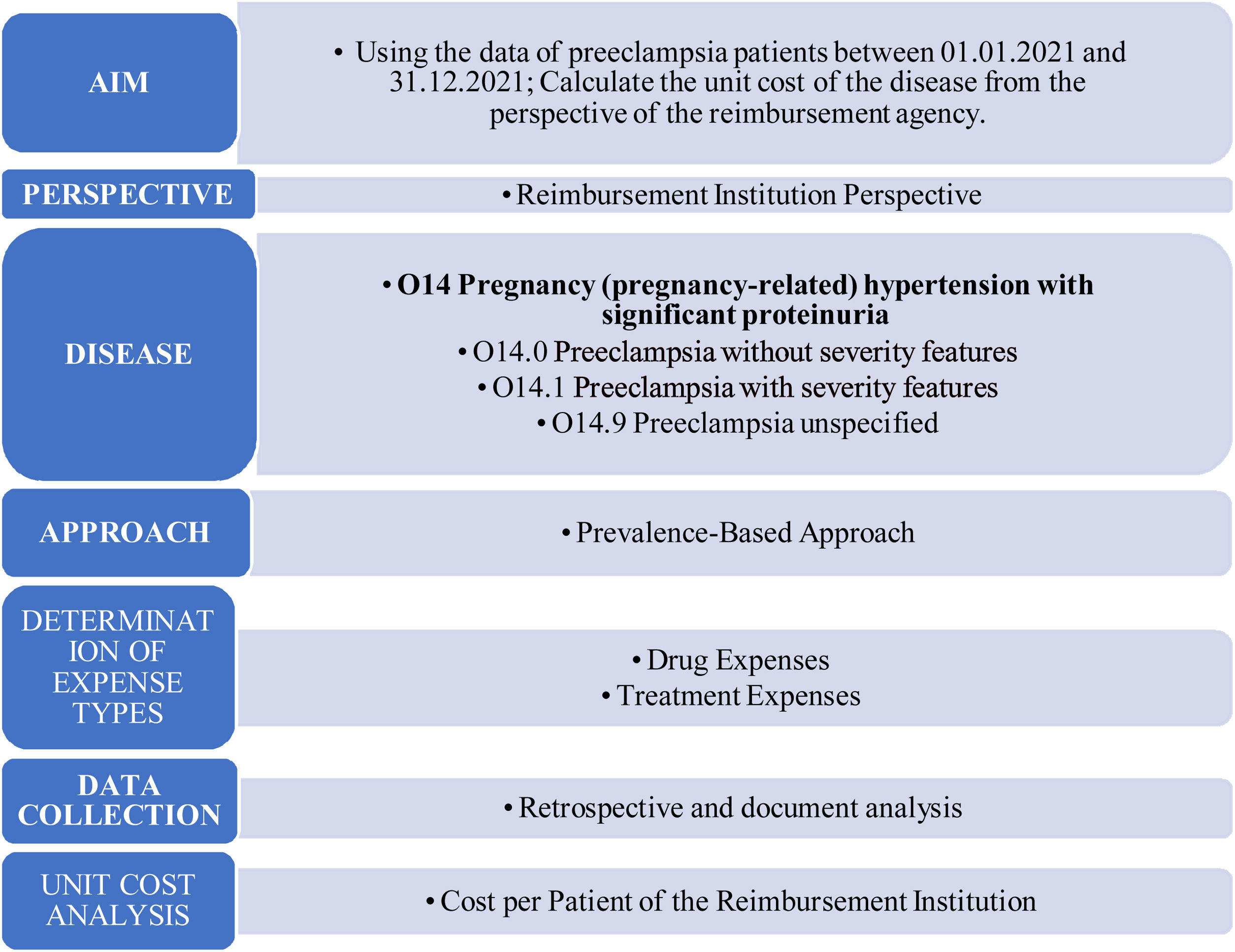
The aim of this study is to determine the financial burden of preeclampsia (PE) from a single institution's perspective and then determine the cost of the illness from the reimbursement institution perspective and finally draw a regression model that predicts the annual cost of a patient.
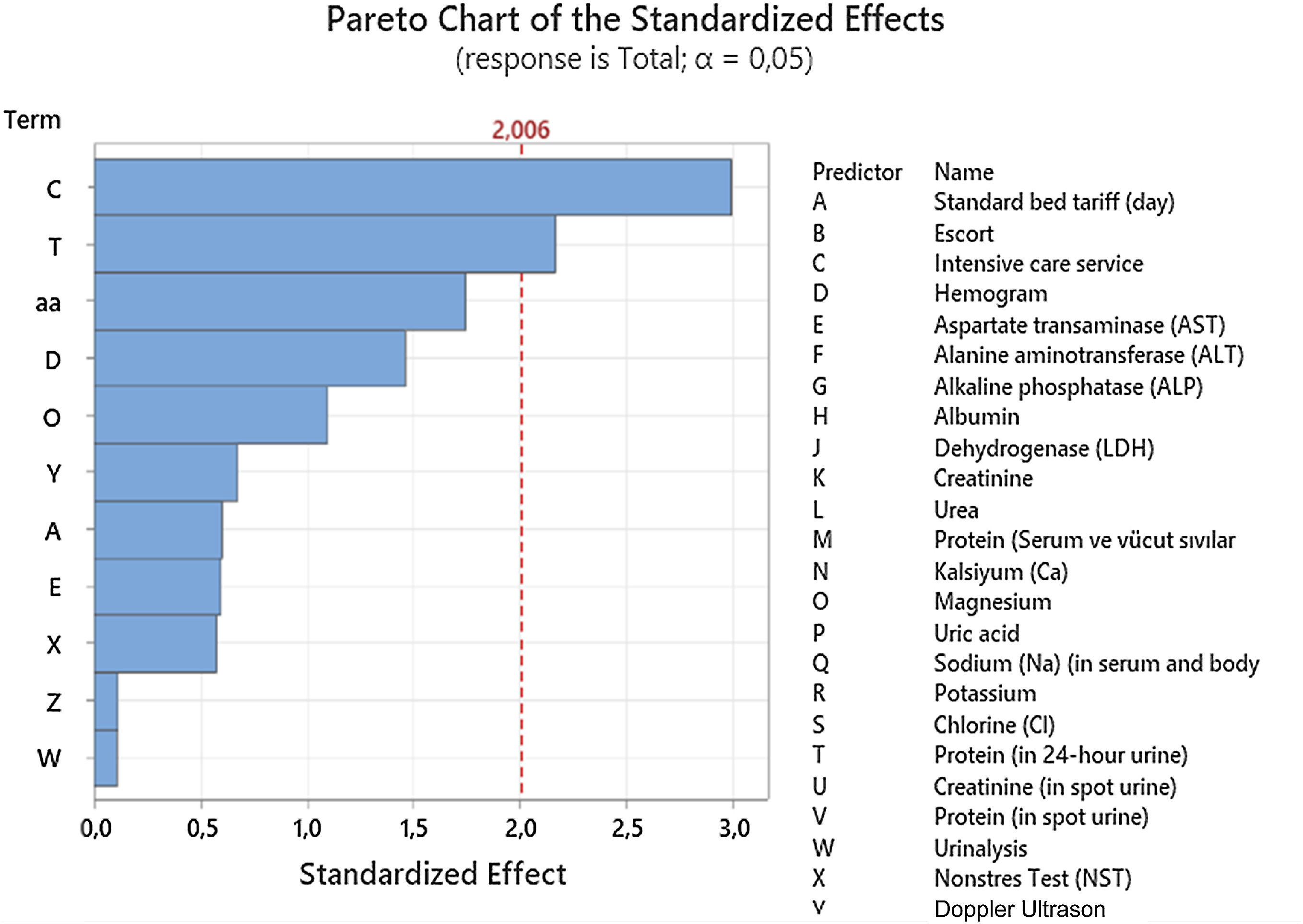
Materials and methodsThe research is a descriptive and cross-sectional type of research and a retrospective cost analysis. Patients diagnosed with PE in 2021 were included in the study. For the regression analysis of the study, a dataset with 29 parameters belonging to 65 patients was created. Regression models were built on top of it.
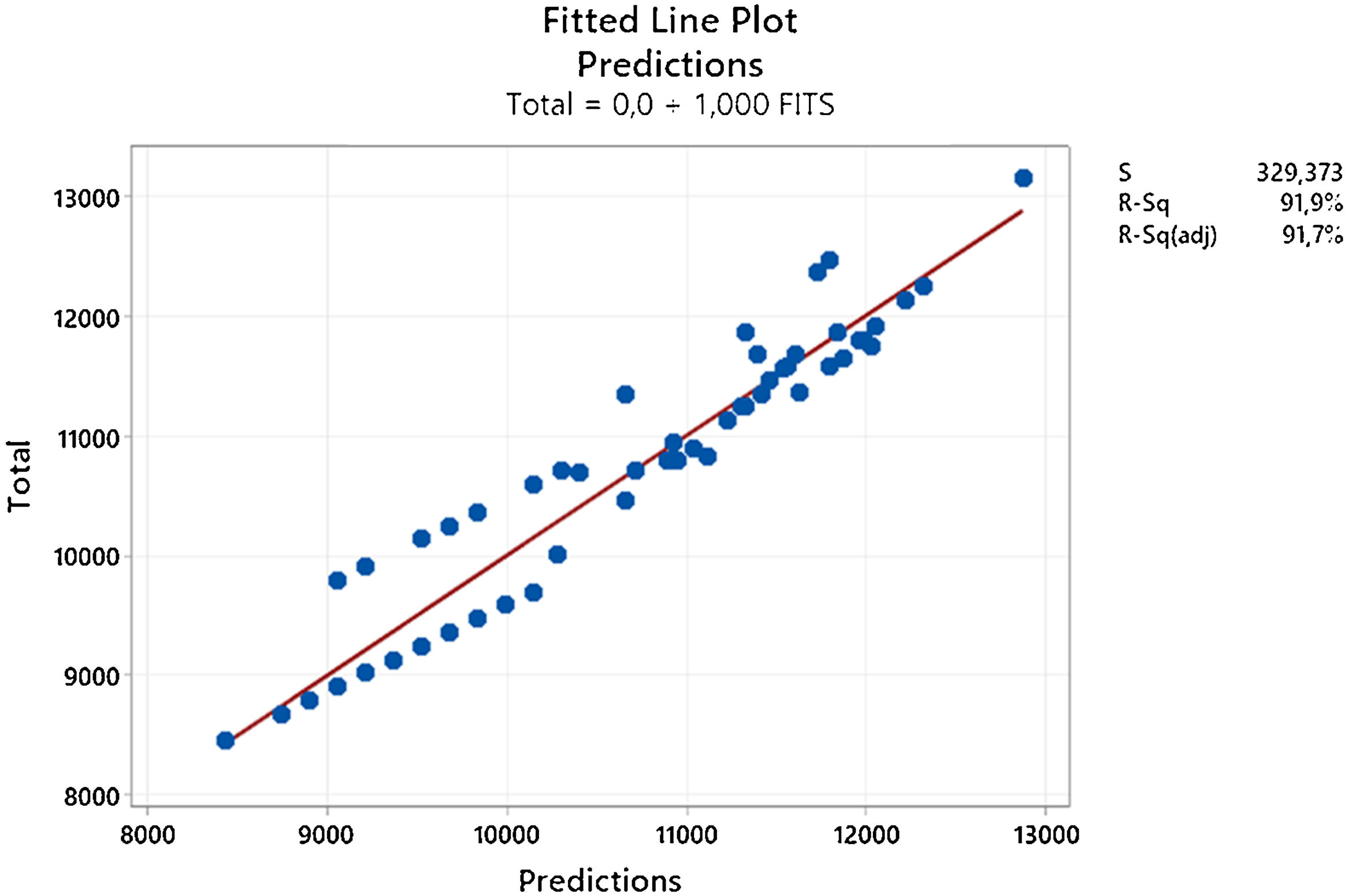
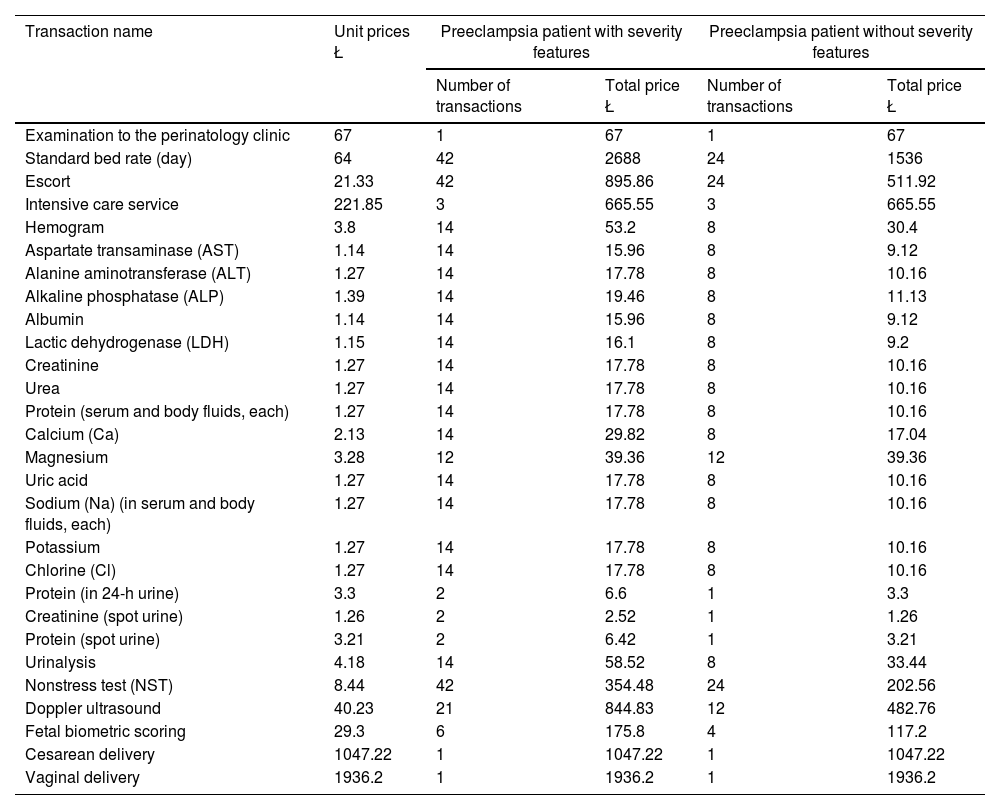
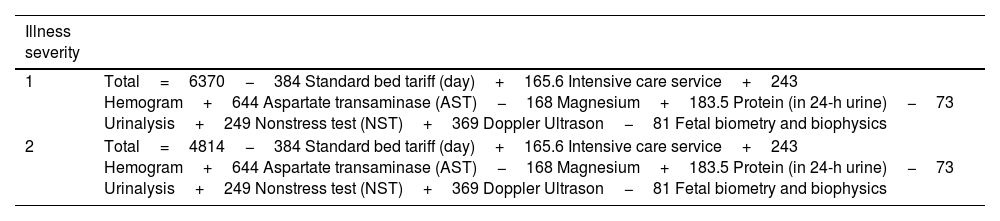
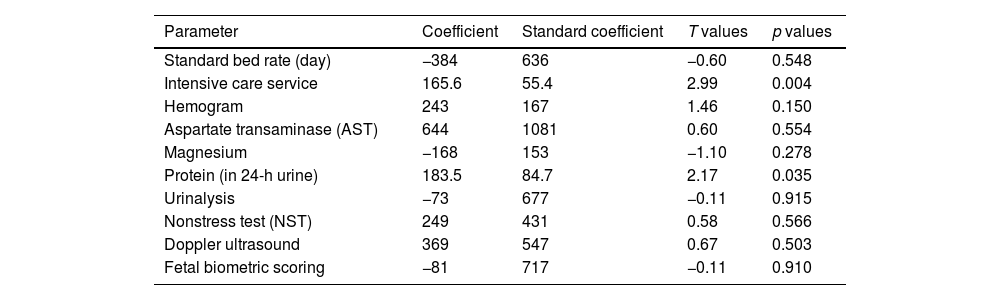
ResultsIn our study, per-patient expenses of PE patients from the perspective of the reimbursement institution were calculated and presented as average costs; severe PE patient with cesarean section 7598.5 Ł ($769.8), severe PE patient with normal vaginal delivery 8487.48 Ł (1050.43 $), mild PE patient with cesarean section 5331.67 Ł ($659.86) and mild PE patient with normal vaginal delivery was calculated as 6220.65 Ł (769.88 $). In the study, different regression formulas were created for the two groups of PE. The created regression model had an R2 score of 91.85%.
ConclusionThe actors involved in the management of the disease should determine the cost-effectiveness of the disease by using the financial data of the patients and choose the right approach. Health costs in Turkey differ from the parameters in the European Union economy. Therefore, there are lower health costs. The financial findings of the disease are a guide for health policy makers, health managers and researchers.
El objetivo de este estudio es determinar la carga financiera de la preeclampsia (PE) desde la perspectiva de una única institución, para luego determinar los costes de la enfermedad desde la perspectiva de la institución de reembolso, y así elaborar un modelo de regresión que prediga el coste anual de un paciente.
Materiales y métodosSe trata de una investigación de tipo descriptivo, transversal y de un análisis retrospectivo de costes. Se incluyeron en el estudio los pacientes diagnosticados de PE en 2021. Para el análisis de regresión del estudio se creó un conjunto de datos con 29 parámetros que pertenecían a 65 pacientes diferentes. Los modelos de regresión se construyeron en base a este.
ResultadosEn nuestro estudio, los gastos por paciente de las pacientes con PE desde la perspectiva de la institución de reembolso se calcularon y presentaron como costos promedio; paciente con PE grave con cesárea 7598.5 (769.8 $), paciente con PE grave con parto vaginal normal 8487.48 (1050.43 $), paciente con PE leve con cesárea 5331.67 (659.86 $) y paciente con PE leve con parto vaginal normal se calculó como 6220.65 (769.88 $). En el estudio se crearon diferentes fórmulas de regresión para los dos grupos de PE. El modelo de regresión creado tuvo una puntuación R2 de 91,85%.
ConclusiónLos agentes implicados en la gestión de la enfermedad tendrán que determinar su rentabilidad utilizando los datos económicos de los pacientes y elegir el enfoque adecuado. Los costes sanitarios en Turquía difieren de los parámetros de la economía de la Unión Europea. Por tanto, los costes sanitarios se reducen. Los hallazgos financieros de la enfermedad servirán de guía para los responsables de las políticas de salud, los gerentes de salud y los investigadores.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora