The parents of premature baby tend to be at risk undergoing postpartum blues and anxiety. It is due to many problems faced by postpartum mother of premature baby. This research is aim to identifying influence of thought stopping and supportive therapy of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature babies.
MethodThis is quantitative with quasi-experiment with control group pretest-posttest design and consecutive sampling method. Sample in this research are 62 postpartum mothers of premature babies in perinatal NICU (neonatal intensive care unit).
ResultsThe results show that there is significant decrease of postpartum blues and anxiety (p value = 0.000) in the group that was treated by using nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy and greater significant decrease than the group that was only treated by nursing intervention.
ConclusionsThought stopping and supportive therapy are able to decrease postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature babies.
Postpartum period is a crisis moment for mother, husband and family due to the physical and psychological changes as well as family structure that need adaptation process1. Physiological adaptation process is begun immediately after the birth of a child until the body recovery is started and it is extending for about six up to eight weeks2, postpartum mother that delivers her baby prematurely in sectio caesarea needs more adaptation process rather than a normal postpartum mother that delivers her baby in enough months. It is because of a post-sectio caesarea mother undergoes parturition period with two problems: post-birth recovery process and SC abdominal-wound healing process3, as well as the premature baby who needs special treatment.
Psychological adaptation of postpartum is classified into three phases: taking in, taking hold and letting go4. Those three phases will be well passed through if postpartum mother is socially supported by the surround people.
Postpartum mother who is failed on taking in phase will face postpartum blues5. The symptoms of postpartum blues are sad reaction, easy-crying, anxiety, touchy, labile, tending to blame themselves, feeling incapable to treat baby, sleep habit disturbance and feeling no appetite. These symptoms appear after birth and they are extending in about fourteen days. Primipara and post sectio caesarea are vulnerably undergoing postpartum blues.
Anxiety is a psychosocial disorder which often experienced by individual6. The individual therapy effective to overcome anxiety are cognitive therapy, behavioral therapy, thought stopping, and cognitive behavioral therapy7. Thought stopping therapy is a mind-stopping technique that can accordingly learned by postpartum mother and it can be used when she wants to eliminate disturbance or negative thinking and consciously unwanted thought8.
Supportive therapy is a part of psychotherapy that is applied on sanity based-community9. The aim of supportive therapy is improving supportive individual, increasing individual’s strength, self-defense ability and using self-defense sources.
The choice of both therapy is due to parents of premature babies undergoes thought disturbance because of their baby’s condition in perinatal NICU (neonatal intensive care unit). They face anxiety and problems, not only about the baby’s condition, but also after the premature baby is brought back home. It is because the treatment of the premature baby needs relative long time and thus the parents of premature baby need internal/external support continually.
The researcher measures the anxiety symptoms and postpartum blues to parents of premature baby in perinatal NICU and then conduct nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy to solve anxiety problems and to know whether the parents of premature baby undergoes postpartum blues.
MethodThis research used quasi-experiment with control group pretest-posttest design that examined the influence of nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy to postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby in perinatal NICU. Sampling method used convenience sampling; there were 62 respondents. The research duration was 25 weeks, starting from December until June 2016. The instruments that used in this research were HARS and EPDS. Furthermore, anxiety is treated by nursing intervention with relaxation techniques and specialist nursing intervention with thought stopping and supportive therapy. The data that have been collected, then, are inputted and analyzed by using software. The data collection is done after the researchers explain a detailed procedure and process to the respondent. The study was conducted after the respondents agreed and filled the informed consent. The planning of this study was legalized through the ethic test by the ethics agency Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Indonesia.
ResultsThe parents of premature baby undergo postpartum blues and high anxiety before gets nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy.
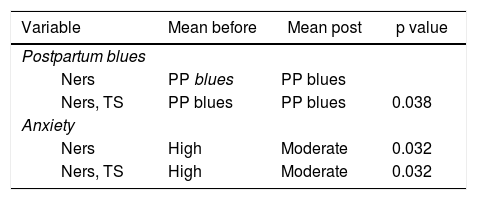
The results of statistical test in Table 1 show that after get nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy, the anxiety is decrease from high to moderate and the value of postpartum blues is decrease, but the value is still in the postpartum blues range.
The difference of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby between before and after get nursing intervention, thought stopping therapy (n = 62).
| Variable | Mean before | Mean post | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Postpartum blues | |||
| Ners | PP blues | PP blues | |
| Ners, TS | PP blues | PP blues | 0.038 |
| Anxiety | |||
| Ners | High | Moderate | 0.032 |
| Ners, TS | High | Moderate | 0.032 |
After performing nursing intervention, there was significant average decrease from high to moderate anxiety and the value of postpartum blues is decrease, but the value is still in the postpartum blues range.
The decrease of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby’s group who get nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy is significantly greater than group that only get nursing intervention.
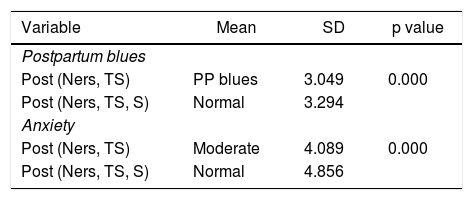
The research’s result show that thought stopping and supportive therapy are able to decrease postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby twice as great than only nursing intervention. The statistical test results in Table 2 show that after nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy were conducted, there was significantly average decrease from moderate anxiety to be normal and the value of postpartum blues is decrease from positively postpartum blues to negatively postpartum blues/normal.
The difference of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby between post nursing intervention, thought stopping and post nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy (n = 62).
| Variable | Mean | SD | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Postpartum blues | |||
| Post (Ners, TS) | PP blues | 3.049 | 0.000 |
| Post (Ners, TS, S) | Normal | 3.294 | |
| Anxiety | |||
| Post (Ners, TS) | Moderate | 4.089 | 0.000 |
| Post (Ners, TS, S) | Normal | 4.856 | |
The research’s result show that before nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy, all parents of premature babies in perinatal NICU suffer postpartum blues and high anxiety.
Lindberg and Ohrling10 research’s result show that mostly mother are not ready having premature baby and they get difficulties being a mother in early moments after delivering their babies. Mother experiences anxiety since she is separated from her baby. Melnyk et al11 state that nursing hospitalization in NICU gives negative impact to parent’s psychological condition and the future premature baby growth.
Nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy influence of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature babyPostpartum blues in the parents of premature baby who was treated by nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy decreased 12.68 and it means postpartum blues. Postpartum blues in the parents who were not treated by thought stopping therapy decreased 8.06 and it means postpartum blues. The decrease of value postpartum blues in parents’ group which was treated by nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy was significantly greater than the group that is only treated by nursing intervention.
The research’s result show that anxiety parents of premature baby who were treated by nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy decreased from high to moderate anxiety (14.46) and the anxiety of parents who were not treated by thought stopping therapy decreased from high to moderate anxiety (12.32).
The decrease of anxiety level in this research is in line with the research results conducted by Agustarika12 who said that the anxiety of client who get thought stopping therapy decreased significantly. Bakker’s research resulted that thought stopping therapy is able to reduce anxiety level and increase individual’s self-defense13. The research of Naikare et al14 resulted that thought stopping technique is able to control industrial workers’ stress level.
Based on the data above, the nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy are able to decrease postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby. The decrease of postpartum blues and anxiety parents group that was treated by nursing intervention and thought stopping therapy was significantly greater than the group that was only treated by nursing intervention.
Influence of nursing intervention to postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature babyThe research’s result show that there was significant average decrease after performing nursing from high to moderate anxiety and the postpartum value decreased 8.06 and it means postpartum blues.
This research result is in line with Bektas and Ozturk15, Fiandini16, Prawitasari17 and Mu’afiro's18 research which addresses that nursing intervention has significant influence of anxiety level decrease.
Based on the data above, the nursing intervention can decrease postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby.
Influence of nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy to postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature babyAfter nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy, the research’s result shows that there was more significant average decrease, from high to be normal/ not anxiety and from postpartum blues to normal condition.
Dochterman explains that one of the psychotherapies that can be used to overcome anxiety especially for emotional problems and focus on how it facilitates client to know and use accessible support system is supportive therapy19. Banowati20 stated that supportive psychotherapy on hemiparesis patient is able to decrease depression and anxiety degree and increase life spirit. Hasmilasari21 proved that by using supportive therapy, anxiety level of pregnant woman decreased. Shechtman and Katz22 proved that supportive group is effective enough to decrease anxiety level of teen group. Rustina et al23 proved that the families have an influence in improving the health status of premature infant. The parents of premature baby as a care giver are a part from a family needs support to take care the baby. Ilda et al24 stated that increased interactions between mother and baby increase the confidence of mother in caring for the premature babies. The nurses as the external support to the parents of premature baby in perinatal NICU should give support to the parents to touch the baby.
Based on the data above, the thought stopping and supportive therapy are able to decrease postpartum blues and the anxiety parents of premature baby twice as great than who were only treated by nursing intervention.
ConclusionsNursing intervention and thought stopping therapy give significant influence toward decrease of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby in perinatal NICU. Nursing intervention also give significant influence toward the decrease of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby in perinatal NICU. Nursing intervention, thought stopping and supportive therapy give significant influence toward the decrease of postpartum blues and anxiety parents of premature baby twice as great than they who were only treated by nursing intervention.
In this research, the researcher wants to deliver gratitude to all respondents that have participated in this research.