To determine the quality of the blood pressure measurements performed during routine care in community health centres.
MethodAn observational, cross-sectional study was conducted in 5 private and public health centres in Maldonado, Uruguay, in July–August 2015. The observations were made during the measurements performed by health personnel, using the requirements established by the American Heart Association. An analysis was made on 36 variables that were grouped in categories related to environment, equipment, interrogation, patient, and observer. Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test or Fisher test. Statistical significance was considered to be less than 5% (p<0.05).
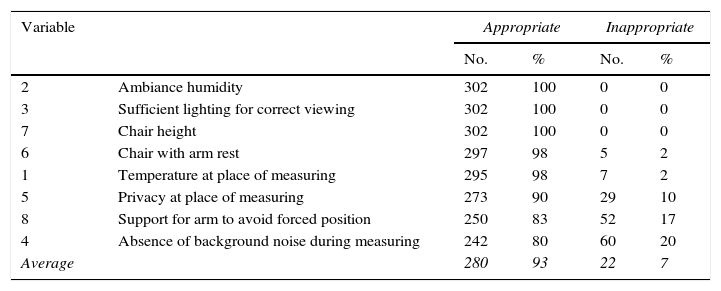
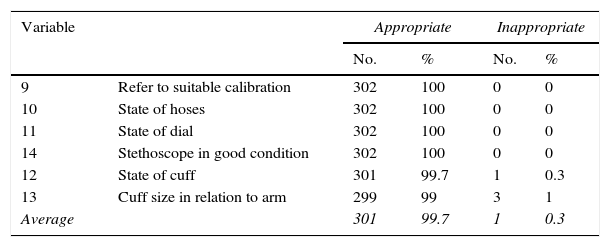
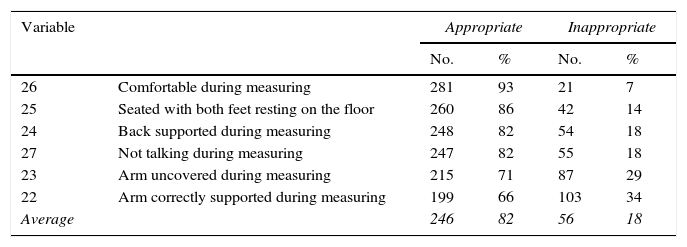
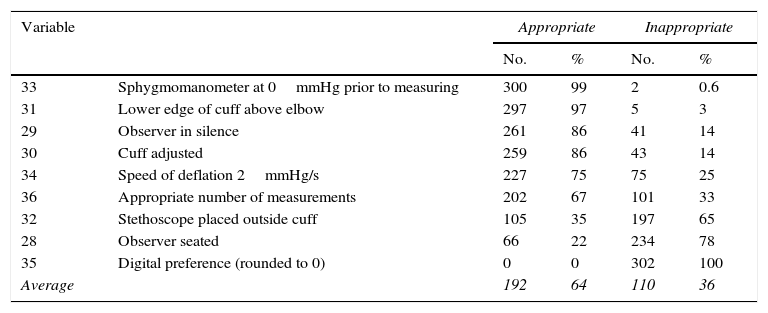
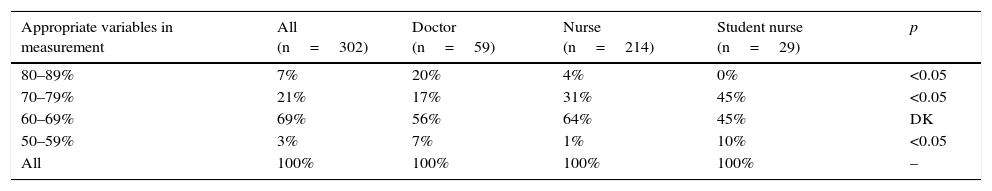
ResultsThe measurements were made by a registered nurse or nurse in 71% of cases, physician in 20%, and student nurse in 9%. An aneroid sphygmomanometer was used in 89%, and mercury 11%. Satisfactory results were found in variables related to environment (93%), equipment (99%), and patient attitude (82%), and intermediate in the attitudes of the operator (64%), and poor in relation to the interrogation (18%), with the mean of correct variables per measurement being 69%.
ConclusionsThe main flaws in the procedure were the operator. The measurement of blood pressure is a manoeuvre that healthcare professionals perform thousands of times a year. If the measurement is used for the diagnosis and/or chronic management of arterial hypertension, not systematically applying the established recommendations leads to an inappropriate care of a very significant number of patients.
Conocer la calidad de la medida de la presión arterial realizada en la asistencia habitual en centros de salud comunitarios.
MétodoEstudio observacional de corte transversal en 5 centros de salud privados y públicos de Maldonado, Uruguay, en julio-agosto de 2015. Se contrastó lo observado durante la medida realizada por personal sanitario con los requisitos establecidos por la American Heart Association. Se analizaron 36 variables que se agruparon en categorías referidas a ambiente, equipamiento, interrogatorio, paciente y observador. Análisis estadístico empleando test de chi2 o test de Fischer. Se consideró significativo el estadístico con valor menor a 5% (p<0,05).
ResultadosMedida realizada por licenciado o enfermero en 71% de los casos, médico en 20% y estudiante de enfermería en 9%. Con esfigmomanómetro aneroide 89% y de mercurio 11%. Se encontraron resultados apropiados en variables referidas a ambiente (93%), equipamiento (99%) y actitudes del paciente (82%), intermedios en las referidas a actitudes del operador (64%) y pobres en las referidas al interrogatorio (18%), siendo 69% el promedio de variables correctas por medida.
ConclusionesLas fallas principales en el procedimiento fueron por parte del operador. La medida de la presión arterial es una maniobra que profesionales sanitarios realizan miles de veces al año. Si la medida está dirigida al diagnóstico y/o manejo crónico de la hipertensión arterial, no aplicar de manera sistemática las recomendaciones establecidas conduce a un cuidado inapropiado de un número muy importante de pacientes.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora