It has been established that the genomic background of Mycobacterium tuberculosis may influence disease progression, in particular for the Beijing family and the Latin American and Mediterranean (LAM)/RDRio strains. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prevalence of the LAM/RDRio genotype in cases of tuberculosis from Mexico and their drug susceptibility profile.
MethodsTwo hundred eighteen M. tuberculosis isolates were screened by 43-spacer spoligotyping. The LAM/RDRio genotype was confirmed by multiplex PCR, and the drug susceptibility testing was carried out in solid Löwenstein-Jensen media.
ResultsAmong the LAM strains identified, 24 (63.1%) were confirmed as M. tuberculosis RDRio. All RDRio strains shared the RD174 deletion, that was associated with isoniazid resistance (p=0.0264).
ConclusionsWe documented for the first time the isolation of the LAM/RDRio genotype in pulmonary cases of tuberculosis in Mexico, and we found resistance to the first-line anti-tuberculosis drug isoniazid in these strains.
El genotipo de Mycobacteriumtuberculosis podría influir en la fisiopatología y la evolución de la tuberculosis, en particular los genotipos Beijing y LAM/RDRio. El propósito de este estudio fue evaluar la prevalencia del genotipo LAM/RDRio en casos de tuberculosis pulmonar en México y determinar su perfil de sensibilidad a los fármacos antituberculosos.
MétodosSe evaluaron 218 cepas de M. tuberculosis mediante spoligotyping. El genotipo LAM/RDRio se confirmó mediante PCR múltiple. Las pruebas de sensibilidad a fármacos antituberculosos se realizaron en medio sólido de Löwenstein-Jensen.
ResultadosEntre las cepas LAM identificadas, 24 (63,1%) fueron confirmadas como M. tuberculosis RDRio y se asociaron significativamente con resistencia a isoniazida (p = 0,0264). Todos los aislamientos RDRio presentaron la deleción del locus RD174.
ConclusiónEn este estudio documentamos por primera vez el aislamiento del genotipo RDRio en casos de tuberculosis pulmonar en México, encontrando una asociación estadísticamente significativa entre este genotipo y la resistencia a isoniazida.
Tuberculosis (TB) remains among the top 10 causes of death. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about a quarter of the world population are infected, and 10% of these individuals will eventually progress to active disease. According to the WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2019, 10 million new cases were reported with 1.2 million deaths occurring worldwide among HIV-negative individuals and 251,000 deaths among HIV-positive individuals.1 In the Americas, Mexico ranks third in the number of cases of pulmonary tuberculosis with a total of 45,929 new TB events reported to the Public Health Care System in the last year.2
Transmission of Beijing strains has been documented in México since 2008, and occasionally is isolated as a low prevalent genotype.3 On the other hand, the LAM/RDRio genotype, which was originally described in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), has drawn attention on recent times due to the descriptions of increasing dissemination throughout the world.4 In Mexico, a limited number of genotyping studies have been conducted, and none of them have previously addressed the prevalence of the M. tuberculosis RDRio. In this study, we summarize the molecular genotyping of M. tuberculosis clinical strains isolated in the Northern Mexican states of Nuevo Leon and Tamaulipas and in the Southern state of Oaxaca, in order to gain insight into the RDRio genotype, its prevalence, and its susceptibility to the first-line anti-TB drugs.
Material and methodsMycobacterial isolates. Strains included in this study corresponded to consecutive isolates received from 2015 through 2018 at the Regional Center for the Control of Infectious Diseases in Monterrey, México, from 218 patients with clinical and radiological evidence of pulmonary tuberculosis disease. Sputum samples or mycobacterial DNA were referred to us from COESIDA/CAPASITS Oaxaca (n=41), Sanitary Jurisdiction N.3 from Matamoros, Tamaulipas (n=125), and the Hospital Dr. Jose Eleuterio Gonzalez in Monterrey, Nuevo León (n=52).
Spoligotyping. Heat inactivated bacilli were subjected to DNA isolation by the CTAB method, followed by phenol/chloroform extraction. Spoligotyping was performed with the Biodyne C membranes from Isogen Bioscience (Maarssen, The Netherlands), essentially as described elsewhere.5
LAM/RDRiogenotyping. The SNP was previously identified at 1212 C>G in the gene Rv3062 (LigB)6 by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP); briefly, a 233-bp fragment was amplified, followed by digestion with Taq I; the wild-type allele yield one 214-bp digest, while the LAM isolates resulted in two major digests of 158 and 56bp. RDRio deletion analysis was carried out by a multiplex PCR with internal and flanking primer pairs targeting IS1561′ as described previously.7
Drug susceptibility testing. For all 218 isolates, the susceptibility to isoniazid (INH/I), rifampicin (RIF/R), streptomycin (STR/S) and ethambutol (EMB/E) was determined by using the indirect proportion method on Löwenstein-Jensen medium. The critical concentration of INH, RIF, EMB and STR were 0.2, 40, 4.0 and 2.0μg/mL, respectively.
ResultsSpoligotypingAnalysis of 218 isolates revealed a high prevalence of Euro-American Lineage 4 (N=166; 76.1%), followed by Indo-Oceanic Lineage 1 (N=36; 16.5%) and surprisingly, a high number of Lineage 2 East Asian Beijing strains (N=16; 7.3%). The most prominent family found was X1 (N=37; 17%) followed by T1 (N=36; 16.5%), H3 (N=17; 7.8%), and finally LAM9, EAI2_MANILLA and BEIJING with sixteen isolates each of them (7.3%). Of all isolates, only 185 (84.8%) had a match to the international SpolDB4 database, corresponding to 54 unique spoligotypes (SITs). We found the highest frequency for SIT119 (N=35; 16.1%) followed by SIT53 (N=22; 10.1%), SIT1 (N=16; 7.3%) and SIT19 (N=15; 6.9%). Thirty-three isolates (15.1%) were genotypes without an entry to the SITVIT database (orphans) (Supplementary file Sp-1).
Susceptibility to first-line drugs (FLD)Overall resistance to any TB drug was found in 36 of 218 isolates (16.5%); among these, we found STR resistance in nineteen (8.7%) of the isolates, followed by seventeen to INH (7.8%), twelve to RIF (5.5%) and one strain was resistant to EMB (0.5%). We also found two strains with combined resistance to INH+RIF, including one East Asian Beijing (SIT 1) and one Euro American X1 (SIT 119), and one Euro American T1 (SIT 205) isolate with combined resistance to all tested first-line TB-drugs, accounting for a total of three MDR strains.
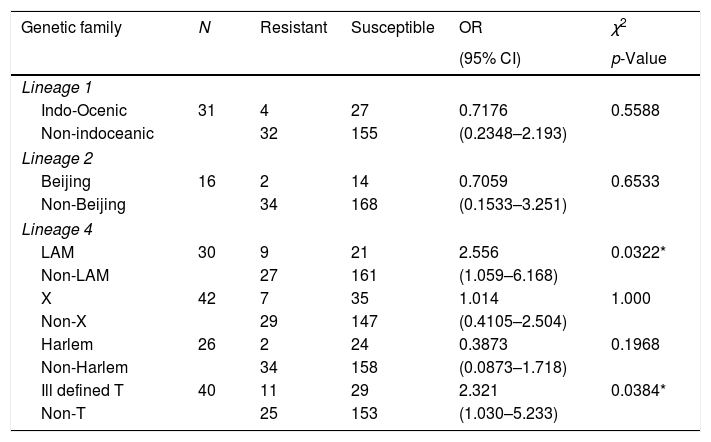
Drug resistance was not associated with Indo-Oceanic (Lineage 1) or Beijing strains (Lineage 2), however we found that Lineage 4, specifically Latin-American-Mediterranean family and the ill-defined T strains were significantly associated with drug-resistance, (p=0.0322 and p=0.0384, respectively; Table 1). In addition to the thirty-five strains included in Table 1, one isolate of the orphan strains was resistant to INH, as is shown in Supplementary-2.
Main genetic lineages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their association with drug-resistance to first-line drugs.
| Genetic family | N | Resistant | Susceptible | OR | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (95% CI) | p-Value | ||||
| Lineage 1 | |||||
| Indo-Ocenic | 31 | 4 | 27 | 0.7176 | 0.5588 |
| Non-indoceanic | 32 | 155 | (0.2348–2.193) | ||
| Lineage 2 | |||||
| Beijing | 16 | 2 | 14 | 0.7059 | 0.6533 |
| Non-Beijing | 34 | 168 | (0.1533–3.251) | ||
| Lineage 4 | |||||
| LAM | 30 | 9 | 21 | 2.556 | 0.0322* |
| Non-LAM | 27 | 161 | (1.059–6.168) | ||
| X | 42 | 7 | 35 | 1.014 | 1.000 |
| Non-X | 29 | 147 | (0.4105–2.504) | ||
| Harlem | 26 | 2 | 24 | 0.3873 | 0.1968 |
| Non-Harlem | 34 | 158 | (0.0873–1.718) | ||
| Ill defined T | 40 | 11 | 29 | 2.321 | 0.0384* |
| Non-T | 25 | 153 | (1.030–5.233) | ||
* Significantly associated with drug-resistance (p < 0.05).
Through the first analysis by spoligotyping we identified thirty LAM strains, and twenty-five “orphans” belonging to the Euro American lineage, however after the recovery from stocks at −70°C, only twenty-eight LAM and twenty-one “orphan” strains were recovered and analyzed for a LAM-specific SNP.6 As expected, all twenty-eight LAM strains harbored the Taq I restriction site, confirming their correct assignment by spoligotyping. In addition, we found ten more LAM strains among the “orphans”, accounting for a total of thirty-eight LAM M. tuberculosis strains for subsequent characterization.
In order to identify the RDRio deletion, we carried out a multiplex PCR protocol previously described by Gibson et al.7 Among the M. tuberculosis LAM strains isolated (N=38), twenty-four were genotyped as RDRio (63.15%). LAM9 was the most frequent sub-lineage (10 isolates; 41.7%), and SIT163 (4/10) and SIT42 (4/10) were the two most prevalent SITs. To further characterize the genetic diversity among the RDRio strains, a RD deletion analysis was performed as was described previously.8 As we shown in Supplementary file Sp-2, all RDRio strains were found to be wild type for the following RD regions (115, 122, 182, 183, 193, 219, 724, 726 and 761).
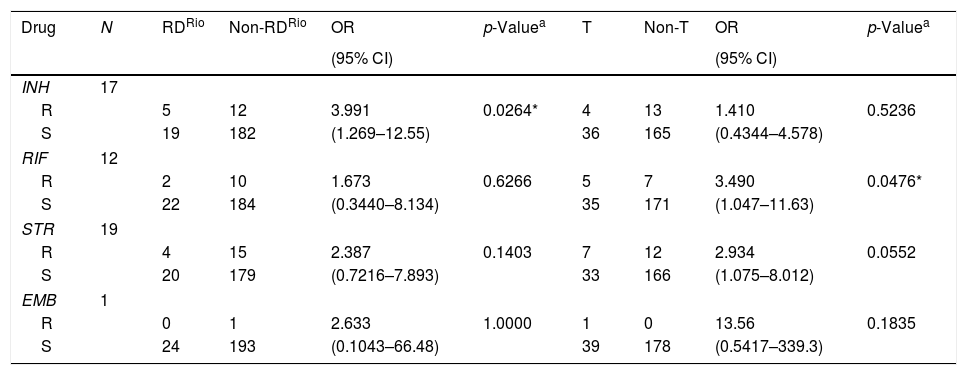
Among the twenty-four M. tuberculosis RDRio strains, eighth isolates (33.3%) were resistant to at least one TB-drug, representing the highest level of drug resistance for a single clade, in contrast with only two among the sixteen Beijing strains isolated from this study (12.5%), and moreover, M. tuberculosis RDRio strains were significantly associated with isoniazid resistance (p=0.0264; Table 2). We also found that ill-defined T strains were associated with resistance to rifampicin (p=0.0476), but we must highlight that ill-defined T is a highly heterogeneous group of strains among the members of the Euro American lineage.
First-line drug susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis RDRio and ill-defined T strains.
| Drug | N | RDRio | Non-RDRio | OR | p-Valuea | T | Non-T | OR | p-Valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (95% CI) | (95% CI) | ||||||||
| INH | 17 | ||||||||
| R | 5 | 12 | 3.991 | 0.0264* | 4 | 13 | 1.410 | 0.5236 | |
| S | 19 | 182 | (1.269–12.55) | 36 | 165 | (0.4344–4.578) | |||
| RIF | 12 | ||||||||
| R | 2 | 10 | 1.673 | 0.6266 | 5 | 7 | 3.490 | 0.0476* | |
| S | 22 | 184 | (0.3440–8.134) | 35 | 171 | (1.047–11.63) | |||
| STR | 19 | ||||||||
| R | 4 | 15 | 2.387 | 0.1403 | 7 | 12 | 2.934 | 0.0552 | |
| S | 20 | 179 | (0.7216–7.893) | 33 | 166 | (1.075–8.012) | |||
| EMB | 1 | ||||||||
| R | 0 | 1 | 2.633 | 1.0000 | 1 | 0 | 13.56 | 0.1835 | |
| S | 24 | 193 | (0.1043–66.48) | 39 | 178 | (0.5417–339.3) | |||
INH (isoniazid), RIF (rifampicin), STR (streptomycin), EMB (ethambutol), R (resistant), S (susceptible).
To further characterize INH-resistance among the M. tuberculosis RDRio strains, we sequenced a region of about 1000 pb in the Rv1908c (KatG) including the codons 315 and 463. Among the eight drug-resistant RDRio isolates, only one strain resistant to INH was harboring the most frequent KatG S315T mutation (LAM1-4, SIT1321; Supplementary file Sp-2), whereas all of them were wild type at the 463 codon.
DiscussionIn this study, only 84.8% of isolates had a match to the SITVIT2 database (http://www.pasteur-guadeloupe.fr:8081/SITVIT2/), which includes 1939 unique spoligotypes from 122 countries.9 The low representation of Euro-American lineages highlights the relevance of carrying out M. tuberculosis genotyping in Latin-American countries. SIT119 and SIT53 accounted for a total of 26.2% of M. tuberculosis strains, as expected from previous studies.10
On the other hand, we found a high prevalence of the RDRio genotype among the LAM strains. We failed to find a significant association between age, sex, diabetes or HIV infection among RDRio infected patients; however 33.3% of the RDRio strains were resistant to at least one first-line TB drug, in contrast to the overall rate of drug resistance found in this study (16.5%), and much higher than among the Beijing strains (12.5%). These data are in line with studies in Brazil, where a significant number of cases with MDR-TB were caused by M. tuberculosis RDRio.11 Among sixteen Beijing strains isolated in this study, one strain was found resistant to INH and a second isolate was resistant to INH and RIF. It has been reported that in Latin-American countries such as Argentina, or in low-prevalence countries such as the United States of America, the Beijing strains are drug-susceptible, in contrast to Beijing strains isolated in Asia, or Africa.12,13
In conclusion, we document for the first time the isolation of the LAM/RDRio genotype in pulmonary cases of tuberculosis in patients from Northern Mexico, and we found that these isolates were significantly associated with resistance to isoniazid. Health authorities in México should seriously consider the occurrence/spread of the M. tuberculosis LAM/RDRio genotype.
StatementThe authors declare that the data and results included in the manuscript are no plagiarism and have not been published elsewhere.
FundingThis work was partially supported by the Fondo Mixto (FOMIX) CONACYT-Gobierno del Estado de Oaxaca, Grant Number: 193298 to YNL, and the PRODEP Grant Number: DSA/103.5/14/10812 to JPPN. We also thanks to the National Council on Science and Technology (CONACyT) by the approval of the Biosafety Grant to Gloria M. González (Grant number: 264118 “Fortalecimiento de la bioseguridad para el proceso de muestras biológicas con patógenos del grupo de riesgo 3, en apoyo a actividades de investigación, formación de recursos humanos y servicio del Centro Regional de Control de Enfermedades Infecciosas, UANL”).
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicting interest to declare.
The authors acknowledge technical assistance of Q.B.P. Carolina Becerril Esquivel, Q.C.B Laura Elizondo Rico and Q.B. Claudia Concepción Cruz Lescas.