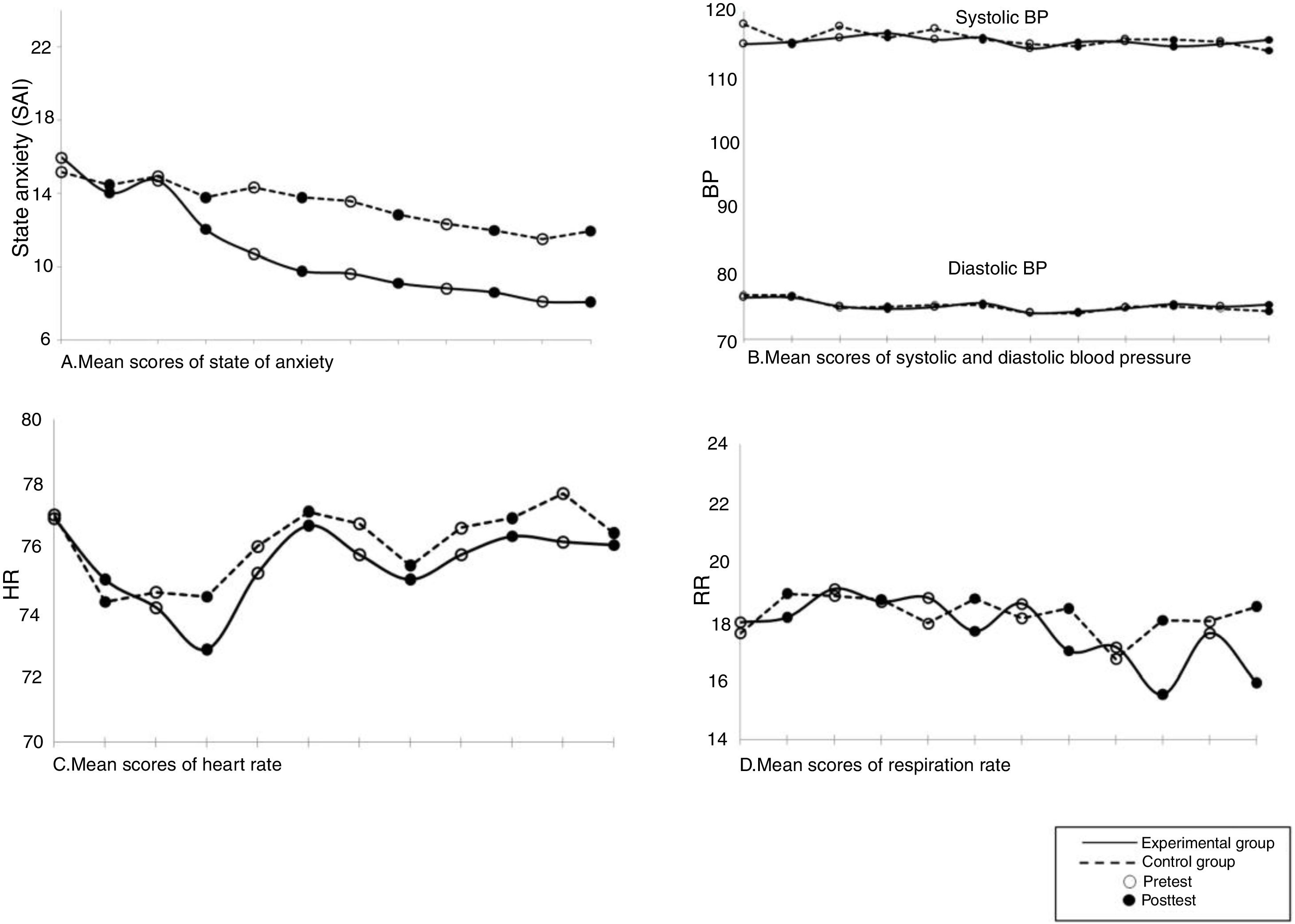
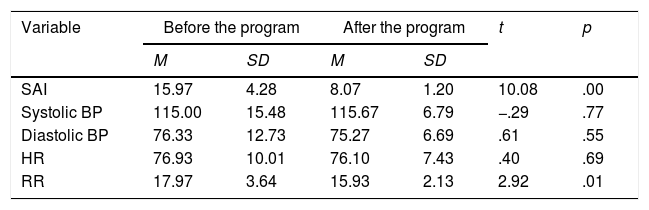
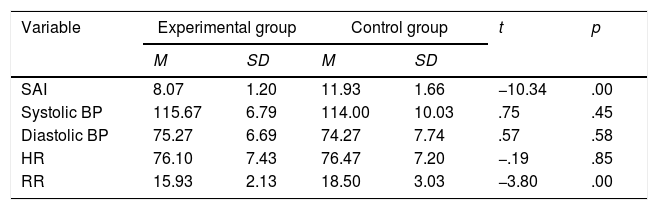
The aim of this study was to examine the effect of an education program and traditional music on anxiety in Myocardial Infarction (MI) patients. This study adopted a pretest and posttest quasi-experimental design. Sixty MI patients admitted to the ICCU of Sanglah Hospital were taken as a sample and assigned to either the experimental or control group. The intervention was given over three days during hospitalization. Anxiety was measured by a 6-item SAI and TAI, while noninvasive measurements were used in measuring physiological responses. The anxiety in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group (t=−10.34, p<.05). However, the physiological responses were not statistically significant, except for the RR (t=−3.80, p<.05). This study provides empirical evidence to support the use of an education program and traditional music on anxiety among MI patients.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora