Wheezing affects children's quality of life, and is related with asthma in childhood. Although prevalence of wheezing has been previously studied in several countries, there is no reference of worldwide prevalence in infants. The aim of this meta-analysis is to estimate the prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing in infants aged up to two years, and compare the prevalence across world regions.
MethodsLiterature search was conducted in MEDLINE and SCOPUS databases, looking for observational studies published up to June 2016, including as keywords “prevalence” or “epidemiology” combined with “wheeze”, “wheezing” or “asthma symptoms” and “infant” or “preschool”. Fast*Pro software and random effects Bayesian model were used. Heterogeneity was estimated using I2 statistic, and sensitivity analyses were performed.
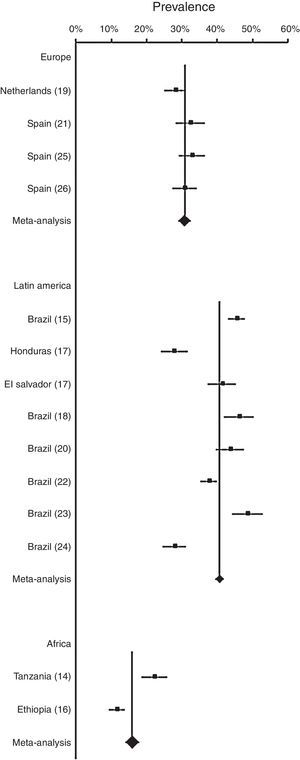
ResultsWe identified 109 studies after duplicates were removed. After exclusions, 14 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing were 36.06% (95% CI 35.17–36.96), and 17.41% (95% CI 16.74–18.09), respectively. In European countries, prevalence of wheezing was 30.68% (95% CI 28.97–32.45), and 12.35% (95% CI 11.27–13.47) for recurrent wheezing. Prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing in Latin America were higher, 40.55% (95% CI 39.40–41.71), and 19.27% (95% CI 18.44–20.11), respectively. In Africa, prevalence of wheezing was 15.97% (95% CI 14.05–18.00). Low or no heterogeneity was found in all cases.
ConclusionsMore than one third of infants suffer from wheezing and almost one fifth from recurrent wheezing, being these illnesses especially prevalent in Latin American countries, pointing out an important public health problem.
Wheezing in infants not only affects children's quality of life,1 but is related to the development of asthma childhood.2 Several risk factors, such as viral respiratory infections,3 prenatal and postnatal tobacco smoke exposure,4 familiar history of asthma,5 or pollution6 have been previously identified.
Prevalence of asthma and wheezing in schoolchildren and adolescents has been studied in the past. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) found highest prevalence of wheezing in children in United Kingdom, Oceania and Latin American countries.7 In Phase III of the same study, increasing trends were found in countries which showed lower prevalence in Phase I, while in the Oceanian countries decreasing trends were found.8
More recently, the International Study of Wheezing in Infants (Estudio Internacional de Sibilancias en Lactantes in Spanish, or EISL), a multicentre study in European and Latin American countries, was conducted to determine the prevalence, severity and risk factors for wheezing in infants.9
However, no previous studies about the worldwide prevalence of wheezing in infants have been conducted. Therefore, the aim of this meta-analysis is to estimate the prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing in infants aged up to two years, and compare the prevalence across different world regions.
Materials and methodsThis meta-analysis has been conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement,10 and its protocol has been registered in PROSPERO (reference CRD42016039446).
Search strategy and selection criteriaThe literature search was performed in MEDLINE and SCOPUS databases, looking for observational studies published up to June 2016.
Search terms were “prevalence” or “epidemiology” (title), combined with “wheeze”, wheezing” or “asthma symptoms” (title), and “infant” or “preschool” (topic). The search terms were combined with Boolean search function “and”. No language filters were used.
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they met the following criteria: (1) Original community-based studies; (2) Participants aged up to two years; (3) Wheezing and/or recurrent wheezing were defined; (4) Provided original data on the prevalence of wheezing and/or recurrent wheezing.
The search was complemented by reviewing the references of the selected articles to identify additional studies. In those cases that we could not have technical access, we requested the article through the Public University of Navarre library to other institutions. Two researchers (I.A.A. and H.N.) conducted the search and evaluate the studies, resolving the discrepancies by discussion.
After excluding duplicates, 109 articles were found. Reviews, pool studies, studies which did not provide wheezing cases, or its study population was older than two years were excluded. Abstracts and non-published studies were also excluded.
Studies quality was assessed using the Quality Assessment Tool for Observational and Cross-Sectional Studies, developed by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI).11 We assigned one point to positive answers, and zero points to negative answers, calculating the percentage. Low, medium and high quality studies were those which scored less than 50%, between 50% and 75%, and more than 75%, respectively. Low quality studies were removed from the analysis.
Data extractionTwo researchers (I.A.A. and H.N.) conducted the data extraction, resolving the differences by consulting another researcher (F.G.G.). The following data were recorded from each article: (1) Author's name and year of publication; (2) Country where the study was conducted; (3) Definition of wheezing and/or recurrent wheezing; (4) Age range; (5) Number of participants in the study; (6) Wheezing and/or recurrent wheezing cases.
Quantitative analysis (meta-analysis)Separate meta-analyses were conducted for wheezing and recurrent wheezing in infants. Besides, we conducted additional meta-analyses for world regions (Europe, Latin America and Africa). Fast*Pro software was used to make the calculations. We used a random effects Bayesian model, showing 95% credibility intervals (95% CI).
In Bayesian analysis, credibility intervals are different from confidence intervals of the frequentist statistics. 95% credible interval means that the probability that the real value is in the range of the 95%, according to our initial belief and the observed data. However, a 95% confidence interval indicates that in many repeated samples, 95% of the intervals will show a true value.
Sensitivity analyses were performed, replicating the results after excluding studies with the lowest and highest prevalence, to study the robustness of the analysis and the influence of the removed study.
To estimate the heterogeneity, I2 statistic was used, estimating the percentage of total variability between studies explained by heterogeneity.12
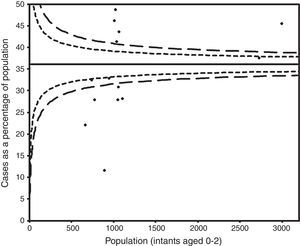
The risk of publication bias was assessed graphically by a funnel plot.
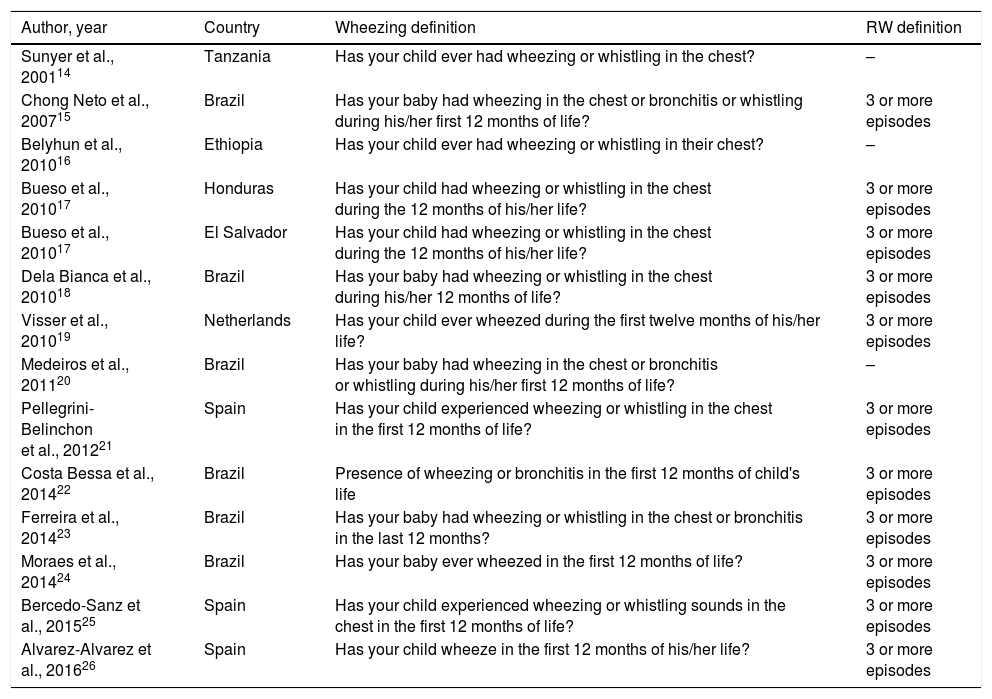
Although no wheezing definition was specified, Dela Bianca et al.,18 Ferreira et al.23 and Moraes et al.24 used the written questionnaire from the EISL study, considering wheezing definitions from this questionnaire.13 Bueso et al.17 provided data from both Honduras and El Salvador EISL studies, which were separately included in this meta-analysis. Recurrent wheezing was defined as three or more episodes of wheezing by all the studies.
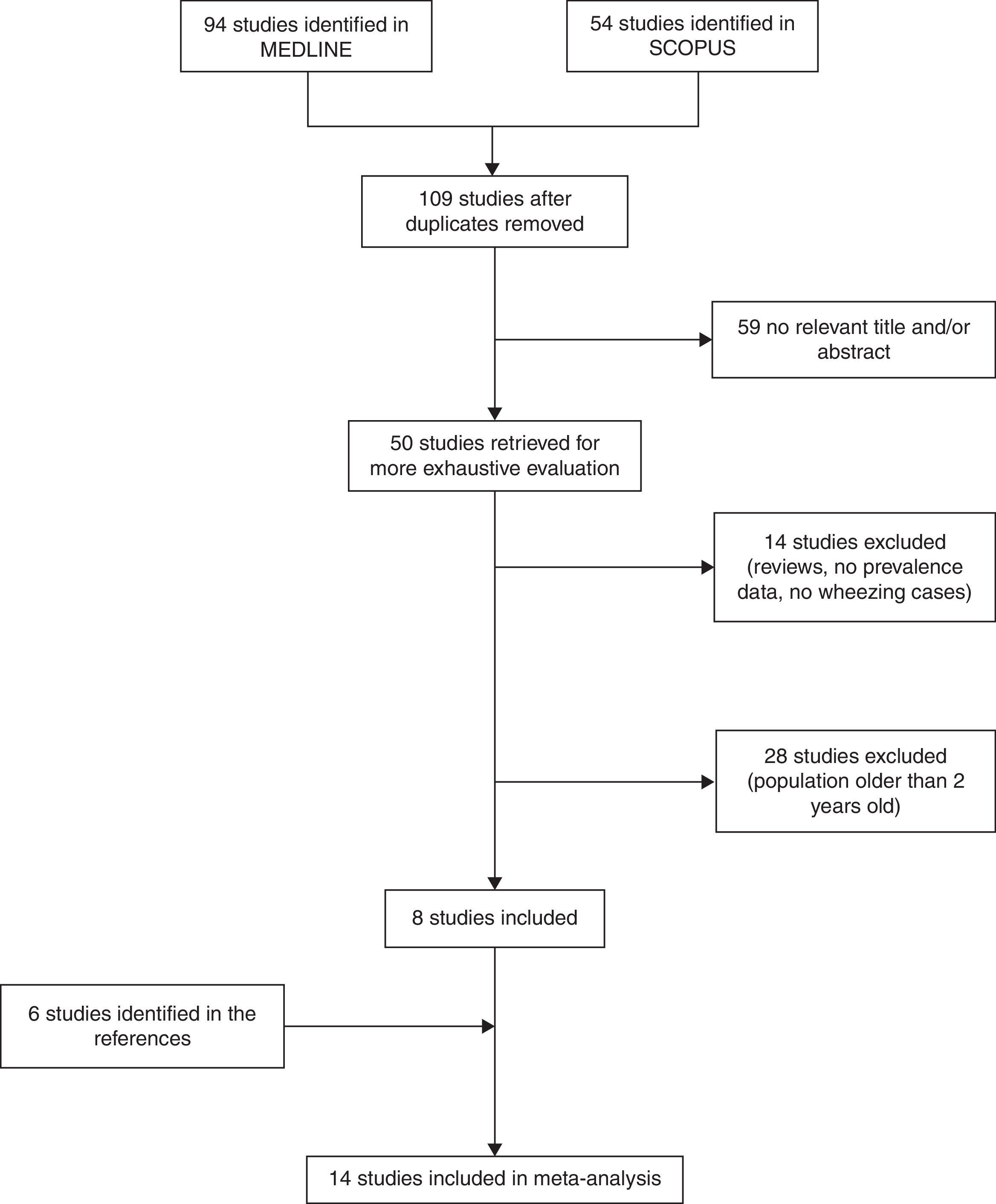
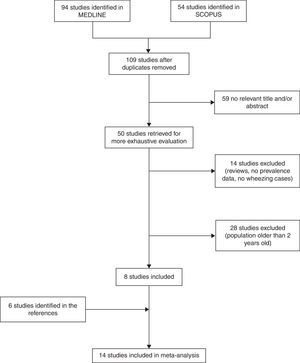
ResultsWe identified 148 studies (94 in MEDLINE and 54 in SCOPUS). After duplicates were removed, we reviewed 109 studies. We excluded 59 studies whose title and/or abstract were not relevant (47 in MEDLINE and 12 in SCOPUS). Of the remaining 50 studies, 14 studies were excluded because they were reviews or pooled studies, studied risk factors for wheezing but did not provide prevalence data, did not define the outcome or provide wheezing cases, and were not community-based studies (14 in MEDLINE), and 28 were excluded because their study population was older than two years old (25 in MEDLINE and 3 in SCOPUS). Finally, eight studies were included.15,16,18–20,22–24
After examining the studies included, we identified and added six studies from the references.14,17,21,25,26 Finally, 14 studies were included in the meta-analysis (Fig. 1).
Of these, 11 defined and provided recurrent wheezing cases, and were included in the meta-analysis of recurrent wheezing.
Study characteristics are shown in Table 1. Studies were conducted in Brazil, Honduras, El Salvador, Spain, Netherlands, Ethiopia and Tanzania. All were cohort studies, population ranged between 673 and 3003 subjects, and their participants’ age ranged between 12 and 24 months.
Characteristics of the studies included in the meta-analysis.
| Author, year | Country | Wheezing definition | RW definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sunyer et al., 200114 | Tanzania | Has your child ever had wheezing or whistling in the chest? | – |
| Chong Neto et al., 200715 | Brazil | Has your baby had wheezing in the chest or bronchitis or whistling during his/her first 12 months of life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Belyhun et al., 201016 | Ethiopia | Has your child ever had wheezing or whistling in their chest? | – |
| Bueso et al., 201017 | Honduras | Has your child had wheezing or whistling in the chest during the 12 months of his/her life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Bueso et al., 201017 | El Salvador | Has your child had wheezing or whistling in the chest during the 12 months of his/her life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Dela Bianca et al., 201018 | Brazil | Has your baby had wheezing or whistling in the chest during his/her 12 months of life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Visser et al., 201019 | Netherlands | Has your child ever wheezed during the first twelve months of his/her life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Medeiros et al., 201120 | Brazil | Has your baby had wheezing in the chest or bronchitis or whistling during his/her first 12 months of life? | – |
| Pellegrini-Belinchon et al., 201221 | Spain | Has your child experienced wheezing or whistling in the chest in the first 12 months of life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Costa Bessa et al., 201422 | Brazil | Presence of wheezing or bronchitis in the first 12 months of child's life | 3 or more episodes |
| Ferreira et al., 201423 | Brazil | Has your baby had wheezing or whistling in the chest or bronchitis in the last 12 months? | 3 or more episodes |
| Moraes et al., 201424 | Brazil | Has your baby ever wheezed in the first 12 months of life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Bercedo-Sanz et al., 201525 | Spain | Has your child experienced wheezing or whistling sounds in the chest in the first 12 months of life? | 3 or more episodes |
| Alvarez-Alvarez et al., 201626 | Spain | Has your child wheeze in the first 12 months of his/her life? | 3 or more episodes |
RW, recurrent wheezing.
Quality assessment showed four studies18,20,21,25 with medium quality, and the rest14–17,19,22–24,26 with high quality. Therefore, no studies were removed from the analysis.
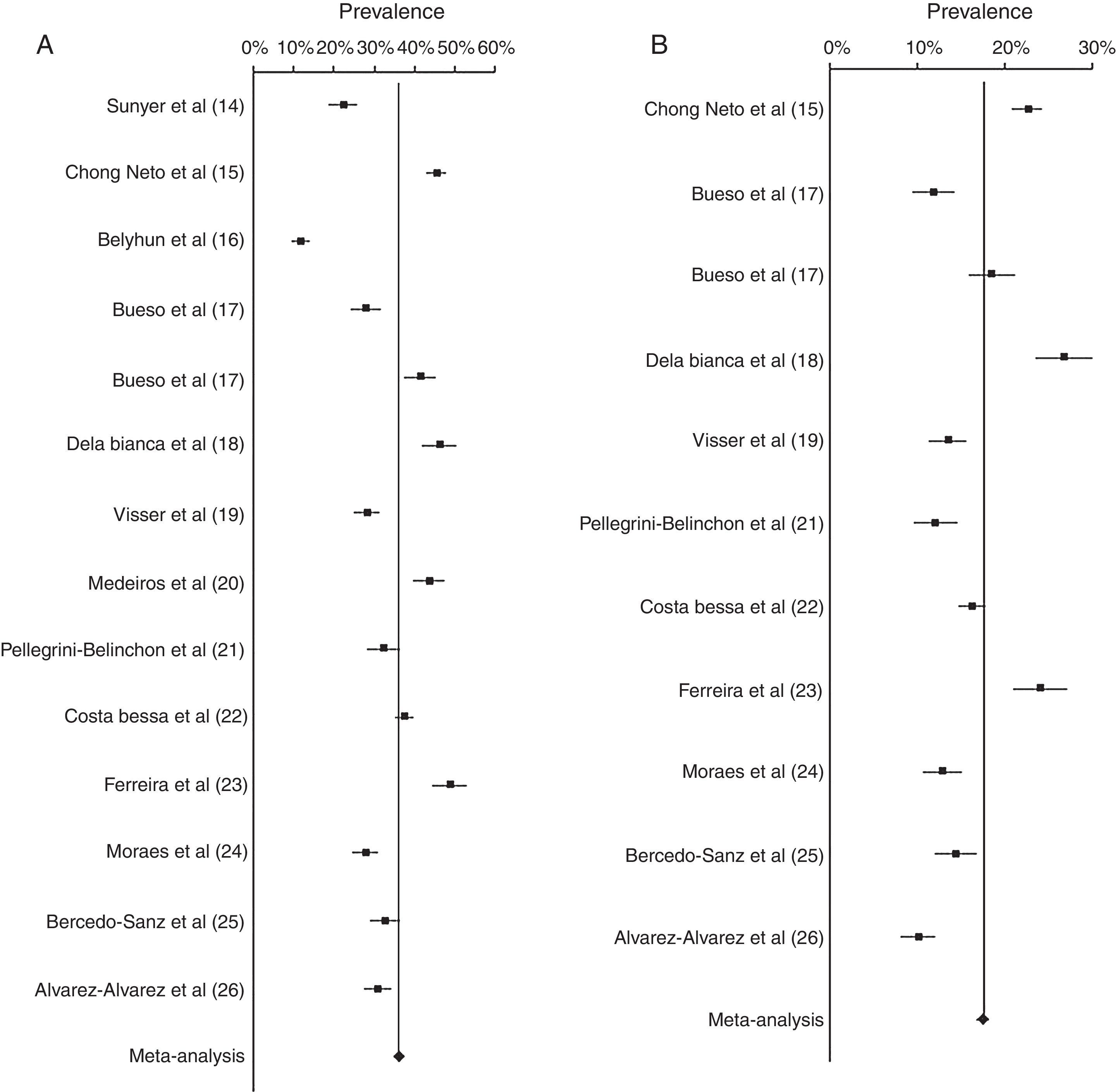
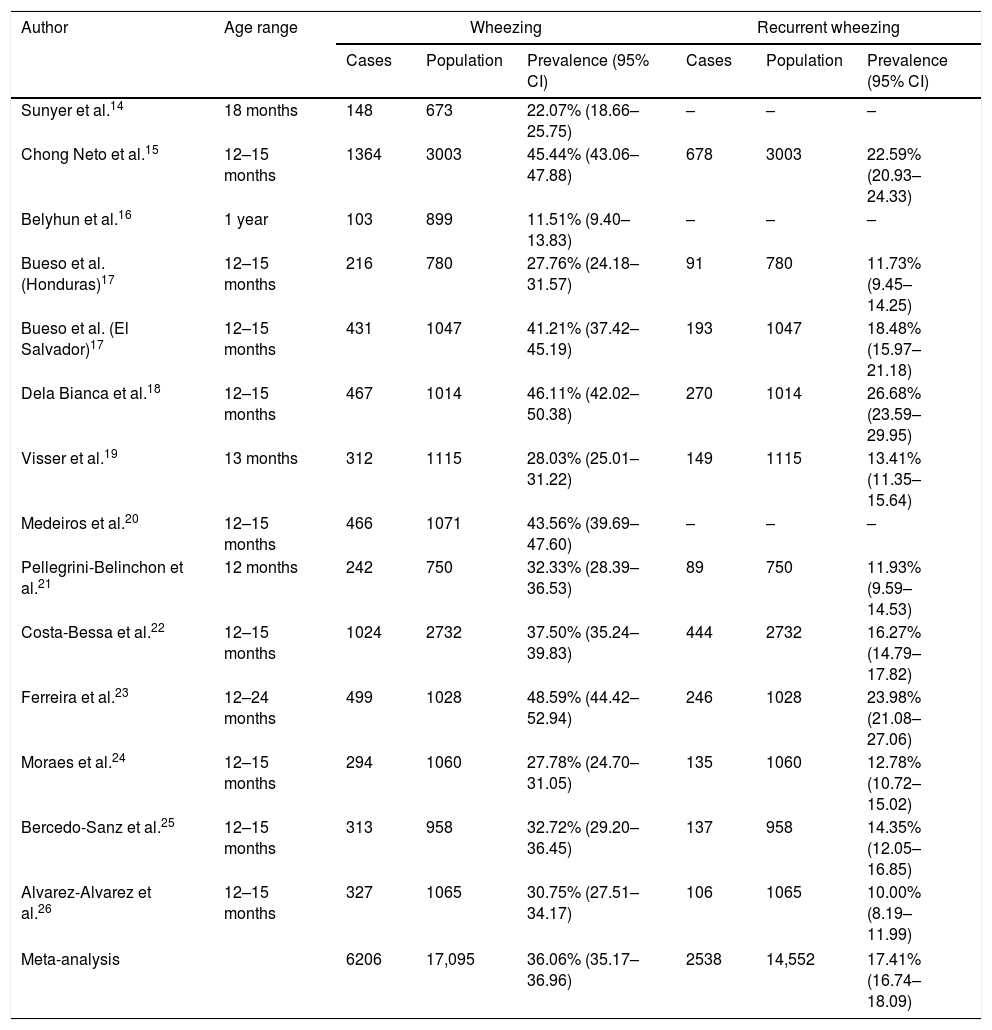
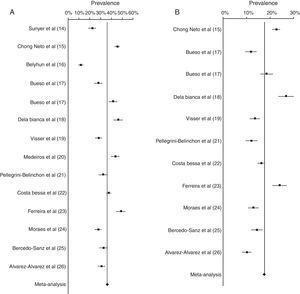
Results of the meta-analysis of wheezing and recurrent wheezing are presented in Table 2 and Fig. 2. The prevalence of wheezing in infants was 36.06% (95% CI 35.17–36.96). No heterogeneity between the studies was found (I2<0). Sensitivity analyses were conducted, removing the Ferreira et al. study,23 finding the prevalence was 35.27% (95% CI 34.36–36.19), with no heterogeneity (I2<0). On the other hand, when the Belyhun et al. study16 was excluded, prevalence was 37.42% (95% CI 36.48–38.36), showing a low heterogeneity (I2=5.98).
Meta-analysis of the prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing in infants.
| Author | Age range | Wheezing | Recurrent wheezing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Population | Prevalence (95% CI) | Cases | Population | Prevalence (95% CI) | ||
| Sunyer et al.14 | 18 months | 148 | 673 | 22.07% (18.66–25.75) | – | – | – |
| Chong Neto et al.15 | 12–15 months | 1364 | 3003 | 45.44% (43.06–47.88) | 678 | 3003 | 22.59% (20.93–24.33) |
| Belyhun et al.16 | 1 year | 103 | 899 | 11.51% (9.40–13.83) | – | – | – |
| Bueso et al. (Honduras)17 | 12–15 months | 216 | 780 | 27.76% (24.18–31.57) | 91 | 780 | 11.73% (9.45–14.25) |
| Bueso et al. (El Salvador)17 | 12–15 months | 431 | 1047 | 41.21% (37.42–45.19) | 193 | 1047 | 18.48% (15.97–21.18) |
| Dela Bianca et al.18 | 12–15 months | 467 | 1014 | 46.11% (42.02–50.38) | 270 | 1014 | 26.68% (23.59–29.95) |
| Visser et al.19 | 13 months | 312 | 1115 | 28.03% (25.01–31.22) | 149 | 1115 | 13.41% (11.35–15.64) |
| Medeiros et al.20 | 12–15 months | 466 | 1071 | 43.56% (39.69–47.60) | – | – | – |
| Pellegrini-Belinchon et al.21 | 12 months | 242 | 750 | 32.33% (28.39–36.53) | 89 | 750 | 11.93% (9.59–14.53) |
| Costa-Bessa et al.22 | 12–15 months | 1024 | 2732 | 37.50% (35.24–39.83) | 444 | 2732 | 16.27% (14.79–17.82) |
| Ferreira et al.23 | 12–24 months | 499 | 1028 | 48.59% (44.42–52.94) | 246 | 1028 | 23.98% (21.08–27.06) |
| Moraes et al.24 | 12–15 months | 294 | 1060 | 27.78% (24.70–31.05) | 135 | 1060 | 12.78% (10.72–15.02) |
| Bercedo-Sanz et al.25 | 12–15 months | 313 | 958 | 32.72% (29.20–36.45) | 137 | 958 | 14.35% (12.05–16.85) |
| Alvarez-Alvarez et al.26 | 12–15 months | 327 | 1065 | 30.75% (27.51–34.17) | 106 | 1065 | 10.00% (8.19–11.99) |
| Meta-analysis | 6206 | 17,095 | 36.06% (35.17–36.96) | 2538 | 14,552 | 17.41% (16.74–18.09) | |
The prevalence of recurrent wheezing was 17.41% (95% CI 16.74–18.09). The estimated heterogeneity was I2=15.81, a low heterogeneity. When sensitivity analyses were conducted, prevalence of recurrent wheezing did not vary substantially. Prevalence when the Dela Bianca et al. study18 was removed from the analysis was 16.72% (95% CI 16.04–17.42), finding low heterogeneity (I2=3.15). When we excluded the Alvarez-Alvarez et al. study,26 prevalence was 18.00% (95% CI 17.29–18.73), also showing a low heterogeneity (I2=18.72).
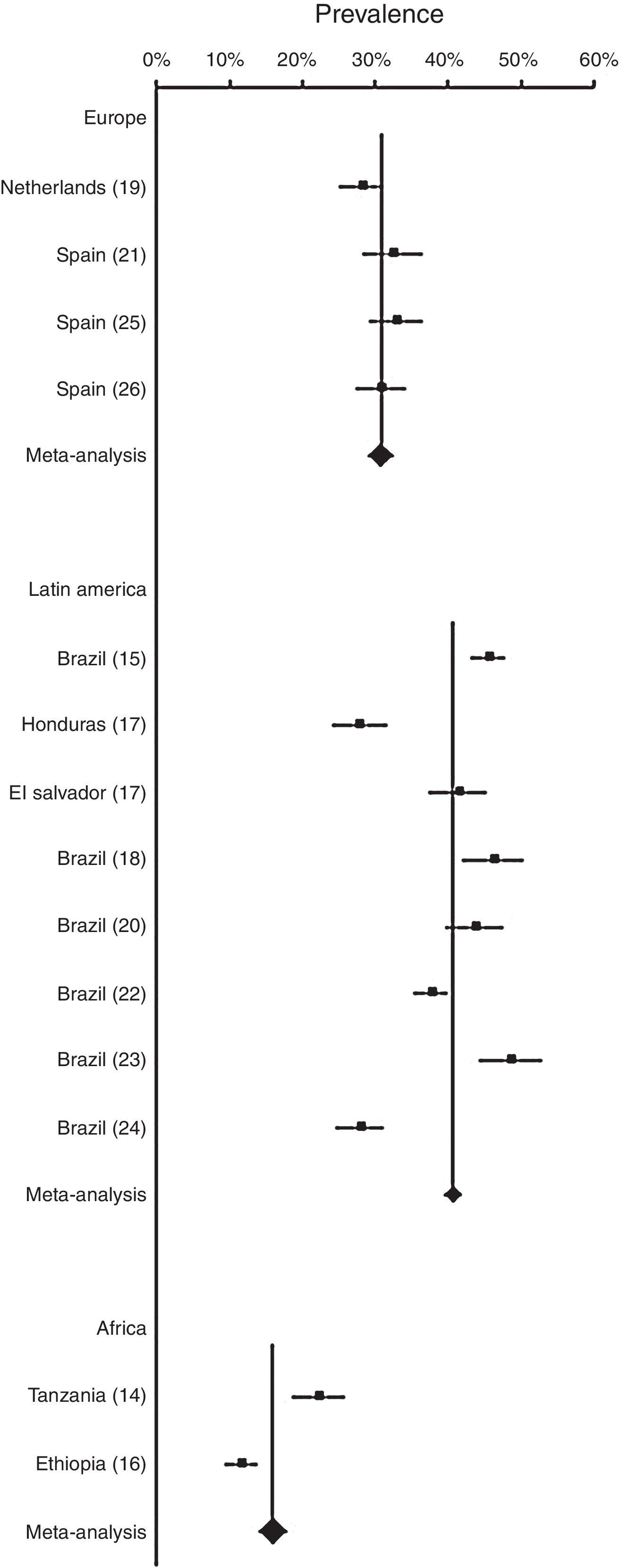
Results of the meta-analyses of prevalence of wheezing across regions (Europe, Latin America and Africa) are shown in Fig. 3. In European countries, prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing were 30.68% (95% CI 28.97–32.45) and 12.35% (95% CI 11.27–13.47), respectively. In both cases, no heterogeneity was revealed (I2<0). In Latin America, prevalence of wheezing, 40.55% (95% CI 39.40–41.71), and recurrent wheezing, 19.27% (95% CI 18.44–20.11), were higher than in Europe, showing a low heterogeneity (I2=7.65, and I2=7.30, respectively). In African countries, prevalence of wheezing in infants was 15.97% (95% CI 14.05–18.00), not evidencing heterogeneity (I2<0).
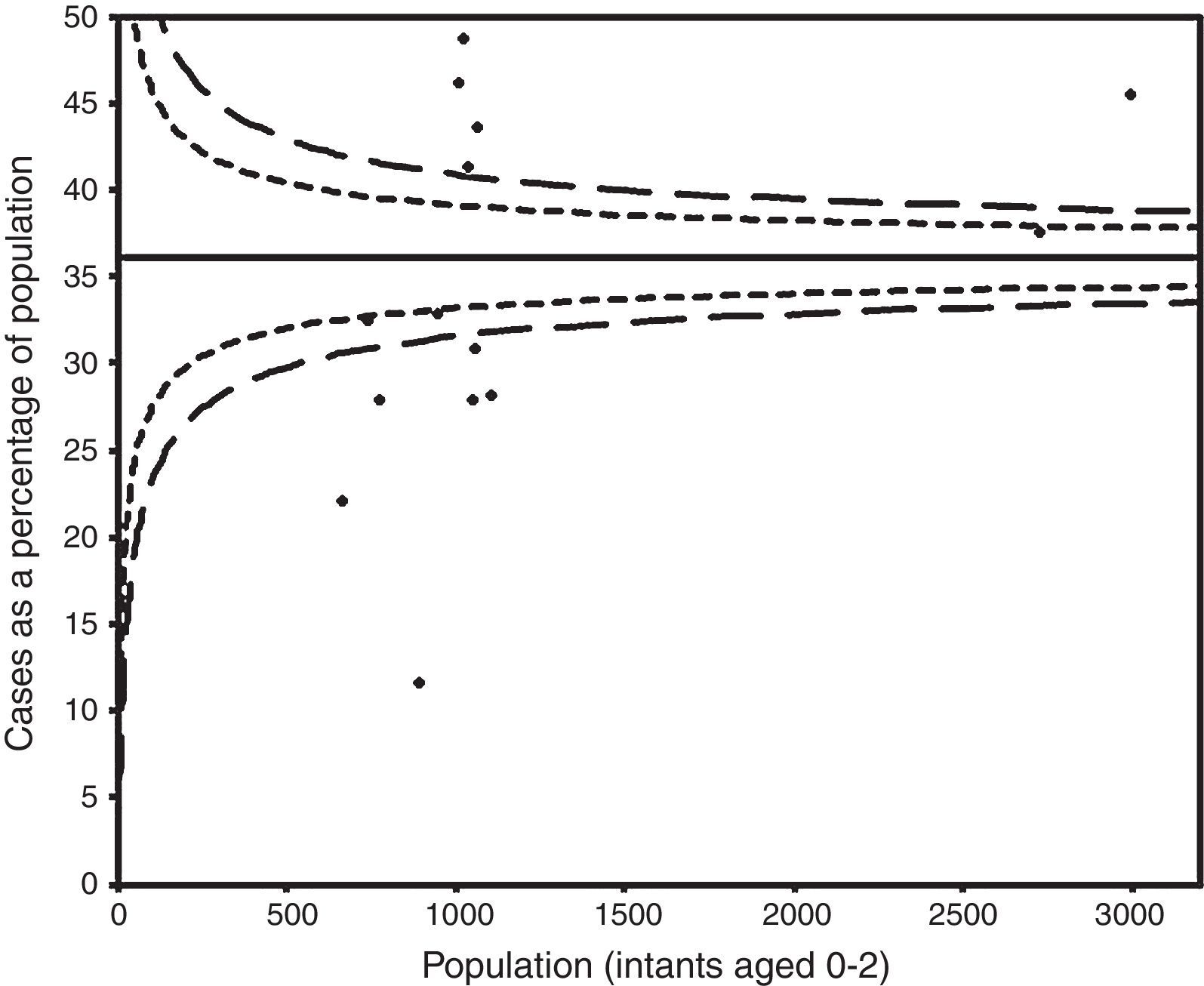
The funnel plot did not indicate publication bias (Fig. 4).
DiscussionThe present meta-analyses evidenced that wheezing in infants is a public health burden, affecting more than one third of infants, with nearly one fifth of infants who are recurrent wheezers, being these illnesses especially prevalent in Latin America. Sensitivity analyses did not substantially change the results when studies were removed, and there was no heterogeneity or was low, thus the meta-analysis seems to be robust.
Previously global studies, as the Phase I and III of the ISAAC study, found a mean prevalence of wheezing in schoolchildren of 11.8% and 11.5%, respectively,7,27 lower than our results. However, the ISAAC study included much more centres than our analysis, and the higher incidence of wheezing in the first three years of life28 could explain our results.
A previous European study found higher prevalence of wheezing, ranging from 29% to 48% in North and South European countries, respectively, in children aged 1–5 years.29 A possible reason to explain the differences might be its different study population and methodology.
In Latin America, more than 40% of infants had wheezing in the first two years of life, and almost 20% were recurrent wheezers. Our results are slightly higher than others from a recent study, which found prevalences of wheezing and recurrent wheezing in the first year of life of 39.9% and 16.6%, respectively.30
Only two African studies were included in the meta-analysis. Prevalence of wheezing in this continent was almost 16%, higher than results from Phase III of ISAAC,27 although the low number of studies included could have led to a wrong estimation.
The analysis showed differences in the prevalence of wheezing and recurrent wheezing across world regions, finding the highest prevalences in Latin America.
Garcia-Marcos et al. found that socioeconomic factors had a major impact in this region.31 Lower parental education32 and factors related with poverty, dirt and infections33 have been also associated with higher prevalence of wheezing in children.
Another explanation to the higher prevalence found in Latin America compared to Europe could be the African ancestry, which has been found as a risk factor for recurrent wheezing.34
According to the World Health Organization, low and middle-income countries in Latin American region showed higher pollution levels than European high-income countries.35 Improvements in air quality are associated with an improved lung-function development,36 and consequently with a lower risk of asthma,37 which might be another possible reason.
Parasitic infections with Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuris trichiura have been described as a risk factor for wheezing in Latin American infants.38 However, findings are controversial, with other studies conducted in Africa which found a reduced risk for the disease,39,40 which might partially explain the differences in the prevalence between these regions.
One of the strengths of this study is its novelty. As far as we know, there is no other meta-analysis which estimates the prevalence of wheezing in infants, providing original results with high-quality scientific evidence. Moreover, because most of the studies included defined the outcome according to the ISAAC or EISL language, the consistency of the definition is high.
Our study also has some limitations. First, there are technical limitations. We could not access other databases, which might have limited our search and findings. Second, it lacks data from more countries. Most Latin American and European data were from Brazil and Spain, respectively, which might not be representative of their respective world regions. Third, only two African studies were included, and we could not find any studies conducted in Asian or Oceanian countries which met the criteria, which would have improved our analysis.
In conclusion, this meta-analysis estimates that wheezing and recurrent wheezing affect a high percentage of infants, especially in Latin American countries, who may develop asthma in later years, evidencing a public health burden. Further studies involving other countries and world regions and trends analyses would be helpful, and promoting measures addressed to preventable risk factors previously identified would be recommendable.
Ethical disclosuresConfidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appears in this article.
Protection of human subjects and animals in researchThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this investigation.
FundingNone.
Conflicts of interestThe authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.