, 19).
Certainly a lot of factors may affect the results of the study. For example, OC and P1CP exhibits diurnal variation. In the present study, all samples were immediately determined or frozen and processed at once to exclude any influence of laboratory handling. To avoid diurnal effects, samples were taken at the same moment of the day and urinary samples were taken after an overnight fast and corrected for creatinin. We couldn't used a placebo group to compare because of ethical limitations, cause in a view of some previous studies supporting delayed onset of treatment with ICS cause reduced improvement of lung function and irreversible remodeling of the airways due to chronic airway limitation and ungoing inflammation (20, 21).
Another point of view to our study is that although our patients did not use a spacer device to inhale their ICS, there was no change in bone markers of the patients. It is also important because, the use of spacer device was said to increase the proportion of inhaled aerosol that is deposited in the lungs and to reduce the amount of swallowed. Thus, the effect on bone metabolism is less than when ICS was taken directly (22).
In addition due to the effects of some other factors on bone turnover, the patients were not different in each group with respect to age, healthy premenopausal nonsmoking status.
We conclude that chronic treatment with FP 400 μg/daily and BUD 800 μg/daily results in a similar antiasthma effect without effecting bone metabolism. It may be of potential interest in the long term with higher doses.