Current oncolytic virotherapy strategies are based in the accumulated understanding of the common molecular mechanisms displayed during cell transformation and viral infection, like cell cycle and apoptosis deregulations. Oncolytic virotherapy aims to achieve a strong cytolytic effect, highly restricted to transformed cells. Here, we describe the oncolytic virotherapy defined as the use of viruses like antitumor agents (wild and gene-modified oncolytic viruses) and the developed strategies to increase antitumor efficacy and safety. In addition, we discuss the advances and challenges concerning the use virotherapy in animal models and clinical trials. Some clinical trials of virotherapy have demonstrated promising results, particularly when combined with standard antineoplastic therapies. These preliminary accomplishments are opening the field for more research in several aspects, like vector modifications, pharmacodynamics, biosafety, new clinical applications, etc.
Advances in science and technology accumulated since the beginning of the 20th century led the establishment of the current standard therapies against cancer, like radiotherapy and chemotherapy and they are widely used, despite their limited efficacy and severe adverse effects that ameliorate the patient’s quality of life. At the beginning of the 21st century there are opportunities for the search of more effective and less toxic new antineoplastic strategies. Interestingly, an approach envisioned in the late 50’s is starting to merge: the oncolytic virotherapy. Cancer and virus infections converge in some molecular mechanisms required for cell cycle deregulation and apoptosis blockade, exploiting regulatory pathways to stimulate DNA replication and to avoid apoptosis.
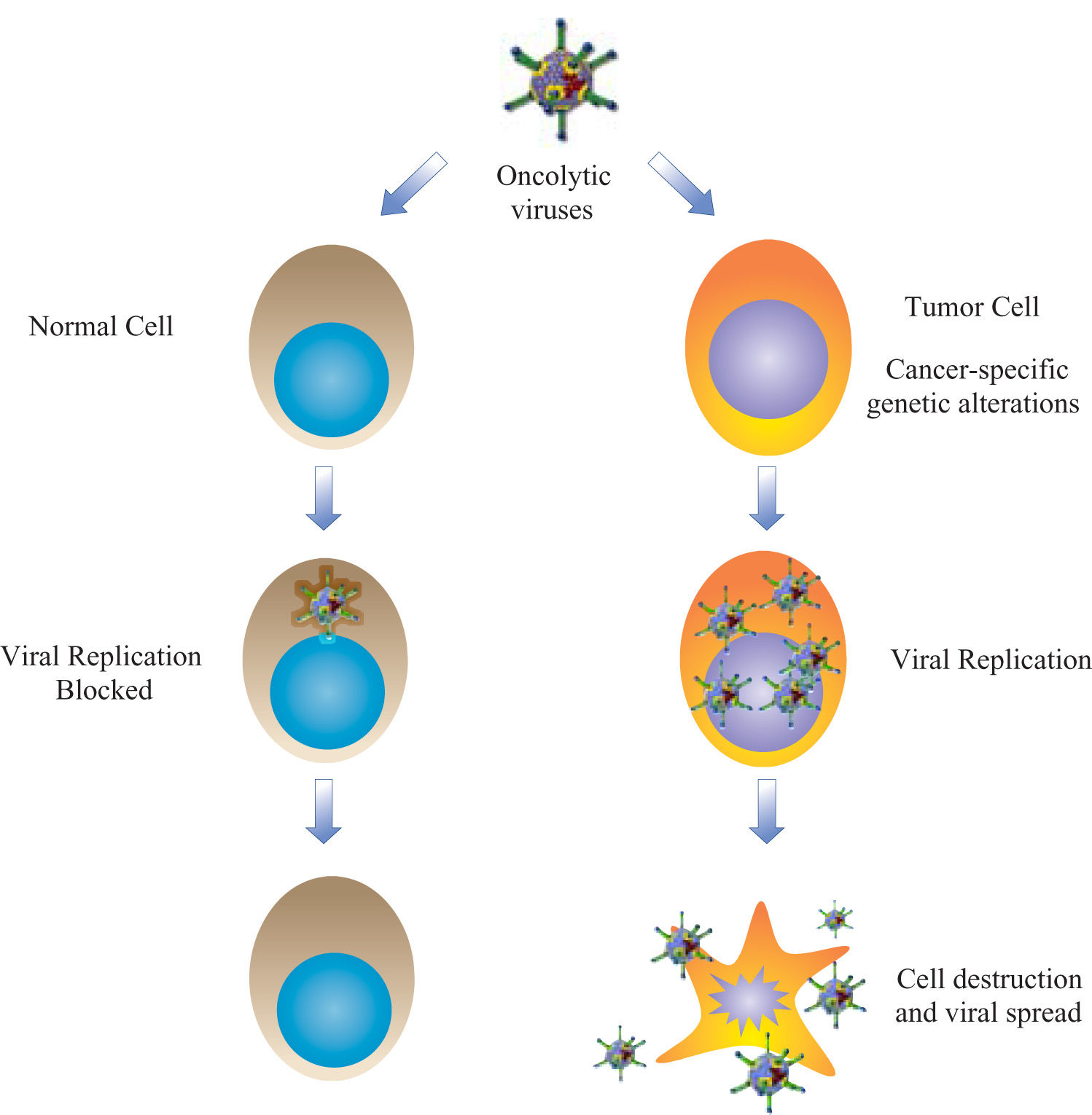
VirotherapyThe use of viruses for therapy was introduced by the field of gene therapy, mainly as vehicles for nucleic acid transfer. Several modalities of gene therapy are aimed to treat cancer, most of them with replication deficient viral vectors to avoid the risk of virus systemic dissemination. These non-replicating vectors may intend to reestablish wild-type copies of mutated tumor-suppressor genes, affect the metabolism of tumor cells, attract the immune response, or sensitize the neoplastic tissues to standard therapies. Clinical trials have demonstrated variable results with all these approaches.1 Virotherapy resurged in the late 90’s as an innovative alternative for oncolysis with a simple idea: to create new vectors with capacity to propagate in deregulated tumor cells and minimum adverse effects in healthy tissues (Figure 1). This therapeutic modality is called «oncolytic virotherapy» and is divided in two approaches: oncolytic wild viruses, or natural occurring viruses with preferential replication in human cancer cells; and gene-modified viruses engineered to achieve selective oncolysis.2
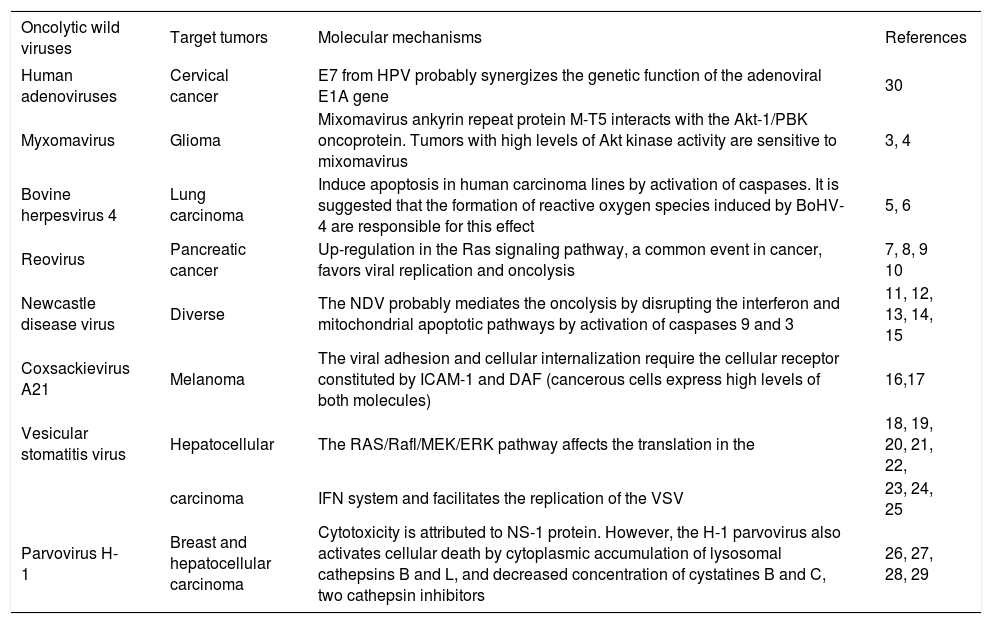
Oncolytic wild virusesSome wild viruses with natural oncolytic activity in human tumors, like myxomaviruses, bovine herpesvirus 4, reovirus, New Castle Disease virus (NDV), Coxsackievirus, vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), parvoviruses, etc. produce unspecific infections in humans, and in some birds and mammals. These viruses are referred as «oncolytic wild viruses» and are under intense research for virotherapy, but their oncolytic efficacy has been limited in some preclinical and clinical assays and trials.2 A growing list of oncolytic wild viruses is briefly described in the table I. Our review will be focused in the adenoviruses, since these vectors have been extensively modified for virotherapy applications, and ongoing clinical trials are demonstrating acceptable therapeutic efficacy and safety. Actually, the first wild-type viruses used as oncolytic vectors were the adenoviruses; as will be described below.
Wild viruses with selective oncolytic activities.
| Oncolytic wild viruses | Target tumors | Molecular mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human adenoviruses | Cervical cancer | E7 from HPV probably synergizes the genetic function of the adenoviral E1A gene | 30 |
| Myxomavirus | Glioma | Mixomavirus ankyrin repeat protein M-T5 interacts with the Akt-1/PBK oncoprotein. Tumors with high levels of Akt kinase activity are sensitive to mixomavirus | 3, 4 |
| Bovine herpesvirus 4 | Lung carcinoma | Induce apoptosis in human carcinoma lines by activation of caspases. It is suggested that the formation of reactive oxygen species induced by BoHV-4 are responsible for this effect | 5, 6 |
| Reovirus | Pancreatic cancer | Up-regulation in the Ras signaling pathway, a common event in cancer, favors viral replication and oncolysis | 7, 8, 9 10 |
| Newcastle disease virus | Diverse | The NDV probably mediates the oncolysis by disrupting the interferon and mitochondrial apoptotic pathways by activation of caspases 9 and 3 | 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
| Coxsackievirus A21 | Melanoma | The viral adhesion and cellular internalization require the cellular receptor constituted by ICAM-1 and DAF (cancerous cells express high levels of both molecules) | 16,17 |
| Vesicular stomatitis virus | Hepatocellular | The RAS/Rafl/MEK/ERK pathway affects the translation in the | 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, |
| carcinoma | IFN system and facilitates the replication of the VSV | 23, 24, 25 | |
| Parvovirus H-1 | Breast and hepatocellular carcinoma | Cytotoxicity is attributed to NS-1 protein. However, the H-1 parvovirus also activates cellular death by cytoplasmic accumulation of lysosomal cathepsins B and L, and decreased concentration of cystatines B and C, two cathepsin inhibitors | 26, 27, 28, 29 |
Adenoviruses are the most broadly studied therapeutic viral vectors, in particular the human serotypes 2 and 5 (Ad2 and Ad5, respectively). The use of adenoviruses for cancer treatment was initially reported in 1956.30 Genetic engineering has made possible to modify the viral genome to create oncolytic and selective adenoviral vectors. The conditionally replicating adenoviruses (CRAds) are being evaluated with relative success in preclinical and clinical trials since the late 90’s.
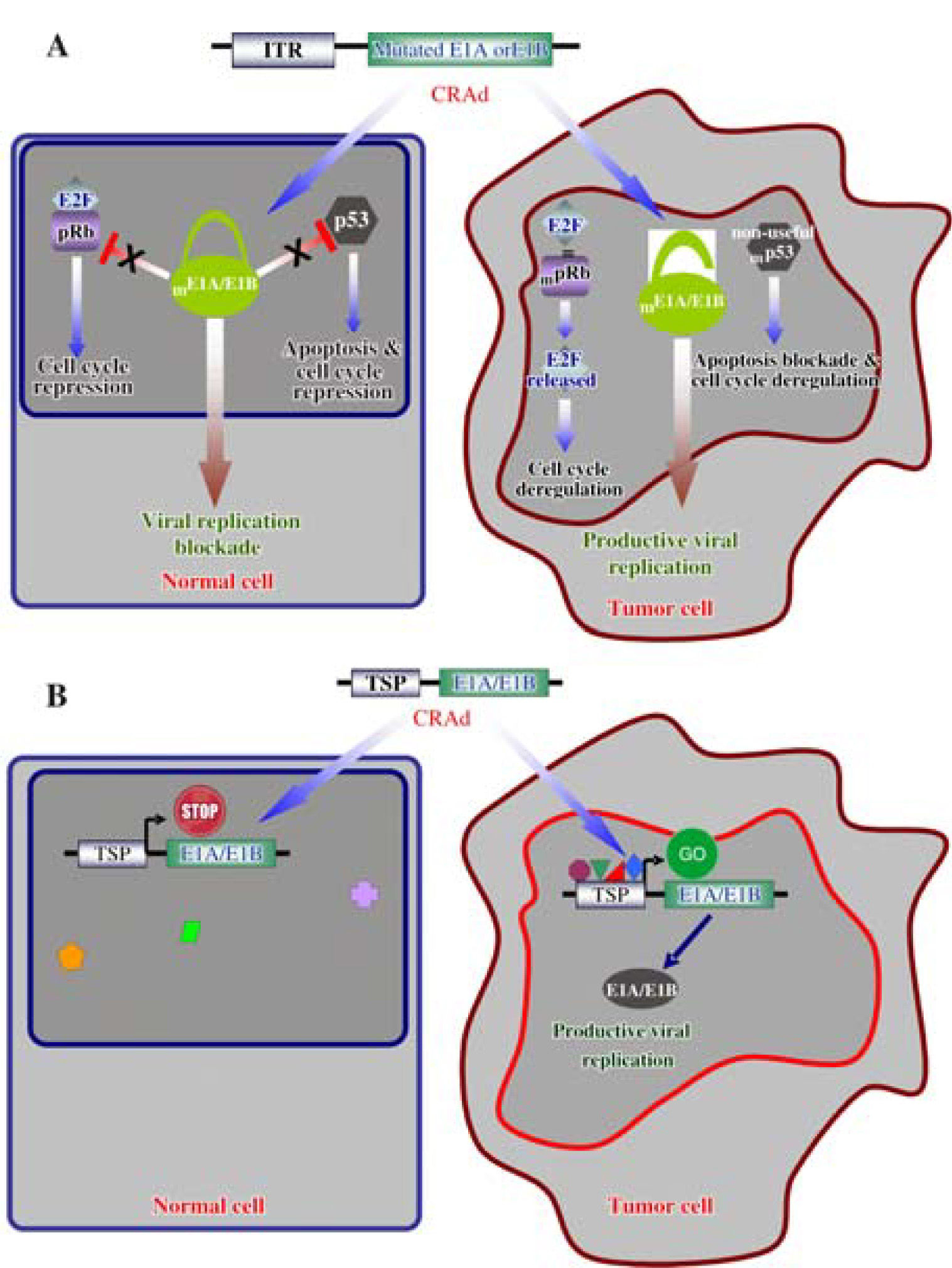
Strategies to develop gene modified oncolyticTwo main molecular strategies have been developed to delivery CRAds directly into tumor cells. The first involves the complete deletion of genes or particular adenoviral sequences necessary for viral replication, as the genes E1A and E1B responsible for the inactivation of the tumor suppressor proteins pRb and p53, respectively.31,32 These crucial regulatory genes are inactivated in cancerous cells.33 The CR2 domain of the E1A adenoviral protein competes with pRb for the binding to the E2F factor, allowing the progression of the cell cycle from phases G1 to S.34,35 On the other hand, the protein E1B- 55 kD binds and inactivates the protein p53, to block apoptosis and deregulate the cell cycle simultaneously (Figure 2A).36,37 Genes P53 and RB1 are frequently mutated during the tumorigenesis to perform the same work as during a viral infection: to deregulate the cell cycle and to block apoptosis;38 for these reasons, the E1A and E1B products are dispensable in an oncolytic adenovirus, which in turn, will not be able to propagate in healthy cells with normal pRB and p53 functions.39,40
Molecular mechanisms of selective oncolytic CRAds. A. Mutated E1A or E1B do not interact with pRb and p53 in normal cells, respectively; consequently, adenoviral replication is prevented. Deregulation of cell cycle and apoptosis blockade, as consequence of cell transformation, allowed replication of the modified adenoviral vector. B. A Tissue/Tumor-specific promoter (TSP) drives the expression of E1A or E1B and allowed adenoviral replication in tumor cells expressing the appropriate transcription factors. Normal cells lacking these transcription factors impede the replication of the CRAd.
The second strategy involves the use of either tumor or tissue-specific promoters, such as AFP, MUC1 and PSA, to control the expression of adenoviral genes involved in viral replication; however, this strategy is limited to specific cell types and tumors were such promoter is active (Figure 2B).41-43 These strategies can also be combined in a singular oncolytic vector to potentiate its cytotoxic activity.44
The first CRAd described, dl 1520 or ONYX-O15, has a partial deletion of the E1B gene, preventing its expression,45 so this vector is preferentially active in tumor cells with p53 deregulation. ONYX-O15 has been tested in more than 250 patients in different clinical trials, showing good tolerance at doses of about 2x1012 viral particles (vp).46 ONYX-015 has shown to be safe and effective in a variety of clinical trials, as will be discussed below. Fueyo et al. (2000) described a different CRAd denominated ***entity*** 24. This CRAd presents a 24 bp deletion in CR2 and has a potent oncolytic activity in cells lacking the pRb function.47
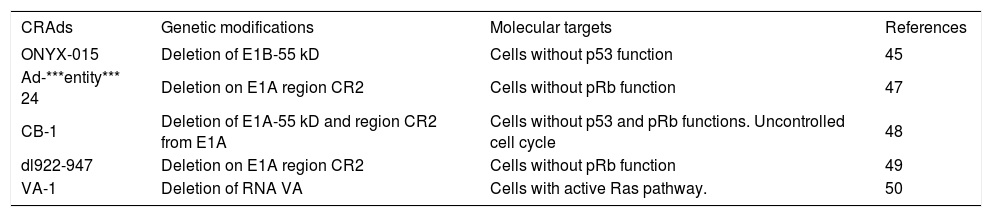
Adenoviral vectors harboring other modifications are being reported; however, the replicative and cytotoxic potentials are usually compromised and unsatisfactory. Table II describes the gene modified CRAds currently reported with their mechanisms and targets. There are several ongoing efforts to identify new modifications to improve the oncolytic and selective activities of the CRAds.
CRAds examples for selective replication in tumor cells.
| CRAds | Genetic modifications | Molecular targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ONYX-015 | Deletion of E1B-55 kD | Cells without p53 function | 45 |
| Ad-***entity*** 24 | Deletion on E1A region CR2 | Cells without pRb function | 47 |
| CB-1 | Deletion of E1A-55 kD and region CR2 from E1A | Cells without p53 and pRb functions. Uncontrolled cell cycle | 48 |
| dl922-947 | Deletion on E1A region CR2 | Cells without pRb function | 49 |
| VA-1 | Deletion of RNA VA | Cells with active Ras pathway. | 50 |
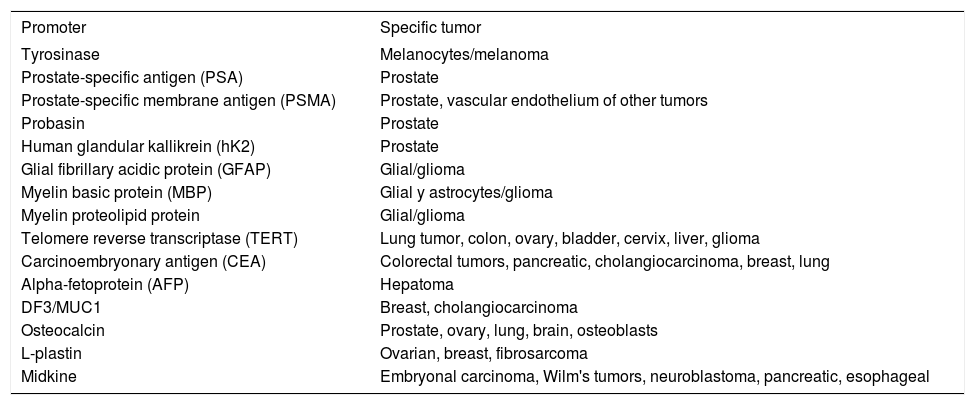
Tumor-specific promoters are listed in the table III;41,51 some of them are being tested in clinical trials. Rodríguez et al. (1997) described the CRAd CV706, in which the PSA promoter controls the selective expression of E1A in prostate tissue. In vitro experiments demonstrated that this CRAd has enhanced replication in the LNCaP prostate line and poor activity in the non-prostate lines, while studies in an immunodeficient mouse model showed tumor regression and declining concentrations of serum PSA.52
Tissue-specific promoters used for control the expression of replication adenoviral or therapeutic genes.
| Promoter | Specific tumor |
|---|---|
| Tyrosinase | Melanocytes/melanoma |
| Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) | Prostate |
| Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) | Prostate, vascular endothelium of other tumors |
| Probasin | Prostate |
| Human glandular kallikrein (hK2) | Prostate |
| Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) | Glial/glioma |
| Myelin basic protein (MBP) | Glial y astrocytes/glioma |
| Myelin proteolipid protein | Glial/glioma |
| Telomere reverse transcriptase (TERT) | Lung tumor, colon, ovary, bladder, cervix, liver, glioma |
| Carcinoembryonary antigen (CEA) | Colorectal tumors, pancreatic, cholangiocarcinoma, breast, lung |
| Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) | Hepatoma |
| DF3/MUC1 | Breast, cholangiocarcinoma |
| Osteocalcin | Prostate, ovary, lung, brain, osteoblasts |
| L-plastin | Ovarian, breast, fibrosarcoma |
| Midkine | Embryonal carcinoma, Wilm's tumors, neuroblastoma, pancreatic, esophageal |
The telomere reverse transcriptase (TERT) directs the synthesis of TTAGGG telomeric repeat present in the ends of the chromosomes. The TERT is very active in fetal tissues but is progressively «turned-off» in post-mitotic tissues after birth. Its high activity in «immortal» cells is a main feature, as happen in many human cancers, including tumors of lung, liver, stomach, breast, bladder, and prostate. Huang et al. (2003) designed a CRAd with a TERT promoter driving the expression of E1A. This CRAd was tested in lines of pulmonary cancer, HCC, cervical cancer, osteosarcoma and normal fibroblasts. The CRAd Adv-TERTp-E1A showed preferential replicative capacity in telomerase-positive lines. These results demonstrate that the TERT promoter can drive vector replication in tumor cells and to achieve oncolysis in vitro, but these activities has not been tested in animal models.53
The oncolytic effect of CRAds maybe enhanced with the combined use of replication-deficient adenoviral vectors designed to deliver a transgene. CRAds can trans-complement the lacking functions of E1A and E1B of the non-replicative vectors to produce viable viral particles with a therapeutic transgene. The intratumoral co-injection of an Ad-***entity*** 24 vector and the replication-deficient IGF-1R/482 adenoviral vector harboring the truncated insulin-like growth factor-1R gene was able to decrease the plasmatic concentration of IGF-1 and induce tumor suppression in a xenografted mouse model of pulmonary cancer.54
The carcinoembryonary antigen (CEA) is usually upregulated in colorectal cancers and is a common clinical marker for this disease. The transcriptional regulatory elements of CEA are being incorporated in an oncolytic adenovirus for CEA positive colon tumors. In this vector, named OV798, the enhancer 1 and the CEA promoter drive the expression of E1A, and it shows increased oncolytic capacity in in vitro and in a mouse model of colon cancer.55
The vector AvE1a04i is a CRAd in which E1A expression is under control of the tumor-specific alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) promoter. It is able to replicate in AFP positive hepatocarcinoma lines. The in vivo administration of AvE1a04i increased survival in more than 50% in a murine liver cancer model.56
Delgado-Enciso et al. (2007) created the CRAd Ad- URR/E1AD24, in which a D24 mutated E1A is under control of the URR promoter (upstream regulatory region from HPV-16AA). This CRAd showed to be highly selectivity for HPV+ lines and attenuated in HPV- lines, an effect probably associated to the URR promoter. This vector was very effective to control tumor growth and to improve survival in immunodeficient mice harboring bilateral xenografted HPV+ tumors, when just one tumor was treated. The presence of viable infectious vector particles at non injected tumors was demonstrated. The high replication activity of this vector maybe the result of genetic complementation mechanisms, in which the papillomavirus oncoprotein E7 present in the tumor sustains the genetic functions of the modified E1A protein of the oncolytic vector.57
Enhancing transduction and improving safetyThe RGD motif. The transduction efficacy and the oncolytic potency of a CRAds are limited by its capacity for tumor cell adhesion.58 This viral adhesion is produced by the direct interaction between the knob domain from the fiber adenoviral with the Coxsackievirus B and Adenovirus receptor (CAR). CAR is a transmembrane protein and member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and plays an important role as a homotypic junctional adhesion protein.59 After the initial union, the motif RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) from the penton base interacts with av integrin proteins, activating the clathrin-dependent endocytosis.60
The expression profile of CAR is variable in cancer cells: while breast cancer cells have increased tropism for the adenovirus, in other tumors, like ovarian and bladder cancer, and melanoma, this tropism is diminished.61-63 Induction of Raf-1 in the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway reduces the expression of CAR in cancer cells.64 Incorporation of the RGD motif in the fiber protein improves the tropism of the adenoviral vector for target cancer cells, enabling the direct interaction with the integrins.65-67 Several CRAds have this modification to homing tumor cells preferentially, with acceptable results in preclinical in vivo studies. Liu et al. (2004) created the Ad.Tyr-E1A (RGD) vector, a CRAd with the RGD motif, in which the E1A gene was under the control of the tyrosinase enhancer/promoter to treat melanoma with low CAR expression. This CRAd showed increased viral replication when compared to a similar vector lacking the RGD motif.68 The infection capacity of the CRAd 0BP-301, in which the TERT promoter drives the simultaneous expression of E1A and E1B that are joined by an IRES (internal ribosome entry site), was significantly increased by the incorporation of the RGD motif in the knob domain. The new vector, named OBP-405, exerted a potent cytotoxic effect in cells with low CAR expression.69
Pseudotyped fiber CRAds. The safety of an adenoviral vector can be modified by exchanging the native fiber protein by fibers from other adenovirus serotypes. Denby et al. (2004) demonstrated the low hepatic transduction and toxicity of pseudotyped adenoviruses through the direct administration of the chimeric adenoviruses Ad5/ 19p and Ad5/37 into the portal vein in a rat model.70 The replacement of the knob domain of a 5 type CRAd by the knob of serotype 3 improved tumor cell transduction and increased liver safety.71
Interaction with Coagulation Factors. New highlights have emerged recently in terms of the contribution of different proteins than CAR and integrins for adenoviral adsorption to the cell surface. The infectivity of adenovirus in liver has shown to be zymogens-binding dependent, involving factors IX and X. These factors bound directly to the fiber and bypass the virus to alternative receptors, like heparan-sulfate proteoglycans and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein.72-74
Additional strategies for vector homing. Viral adsorption in tumor cells can be improved by antibody conjugation. Designed antibodies can be directed against receptors differentially displayed by transformed cells. Douglas et al. (1996) performed an interesting experiment with an E1B deleted CRAd linked to an anti-knob monoclonal immunoglobulin conjugated with folate. As expected, they demonstrated an oncolytic effect restricted to lines overexpressing the folate receptor.75 Ranki et al. (2007) incorporated a polylysine motif in the C-termini of the fiber of the CRAd Ad5.pK7-Delta24 to facilitate the vector interaction with heparan-sulfate proteoglycans. This strategy showed to be effective against breast cancer lines.76
Armed CRAdsThe genome of a CRAds can be engineered to incorporate an anti-tumor transgene in their genomes, as those traditionally used in anti-cancer approaches of gene therapy with replication-deficient adenoviral vectors. Zhang et al. (2004) constructed a vector with a TERT promoter controlling the expression of gene E1A and with the CMV promoter driving the endostatin transgene. This vector was tested in a murine model of gastric cancer, achieving important antiangiogenic and antineoplastic effects.77 The vector AdCB016-mp53(268N) has deletions in the CR1 and CR2 domains of E1A and a transgene expressing a p53 protein variant resistant to E6-induced degradation in HPV associated tumors. This vector showed increased oncolytic potency in HPV positive lines.78 The vector Ad.HS4.AFP.E1A/TRAIL is a CRAd with an AFP promoter driving E1A and the TRAIL transgene joined by a bidirectional IRES element. This vector was successfully tested in hepatocarcinoma lines, and the cooperative effect of TRAIL was demonstrated.79 The combined treatment of a replication-deficient adenoviral TRAIL vector and the Ad-***entity*** 24 in a murine model of breast cancer improved oncolysis when compared with the Ad-***entity*** 24 treatment alone.80
Transgenes used in suicide-gene therapy had been incorporated in oncolytic adenoviruses. The cytosine desaminase gene (which converts the prodrug 5-fluorocytosine into the chemotoxin 5-fluorouracil) was included in the genome of the ONYX-O15, and the resulting vector enhanced the oncolytic activity of this CRAd in a murine model of colon cancer.81 The secretory carboxylesterase-2 gene (which codifies for an enzyme that transforms the prodrug CPT-11 into the toxic SN-38 drug) showed increased cytolysis in three different colon cancer lines, but it was observed that the therapy should be synchronized, because the chemical cytolysis can limit the oncolytic effect if early administered to transduced tumor cells engaged in producing the infective oncolytic virus.82
Combining standard antineoplastic treatments with CRAd therapyCRAds have been combined with conventional chemotherapy in preclinical and clinical trials. A combined treatment of head and neck cancer with ONYX-015 and cisplatin showed better efficacy than with individual therapies.83 Radiation has been combined with CRAd therapy on in vitro assays in prostate cancer lines. The CRAd CG7870 which has the probasine rat promoter driving the E1A gene and the PSA promoter controlling the expression of E1B was used in combination with ionizing radiation. The combination of both treatments had a synergistic effect. These results were confirmed in a mouse model of heterotopic prostate cancer.84
Oncolytic virotherapy for liver cancerLiver cancer is the fifth more common neoplasia and the third cause of mortality related to cancer in the world.85 Liver cancer is relatively common in Mexico, with an incidence of 4.5 cases for 100,000 habitants in 2005.86 The VSV vector has been tested for the treatment of HCC. In a late report, Shinozaki et al. (2005) test the biosafety of repeated administrations of VSV at low doses, showing tumor necrotic nodules surrounded by mononuclear phagocytes, followed by fibrosis and calcification of lesions, regeneration of normal hepatic tissue, and increased survival in treated animals.87
A new strain of measles virus has been employed recently as a potent oncolytic virotherapy for the treatment of HCC. The Edmonston strain (MV-Edm) has high affinity for CD46-overexpressing cells, like HCC-related Huh- 7 and Hep3B lines. Conversely, this strain shows low affinity for normal hepatic cultured cells.88
Regarding adenoviral oncolytic vectors for liver cancer, the vector SG300, a CRAd with a TERT promoter driving viral replication, has been effective and selective against hepatic tumor cells.89 An additional vector, denominated CNHK500, is also under control of the TERT promoter, but E1B gene is regulated by the hypoxia response promoter to reduce CRAd toxicity in normal liver cells.90 Some authors have suggested the combination of the TERT promoter-dependent CRAds with immunomodulators or chemotherapy to synergize the efficacy of the antineoplastic therapy in tumors displaying drug resistance.91
In vivo modelsSince virus-host interactions are species specific for every adenovirus serotype, is necessary to use animal models to recreate the therapeutic and toxic effects for future clinical trials. Immunodeficient mice are useful to determine the oncolytic effects of vectors in a human xenografted tumor; however, to evaluate the therapeutic and adverse effects of a CRAd, a permissive animal model is required. Some of the useful animal models are described below.
The cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) may display interstitial pneumonia, epicardial inflammation, and spleen hemosiderosis during the course of human adenoviral infections.92-94 They also develop infections with other pathogens, like influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, herpes simplex virus type 2, human metapneumovirus, HIV-1, pulmonary tuberculosis, and Helicobacter pylori infections.95-102 Steel et al. (2007) demonstrated the ability of Ad5 to efficiently infect, replicate and induce in vitro and in vivo oncolysis in the cotton rat model, highlighting the relevance of this model for CRAds evaluation.103
Other animal models for the study of oncolytic viruses are the hamster (Cricetus cricetus) and the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus), which develop pulmonary lesions, similar to those developed in humans, or lethal infections when injected with Ad5 in high doses.104-106 The Syrian hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) sustains active adenoviral replication after nasal instillation, and is able to resolve the infection.107 This animal model also allowed the study of the cell immune response and the antiangiogenic activity in a syngeneic model of pancreatic cancer treated with an non-replicative adenovirus carrying the IFN-***entity***gene.108
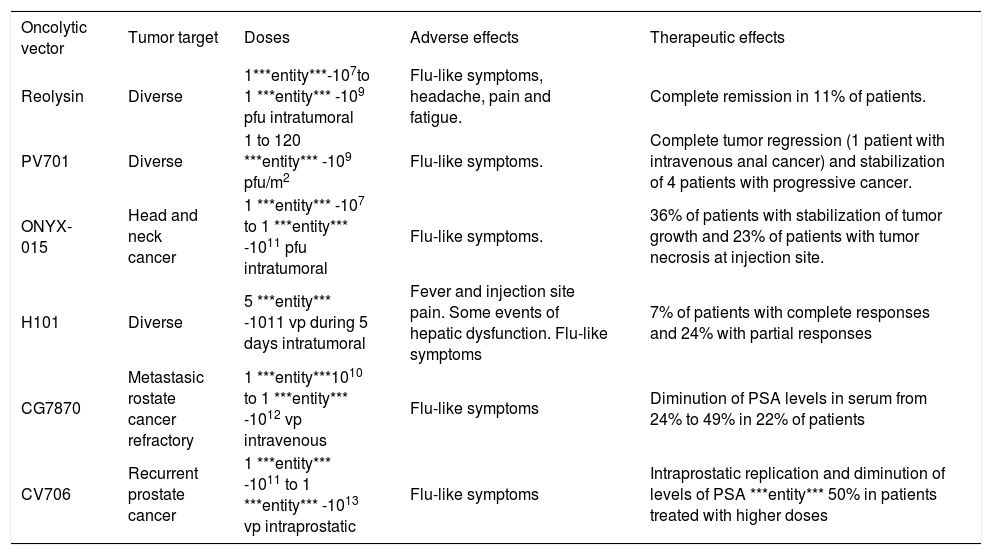
Clinical trialsThe promising results regarding safety in preclinical trials with oncolytic viruses have permitted the introduction of these vectors in the field of the clinical trials. Several aspects in oncolytic therapy must be considered during the planning of a clinical trial, like tumor type, previous exposure to vector-related viruses, presence of viral receptors in target tissue, genetic disturbances of tumor, concurrent viral infections, and patient’s immune status, among others. Examples of reported clinical trials are listed in the table IV. Considerations on some of these trials will be discussed.
Examples of clinical trials for oncolytic virotherapy.
| Oncolytic vector | Tumor target | Doses | Adverse effects | Therapeutic effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reolysin | Diverse | 1***entity***-107to 1 ***entity*** -109 pfu intratumoral | Flu-like symptoms, headache, pain and fatigue. | Complete remission in 11% of patients. |
| PV701 | Diverse | 1 to 120 ***entity*** -109 pfu/m2 | Flu-like symptoms. | Complete tumor regression (1 patient with intravenous anal cancer) and stabilization of 4 patients with progressive cancer. |
| ONYX-015 | Head and neck cancer | 1 ***entity*** -107 to 1 ***entity*** -1011 pfu intratumoral | Flu-like symptoms. | 36% of patients with stabilization of tumor growth and 23% of patients with tumor necrosis at injection site. |
| H101 | Diverse | 5 ***entity*** -1011 vp during 5 days intratumoral | Fever and injection site pain. Some events of hepatic dysfunction. Flu-like symptoms | 7% of patients with complete responses and 24% with partial responses |
| CG7870 | Metastasic rostate cancer refractory | 1 ***entity***1010 to 1 ***entity*** -1012 vp intravenous | Flu-like symptoms | Diminution of PSA levels in serum from 24% to 49% in 22% of patients |
| CV706 | Recurrent prostate cancer | 1 ***entity*** -1011 to 1 ***entity*** -1013 vp intraprostatic | Flu-like symptoms | Intraprostatic replication and diminution of levels of PSA ***entity*** 50% in patients treated with higher doses |
Wild-type adenovirus. As mentioned earlier, wild-type adenoviruses were used as oncolytic agents in the middle 50’s and the results of this protocol provide interesting considerations in terms of safety and efficacy for the current clinical trials with modified adenoviruses. In this study, several serotypes of adenovirus were injected in different routes of administration in women with advanced stages of cervical cancer. They showed that hemorrhagic necrosis was achieved by the virus in the tumor and the stroma, without affecting distant organs, including the liver. Fatalities observed during the study were probably non-related to the adenovirus administration.30
ONYX-O15. More than 18 clinical trials using ONYX- 015 are reported to date. Ganly et al. (2000) administered increasing intratumor doses from 1´107 to 1´10u pfu in patients with head and neck cancer. The most common adverse events were flu-like symptoms. Stabilization of tumor growth was achieved in 8/22 patients, and tumor necrosis was observed at the injection site in 5 patients (4 of them presented mutations in the p53 gene).111 A phase II clinical trial with 0NYX-015 administered intratumorally for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil demonstrated tumor remission in 27% of patients and partial response in 36% additional subjects. Adverse events were also common cold symptoms, and pain at the injection site, without substantial hepatic dysfunction.112 A phase I/II trial for liver metastases of gastrointestinal neoplasias, in which the vector was infused via hepatic artery with doses of 2´1012 vp during 8 days and combined with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin, demonstrated total tumor regression in 15% of the patients, more than 50% regression in 11% of the patients, and delayed tumor growth in the remaining 33% of the patients.113 An additional trial determined that the intratumor injection in patients with recurrent squamous cell carcinoma produced a modest antitumor activity and minimum adverse events.114
H101. This is the first clinically approved oncolytic vector worldwide. It was announced by the Chinese company Shangai Sunway Biotech in November, 2006. This virus has a deletion in the E1B-55kD gene (similar to the mutation of 0NYX-015), and a larger deletion in the E3 gene, aimed to restrict the immune response against the vector more effectively. The reported clinical trial for solid tumors refers 3/46 complete tumor remissions and 11/46 partial responses. The most common adverse events were fever, pain at the injection site, and liver dysfunction without systemic compromise in few cases (5.7%).115
CG7870. A phase I/II clinical trial for hormone-refractory prostate cancer performed in 23 patients showed serum PSA decrement in 5 patients. The most common adverse events associated to this vector were flu-like symptoms. No remissions were reported.116
CV706. This vector was tested in another clinical trial for recurrent prostate cancer in a group of 20 patients. No remissions were reported, but serum PSA levels decreased up to more than 50% in about the 30% of the patients treated intra-prostatic with 1´1013 vp.117 There was some evidence of intraprostatic viral replication.
DiscussionThe idea of the «oncolytic virotherapy» was initially elucidated and tested in the middle of the 20th century with a moderate success, but merged with renewed strength during the last decade of the same century, due to the technologic advances in virology and in the use of viruses as vectors for gene transfer. The aim of the oncolytic virotherapy is to achieve a strong cytolytic effect highly restricted to transformed cells. Several kinds of viruses have been used for oncolytic virotherapy. The first viruses reported were human wild-type adenoviruses for the treatment of cervical cancer. Oncolytic viruses can be divided in two categories: wild-type oncolytic viruses (myxomavirus, reovirus, herpesvirus, parvovirus, etc.) and genetically modified, particularly, adenoviruses with genetic modifications for conditioned replication, by tissuespecific promoter activities controlling viral functions, or «arming» an adenoviral vector with cytotoxic genes.
The accumulated knowledge on the adenoviral vectors and the technical advances in the manipulation of their genomes, mainly after their introduction in the field of gene therapy, allowed the most important progresses in the field of oncolytic virotherapy. CRAds lead the field of oncolytic virotherapy and worldwide ongoing research is in progress to improve their efficacy and safety. These efforts include the study of genome modifications involved in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis that have a minimal effect in the viral replication capacity in a transformed cell, the use of tissue-specific promoters to drive viral replication in target tissues, regions that allow insertion of cytotoxic genes, modifications in the fiber protein for virus homing, etc. For most of the CRAds described to date, the results obtained in tumor lines show highly therapeutic potential; however, in some cases the in vivo evaluations demonstrate their limited efficacy for factors like immune response, efficiency of viral dissemination, tumor cell heterogeneity, expression of genes involved in tumor development, and administration routes among others. Although it has been suggested that the intratumor delivery of a CRAd requires a much smaller dose than the systemic administration to achieve therapeutic efficacy,118 this last route is considered crucial for the anti-metastatic effect of the vector, and several ongoing investigations are underway to adopt this delivery route, while preventing the adverse effects of this systemic delivery on some target organs like the liver. Several studies suggest that the combination of oncolytic virotherapy with chemotherapy results in a synergic antitumor effect; however, the mechanisms for that synergy remain elusive, but there are some suggestions like the positive effect of chemotherapy on viral replication, the improved antitumor effect of the antineoplastic drugs when coadministered with a CRAd, the CAR gene upregulation mediated by the chemotherapeutic agents, the increased antitumor immune response triggered by the delivery of a CRAd, etc.
CRAd biosafety issues confront several challenges to overcome before being tested in a clinical trial. Some animal models allow studying the CRAd-tumor interactions; however, safety testing in these models is complex due the involvement of the immune system in the clearing of circulating CRAds and difficulties to extrapolate possible vector-related injuries in normal tissues. For example, researchers are very interested to determine the interaction of the CRAds with the normal human liver tissue, but Ad5, the main backbone used for CRAd constructions, does not replicate efficiently in murine cells. The limited immune response against human adenovirus in the known animal models is also a hurdle, and the frequently reported assays in immunodeficient mice limit scientific observations to the merely antitumor effect, while concealing the negative and positive effects of the immune response. Some rodents, particularly the cotton rats, sustain a limited capacity of adenoviral replication and are the most advocated animal models for in vivo evaluation of CRAds, but definitive answers regarding patient safety must be defined in clinical trials.
The initial clinical trials provide valuable information to support the potential antitumor activity of these vectors and provide valuable data about very important pharmacologic aspects of the CRAds, like biodistribution, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic effect, and biosafety. Five different viruses are being studied in phase I and II clinical trials, involving a number of more than 300 patients to date. These studies report very promising antitumor efficacy and acceptable safety. In fact, some of these vectors are closer to overcome phase III clinical trials than other gene therapy vectors or strategies.46,119
The future of oncolytic virotherapy looks very promising at short or middle term and we can expect vectors that disseminate with high efficiency in solid tumor masses and spread to distant metastases once they reach the systemic circulation, while demonstrating acceptable minimal adverse events. In addition, it is predictable that the use of virotherapy in the clinics will be facilitated by the advances in the ongoing trials in which CRAd administration is being combined with oncologic standard therapies like chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery.
AcknowledgementsDaniel Cervantes-García is a recipient of a D.Sc. scholarship from CONACyT (Mexico).