To know more about the potential roles of endophytic fungi in the formation mechanism of Daodi medicinal material, diversity and communities of culturable endophytic fungi in three types of tree peonies were investigated. Endophytic fungi of three types of tree peonies were isolated and identified. The diversity was analyzed. Bayesian trees constructed by MrBayes 3.2.6 after phylogenetic analysis of the ITS sequences. The endophytic fungi potential for synthesis of natural products was assessed by means of detecting NRPS and PKS gene sequences. In total, 364 endophytic fungi isolates representing 26 genera were recovered from Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’, Paeonia ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’, and Paeonia suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’. More culturable endophytic fungi appeared in P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ (206) compared with P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ (60) and P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ (98). The fungal community of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ had the highest richness and diversity. PKSs and NRPS detection rates of endophytic fungi from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ are both the highest among the three types of tree peonies. Results indicate that endophytic fungus is an important factor of Daodi Cortex Moutan forming, and endophytic fungi in peony are related to genuineness of Cortex Moutan.
Some traditional Chinese medicinal materials that are produced in specific geographic regions with designated natural conditions and ecological environment, and widely recognized as having better beneficial clinical therapeutic effects are called Daodi medicinal materials or geoherbs.1 As the essence of Chinese medicinal materials, Daodi medicinal materials have enjoyed a good reputation and have been playing an important role in treating disease and preserving health for thousands of years. From a biological point of view, heterogeneous individuals of the same species can be classified as either geoherbs or non-geoherbs, with their unique chemical constituents resulting from the interaction between minor polygenes and differential ecology.2 For instance, Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews, commonly called the tree peony, belongs to the Ranunculaceae family. The root bark of P. suffruticosa is called Cortex Moutan, which is a famous Chinese medicinal material and widely used in traditional Chinese medicine. Cortex Moutan produced from Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ in Tongling city, located in Anhui Province is considered a Daodi medicinal material (also called geoherbs). However, Cortex Moutan, which produced from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ that were transplanted in other regions of China or from other peony varieties, are called non-Daodi medicinal material (also called non-geoherbs). In recent years, researchers have studied the formation mechanism of Daodi Cortex Moutan from the perspectives of processing technique, environmental conditions, geochemistry, rhizosphere soil microorganism, trace elements, metabolism in animals, and obtained a series of important achievements. But the dominant factors of Daodi Cortex Moutan forming are not yet clear, the formation mechanism of Cortex Moutan needs further research.
Endophytic fungi are a group of diverse, fungal microorganisms that spend the whole or part of their life cycle in living plant tissues without causing any noticeable symptom of disease.3,4 It is noteworthy that endophytic fungi are ubiquitous in plant species that exist on the earth, and the endophytic colonization differs from tissues to tissues.5,6 They play important roles in the process of host plant growth and systematic evolution. Studies have shown that endophytic fungi have the capability to produce many kinds of identical or similar biologically active constituents as their host plants. These active constituents include antineoplastic paclitaxel,7 camptothecin,8 deoxypodophyllotoxin,9 the hypericin, etc.10 Polyketide synthetases (PKS) and non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) are multifunctional enzymes catalyzing the biosynthesis of structurally diverse bioactive natural products. Polyketides and non-ribosomal peptides have been immensely concerned over the past decades, and numbers of various novel polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide compounds have been found from endophytic fungi. The presence of PKS and NRPS in fungi suggest their potential in producing related compounds and guides in producing related natural products.11–13 Endophytic fungi are widely distributed in healthy plant tissues. In addition, endophytic fungi can produce secondary metabolites that are also biosynthesized by their host plants. Is there an interrelationship between endophytic fungi and the formation of Daodi medicinal material? Is there a difference in diversity and communities of endophytic fungi between Daodi medicinal material and non-Daodi medicinal material?
In this study, with the aim to know more about the tree peony endophytic fungal diversity and find evidence for the potential roles of endophytic fungi in the formation mechanism of Daodi medicinal material, our objectives were therefore to (1) isolate and identify genetically and morphologically filamentous endophytic fungi of tree peonies from two different regions, (2) investigate the variation in the diversity and communities of the endophytic fungi population of tree peonies (geoherbs and non-geoherbs), (3) the potential of endophytic fungi in producing bioactive natural products was estimated based on the detection of PKS and non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) genes.
Materials and methodsPlant sample collectionP. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ belongs to the section Moutan of the genus Paeonia and the family Paeoniaceae.14 Five-year-old P. ostii ‘Fen Dan’ plants, which were considered as the raw material of Daodi medicinal material, were collected from Phoenix Mountain Peony Garden, Tongling city, Anhui Province, China.
P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ seedlings had grown in Anhui province for two years, and then the two-year-old seedlings have been transplanted in Luoyang city for three years. These five-year-old peony samples were collected from peony cultivation base of National Flower Park of China, Luoyang, Henan, China. In order to distinguish them from the above peony variety, we named them as P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’. In essence, P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ are the same peony varieties, but their growing regions are different. P. ostii in Tongling city and Luoyang city were named after P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ and P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ respectively in the following narrative.
P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’, a typical purplish red-flowered cultivar of Chinese traditional P. suffruticosa cultivars, is particularly appreciated by Chinese. In our study, P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ was also collected in peony cultivation base of National Flower Park of China, Luoyang city, Henan Province, China. The three types of tree peonies were collected in October 2014. A total of 30 individuals of each kind of tree peonies were collected. All plant materials were immediately brought to the laboratory, stored at 4°C in refrigerator and preprocessed within 24h. The tree peonies endophytic fungi were isolated according to the surface sterilization method described by Li Peng et al.15
Isolation and identification of endophytic fungiThe endophytic fungi were incubated on potato dextrose agar (PDA: 200g scrubbed and diced potatoes, 15g dextrose, 20g agar, and 1L distilled water) plates at 25°C in the dark until the colonies reached the rim of the dishes (9cm in diameter). All fungi isolates were examined periodically, and were classified into morphotypes based on their growth rates and morphological and microscopic characteristics (including shape of the mycelium, texture of the mycelium surface, production of spores (conidia, blastospores, sporangiospores or ascospores), color of the fungi, production of pigments and their diffusion into the medium). A total of 156 morphotypes were then identified based on the ITS sequence data. Mycelia of the fungal endophytes were ground completely with liquid nitrogen in a sterile mortar, and Genomic DNA extraction from all endophytic fungi was performed using a DN41 rapid DNA extraction kit (Aidlab Biotechnologies Co. Ltd., Beijing, PR China) following the manufacturer's recommendations for fungi. The internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region was amplified with universal primers ITS1(5′TCCGTTGGTGAAC CTGCGG3′) and ITS4(5′TCCTCCGGTTATTGATATGC3′). PCR mixture contained 12.5μL 2× Taq PCR Master Mix (Taq DNA Polymerase, Buffer, MgCl2 and deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) were contained), 1μL DNA sample, 1μL of each primer and 9.5μL double distilled water. The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: initial pre-heating at 94°C for 3min, 30 cycles of 94°C for 30s, 58°C for 30s, 72°C for 30s, and a final extension at 72°C for 10min. After amplification, the PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on a 1.2% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide (0.5ng/mL agarose) by stirring gently for 15min; the products were then visualized under UV light. The PCR products were separated on 1% (w/v) agarose gel and purified using a DNA Gel Exaction Kit (AXYGEN, Suzhou, PR China). The resulting DNA was sequenced directly using the same primers (Beijing Honor Tech Co. Ltd., Beijing, PR China).
The ITS sequence data of the endophytic fungi were submitted to the GenBank database. The ITS sequence was compared with that of the most closely-related fungal species (identity values higher than 95%) in the NCBI database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) using the BLAST program, in consultation with observed colony and spore morphology to confirm the taxonomic status of the investigated fungal isolate. The sequence of Psilocybe cubensis was used as an outgroup. Bayesian trees constructed by PAUP 4.0b10 and MrBayes 3.2.6 after phylogenetic analysis of the ITS sequence data.
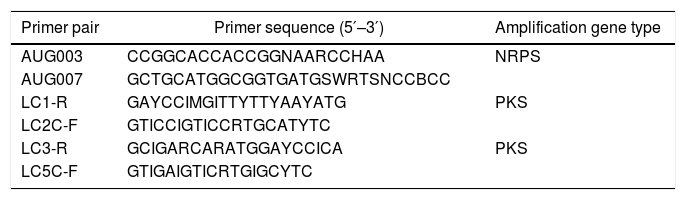
Screening of PKS and NRPS genes in tree peonies endophytic fungiThe highly conserved sequences of β-ketoacyl synthase (KS) domains are shared among all PKSs; thus, the KS domains are useful in screening for PKSs in fungi. Therefore, LC series primers (Table 1) were used to detect PKS genes in the fungal isolates.16 Similarly, the most conserved A domain can be used for PCR primer design to survey NRPSs gene diversity. Primers AUG003 and AUG007 (Table 1) were used for amplification of NRPS genes.17 The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: initial pre-heating at 94°C for 5min, 35 cycles of 95°C for 1min, 55°C for 1.5min, 72°C for 3min, and a final extension at 72°C for 10min. After amplification, the PCR products were inspected by electrophoresis on a 1.2% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide (0.5ng/mL agarose) by stirring gently for 15min; the products were then visualized under UV light. Prior to cloning, PCR products were purified with DNA Gel Extraction Kit (San Prep SK8131, PR China). The sequences encoding the PKS or NRPS were cloned into a pUCm-T cloning vector (Sangon SK2211, PR China) and transformed into competent Escherichia coli cell (B529303 Ultra-Competent Cell Preps Kit, PR China) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The purified plasmid (using SanPrep Column Plasmid Mini-Preps Kit B518191, PR China) was sequenced.
Date analysisThe colonization rate (CR) was calculated according to the method of Hata and Futai,18 CR=NCOL/Nt where NCOL is the number of segments colonized by each endophytic fungi; Nt is the total number of segments. The isolation rate (IR) was calculated as follow: IR=the number of EF isolated/the total number of fragments incubated.19 The Shannon diversity index (H′) and the Simpson's diversity index (D) were used to analyze the diversity of endophytic fungi and calculated as follows: Shannon diversity index, Simpson's diversity index, where k is the total number of fungal taxon, and Pi is the relative abundance of taxon i. Evenness values were calculated following Pielou's Evenness Index. Pielou's Evenness Index J=H/log (S), where H is the Shannon–Weaver diversity index and S is the number of species (species richness).20 Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics Software (Version 20). The fungal phylotypes richness, the detection rates of PKSs and NRPS were subjected to ANOVA to test for significant differences between different types of tree peonies.
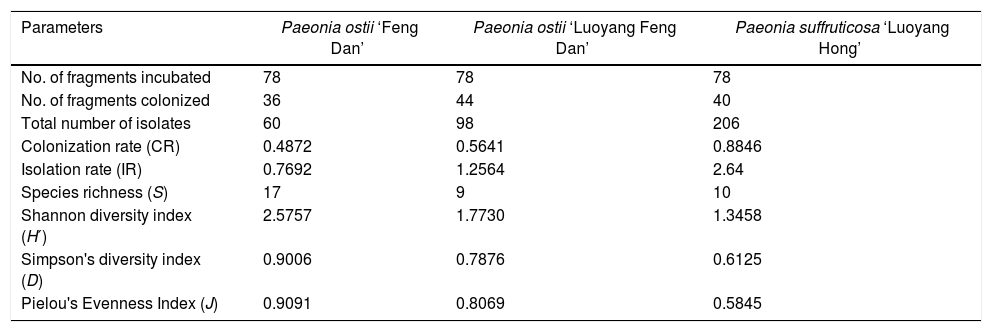
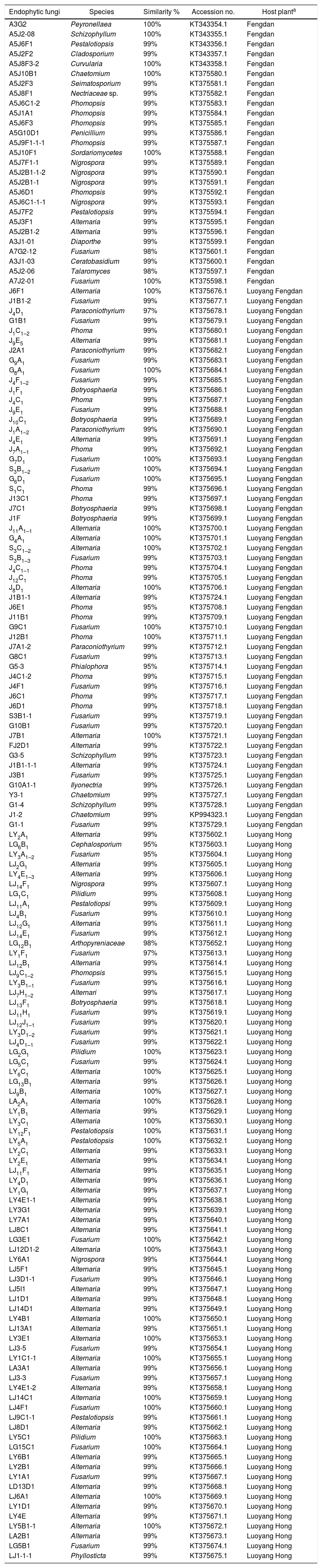
ResultsAbundance and diversity of endophytic fungiA total of 364 endophytic fungal isolates were isolated from asymptomatic leaf, stem, and root segments of tree peonies plants following a standard isolation protocol. Results showed that P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ exhibited the highest number of endophytic fungi (206 isolates), followed by P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ (98 isolates), P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ (60 isolates) (p<0.05) (Table 2). The colonization rate of P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ was the highest, flowed by P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’, while P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ is the lowest. A similar situation exists with the IR. The isolation rate of P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ was significant higher than that of P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’. The 364 isolated endophytic fungi were assigned to 156 morphospecies. All the morphotypes were identified based on the morphological characteristics and ITS sequence data (Table 3). Multiple alignment of the ITS sequence data was performed by Clustal W of MEGA ver. 6. MrModeltest 2.1 was used to choose the substitution model that best fit the data using the AIC criterion. The best model computed for Bayesian analysis was GTR+G. Bayesian analyses used one cold and three heated Monte Carlo Markov chains in two simultaneous runs. Bayesian analyses was computed with MrBayes 3.2.6 and carried out using 1.5×107 generations and a sample frequency of 100. The burn-in ratio was set at 0.25 (Fig. 1).
Colonization and isolation rate, species richness of tree peonies endophytic fungi.
| Parameters | Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ | Paeonia ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ | Paeonia suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of fragments incubated | 78 | 78 | 78 |
| No. of fragments colonized | 36 | 44 | 40 |
| Total number of isolates | 60 | 98 | 206 |
| Colonization rate (CR) | 0.4872 | 0.5641 | 0.8846 |
| Isolation rate (IR) | 0.7692 | 1.2564 | 2.64 |
| Species richness (S) | 17 | 9 | 10 |
| Shannon diversity index (H′) | 2.5757 | 1.7730 | 1.3458 |
| Simpson's diversity index (D) | 0.9006 | 0.7876 | 0.6125 |
| Pielou's Evenness Index (J) | 0.9091 | 0.8069 | 0.5845 |
Taxonomic affinities of tree peonies endophytic fungi.
| Endophytic fungi | Species | Similarity % | Accession no. | Host planta |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A3G2 | Peyronellaea | 100% | KT343354.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2-08 | Schizophyllum | 100% | KT343355.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J6F1 | Pestalotiopsis | 99% | KT343356.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2F2 | Cladosporium | 99% | KT343357.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J8F3-2 | Curvularia | 100% | KT343358.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J10B1 | Chaetomium | 100% | KT375580.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2F3 | Seimatosporium | 99% | KT375581.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J8F1 | Nectriaceae sp. | 99% | KT375582.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J6C1-2 | Phomopsis | 99% | KT375583.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J1A1 | Phomopsis | 99% | KT375584.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J6F3 | Phomopsis | 99% | KT375585.1 | Fengdan |
| A5G10D1 | Penicillium | 99% | KT375586.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J9F1-1-1 | Phomopsis | 99% | KT375587.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J10F1 | Sordariomycetes | 100% | KT375588.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J7F1-1 | Nigrospora | 99% | KT375589.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2B1-1-2 | Nigrospora | 99% | KT375590.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2B1-1 | Nigrospora | 99% | KT375591.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J6D1 | Phomopsis | 99% | KT375592.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J6C1-1-1 | Nigrospora | 99% | KT375593.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J7F2 | Pestalotiopsis | 99% | KT375594.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J3F1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375595.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2B1-2 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375596.1 | Fengdan |
| A3J1-01 | Diaporthe | 99% | KT375599.1 | Fengdan |
| A7G2-12 | Fusarium | 98% | KT375601.1 | Fengdan |
| A3J1-03 | Ceratobasidium | 99% | KT375600.1 | Fengdan |
| A5J2-06 | Talaromyces | 98% | KT375597.1 | Fengdan |
| A7J2-01 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375598.1 | Fengdan |
| J6F1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375676.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1B1-2 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375677.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4D1 | Paraconiothyrium | 97% | KT375678.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G1B1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375679.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1C1–2 | Phoma | 99% | KT375680.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J9E5 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375681.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J2A1 | Paraconiothyrium | 99% | KT375682.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G9A1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375683.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G8A1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375684.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4F1–2 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375685.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1F1 | Botryosphaeria | 99% | KT375686.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4C1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375687.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J9E1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375688.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J10C1 | Botryosphaeria | 99% | KT375689.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1A1–2 | Paraconiothyrium | 99% | KT375690.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4E1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375691.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J7A1–1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375692.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G7D1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375693.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| S3B1–2 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375694.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G6D1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375695.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| S1C1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375696.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J13C1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375697.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J7C1 | Botryosphaeria | 99% | KT375698.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1F | Botryosphaeria | 99% | KT375699.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J11A1–1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375700.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G4A1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375701.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| S3C1–2 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375702.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| S3B1–3 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375703.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4C1–1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375704.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J12C1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375705.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J8D1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375706.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1B1-1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375724.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J6E1 | Phoma | 95% | KT375708.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J11B1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375709.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G9C1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375710.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J12B1 | Phoma | 100% | KT375711.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J7A1-2 | Paraconiothyrium | 99% | KT375712.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G8C1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375713.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G5-3 | Phialophora | 95% | KT375714.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4C1-2 | Phoma | 99% | KT375715.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J4F1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375716.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J6C1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375717.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J6D1 | Phoma | 99% | KT375718.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| S3B1-1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375719.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G10B1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375720.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J7B1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375721.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| FJ2D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375722.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G3-5 | Schizophyllum | 99% | KT375723.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1B1-1-1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375724.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J3B1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375725.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G10A1-1 | Ilyonectria | 99% | KT375726.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| Y3-1 | Chaetomium | 99% | KT375727.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G1-4 | Schizophyllum | 99% | KT375728.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| J1-2 | Chaetomium | 99% | KP994323.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| G1-1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375729.1 | Luoyang Fengdan |
| LY2A1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375602.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG6B1 | Cephalosporium | 95% | KT375603.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY3A1–2 | Fusarium | 95% | KT375604.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ2G1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375605.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY4E1–3 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375606.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ14F1 | Nigrospora | 99% | KT375607.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG1C1 | Pilidium | 99% | KT375608.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ11A1 | Pestalotiopsi | 99% | KT375609.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ4B1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375610.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ12G1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375611.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ14E1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375612.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG12B1 | Arthopyreniaceae | 98% | KT375652.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY1F1 | Fusarium | 97% | KT375613.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ12B1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375614.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ9C1–2 | Phomopsis | 99% | KT375615.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY3B1–1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375616.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ7H1–2 | Alternari | 99% | KT375617.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ13F1 | Botryosphaeria | 99% | KT375618.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ11H1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375619.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ12J1–1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375620.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY3D1–2 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375621.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ4D1–1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375622.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG2G1 | Pilidium | 100% | KT375623.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG5C1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375624.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY6C1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375625.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG13B1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375626.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ9B1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375627.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LA2A1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375628.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY1B1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375629.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY3C1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375630.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY12F1 | Pestalotiopsis | 100% | KT375631.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY5A1 | Pestalotiopsis | 100% | KT375632.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY2C1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375633.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY2E1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375634.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ11F1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375635.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY4D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375636.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY1G1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375637.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY4E1-1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375638.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY3G1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375639.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY7A1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375640.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ8C1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375641.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG3E1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375642.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ12D1-2 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375643.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY6A1 | Nigrospora | 99% | KT375644.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ5F1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375645.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ3D1-1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375646.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ5I1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375647.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ1D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375648.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ14D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375649.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY4B1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375650.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ13A1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375651.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY3E1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375653.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ3-5 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375654.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY1C1-1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375655.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LA3A1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375656.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ3-3 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375657.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY4E1-2 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375658.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ14C1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375659.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ4F1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375660.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ9C1-1 | Pestalotiopsis | 99% | KT375661.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ8D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375662.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY5C1 | Pilidium | 100% | KT375663.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG15C1 | Fusarium | 100% | KT375664.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY6B1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375665.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY2B1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375666.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY1A1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375667.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LD13D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375668.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ6A1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375669.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY1D1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375670.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY4E | Alternaria | 99% | KT375671.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LY5B1-1 | Alternaria | 100% | KT375672.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LA2B1 | Alternaria | 99% | KT375673.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LG5B1 | Fusarium | 99% | KT375674.1 | Luoyang Hong |
| LJ1-1-1 | Phyllosticta | 99% | KT375675.1 | Luoyang Hong |
ITS sequences based on BLAST search through GenBank.
Phylogenetic tree based on the ITS1, 5.8S and ITS2 region of rDNA obtained from endophytic fungi of three types of tree peonies. The tree was constructed via the Bayesian inference method. An individual of each taxon isolated was used in the construction of the clustering together with a reference sequence retrieved from GenBank (●). The fungus Psilocybe cubensis was used as outgroup for the construction of the tree.
To characterize the biodiversity of our samples, we calculated Species richness (S), Shannon diversity index (H′), Simpson's diversity index (D), and Pielou evenness index (J). The values obtained by these tests (17, 2.5757, 0.9006, and 0.9091, based on P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’; 9, 1.7730, 0.7876, and 0.8069, based on P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’; 10, 1.3458, 0.6125, and 0.5845, based on P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’, respectively) were shown in Table 2.
Community composition of endophytic fungiIn each of the three types of tree peonies, the composition of the endophytic fungi communities exhibited a high degree of variability. Among those detected, for P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’, a total of 17 different genera of endophytic fungi were isolated, Phomopsis was the dominant genus with relative frequency of 19.2%, followed by Nigrospora, Alternaria and Pestalotiopsis with relative frequencies of 15.4%, 7.7% and 7.7%, respectively; for P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’, a total of 9 different genera of endophytic fungi were isolated, Fusarium was the dominant genus with relative frequency of 27.4%, followed by Phoma, Alternaria and Paraconiothyrium with relative frequencies of 23.5%, 19.6%, and 9.8%, respectively; for P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’, a total of 10 different genera of endophytic fungi were isolated, Alternaria was the dominant genus with relative frequency of 55.7%, followed by Fusarium and Pestalotiopsis with relative frequencies of 25.7% and 5.8%, respectively (Fig. 2). A total of 26 different fungal genera were recovered from three types of tree peonies, of which, ten (38.5%) were exclusively isolated from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’, four (15.4%) were only recovered from P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’, four (15.4%) were merely obtained from P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’, and eight (30.8%) were jointly found in the three types of tree peonies (Fig. 2). On the whole, the stems of tree peonies exhibited the highest number of endophytic fungi (221 isolates), followed by the leaves (85 isolates) and roots (58 isolates).
Pie charts show the relative abundance of the dominant culturable endophytic fungi phyla in three types of tree peonies. Venn's diagrams showing unique and shared genus in culturable endophytic fungi of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’, P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ samples.
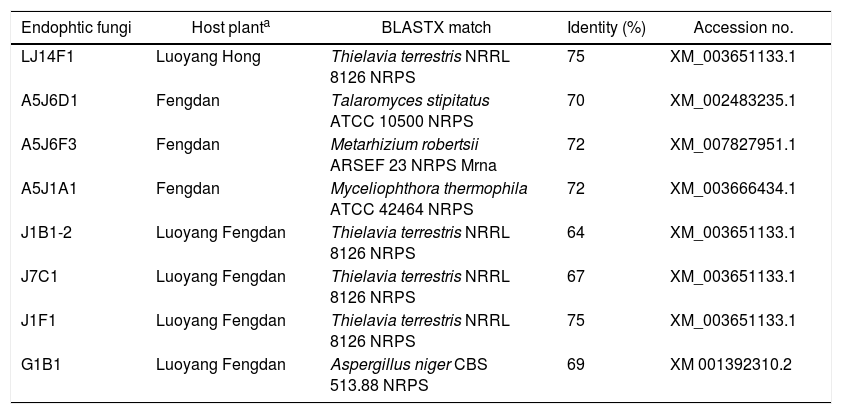
Degenerate PCRs were used to detect putative NRPS and PKS gene sequences originating from fungal endophytes in the DNA extracts. Amplification of fungal KS domains and A domains was confirmed via sequencing and BLASTX (translated) analysis. Based on the BLASTX analysis, a total of 69 endophytic fungi isolated from the three types of tree peonies were detected to contain fungal KS domain sequences (∼700bp). The amplified sequences possessed between 90% and 100% amino acid identity to known fungal PKSs. The detection rates of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi, P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi, P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ are 48.15%(13/27), 41.07%(23/56), and 44.59%(33/74) (p<0.05), respectively (Table 4). A total of 8 endophytic fungi isolated from the three types of tree peonies were detected to contain fungal A domains sequences (∼1500bp). The amplified sequences possessed between 64% and 75% amino acid identity to known fungal NRPS. The detection rates of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi, P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi, P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ endophytic fungi are 11.11% (3/27), 7.14% (4/56), and 1.35% (1/74) (p<0.05), respectively (Table 5).
PKS genes identified with degenerate PCR primers.
| Endophtic fungi | Host planta | BLASTX match | Identity (%) | Accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5J9F1-1-1 | Fengdan | Dothiorella aegiceri putative PKS | 99 | ABS85549.1 |
| A7J201 | Fengdan | Dipiodia seriata putative PKS | 99 | KKY20157.1 |
| A5J1A1 | Fengdan | Dothiorella aegiceri putative PKS | 99 | ABS85549.1 |
| A5J3F1 | Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 100 | AEH76763.1 |
| A5J7F2 | Fengdan | Cladosporium phlei non-reducing PKS | 99 | AFP89389.1 |
| A5J6C1-2 | Fengdan | Dothiorella aegiceri putative PKS | 99 | ABS85549.1 |
| A5J2B1-1 | Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 100 | AEH76763.1 |
| A5J6D1 | Fengdan | Dothiorella aegiceri putative PKS | 98 | ABS85549.1 |
| A5J2B1-1-2 | Fengdan | Pestalotiopsis malicola PKS | 94 | AGT56219.1 |
| A5J10F1 | Fengdan | Ascochyta anemones PKS | 99 | AGF50217.1 |
| A5G10D1 | Fengdan | Talaromyces marneffei ATCC 18224 conidial PKS | 98 | XP 002147717.1 |
| A5J8F3-2 | Fengdan | Bipolaris maydis PKS | 99 | AAR90272.1 |
| A5J6F3 | Fengdan | Dothiorella aegiceri putative PKS | 99 | ABS85549.1 |
| J13C1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Phoma sp. F41 PKS | 98 | AFH77855.1 |
| J6D1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta anemones PKS | 99 | AGF50217.1 |
| J4E1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| J6F1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| J12B1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 99 | ACS74449.1 |
| J9E5 | Luoyang Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| J10C1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Diplodia seriata putative PKS | 98 | KKY20157.1 |
| J4C1-2 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 98 | ACS74449.1 |
| J2A1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Bipolaris maydis PKS | 97 | AAR90272.1 |
| J6C1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 99 | ACS74449.1 |
| J4D1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Bipolaris maydis PKS | 97 | AAR90272.1 |
| J1F1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Diplodia seriata putative PKS | 98 | KKY20157.1 |
| J1A1-2 | Luoyang Fengdan | Bipolaris maydis PKS | 97 | AAR90272.1 |
| J1B1-2 | Luoyang Fengdan | Diplodia seriata putative PKS | 99 | KKY20157.1 |
| J4C1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 99 | ACS74449.1 |
| G5-3 | Luoyang Fengdan | Marssonina brunneaf sp. ‘multigermtubi’ MB-m1 PKS | 94 | XP007295542.1 |
| J7C1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Diplodia seriata putative PKS | 99 | KKY20157.1 |
| J11B1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 98 | ACS74449.1 |
| S3C1-2 | Luoyang Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| J8D1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 100 | AEH76763.1 |
| J4C1-1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 99 | ACS74449.1 |
| G4A1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| J6E1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Ascochyta rabiei 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene PKS | 98 | ACS74449.1 |
| LJ14F1 | Luoyang Hong | Trichoderma sp. CBMAI 1018 PKS | 93 | ADY75766.1 |
| LJ12B1 | Luoyang Hong | Conidial yellow piqment biosynthesis PKS | 99 | XP001933656.1 |
| LJ13F1 | Luoyang Hong | Dipiodia seriata putative PKS | 99 | KKY20157.1 |
| LY4B1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria sp. ALF3-2 PKS | 100 | AIR77264.1 |
| LY7A1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata putative 6-MSA-type PKS | 93 | BAG80613.1 |
| LJ9B1 | Luoyang Hong | Conidial yellow piqment biosynthesis PKS | 99 | XP001933656.1 |
| LY1G1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY2A1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY4E1-1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LJ8D1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY4E1-3 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LJ12G1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY2E1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LA2A1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY1C1-1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY4D1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LJ12D1-2 | Luoyang Hong | Humicolopsis cephalosporioides PKS | 90 | AGH27151.1 |
| LG1C1 | Luoyang Hong | Humicolopsis cephalosporioides PKS | 90 | AGH27151.1 |
| LJ7H1-2 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 100 | AEH76763.1 |
| LA3A1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LJ13A1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY6C1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LJ2G1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LG2G1 | Luoyang Hong | Humicolopsis cephalosporioides PKS | 90 | AGH27151.1 |
| LY5C1 | Luoyang Hong | Humicolopsis cephalosporioides PKS | 90 | AGH27151.1 |
| LJ8C1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY3G1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LG12B1 | Luoyang Hong | Dipiodia seriata putative PKS | 98 | KKY20157.1 |
| LJ9C1-2 | Luoyang Hong | Dothiorella aegiceri putative PKS | 99 | ABS85549.1 |
| LY2C1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LY1B1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 99 | AEH76763.1 |
| LJ11H1 | Luoyang Hong | Dipiodia seriata putative PKS | 98 | KKY20157.1 |
| LY3C1 | Luoyang Hong | Alternaria alternata PKS | 100 | AEH76763.1 |
NRPS genes identified with degenerate PCR primers.
| Endophtic fungi | Host planta | BLASTX match | Identity (%) | Accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LJ14F1 | Luoyang Hong | Thielavia terrestris NRRL 8126 NRPS | 75 | XM_003651133.1 |
| A5J6D1 | Fengdan | Talaromyces stipitatus ATCC 10500 NRPS | 70 | XM_002483235.1 |
| A5J6F3 | Fengdan | Metarhizium robertsii ARSEF 23 NRPS Mrna | 72 | XM_007827951.1 |
| A5J1A1 | Fengdan | Myceliophthora thermophila ATCC 42464 NRPS | 72 | XM_003666434.1 |
| J1B1-2 | Luoyang Fengdan | Thielavia terrestris NRRL 8126 NRPS | 64 | XM_003651133.1 |
| J7C1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Thielavia terrestris NRRL 8126 NRPS | 67 | XM_003651133.1 |
| J1F1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Thielavia terrestris NRRL 8126 NRPS | 75 | XM_003651133.1 |
| G1B1 | Luoyang Fengdan | Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88 NRPS | 69 | XM 001392310.2 |
In this study, endophytic fungal isolated from three types of tree peonies were identified, and their communities’ composition were analyzed. The research results indicate that the biodiversity of fungal endophytes in the three types of tree peonies exhibited a high degree of difference. P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ yielded low abundance strains and showed lower CR and IR, yet the Species richness (S), Shannon diversity index (H′), Simpson's diversity index (D) of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ were all higher than that of P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ (Table 2). There are altogether 26 different fungal genera recovered from three types of tree peonies, of which, 10 different fungal genera were exclusively isolated from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’, 4 different fungal genera were only recovered from P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’, 4 different fungal genera were merely obtained from P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’, and 8 different fungal genera were jointly found in the three types of tree peonies. Compared with P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’, P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ which is the raw material of Daodi Cortex Moutan has more types of endophytic fungi. The diversity of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi is the highest, flowed by that of P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’, the diversity of endophytic fungi from the P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ is the lowest. In this study, P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ and P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ are essentially the same variety of tree peonies, they just grow in the different geographical environment. But the diversity of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi is significantly higher than that of P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ endophytic fungi. P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’ are the different varieties of tree peonies, they grow in the same geographical environment. There is not much difference between the endophytic fungi diversity of P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’. The results of the above studies suggest that, compared with the variety of tree peonies, geographical environment plays a more important role in affecting the diversity of tree peonies endophytic fungi.
From the perspective of endophytic fungi community composition, all the three types of tree peonies have different dominant genera. Ecological or environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, illumination, geographic location, and vegetation significantly affected the distribution pattern and population structure of the endophytic fungi.21Phomopsis is the dominant genus in the endophytic fungi community of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’. That may have relevance to soil nutrition and geochemistry characteristic of Tongling city, Anhui Province, China. The study on the soil Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn at the copper-tailings reservoir of Tongling City showed that the Cu and Cd contents in soil were 4.36–14.43 and 3.67–3.86 times of the 2nd China national standard for soil environmental quality, respectively.22,23Phomopsis sp. is an ascomycete, that has attracted researcher's attention as a potential tool for heavy metal (copper, lead, zinc, etc.) contamination remediation. Research results indicate that after 24h contact time, up to 870mmol/g of lead, 390mmol/g of copper, 230mmol/g of cadmium, 150mmol/g of zinc and 110mmol/g of nickel ions are adsorbed into Phomopsis sp. biomaterial.24,25 In addition, endophytic fungi of Phomopsis sp. are excellent potential sources of novel, bioactive natural products for exploitation in medicine, agriculture, and industry.26,27Fusarium and Alternaria are the dominant genera in the endophytic fungi community of P. ostii ‘Luoyang Feng Dan’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Luoyang Hong’. They are the major plant pathogenic genera and the common genera in plant endophytic fungi community.28–31
Over centuries of treating disease and attempting to preserve health, ancestors of the Chinese people developed the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). In addition, China also has abundant natural resources of medicinal materials, which are the material basis for the application of TCM theory in preventing and treating disease. As the essence of Chinese medicinal materials, Daodi medicinal material has been playing an important role in treating disease and preserving health for thousands of years.1 Cortex Moutan, which was produced from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ in Tongling city, located in Anhui Province, is considered as Daodi medicinal material. However, Cortex Moutan, which was produced from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ that were transplanted in other regions of China or from other peony varieties, is called non-Daodi medicinal material. To date, the dominant factor of Daodi Cortex Moutan forming is not yet clear. Bioactive components are the material basis for Daodi medicinal material to exert positive effect in preventing and treating disease. The most intrinsic difference between Daodi medicinal material and non-Daodi medicinal material is the difference in the types and amounts of bioactive components in medicinal plant. The NRPS and PKS are responsible for synthesizing many secondary metabolites that exhibit an important biological activity and may be valuable drugs.32 NRPS and PKS genomic analysis of the endophytic fungus reveals its potential for synthesis of natural products.32,33 In this study, NRPS and PKS gene sequences originating from fungal endophytes of three types of tree peonies were detected by Degenerate PCRs. As can be seen from the results (Tables 4 and 5), the PKSs and NRPS detection rates of endophytic fungi from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’, which is the raw material of Daodi Cortex Moutan, are both the highest among the three types of tree peonies. The results of the above studies indicate that the endophytic fungi from P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ have bigger potential for synthesis of natural products.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
The authors wish to acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China for financial support (project number 31302133).