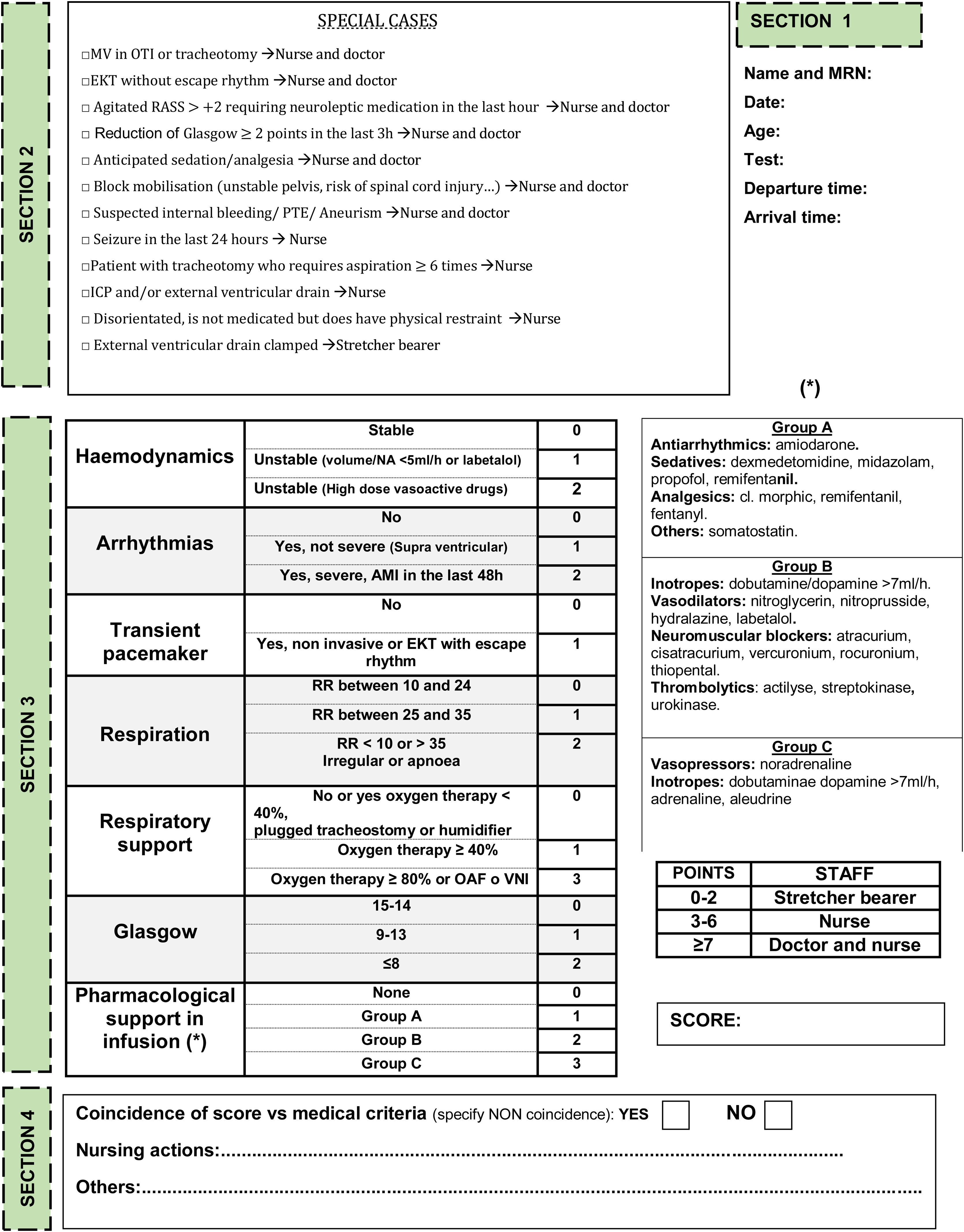
Currently, in intensive care units (ICUs), the in-hospital transport (HIT) of patients is carried out without a unified criterion of personnel necessary for it.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the concordance of the Patient Assessment System for Transport-ICU (PAST-ICU) with the medical criteria (CM) to determine the Human Resources (HR) and identify Adverse Effects (AE).
MethodsDescriptive, cross-sectional and prospective study of the IHT of patients admitted to an area of adult medical-surgical critical patients. The PAST-ICU instrument was created to recommend the HR of HIT. Through the assessment of clinical parameters, the Past-ICU indicates whether the HIT should be performed with (1) a stretcher-bearer (2) Stretcher-bearer/nurse or (3) stretcher-bearer/nurse/doctor. AE were recorded during the hospital transfer. Prior to the IHT, the nurse performed the PAST-ICU and the result was contrasted with the Medical Criteria (MC) responsible for the patient, the latter prevailing.
Study periodPhase 1: pilot test 2013–2014. Phase 2: 2015–2021.
VariablesReason and duration HIT, PAST-ICU sheet, checklist, AE.
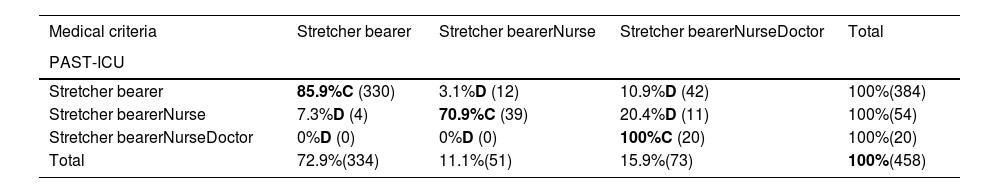
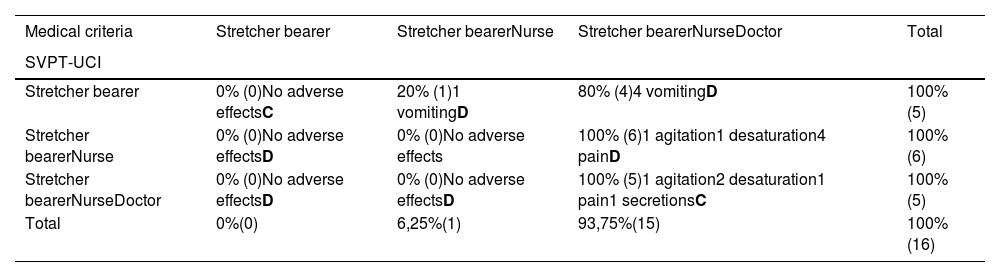
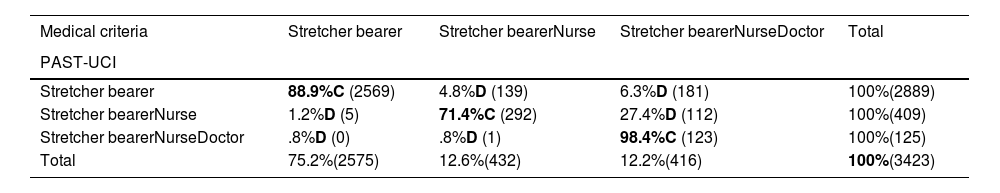
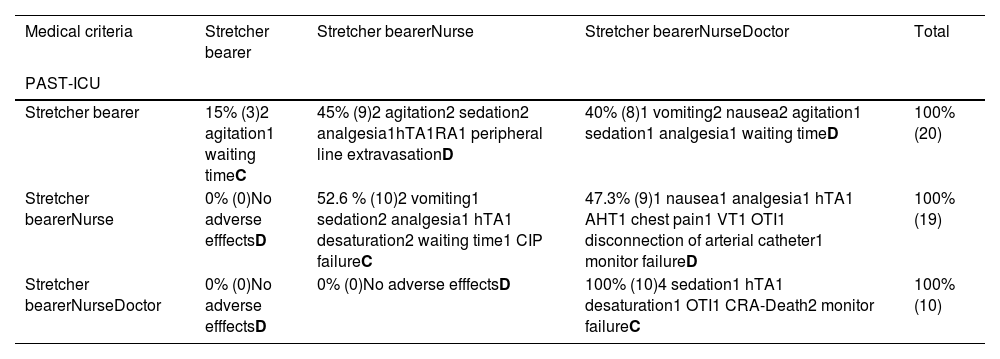
ResultsPhase 1: 458 IHT were analyzed. The concordance index between the PAST-ICU and the MC was 84,9% (389 IHT). The Cohen Kappa of 58,5% and p < 0,001. There were a total of 16 AE. Phase 2: 3423 IHT. The Concordance index of 87,2% (2984 TIH). The Cohen Kappa of 63%and the P < 0,001. Registered 49 AE.
ConclusionThe PAST-ICU could be a useful, safe and reliable tool to adapt the necessary HR. There was good concordance between the PAST-ICU vs the MC to determine the HR in the HIT. The percentage of AE was low.
Actualmente en las unidades de cuidados intensivos (UCI), el transporte intrahospitalario (TIH) de los pacientes, se realiza sin un criterio unificado de personal necesario para el mismo.
ObjetivoEvaluar la concordancia del Sistema de Valoración para el Transporte de UCI (SVPT-UCI) con el criterio médico (CM) para determinar el Recurso Humano (RH) en el traslado intrahospitalario. Identificar los Efectos Adversos (EA).
MétodoEstudio descriptivo, transversal y prospectivo de los TIH de los pacientes de un área de críticos médico-quirúrgica de adultos. Se creó el instrumento SVPT-UCI para recomendar el RH óptimo del TIH. Mediante valoración de parámetros clínicos el SVPT-UCI indica si el TIH debe efectuarse con: camillero o camillero/enfermera o camillero/enfermera/médico. Previamente al TIH la enfermera cumplimentó el SVPT-UCI contrastándose el resultado con el criterio médico (CM), prevaleciendo éste último.
Período de estudioFase 1: prueba piloto 2013-2014. Fase 2: 2015-2021.
VariablesMotivo y duración TIH, documento SVPT-UCI, listado de verificación, efectos adversos (EA).
ResultadosFase 1: 485 TIH incluidos. Índice de concordancia entre SVPT-UCI y CM del 84,9% (389 TIH). Se obtuvo una Kappa de Cohen del 58,5% y una p < 0,001. Registrados 16 EA. Fase2: 3423 TIH incluidos. Índice de concordancia de 87,2% (2984 TIH). Se obtuvo una Kappa de Cohen del 63% y una p < 0,001. Registrados 49 EA.
ConclusiónEl SVPT-UCI podría ser una herramienta útil, segura y fiable para adecuar el RH necesario. Hubo una buena concordancia entre el SVPT-UCI vs el CM para determinar el RH en el TIH. El porcentaje de EA fue bajo.
Artículo
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora