Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is linked with increased risk of fetal complications. An accurate diagnostic test is needed to diagnose this disorder on time. We aimed to assess sensitivity and specificity of laboratory tests used for diagnosis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and determine more reliable cut-off values of transaminases.
Material and methodsSixty one symptomatic patients with ICP and 29 healthy pregnant women were included in the retrospective analysis.
ResultsICP patients had higher total bile acids (TBA) levels than healthy women (32 vs. 6; P < 0.0001) due to increase in cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). CA/CDCA ratio was significantly higher in ICP patients compared to healthy pregnant women (1.13 vs. 0.68; P < 0.00002). TBA, CA, CDCA and CA/CDCA ratio demonstrate the following sensitivity (94%, 96%, 89%, 71.9%) and specificity (63%, 63%, 59%, 79.3%, respectively) for ICP diagnosis. Lowering cut-off values for ALT (31 U/ L) and AST (30 U/L) resulted only in minimal increase of sensitivity to 92.2% vs. 90.1% for ALT and to 92.2%, vs. 90.6% for AST.
ConclusionThe present study did not reveal any single specific and sensitive marker for reliable diagnosis of ICP. Establishment of lower cut-off values for transaminases activity might only minimally increase the accuracy of diagnosing ICP.
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is a liver disorder unique to pregnancy. Pruritus with abnormal serum liver tests is the classical presentation of this disease.
ICP predominantly occurs during the third trimester of pregnancy and disappears after delivery.1-3 The cause of ICP remains unknown. Current research on the pathogenesis of ICP focuses on genetic and hormonal factors.4,5 While maternal prognosis is benign, there is a clear association between ICP and higher frequency of fetal distress, preterm delivery, and sudden intrauterine fetal death.6-12 An accurate test is needed to make timely diagnosis of this high-risk disorder. Serum bile acid measurement is considered the most sensitive laboratory abnormality in ICP; however, the levels of bile acids can fluctuate depending on the fasting state or gestational age.7-15 In addition, the turnaround time for receiving the laboratory results may be 1 or 2 weeks, making it difficult to await the results when deciding on induction of labour to reduce potential fetal complications. Serum liver enzymes are an important component for diagnosis but they may be normal in up to one third of cases. The upper normal limit of transaminases normal range was recently challenged, because possible modulators are often ignored in determining normal range.16 Reference ranges for transaminases also require re-evaluation in pregnancy. No single reliable test can currently unequivocally distinguish all cases of ICP and other liver diseases or dermatoses of pregnancy. New diagnostic autotaxin test with high specificity and sensitivity was recently suggested; however, it may be hardly accessible in clinical practice.17,18
The aim of our study was to estimate sensitivity and specificity of total and individual bile acids and to determine a more reliable cut-off value of transaminases activity for diagnosing ICP.
Material and MethodsWe conducted a retrospective analysis of 61 pregnancies complicated by ICP. Inclusion criteria were: skin pruritus starting in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, and elevation of fasting serum total bile acids (TBA) > 10 μmol/L. Exclusion criteria were: chronic liver disease, hepatic viral infections (HAV, HBV, HCV, cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus), skin disease, allergic disease, symptomatic cholelithiasis. Patients with ICP were compared with 29 healthy consecutive pregnant women in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. Serum samples were collected prospectively from healthy pregnant and ICP patients. This patients’ cohort is a subgroup of our previously described cases.19 In contrast to the previous study, in the actual retrospective analysis we include only patients having elevation of fasting serum total bile acids (TBA) > 10 μmol/L and control group of healthy pregnant women.
All serum samples were processed in the same laboratory using the same methods and the same reference values: ALT- 5-45 U/L, AST- 5-40 U/L, alkaline phosphatase (AP)- 80- 290 U/L, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT)- 5-35 U/L, total bilirubin 2.0-22.0- μmol/L, direct bilirubin- 0-6.8 μmol/L. Serum liver tests were determined using routine laboratory techniques. Fasting serum bile acids and cholic acid (CA), chenodeoxycholic (CDCA), deoxycholic (DCA), lithocholic (LCA), ursodeoxycholic (UDCA) were analyzed by gasliquid chromatography as described previously.20 Fasting serum samples were stored at -20 °C until analyzed.
Statistical analysisStatistical analysis was performed using the SPSS software version 20.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, U.S.A.). Results are presented as median (range) or mean ± SD. The Mann-Whitney test for non-parametric data was used for comparison between groups. Cut-off levels for transaminases were determined. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC) of all significant biochemical tests was calculated. The percentage of cases correctly classified by each diagnostic test as well as sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were calculated by discriminant analysis. The likelihood - ratio was calculated according to the formula: positive (LR + ) = sensitivity/1-specificity and negative (LR-) = 1-sensitivity/ specificity. In all cases, tests of significance were two-tailed, with a significance level < 0.05.
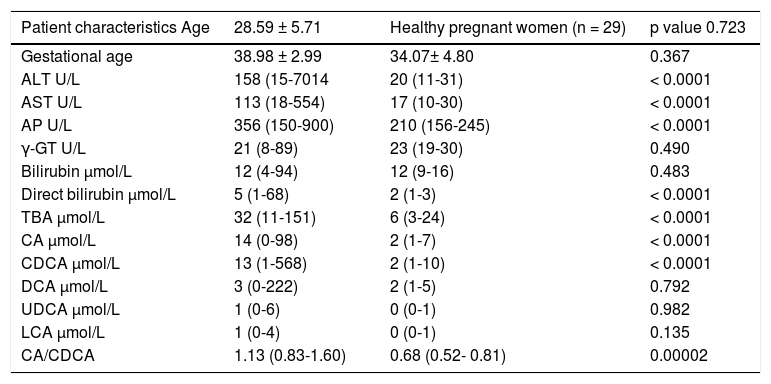
ResultsThe clinical and biochemical characteristics of all patients are shown in the table 1. There were no differences between groups regarding age, gestational age, total bilirubin, γ-GT, DCA, LCA, UDCA levels. Significantly higher levels of ALT, AST, AP, direct bilirubin, TBA, CA, CDCA were found in ICP patients when compared with healthy pregnant women.
Clinical, biochemical characteristics of patients with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and healthy pregnant women.
| Patient characteristics Age | 28.59 ± 5.71 | Healthy pregnant women (n = 29) | p value 0.723 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age | 38.98 ± 2.99 | 34.07± 4.80 | 0.367 |
| ALT U/L | 158 (15-7014 | 20 (11-31) | < 0.0001 |
| AST U/L | 113 (18-554) | 17 (10-30) | < 0.0001 |
| AP U/L | 356 (150-900) | 210 (156-245) | < 0.0001 |
| γ-GT U/L | 21 (8-89) | 23 (19-30) | 0.490 |
| Bilirubin μmol/L | 12 (4-94) | 12 (9-16) | 0.483 |
| Direct bilirubin μmol/L | 5 (1-68) | 2 (1-3) | < 0.0001 |
| TBA μmol/L | 32 (11-151) | 6 (3-24) | < 0.0001 |
| CA μmol/L | 14 (0-98) | 2 (1-7) | < 0.0001 |
| CDCA μmol/L | 13 (1-568) | 2 (1-10) | < 0.0001 |
| DCA μmol/L | 3 (0-222) | 2 (1-5) | 0.792 |
| UDCA μmol/L | 1 (0-6) | 0 (0-1) | 0.982 |
| LCA μmol/L | 1 (0-4) | 0 (0-1) | 0.135 |
| CA/CDCA | 1.13 (0.83-1.60) | 0.68 (0.52- 0.81) | 0.00002 |
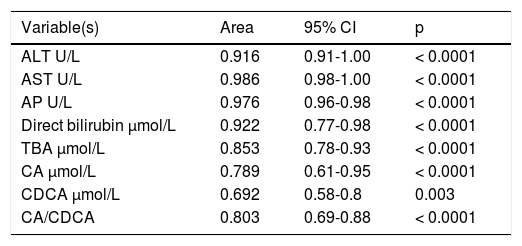
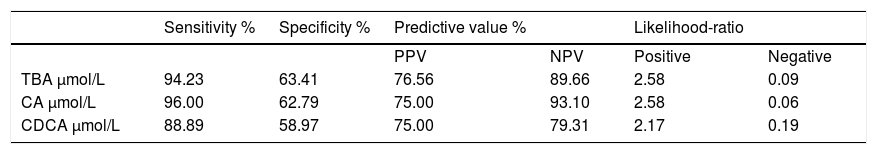
ICP patients had higher TBA levels than healthy women (32 vs. 6; p < 0.0001) due to increase in CA, CDCA. We observed TBA increase over upper normal limit (10 μmol/L) in 3 (10%) healthy women: 24.1, 10.8 and 10.7 μmol/L. CA was more elevated than CDCA in 41 (64%) ICP patients. In all healthy patients CDCA was higher than CA. Cholic/ chenodeoxycholic acid ratio was significantly higher in ICP patients compared to healthy pregnant women: 1.13 vs. 0.68; P < 0.00002. Calculation of the area under the curve (AUC) confirmed diagnostic accuracy of all significant biochemical parameters (Table 2). No significant difference was found between sensitivity and specificity of serum TBA, CA and CDCA (Table 3). CA/CDCA < 0.8 resulted in sensitivity 71.9% and specificity 79.3%.
Area under the curve (AUC) of all significant biochemical parameters.
| Variable(s) | Area | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT U/L | 0.916 | 0.91-1.00 | < 0.0001 |
| AST U/L | 0.986 | 0.98-1.00 | < 0.0001 |
| AP U/L | 0.976 | 0.96-0.98 | < 0.0001 |
| Direct bilirubin μmol/L | 0.922 | 0.77-0.98 | < 0.0001 |
| TBA μmol/L | 0.853 | 0.78-0.93 | < 0.0001 |
| CA μmol/L | 0.789 | 0.61-0.95 | < 0.0001 |
| CDCA μmol/L | 0.692 | 0.58-0.8 | 0.003 |
| CA/CDCA | 0.803 | 0.69-0.88 | < 0.0001 |
Sensitivity, specificity, predictive value and likelihood-ratio of total and individual bile acids for the diagnosis of ICP.
| Sensitivity % | Specificity % | Predictive value % | Likelihood-ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPV | NPV | Positive | Negative | |||
| TBA μmol/L | 94.23 | 63.41 | 76.56 | 89.66 | 2.58 | 0.09 |
| CA μmol/L | 96.00 | 62.79 | 75.00 | 93.10 | 2.58 | 0.06 |
| CDCA μmol/L | 88.89 | 58.97 | 75.00 | 79.31 | 2.17 | 0.19 |
We intended to establish a more reliable cut-off value of transaminases (Table 4). A cut-off value of ALT 31 U/ L resulted in sensitivity 92.2%, specificity 100% (compared to current range of ALT 45 U/L- sensitivity 90.1%, specificity 100%), and accuracy with -LR of 0.078, a positive predictive value 100%; negative predictive value 85%. When cut-off value of AST 30 U/L was used, sensitivity 92.2%, specificity 100% (current range of AST 40 U/L -sensitivity 90.6%, specificity 100%), accuracy with LR- of 0.078, a positive predictive value 100%; negative predictive value 85%.
Validity of new cut- off levels of transaminases for diagnosis of ICP.
| ALT U/L | New cut-off value 31 | Sensitivity 92.2 | 95% CI 82.7-97.4 | Specificity 100.0 | 95% CI 87.9-100.0 | p < 0.0001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST U/L | 30 | 92.2 | 82.7-97.4 | 100.0 | 87.9-100.0 | < 0.0001 |
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is associated with increased risk of fetal complications. Therefore it is important to determine sensitive biochemical parameters that aid in timely diagnosis of this disorder. The present study did not confirm any single specific and sensitive marker for early diagnosis of ICP despite of significantly higher serum TBA and CA levels in addition with markedly elevated CA/CDCA ratio in ICP patients. We also intended to show that adoption of lower limits for transaminases values might increase the effectiveness of case finding for ICP.
The biochemical parameter commonly used in the diagnosis of ICP is determination of the concentration of serum bile acids.1,3 In the large prospective study of perinatal out-comes in women with severe ICP, significant relationships were found between the maternal serum bile acid level and preterm delivery, spontaneous preterm delivery, stillbirth. In this study, the risk of fetal complications was statistically increased at bile acid levels ≥40 μmol/L.7 However, an unexplainable fetal death was reported at 39 weeks despite treatment with UDCA and low bile acid values.21 On the other hand, a study from Argentina showed that asymptomatic hypercholanemia of pregnancy does not necessarily lead to ICP.22 Recently, it has been reported that elevated autotaxin activity is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic biomarker.17,18 In contrast to the current gold standard for diagnosis total fasting serum bile salt levels, autotaxin is not influenced by food intake.18
In our retrospective analysis we showed that TBA levels alone cannot serve as sensitive and specific marker of the disease. In agreement with other reports we found that the cholic acid level and cholic/chenodeoxycholic acid ratio were significantly higher in ICP patients compared to healthy pregnant women, indicating that CA and CA/ CDCA are more relevant in diagnosis of ICP. Huang, et al. assessed the addition of bile acid CA/CDCA ratio information in diagnosing ICP and found similar results that CA/CDCA ratio contributed little to the diagnosis of ICP. The use of total bile acid and transaminases without bile acid ratios decreased positive tests by less than 2%.14
It is difficult to diagnose ICP only by routine biochemical tests, however, activity of transaminases and direct bilirubin concentration were considerably higher in ICP patients.
Significant increase of AP also was noticed in ICP group compared to healthy patients, but AP is of poor diagnostic value due to placental and bone production. No difference was found in activity of γ-GT in both groups. Genes, et al. found that ALT has a significant, although weaker than level of serum bile acids, positive correlation with preterm delivery.8
The level of transaminases elevation that is considered abnormal varies widely and has recently been brought into question.16 The determination of a more reliable cut-off value for liver tests is very important for diagnosing liver disease. There is also a debate as to whether or not different cutoff's are indicated for normal ranges of liver enzymes. Recently, it has been suggested that the upper normal limit for ALT should be decreased to 30 IU/L for men and 19 IU/L for women.23 Liver function tests can be lower in normal pregnancy than the reference ranges currently used. Girling, et al. in a prospective, cross-sectional study determines reference ranges for liver function tests that allow more precise identification of abnormal liver function in women with pre-eclampsia. Using the new ranges, the prevalence of elevated liver function tests was significantly higher in the pre-eclampsia group (54%) than in those with pregnancy induced hypertension (14%) (P < 0.01).24 We evaluated significance of lower cut-off values for ALT (31 U/L) and AST (30 U/L) in our ICP patients. Decreasing the ULN values for transaminases levels only minimally increased the ability to diagnose ICP. There are some limitations to our retrospective analysis. Relatively small number of healthy controls was included into study and specificity of the test was likely to be lower if a larger control set was used. ICP is a diagnosis of exclusion. In our study we excluded patients with other hepatobiliary and skin diseases. However, in a real world situation there may be coexisting latent hepatobiliary diseases during pregnancy that could also affect the specificity of the tests.25,26
ConclusionThe present study did not reveal any single specific and sensitive marker for reliable diagnosis of ICP despite of significantly higher serum TBA and CA levels and CA:CDCA ratio in ICP patients in comparison to healthy pregnant woman. Establishment of lower cut-off values for transaminases activity might only minimally increase the accuracy of diagnosing ICP.
Abbreviations- •
ALT: alanine aminotransferase.
- •
AP: alkaline phosphatase.
- •
AST: aspartate aminotransferase.
- •
CDCA: chenodeoxycholic acid.
- •
CA: cholic acid.
- •
DCA: deoxycholic acid.
- •
γ-GT: gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase.
- •
ICP: intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy.
- •
LCA: lithocholic acid.
- •
TBA: total bile acids.
- •
UDCA: ursodeoxycholic acid.