Small volume hypertonic resuscitation is a relatively new conceptual approach to shock therapy. It was originally based on the idea that a relatively large blood volume expansion could be obtained by administering a relatively small volume of fluid, taking advantage of osmosis. It was soon realized that the physiological vasodilator property of hypertonicity was a useful byproduct of small volume resuscitation in that it induced reperfusion of previously ischemic territories, even though such an effect encroached upon the malefic effects of the ischemia-reperfusion process. Subsequent research disclosed a number of previously unsuspected properties of hypertonic resuscitation, amongst them the correction of endothelial and red cell edema with significant consequences in terms of capillary blood flow. A whole set of actions of hypertonicity upon the immune system are being gradually uncovered, but the full implication of these observations with regard to the clinical scenario are still under study. Small volume resuscitation for shock is in current clinical use in some parts of the world, in spite of objections raised concerning its safety under conditions of uncontrolled bleeding. These objections stem mainly from experimental studies, but there are few signs that they may be of real clinical significance. This review attempts to cover the earlier and the more recent developments in this field.
O uso de soluções hipertônicas para reanimação de pacientes em choque é um conceito relativamente novo. Baseou-se originalmente na idéia de que uma expansão volêmica significativa podia ser obtida às custas de um volume relativamente diminuto de infusão, aproveitando a propriedade física de osmose. Logo ficou claro que a capacidade fisiológica de produzir vasodilatação, compartilhada por todas as soluções hipertônicas, seria valiosa para reperfundir territórios tornados isquêmicos pelo choque, embora os malefícios da seqüência isquemia – reperfusão devessem ser considerados. Pesquisa subseqüente revelou propriedades antes insuspeitadas da reanimação hipertônica. Verificou-se que este procedimento revertia instantaneamente o edema endotelial e de hemácias, com importantes conseqüências em termos de circulação capilar. Mais recentemente, um conjunto de efeitos da hipertonicidade sobre o sistema imune vem sendo estudado, mas as possíveis implicações destas descobertas em relação ao cenário clínico ainda suscitam discussão. As soluções hipertônicas estão em uso em algumas partes do mundo, apesar de objeções levantadas contra tal uso, em virtude de dados experimentais derivados de experimentos de hemorragia não controlada. Tais objeções não parecem se justificar em face dos resultados obtidos numa série de ensaios clínicos e no uso corrente destas soluções. Esta revisão procura cobrir um pouco da história, remota e recente, deste campo do conhecimento.
Hypertonic salt solutions (HS) have been viewed with interest as possible therapeutic agents for hemorrhage since 1917, when Penfield published a report showing that a relatively small volume of 1.8% NaCl induced a transient recovery of the hypotension caused by blood loss in dogs1. Later, a 5% NaCl solution was unsuccessfully tried for the treatment of Buerger's disease2. No other interesting data on this interaction appeared in press till the sixties, when Baue et al. and Messmer et al. reported equally transient effects of 5% NaCl and 7.5% NaHCO3 in severely hemorrhaged dogs3–5. Gazitua et al. demonstrated that hyperosmotic NaCl solutions induced vasodilation when selectively infused in the renal, coronary, and limb circulations6.
However, interest for the use of hypertonic solutions for the treatment of shock was enhanced when we showed that severely hemorrhaged dogs (40 ml/kg blood loss) responded with a restored arterial pressure and cardiac output following IV bolus injections of 4 mL/kg of 7.5% NaCl, a volume equivalent to only 10% of the volume of shed blood7. Long term survival was observed in all 10 HS treated dogs; in contrast, control animals, treated with an equal volume of isotonic saline, responded with neither hemodynamic improvement, nor survival.
In the same year, Fellippe et al. pioneered human studies: Hypertonic NaCl solutions (7.5% in successive 50 ml aliquots) given to patients in refractory shock at an emergency intensive care unit induced hemodynamic benefits.8 These reports stimulated hundreds of studies, including experimental and more than 60 clinical trials with 7.5% NaCl in the treatment of several conditions, such as hemorrhagic, cardiogenic, and septic shock, as well as a volume supporting solution during major surgical procedures.9 Several groups confirmed our findings that a small volume of 7.5% NaCl, infused to animals which had lost 40 – 50% of their blood volumes, rapidly restored arterial pressure, cardiac output and blood flows to vital organs.10–14 The hypertonic saline dextran (HSD) association, combining the hyperosmotic effects of NaCl to the hyperoncotic effects of dextran12 added new conceptual and practical possibilities. In this review we cover a number of significant aspects of the interaction of hypertonic solutions with severe hemorrhage and circulatory shock.
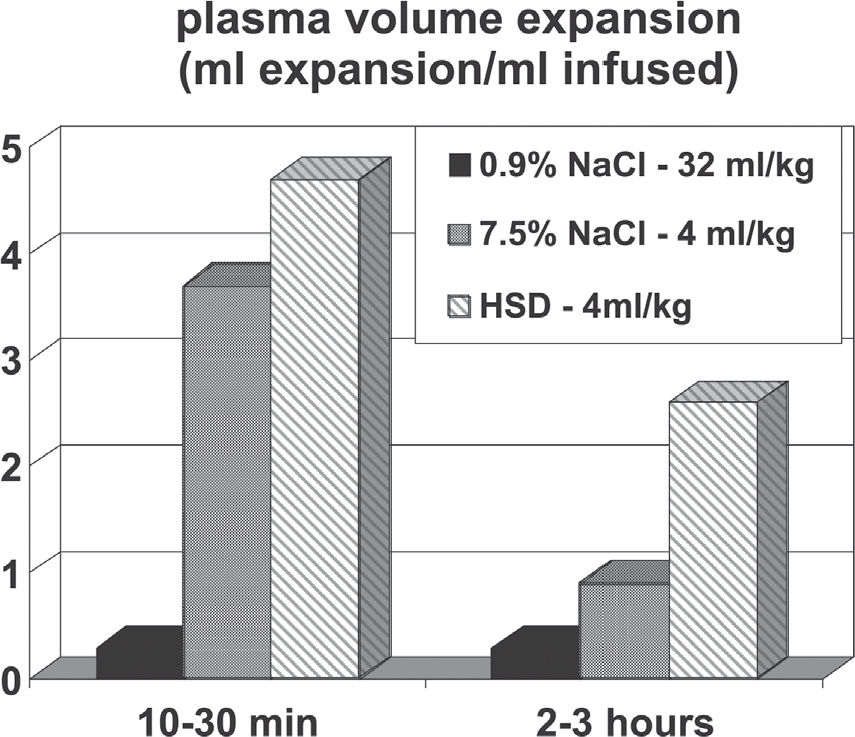
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF HS AND HSDA simple physical interaction is mainly responsible for the initial effect of HS, namely a significant plasma volume expansion. The standard dose of HS (4 mL/kg of 7.5% NaCl) adds a load of 5.12 mEq Na+/kg body weight. In theory, if diluted exclusively into the plasma volume of a normovolemic animal (40 mL/kg), this Na+ load should increase plasma Na+ to approximately 263 – 268 mEq/L (128 mEq/l above the basal level of 135-140 mEq/L). However, such values are never observed in laboratory or clinical trials. Figure 1 shows the only way by which such a concentration may be achieved: the full Na+ load (5.12 mEq/kg) must be administered intravenously over 10 seconds, and plasma Na+ read immediately thereafter. Under these conditions plasma Na+ effectively rose to 267 mEq/l. Such a rapid injection is only feasible if we employ a saturated 30% NaCl solution, thereby reducing the injected volume to 1 mL/kg. Figure 1 also shows that using the standard 7.5% NaCl HS, the same Na+ load can be injected within one minute: in this manner, it increases plasma Na+ concentration by 25 mEq/L, from 140 to 165 mEq/L. The latter value is almost identical to that observed one minute after the ten second 30% NaCl injection. The 25 mEq/L Na+ increase is the correct theoretical value for the dilution of 5.12 mEq/kg across the entire extracellular space (approximately 200 ml/kg). Finally, Figure 1 shows that when the Na+ load is given over 2 min, the observed Na+ peak is 152 mEq/L. Again this value is almost identical to that obtained at 2 min following the ten seconds injection. More significantly, this is also the Na+ peak value typically observed in experimental and clinical trials with HS15. It clearly demonstrates that the extravascular compartment has been expanded by HS, a fact which can only be accounted for by assuming that water has been osmotically drawn out of the intracellular compartment by HS. In summary, these three decay curves of Na+ indicate that the theoretical distribution space is the intravascular compartment at zero time, the extracellular space at 1 min. At 2 min, the Na+ decay from 165 to 152 mEq/L indicates that the extracellular compartment has been expanded by approximately 8% to 216 ml/kg. These theoretical considerations apply to a normovolemic animal. In an oligovolemic animal, after severe bleeding, extracellular expansion would be theoretically greater. In our original paper,7 using plasma volume and hematocrit measurements after hypertonic resuscitation, we detected an initial increment in plasma volume of 11 mL/kg. This represents a 30% increase of pre-existing volumes, or about 2.75 mL of plasma for each mL of the injected solution. In contrast, standard isotonic solutions only induce an expansion of 0.33 mL for each mL injected, as a consequence of its distribution throughout the extra vascular compartment.
Sodium plasma levels after intravenous injections of 5.12 mEq/kg de Na+ to normovolemic anesthetized dogs. This sodium load was infused in three different regiments: as 30% NaCl in 10 seconds (in circles), as 7.5% NaCl in one minute (in triangles), and as 7.5% NaCl in two minutes (in squares).
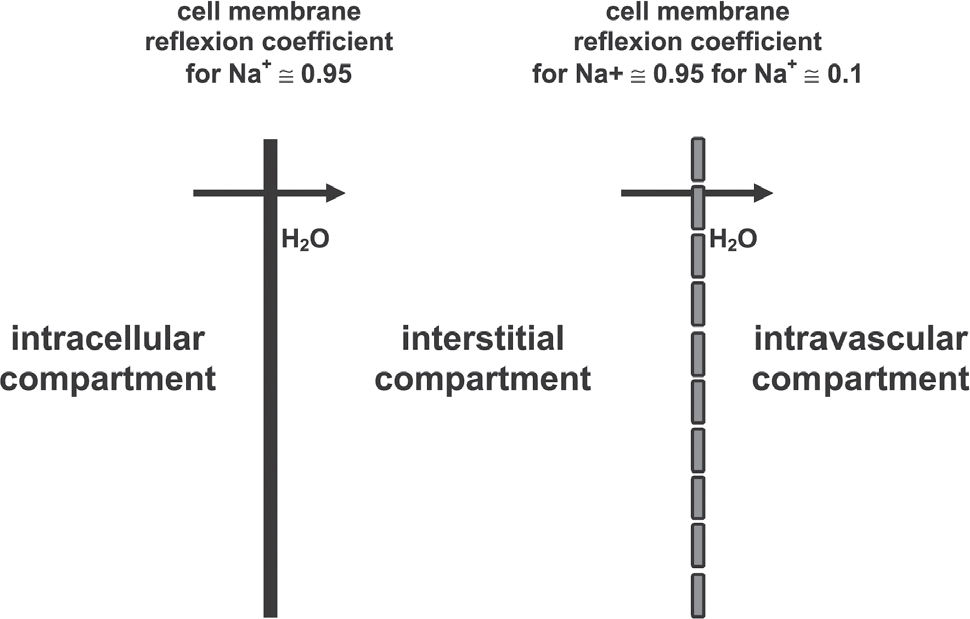
The association of 6% dextran-70 to the 7.5% NaCl solution (HSD) introduced by Kramer et al.,12 somewhat enhances the initial plasma expansion. However, it's most important effect is the maintenance of intravascular expansion for longer periods, thus prolonging the hemodynamic and metabolic benefits of the hypertonic solutions.11,12,16Figure 2 shows plasma expansion produced by isotonic crystalloid, HS and HSD. The addition of HSD alters the dynamics of fluid shift by generating an extra oncotic gradient across the endothelial barrier. This further expands the intravascular compartment, but now at the expense of fluid moved from the interstitial space. The 6% Dextran-70 solution exerts an oncotic pressure of 70 mm Hg, greater than that observed with a similar concentration of human albumin. Results described for HSD have also been demonstrated with HSS, in which 6% hetastarch is added to the 7.5% NaCl solution.17Figure 3 summarizes the physical properties of HS and HSD. The respective reflection coefficients of the endothelial barrier and cellular membrane to Na+ must be considered in the determination of the osmotic force generated by the gradients established after the use of hypertonic saline solution. The endothelial barrier reflection coefficient is 0.1, while the cell membrane coefficient is 1. Thus, for instance, a gradient of 25 mOsm/L exerts an osmotic pressure of 500 mmHg across the cellular membrane, but only 50 mmHg across the endothelial membrane. Equilibrium will be reached 1 min across the endothelial membrane, in 2 min across the cell membrane. Thus, the intravascular expansion induced by hypertonic resuscitation occurs from the intracellular compartment and not from the interstitial compartment, which is also expanded. This fluid shift from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment may be regarded as beneficial, since during shock states, ischemia-reperfusion, extracorporeal circulation and sepsis, among other conditions, there is cellular edema, due to the action of inflammatory mediators and because of sodium/potassium pump dysfunction in the cellular membranes.18Figure 3 also shows how dextran enhances the water shift from the interstitial to the intravascular compartment.
When a 4 ml/kg of 2,400 mOsm/L sodium salt solution is administered to animal previously submitted to severe blood loss, a cardiovascular improvement consisting of partial recovery of mean arterial pressure and cardiac output is observed. It has been variously attributed to plasma volume expansion, vasodilatation in several vascular beds6 and to a direct cardiac inotropic effect.19,20 Renal and mesenteric vasodilation6,7 appear to be particularly important because hemorrhage induces critical flow restrictions to these territories.
Acid base equilibrium is also affected by HS. An initial enhancement of the metabolic acidosis induced by shock is generally observed and has been attributed to hyperchloremic acidosis. This is, however, followed by a recovery towards baseline levels, which has been attributed to a recovery of nutrient flow through previously constricted territories.1,20,21,22
Catecholamine and vasopressin release are also affected by the hemorrhage – HS/HSD interaction. Hemorrhage induces elevated levels of vasopressin and catecholamines; these effects are partially offset by resuscitation with HS/HSD.23 Some of these physiological responses to hypertonicity will be re-examined in the following paragraphs.
Effects of HS on the microcirculation. The classical papers of Mazzoni et al.24,25 demonstrated that the main sources for the observed plasma volume expansion after 7.5% NaCl injection are the red blood cells and the endothelium, mainly on account of their immediate physical contact with the intravascular hypertonicity. These cell species, which had been made edematous by shock, lose 8% of their volumes directly to the intravascular compartment. Apart from the volume expansion, this fluid shift has important hemodynamic consequences, at the microcirculatory level. The hemorrhage induced edema of the endothelial and of the red blood cells are of critical importance in terms of capillary flow, where the ratio between the vascular lumen and red blood cell cross section approaches unity. Endothelial edema reduces the lumen and red cell edema increases red cell cross section, thereby increasing viscosity and hydraulic resistance. Under these circumstances, cellular edema compromises the microcirculatory blood flow. Small volume hypertonic resuscitation instantly corrects this geometric anomaly, whereas larger volume isotonic resuscitation will only correct this over a much more extended period, after the successful correction of oxygen supply.24,25
These microcirculatory disturbances have been implicated in the origin of sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction that occur after an initially successful resuscitation of posttraumatic shock.26 The resulting sustained splanchnic vasoconstriction may cause gut mucosal ischemia and consequent compromise of its integrity, with the consequent predisposition to bacterial and toxin penetration from the intestinal lumen into the systemic circulation. Microcirculation in the gut mucosa may be even more severely compromised during the reperfusion period. This secondary effect, mediated by oxygen free radicals, also results in capillary lumen narrowing, leukocyte adhesion and activation, and stimulation of several inflammatory mediators and cytokines, which may cause local tissue and remote organ injuries.26–28
Under these conditions, hypertonic solutions may produce several beneficial effects through the rapid hemodynamic restoration at the macro and microcirculatory levels. Based on these observed effects in posttraumatic shock, studies with 7.5% NaCl solutions, with and without dextran or hetastarch, have been performed using several models of sepsis and septic shock. Benefits have been observed at the level of global and regional hemodynamics.29–31
Effects of HS on the vascular resistance. The hypertonicity induced by the 7.5% NaCl injection is responsible for the increased blood flow in the peripheral circulation and in the microcirculation as a consequence of a reduced vascular resistance, primarily by arteriolar vasodilatation. This response is caused by a direct relaxant effect of hypertonicity on vascular smooth muscle.
The reduction in blood viscosity, by the hemodilution rapidly induced by the hypertonic solution, also contributes to the reduction in vascular resistance. The use of 7.5% NaCl in shock produces vasodilatation and increased regional blood flow to coronary32, renal6,33, intestinal14,19,34 and skeletal muscle14 circulations.
Effects of HS on myocardial contractility. The hemodynamic benefits observed after 7.5% NaCl have been partially attributed to a direct cardiac inotropic effect induced by hypertonicity.35,36 However, an evaluation of left ventricular contractility after 7.2% NaCl / 6% hetastarch in anesthetized, stable patients without cardiovascular disease, did not demonstrate any clinically relevant positive inotropic effect. All hemodynamic benefits were therefore attributed to the combination of volume expansion and decreased afterload.37
Some authors showed no direct inotropic effect with hypertonic solutions in the treatment of hemorrhagic shock,38 while others showed negative inotropic effects in normovolemic dogs.39 Thus, whether or not hypertonic solutions have a direct positive inotropic effect contributing to the hemodynamic benefits remains controversial.
Additional regional effects. Improvements in renal function have been observed after HSD infusion to animals in shock. This benefit is probably multifactorial, resulting from volume expansion, general hemodynamic improvement and increased renal blood flow.40
A great benefit with hypertonic resuscitation has been observed on cerebral hemodynamics during hemorrhagic shock, particularly in the presence of intracranial hypertension and systemic hypotension.41,42 The rapid restoration of the arterial pressure associated with a reduction in intracranial hypertension induced by hypertonic solutions suggests a potential clinical application of these solutions for trauma victims with head injury and associated lesions with hypotension, a subset of trauma victims with poor prognosis.43
In the clinical trials, patients with low Glasgow coma score and hypotension after trauma benefited from an initial infusion of hypertonic solutions.44
IMMUNE AND INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF HS/HSDThe physical and physiological effects of small volume hypertonic resuscitation are essentially short term in duration, which contrasts with the long term survival produced by HS. The long-term effects of hypertonic resuscitation which shall now be discussed only began to be adequately evaluated in the last decade.
The role of the dextran component as a oxygen free radicals scavenger and the role of HSD as an inhibitor of leukocyte activation had already been recognized.45 More recently, a series of experiments have shown that hypertonic saline solution, even without dextran, significantly interferes with the immune responses, both in vitro and in vivo.46–57
The addition of hypertonic saline solution to a lymphocyte culture media, in concentrations similar to those obtained with systemic infusion of 4 mL/kg of 7.5% NaCl in humans, determined a significant increase in lymphocyte proliferation.46 The addition of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) to the culture media, in the absence of hypertonic saline, caused a reduction in T-cells proliferation, when compared to control cultures. On the other hand, when hypertonic saline was added to the culture media containing PGE2, there was a complete reversal on the PGE2-induced immunosupression.47,48
These in vitro findings were confirmed in vivo using a hemorrhagic shock model in mice, in which the infusion of 7.5% NaCl reversed the cellular immune function depression that occurs after hemorrhage. Plasma levels of several cytokines were determined, and it was concluded that hypertonic saline solution prevents immunossupression probably by decreasing plasma levels of IL-4 and PGE2.48 A double hit model in mice, hemorrhagic shock, followed by resuscitation then by cecal puncture 24 hours later, showed that 7.5% NaCl resuscitation was associated to a significant decrease in mortality 72 hours after peritonitis induction, compared to conventional isotonic resuscitation. Moreover, a significant reduction in pulmonary and hepatic changes after hypertonic solutions was observed.49 Neutrophile activation after the trauma-hemorrhagic shock interaction is significantly limited by treatment with HS.50 Significant reductions have been detected in bacterial translocation and pulmonary lesions in rats with hemorrhagic shock which were treated with hypertonic saline solution.51 More recently it has been shown that polymorph nuclear rolling and sticking, as well as lung expression of ICAM 1, and leakage are inhibited by treating severe hemorrhage with HS. 52,53 It has also be shown that hypertonic saline inhibits neutrophile priming via attenuation of p38 MAPK signaling.54 Inhibition of alveolar macrophage activation by prevention of the systemic oxidative stress due to gut ischemia/reperfusion has also been claimed.55
A possible interaction between hypertonic saline for the treatment of hemorrhage, apoptosis, and tissue damage of the small intestine has also been recently suggested.57 In another study, we have shown that hypertonic saline may exert its long-term benefits after hemorrhagic shock by modulating bone marrow apoptosis.58, a mechanism that has been linked to sepsis and multiple organ dysfunctions.59
Hypertonic saline resuscitation may also influence the transcriptional, functional and protein expression of genes related to Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their specific physiological inhibitors, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), which are thought to play an essential role in tissue repair, cell death and morphogenesis.60
Based on these evidences, it has been suggested that resuscitation with hypertonic saline solutions present significant potential as an immunomodulator agent for trauma victims.61 Hypertonic saline induced systemic, regional and immunomodullatory beneficial effects were recommended for the potential use as treatment of septic shock.62,63. However, all this evidence requires additional research and careful evaluation in clinical trials using these solutions. A recent review by Kolsen-Petersen suggests that many of the effects described in animal models may be inapplicable to the clinical scenario.64
ASSOCIATION WITH OXYGEN CARRIERSThere is a great interest in the association of hypertonic saline, which causes hemodilution with oxygen carriers, particularly modified cell-free hemoglobins, which are currently undergoing phase III clinical trials. It has been well demonstrated that small volumes of these solutions restore arterial pressure in animals in hemorrhagic shock. However, this benefit is achieved through marked vasoconstriction secondary to nitric oxide scavenging by the free hemoglobin.
Severe pulmonary hypertension and coronary, splanchnic and renal vasoconstriction have been also attributed to cell-free hemoglobin solutions.65–68 The association of hypertonic sodium acetate solution, 2400 mOsm/L, with cell-free hemoglobin limited the potent arteriolar vasodilator properties of this variety of hypertonic solution, because of the marked hemoglobin-induced vasoconstriction. With this combination, it has been shown that the association of peripheral vasodilatation, induced by the hypertonic solution, with the pulmonary hypertension, induced by the hemoglobin, may result in severe hemodynamic stability.67 Slower infusions of the combined hypertonic-hemoglobin solution, the use of inhaled nitric oxide to selectively reverse pulmonary hypertension, 68 and the use of encapsulated hemoglobin,69 which is definitely less vasoconstrictive, are some of the potential alternatives that have been tested to expand the benefits of hypertonic saline resuscitation for the next years.
CLINICAL EXPERIENCE AND PERSPECTIVESA substantial clinical experience has accumulated regarding the use of 7.5% NaCl solutions.17 Such studies have provided valuable insights regarding safety and efficacy of hypertonic saline solutions. A majority of patients received these solutions as the initial treatment for posttraumatic hypotension followed by standard-of-care isotonic crystalloid solutions, both in pre-hospital or in the emergency room environment, including several prospective and double-blind studies.70–78
These patients have been submitted to extensive clinical and laboratory evaluation, demonstrating the highly desirable safety profile of the tested solutions even when infused to very sick patients such as trauma victims with immediate risk of death from hypovolemia, hemodynamic instability and severe associated lesions. Studies performed in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgeries and in those who are critically ill in intensive care units provide data regarding the effects of hypertonic saline solutions in subjects with associated pre-existing diseases and with limited organ reserve, situations which are seldom seen in young trauma victims.
Questions raised from clinical trials have been addressed by experimental studies using clinically relevant large animal models, particularly addressing concerns and perspectives with the use of hypertonic solutions for uncontrolled hemorrhage and head trauma.
EFFICACYThe ultimate test of efficacy for treatment of trauma with shock is enhanced survival, followed by other important endpoints such as reduced occurrence of multiple organ dysfunctions and of long-term disabilities. A number of reports have demonstrated significantly increased efficacy in patients treated with hypertonic saline followed by stand-ard-of-care crystalloid infusion, when compared to equivalent patients receiving standard-of-care.
In the first performed trial, by Younes et al, 105 patients in hypovolemic shock patients treated in our institution with hypertonic saline showed a significant initial improvement of arterial pressure and reduced intravenous fluid requirements. No significant difference in mortality was detected. 70 In a subsequent study in which 212 hypotensive patients were enrolled, the same group showed that hypertonic saline as initial treatment caused a significant decrease in long-term mortality rate for the subpopulation with an entry mean arterial pressure below 70 mm Hg.752
The largest controlled trial so far performed, the USA multicenter trial enrolled 422 patients.75 A significant increase in survival for the HSD treated patients in the subpopulation requiring surgery was shown. It also showed a greater incidence of adult respiratory distress syndrome, renal failure and coagulopathy in the standard-of-care alone treatment group. An extensive evaluation of coagulation profile and detailed laboratory workout demonstrated safety of HSD in this severely injured population. 75
Hypotensive patients sustaining head injury with Glasgow Coma Scale scores of 8 or less which received hypertonic saline treatment presented higher survival to hospital discharge. This was demonstrated in a multicenter trial 77 as well as in a meta-analysis of individual patients from all the known clinical trials.44 A meta-analysis conducted on the individual patient records from controlled clinical studies on trauma demonstrated a significant increase in survival favoring HSD versus standard of care.78
SAFETY AND CONTROVERSIESBleeding. Since hypertonic saline resuscitation induces an immediate restoration of both cardiac output and arterial pressure, vasodilatation and hemodilution, several investigators raised concerns that these effects could overcome homeostatic mechanisms, such as vasoconstriction and local tamponade, and even hypotension. The solutions would therefore represent a potential risk for increased internal bleeding in humans, 79,80 as shown in a series of experimental models of uncontrolled hemorrhage in rats,81–85 and pigs.86
These concerns were highlighted by the very controversial study which challenged the guidelines recommended by the Advanced Trauma Life Support Course,87 for the resuscitation of penetrating trauma victims and hypotension with large volumes of isotonic crystalloid solutions.88 This study suggested that standard-of-care pre-hospital and emergency room fluid infusion for these patients resulted in higher mortality and morbidity than what was observed for patients in whom delayed fluid resuscitation, i.e. after operative bleeding control.88 Unfortunately, the study is marred by a number of unresolved flaws.
On the other hand, the USA Multicenter Trial which compared standard-of-care fluid infusion to HSD followed by standard-of-care in the pre-hospital treatment of posttraumatic hypotension demonstrated that penetrating trauma victims with hypotension that received HSD presented higher arterial blood pressure and trends toward higher survival and less complications, when compared to standard-of-care fluid treatment alone.74 Similar results were observed by a meta-analysis of posttraumatic hypotension treated by hypertonic saline as the first fluid infused followed by standard of care treatment.78 Based on these data, we could speculate that the negative effects of large volume infusion of crystalloid solutions are not related solely to increased arterial pressure but to factors related to the isotonic solution itself. A trial comparing standard-of-care, HSD and delayed resuscitation would be needed to establish the best means to treat posttraumatic hypotension. Such a trial, conducted on sick human patients would however be open to severe ethical criticism.
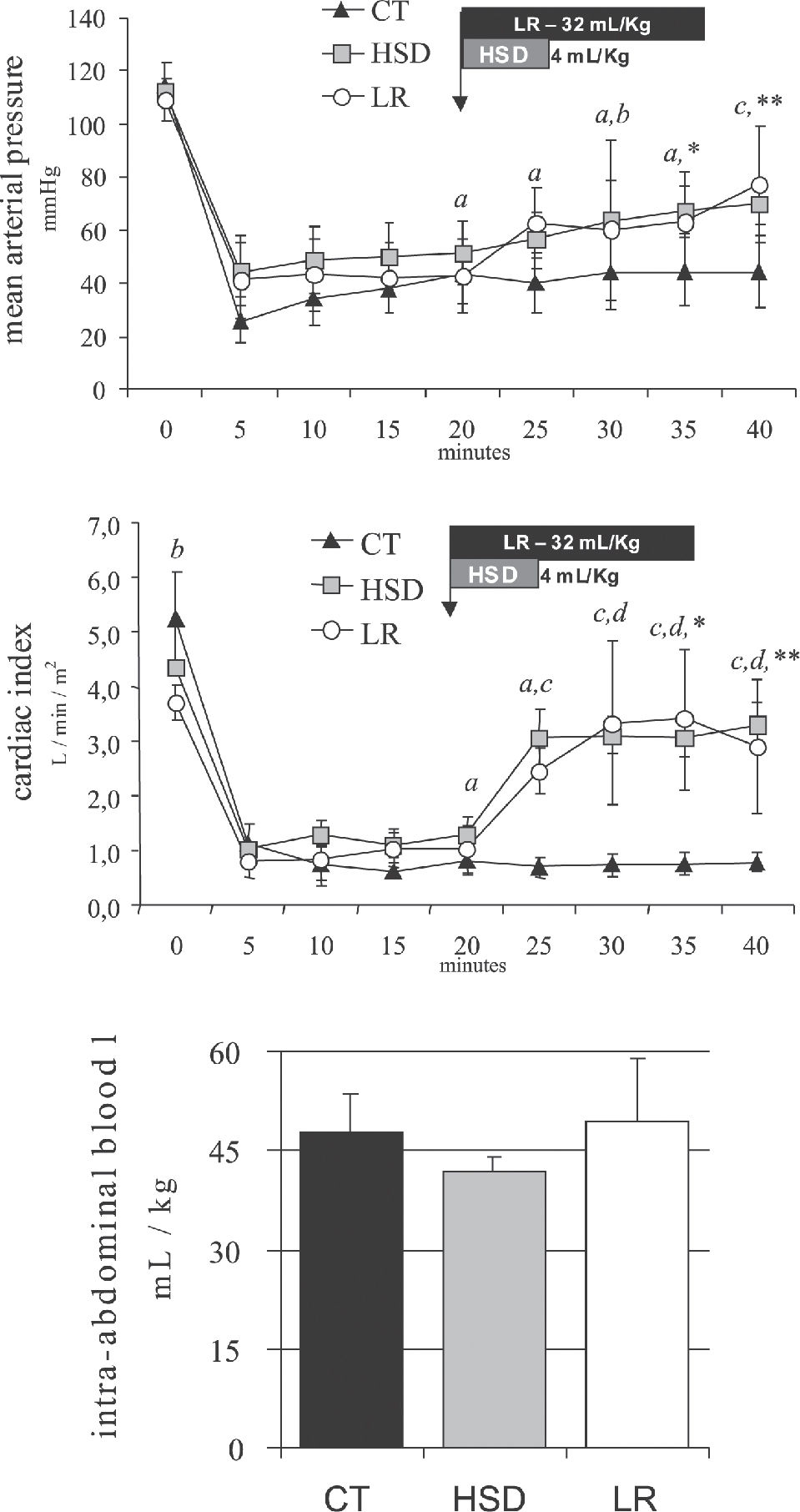
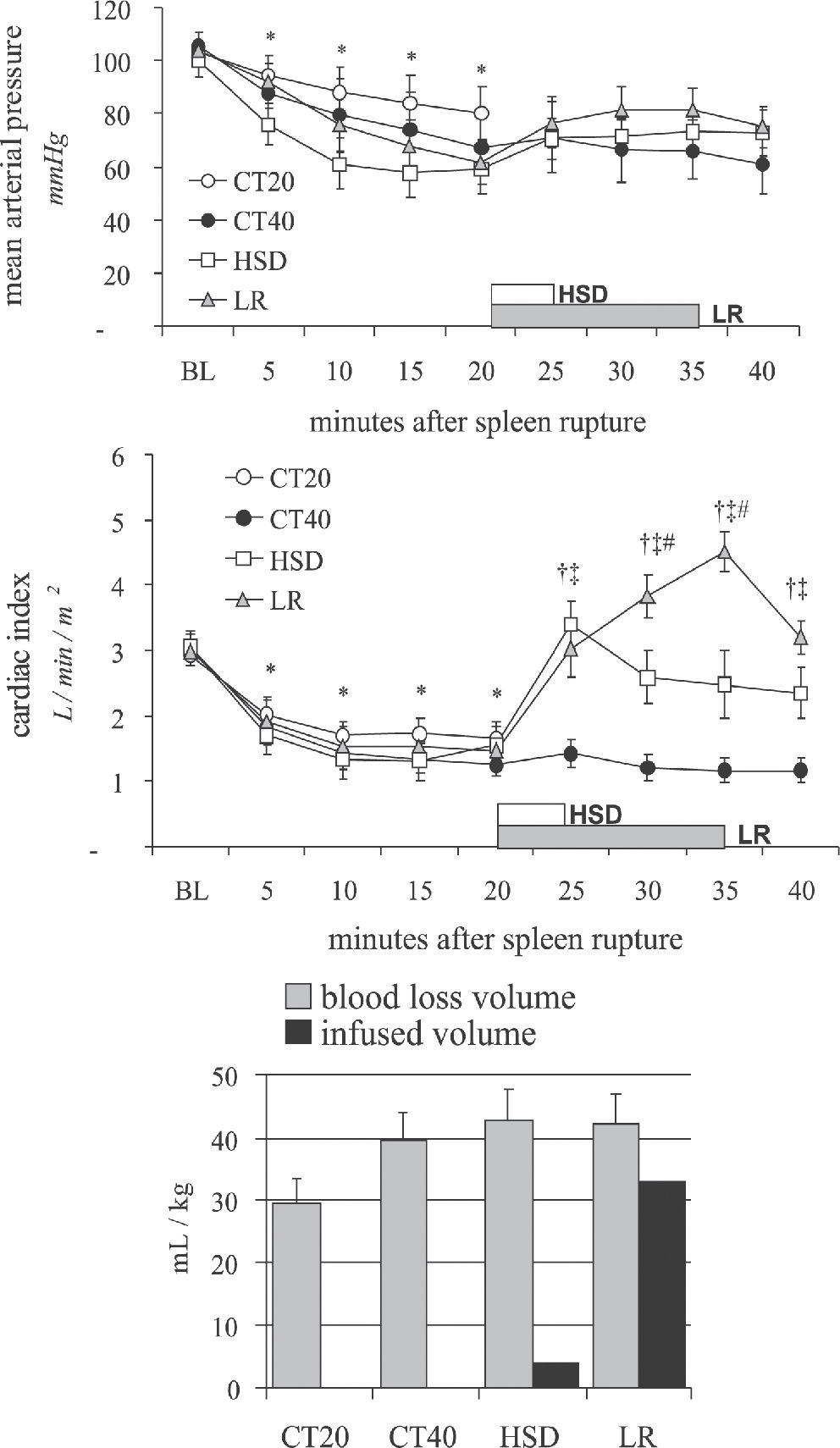
While such a trial remains problematic, we have performed two studies comparing intra-abdominal blood loss measured 20 minutes after the beginning of small volume hypertonic saline bolus (4 mL/Kg 7.5% NaCl in 5 min), large volume lactated Ringer's (32 mL/kg in 15 min) or delayed resuscitation (no fluids). When administered, treatment was infused after 20 minutes of uncontrolled hemorrhage simulating a penetrating (Figure 4, iliac artery tear)89 or a blunt abdominal injury (Figure 5, splenic rupture)90. In both experimental models, untreated controls remained in severe hypotension and low blood flows. Blood loss was not significantly increased by either treatment, suggesting that the hemodynamic benefits observed with fluid treatment were not associated with increased bleeding, which was directly measured after 40 minutes of uncontrolled bleeding. Our experimental data support observations of no increase in blood loss or blood product requirement
Mean arterial pressure, cardiac index and blood volume loss during 40 minutes of uncontrolled intra-abdominal hemorrhage from an iliac artery tear for the CT group (no fluids), HSD group (4 mL/kg over 5 min), and the LR group (32 mL/kg over 15 min). Adapted from Bruscagin et al, 2002.89
Mean arterial pressure, cardiac index and blood volume loss during 40 minutes of uncontrolled intra-abdominal hemorrhage from a splenic rupture for the CT20 group (no fluids, 20 min), CT40 (no fluids, 40 min); HSD group (4 mL/kg over 5 min), and the LR group (32 mL/kg over 15 min). Adapted from Varicoda et al, 2003.90
after HS or HSD in every human trauma trial of posttraumatic hypotension. In most experimental studies showing increased blood loss and mortality, fluid infusion was started immediately after the induction of uncontrolled hemorrhage, a scenario which is extremely uncommon following civilian and military trauma.81–84,86
Moreover, patients receiving hypertonic solutions in these posttraumatic hypotension studies underwent extensive laboratorial investigation, which showed that the coagulation profile was not altered by the amount of dextran 70 in the HSD formulation. Additionally, none of the studies with trauma victims or those trials to test the intraoperative use of HSD demonstrated any association between hypertonic solutions and blood loss or with increased requirements of blood products. In all studies so far performed, blood product requirements have always been associated with the severity and mechanism of injury, and not to the solution used. In fact, a reduction in subsequent fluid requirements is a common finding after the use of HSD.78
The use of HSD during complex cardiovascular surgeries, in which hemostasis alterations are common,91 was not associated with increased blood loss or increased blood product requirements. On the other hand, the use hypertonic solutions in cardiac and aortic surgeries has been frequently associated with hemodynamic stability and less, rather than more postoperative fluid requirements.92–95
Overall, the common observation of less fluid requirements, no increase in blood products requirements, and trends toward less morbidity and mortality with the use of hypertonic solutions suggest that there is no increase in bleeding associated with its use, even in patients sustaining penetrating trauma or during complex cardiovascular surgeries.
Hypernatremia and neurological dysfunction. A frequent concern with hypertonic resuscitation is that it might possibly induce significant hypernatremia with potentially deleterious consequences. Such hypernatremia would of course result from cellular dehydration produced by the osmotic mechanisms already described. In severe hypernatremia, evidence of cellular dehydration is manifest much earlier in the central nervous system than in other organs or systems. Symptoms of hypernatremia include lethargy, tremors, weakness, irritability, delirium, mental confusion, seizures, coma and death. They occur in severe cases and, particularly, in small children and in the elderly.
The use of hypertonic sodium solutions to rapidly correct hyponatremia in patients with severe malnutrition or alcoholism may result in central pontine myelinolysis, which is manifest through dysartria, paraparesis or paraplegia.96 Another described complication with hypertonic sodium solutions for the correction of hyponatremia in neonates is the rupture of cerebral veins and intracranial hemorrhage, caused by the retraction of the cerebral tissue.97
With these questions in the forefront of all clinical trials, patients receiving 7.5% NaCl were carefully evaluated for signs and symptoms of hypernatremia, particularly for the associated neurological alterations. This was especially true for patients at highest risk for neurological dysfunction and intracranial hypertension, i.e. those sustaining head trauma and systemic hypotension.
Despite the fact that moderate hypernatremia and hyperosmolarity have been detected in the overwhelming majority of patients receiving 7.5% NaCl solutions, there was not a single case, among more than 1700 patients, of seizures, intracranial bleeding or neurological deterioration induced by the hypertonic solution.44,78 Necropsies and careful anatomic-pathological studies of the brain tissues were performed in trauma victims, and produced no evidence of central pontine desmyelinization or of focal intracranial bleeding which could be attributed to the use of 7.5% NaCl. 44,78
The short duration of the moderate hypernatremia, the absence of pre-existing hyponatremia, the exclusion of children and patients with chronic disabling diseases may have contributed to the lack of hypernatremia-related undesirable effects. On the other hand, hypotensive patients with head trauma and low Glasgow Coma Scale were one of the subgroups that most benefited from 7.5% NaCl solutions as the initial treatment, presenting better neurological outcome and a significant increase in survival.44 Thus, 7.5% NaCl-induced hypernatremia and hyperosmolarity were actually associated with neurological benefits, not with neurological dysfunction.
The well demonstrated findings that hypertonic saline induces favorable effects on both systemic hemodynamics and intracranial pressure in laboratory and clinical settings have stimulated a number of studies. In Figure 6, we show that in hemorrhaged dogs sustaining a unilateral cryogenic cerebral lesion, a small volume hypertonic saline bolus (4 mL/Kg 7.5% NaCl in 5 min) reduced intracranial pressure. Mean arterial pressure was greater after large volume lactated Ringer's (32 mL/kg in 15 min), but increased intracranial pressure was also observed Both treated groups showed similar improvement in cerebral perfusion pressure. No fluid infusion was associated with worse cerebral and systemic hemodynamics and greater increase in intraneural calcium at the penumbra area.98
Mean arterial, intracranial and cerebral perfusion pressures in hemorrhaged dogs sustaining an unilateral cerebral cryogenic lesion for the CT group (no fluids), HSD group (4 mL/kg over 5 min), and the LR group (32 mL/kg over 15 min). Intraneural calcium measured from cerebral byopsies from the penumbra area and contralateral hemisphere. Adapted from Balbino, 2001.98
Existing preliminary evidence supports the need for controlled clinical trials evaluating hypertonic saline use as resuscitative fluid in brain-injured patients with hemorrhagic shock, as therapy for intracranial hypertension resistant to standard therapy, as first line therapy for intracranial hypertension in certain intracranial pathologies, as small volume fluid resuscitation during spinal shock, and as maintenance intravenous fluid in neurocritical care units.99,100 Bolus infusions of 7.5% NaCl or even of 23%NaCl were the only means to achieve sustained control of intracranial hypertension after every other known measure failed.101
Although we cannot exclude that higher doses of hypertonic saline might induce hypernatremia-related side effects, it is also true that the prescribed dose cannot result in such effects. However, it does seem prudent to avoid these solutions for patients with the highest risk for severe neurological disturbances induced by hypernatremia, i.e. patients with chronic debilitating diseases and children.
Cardiac dysfunction. Experiments with anesthetized animals in shock have shown that a rapid injection of 7.5 NaCl may cause hypotension and arrhythmia, caused by hypertonicity-induced vasodilatation and reduction in peripheral vascular resistance.102 These events may be particularly dangerous when the arterial pressure is very low before the infusion of the solution. This hemodynamic instability is directly dependent on the speed with which the solution is being infused and may be avoided with infusion times greater than two minutes.
The majority of trials with intraoperative use of 7.5% NaCl has demonstrated physiologic benefits and no side-effects.92–95 There is however one study in patients with myocardial dysfunction undergoing coronary artery bypass in which pre-operative volume expansion with 250 mL of HSS caused hypotension and transient left ventricular failure.103 This study showed that 7.5% NaCl solutions can be deleterious if rapidly infused in patients with ventricular dysfunction.104 In a similar study, in patients with cardiac dysfunction, in which the volume of 7.5% NaCl solution was titrated to a target cardiac filling pressure, it was found that a lower dosage was enough to achieve the desired hemodynamic profile, with no hemodynamic instability.104
In a separate study, a fixed dose of HSD (250 mL) was used during extracorporeal circulation in Jehovah's witness, with no hemodynamic changes and reduced fluid requirements in the postoperative period.95 A similar dose was used in surgical procedures for correction of thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms.92,93,105 These procedures are normally associated with sudden hemodynamic changes, marked fluid loss to the third space and high incidence of postoperative complications.106 The use of hypertonic saline solutions resulted in hemodynamic stability and fluid sparing in the postoperative period in these procedures.
The use of 7.5% NaCl solution to patients with cardiogenic shock after right ventricular infarction also produced sustained hemodynamic benefits.107
When the whole population of 1700 patients in which 7.5% NaCl solutions were used is examined, there were no cases of cardiac death. However, it seems prudent to recommend caution with the use of hypertonic solutions in patients with heart diseases. Rigorous monitoring is mandatory and gradual and slower infusions should be employed. The safety profile for the use of 7.5% NaCl solutions in children was recently established by Rocha e Silva et al. during the surgical correction of congenital cardiac defects.108
Hyperchloremic acidosis. Hypertonic NaCl (7.5%) solutions induce a significant increase in chloride plasma levels, and this could predispose to hyperchloremic acidosis. Clinically relevant acidosis was observed in trauma victims that were moribund on arrival and the acidosis was associated with pre-existing conditions such as cardiac arrest or severe hypothermia.72 Despite hemodynamic and metabolic improvement after 7.5% NaCl solutions in the majority of patients, it is reasonable to suggest, based on the clinical evidence, that these solutions should be avoided in patients with preexisting severe acidosis, especially when such acidosis follows cardiac arrest or prolonged pre-hospital times.
CONCLUSIONBased on the available clinical experience with 7.5% NaCl solutions, we conclude that the use of hypertonic solutions is safe, but it is prudent to avoid their use for a well defined patient population, i.e. moribund, or chronic debilitating diseases. Although safety in children undergoing elective cardiac surgery has been demonstrated, additional studies under other disease conditions are warranted. Efficacy has been suggested for this procedure as the first treatment for posttraumatic hypotension, particularly for penetrating trauma victims requiring surgery and for those sustaining head trauma. Elective intraoperative use of these solutions has been associated with hemodynamic stability and fluid sparing. However, in patients with cardiac failure, titrated dosage and careful monitoring are required. Increased bleeding, clinically significant hypernatremia and allergic reactions were not associated with hypertonic resuscitation. Hypertonic solutions are commercially available and have been used in several European countries. A large USA trial is been designed to obtain approval by the FDA. Although the safety issue has been well established, it does appear that a larger prospective, multicenter trials is required to better define the patient population to maximally benefit from hypertonic saline solutions.