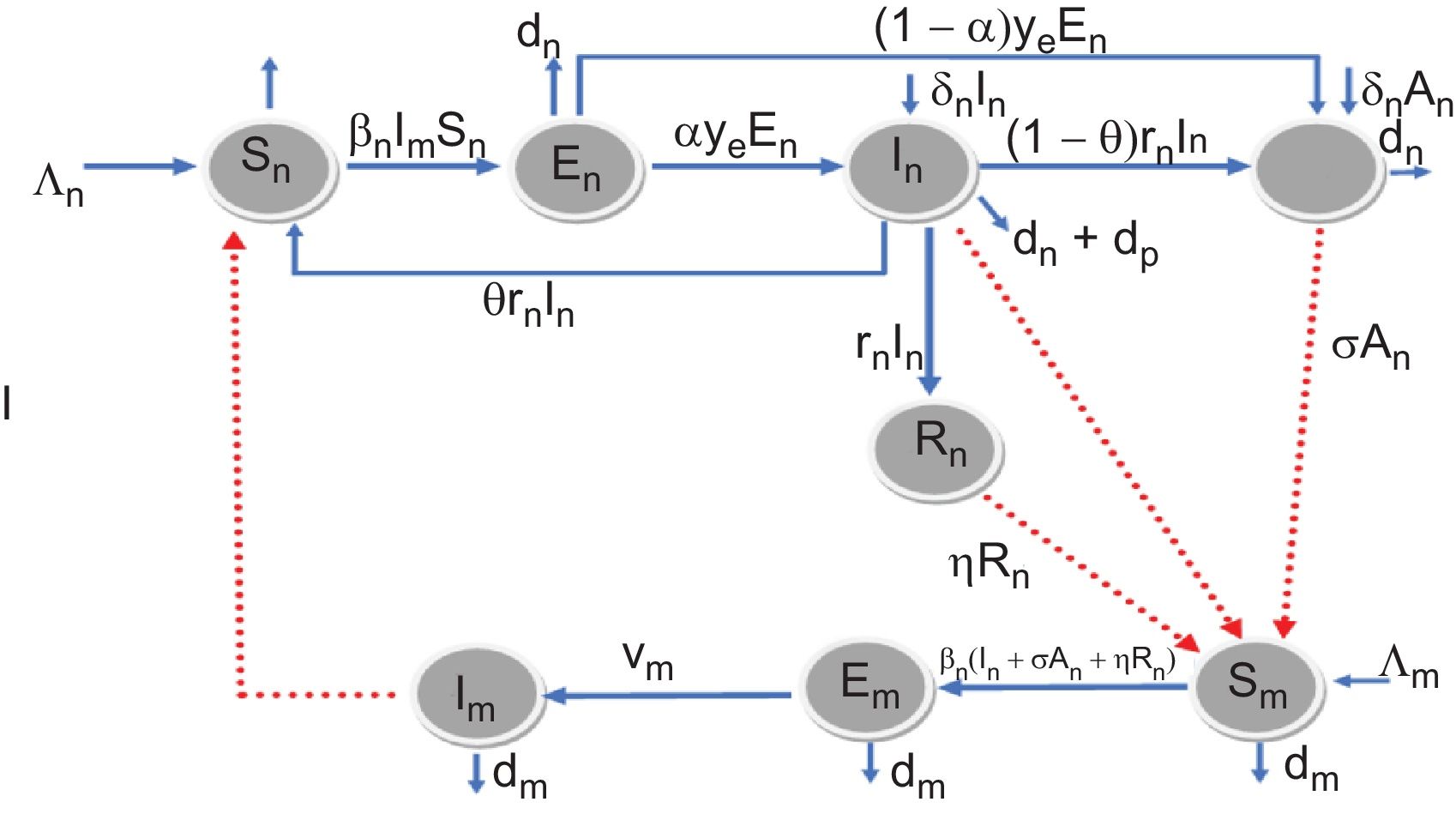
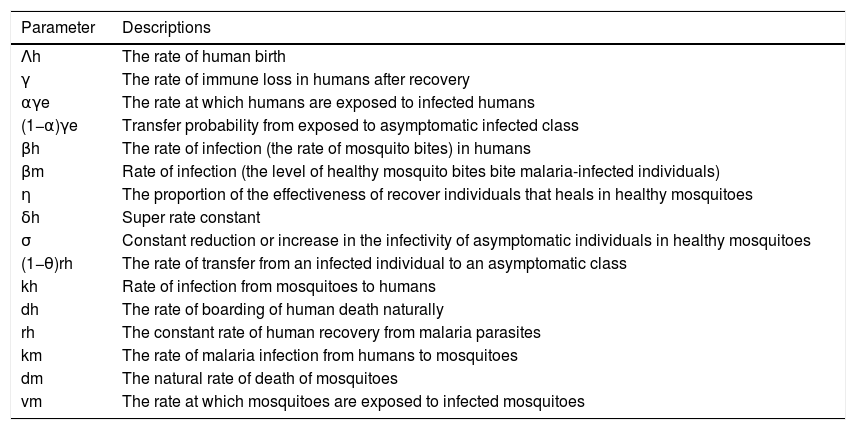
This study aimed to determine the balance point and analyze the stability of the SEIAR-SEI model in malaria with the influence of immigrant infections in patients with symptomatic infections and asymptomatic infections. This study also aimed to measure the level of sensitivity of the spread of malaria to immigrant infection parameters to the magnitude of ℛ0.
MethodThe method used in this study is a qualitative method with steps: determining the disease-free and endemic balance points and determining basic reproductive numbers ℛ0 Sensitivity analysis of basic reproductive numbers was carried out on immigrant infection parameters.
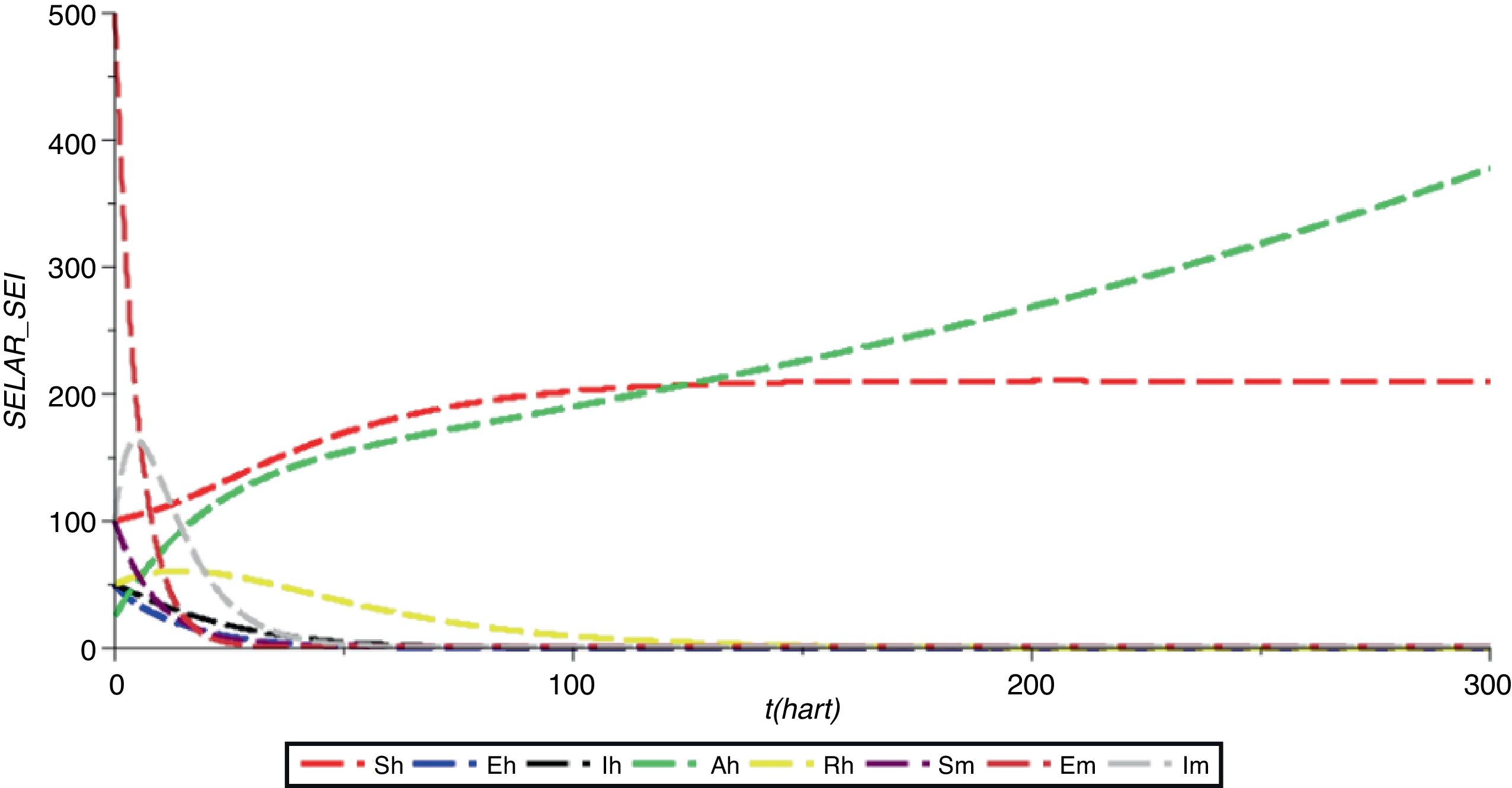
ResultThe results obtained showed that the parameter δh fected basic reproductive numbers (ℛ0) Immigrant infection factors in symptomatic and asymptomatic infections affect the increase in malaria infection.
ConclusionIt is concluded that immigrant infections that occur in symptomatic and asymptomatic malaria sufferers cause an increase in the number of malaria infections, especially in the symptomatic infection class (Ih).
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora