The evacuant solution (ES) is a drug that has been used to clean the colon. The most common described side effects when using this drug are abdominal symptoms; skin rash is rare.
We report on two patients who presented urticaria and angioedem after the intake of an evacuant solution to make a rectoscopy.
We performed allergy studies: skin prick tests with common inhalants, pure ES and the components (polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000), KCI, NaCO3, NaPO3, NaSO3, NaCI, neohesperydine, potasic acesulfam and orange flavouring), intradermic test, total serum IgE and single-blind placebo oral challenge with ES and the components.
We report on the first cases of immediate allergy reactions (type1) caused by oral intake of a drug containing PEG 4000 which were demonstrated by intradermic tests and oral challenge.
The evacuant solution is a drug that has been used to clean the colon, like an enema to study some colonic lesions such as polyps, neoplasm or arteriovenus malformations and before practising surgery to this organ.
The most commonly described side effects when using this drug are: bloating, nausea, abdominal or stomach cramps, anus irritation or vomiting. Skin rash is rare.
We report on two patients who presented urticaria and angioedem after the intake of an evacuant solution to make a rectoscopy.
FIRST CASEA 36 year-old man referred to our Allergology Department for an episode of urticaria and lip swelling after the intake of an evacuant solution (Bohm®)
The reaction appeared half an hour afther the drug consumption and he had not taken other drugs that day or on previous days. He was not atopic and he needed study of spastic colon.
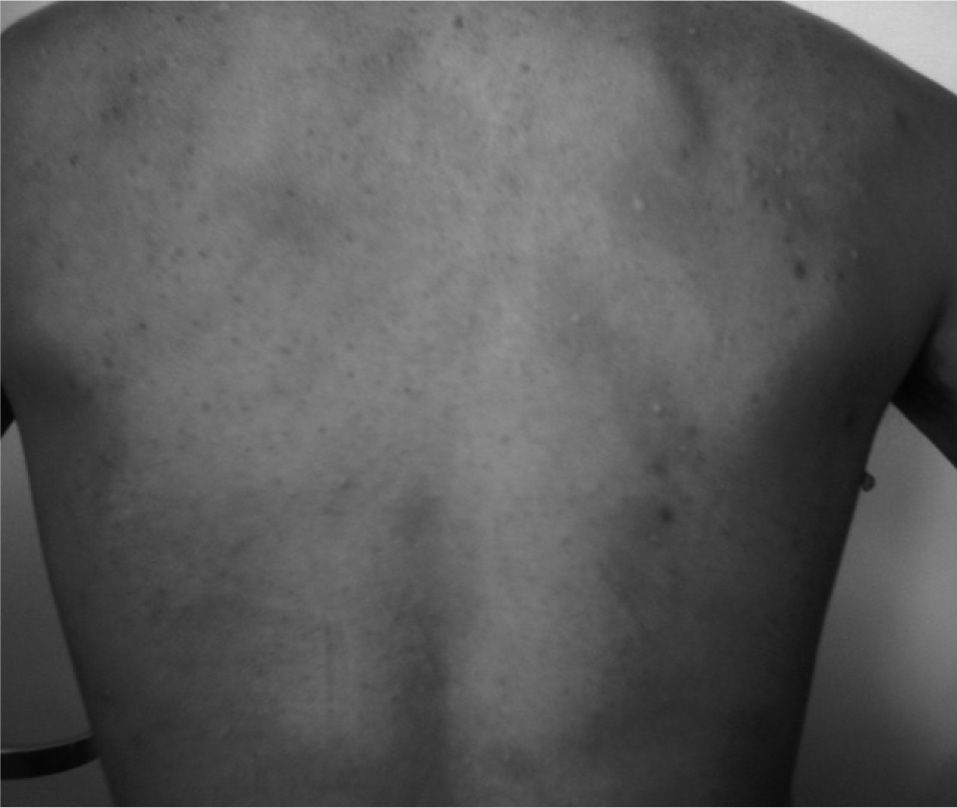
We performed allergy studies: skin prick tests with common inhalants were negative; total serum IgE was 98 kU/l. We prepared 250ml of evacuant solution (ES) following the instructions of Bohm laboratories: skin prick test with pure solution was negative, but single-blind placebo oral challenge was positive with similar symptoms to the reaction that the patient suffered (Fig. 1).
Subsequently, we contacted Bohm laboratories in Spain and they furnished us the components of ES: polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG 4000), KCI, NaCO3, NaPO3, NaSO3, NaCI, neohesperydine, potasic acesulfam and orange flavouring.
Skin prick test were performed with: ES components and saline solution; ES and PBS; and ES components and human seric albumin to 1/10 concentration for each one. The results were negative, but single-blind placebo oral challenge with increasing doses of each component of ES on consecutive days was positive 5 minutes after the intake of 25cc of PEG 4000.
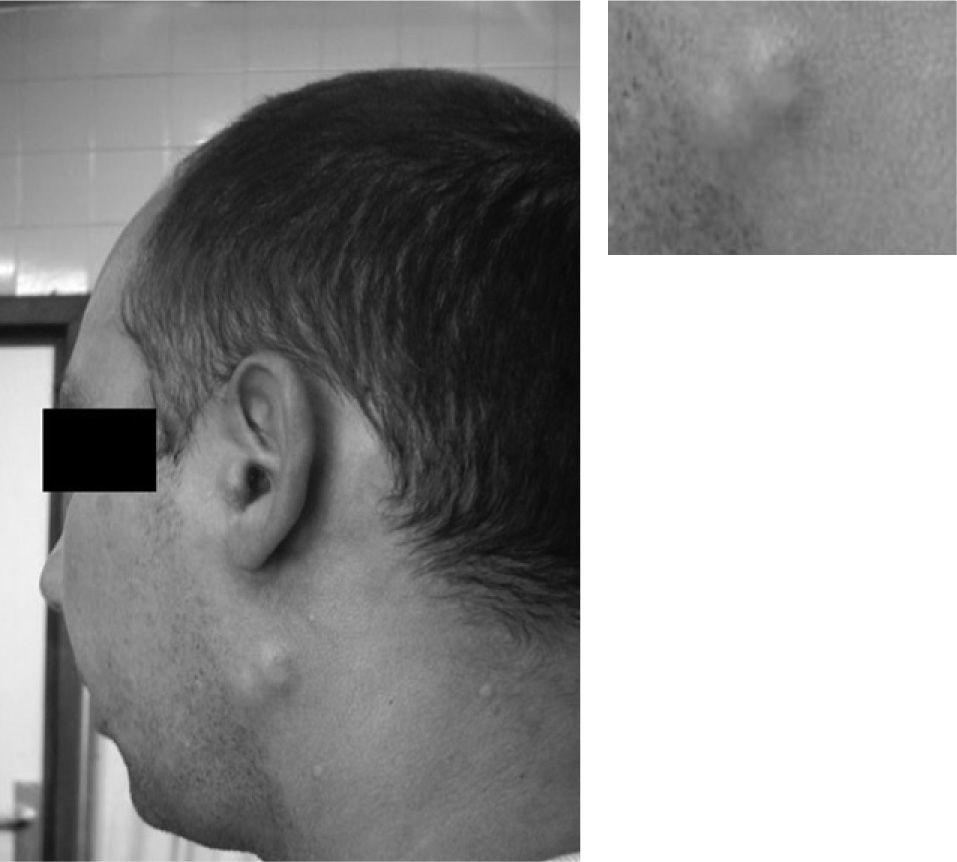
We wanted to know the immunologic mechanism of the reaction so we performed an intradermic test with PEG 4000 which was immediately positive to the 1/10 concentration (Fig. 2). The patient presented general urticaria with hives and nodules, rhinitis, nauseas and vomiting; and he needed treatment.
SECOND CASEA non-atopic 44 year-old man referred to our Allergology Department for an episode of urticaria and angioedem one minute after the intake of ES, as above.
We performed similar allergy studies: skin prick test with common inhalants and ES and its components were negative, but single-blind placebo oral challenge with ES and PEG 4000 were positive; intradermic test was positive to the 1/10000 concentration of PEG 4000.
Despite the symptoms being “type I immunologic mechanism”, we did not know the mechanism which made the reaction so serious. We performed patch tests with ES and its components and all of them were negative.
Control tests were performed on ten patients (five atopic and five non-atopic) and the results were negative.
DISCUSSIONPolyethylene glycol 4000 is a hydrosoluble base used as a carrier in a lot of topical drugs, in creams and in body oils as an emulsion1 (Table I).
It is a polymer of ethylen glycol molecules [H(OCH2 CH) nOH] and its physical and chemical characteristics depend on the number of molecules. PEG slow molecular weight (200–700) are liquids and PEG high molecular weight (1000–7500) are soft or hard solids.
There are no references of other cases of allergic reactions after oral intake of ES or PEG. Side effects with PEG described to date have been nauseas, vomiting, abdominal pain and rectal irritation if taken orally; and skin rash with a topical drug.
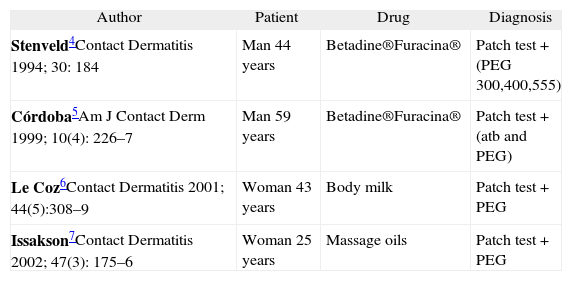
Bohm laboratories have no news of allergy reactions with ES. PEG can be the cause of eczemas or contact dermatitis as some articles about patch tests have demonstrated 2–7(Table II).
Contact dermatitis with PEG
| Author | Patient | Drug | Diagnosis |
| Stenveld4Contact Dermatitis 1994; 30: 184 | Man 44 years | Betadine®Furacina® | Patch test + (PEG 300,400,555) |
| Córdoba5Am J Contact Derm 1999; 10(4): 226–7 | Man 59 years | Betadine®Furacina® | Patch test + (atb and PEG) |
| Le Coz6Contact Dermatitis 2001; 44(5):308–9 | Woman 43 years | Body milk | Patch test + PEG |
| Issakson7Contact Dermatitis 2002; 47(3): 175–6 | Woman 25 years | Massage oils | Patch test + PEG |
We report on the first cases of immediate allergy reactions (type1) caused by the oral intake of a drug containing PEG 4000 which were demonstrated by intradermic tests and oral challenge.
This report has been translated by Aurea Moreno Pastor.