This study aims to analyze level of risk, target danger and management of health risks due to exposure to mercury and cyanide in river water, well water and plants.
MethodsThis study used environmental health risk analysis, data collection through environmental observations, laboratory and questionnaires.
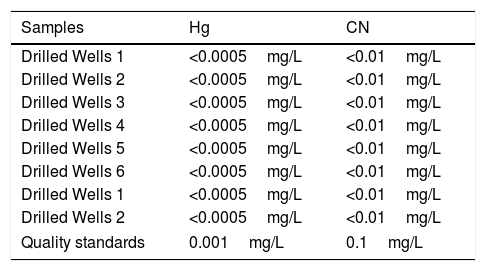
ResultsMercury concentrations in river water and well water were below the detection limit was <0.005mg/L and plants ranging from 0.0076μg/g to 0.0517μg/g while cyanide concentration in river water and well water is <0.01mg/L and plants<0.01μg/g, 40% having risk level (RQ) values>1 for non-carcinogen effects and for carcinogenic effects all respondents have RQ≤1 while for hazard target values (THQ) non carcinogenic and carcinogenic effects 85 people respondents have THQ value 1.
ConclusionCommunity is expected to be able maintain and limit amount of consumption frequency, especially in plants.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora