La monitorización electrofisiológica del dolor aporta medidas objetivas que permiten controlar el dolor y ajustar la analgesia en pacientes no comunicativos.
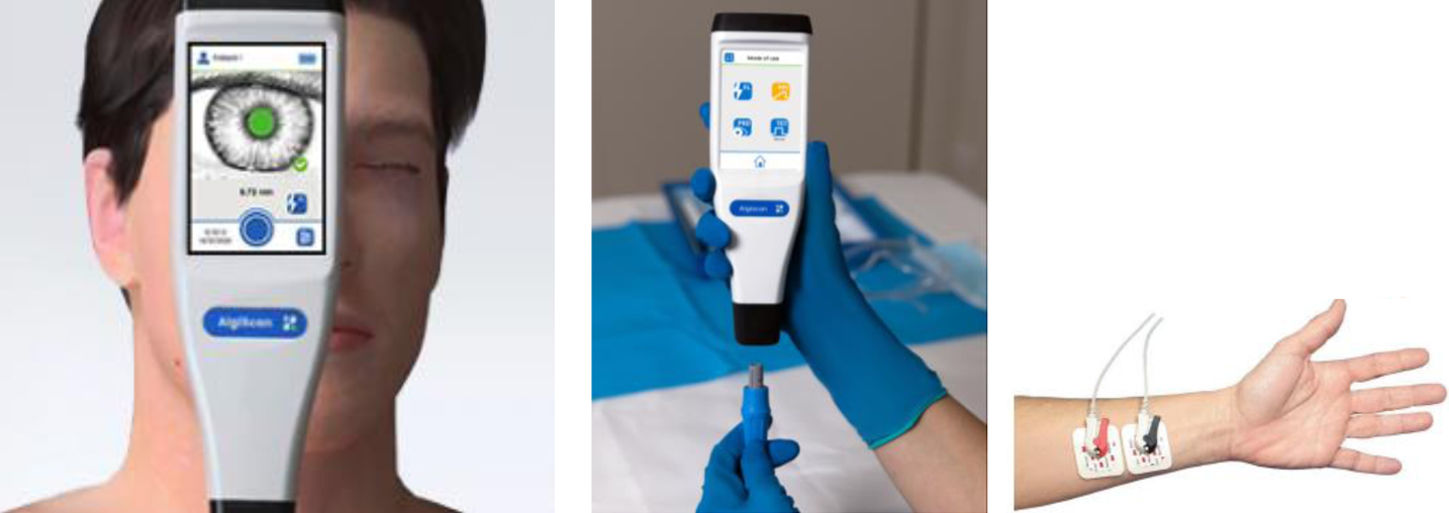
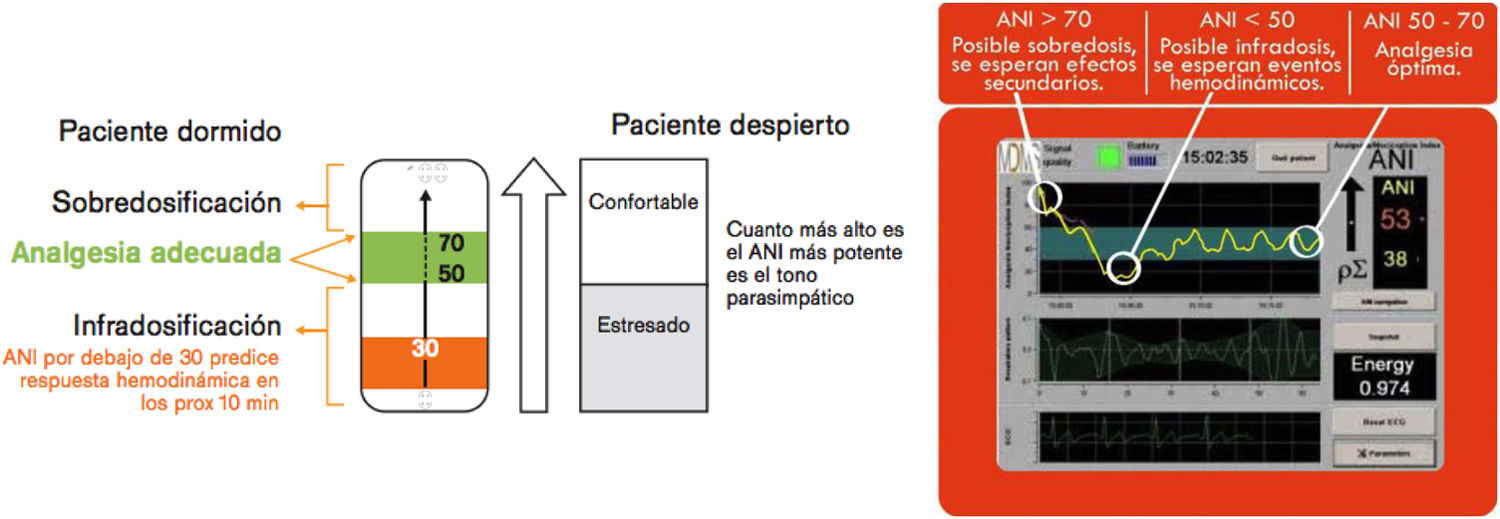
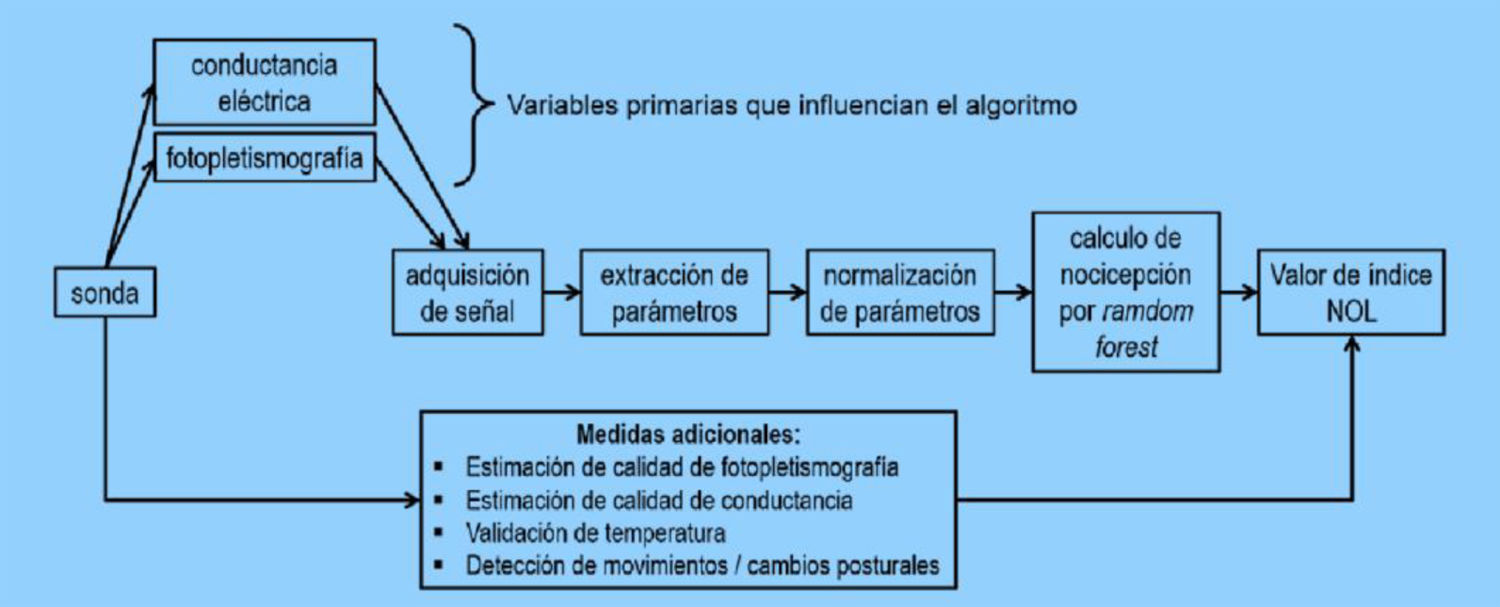
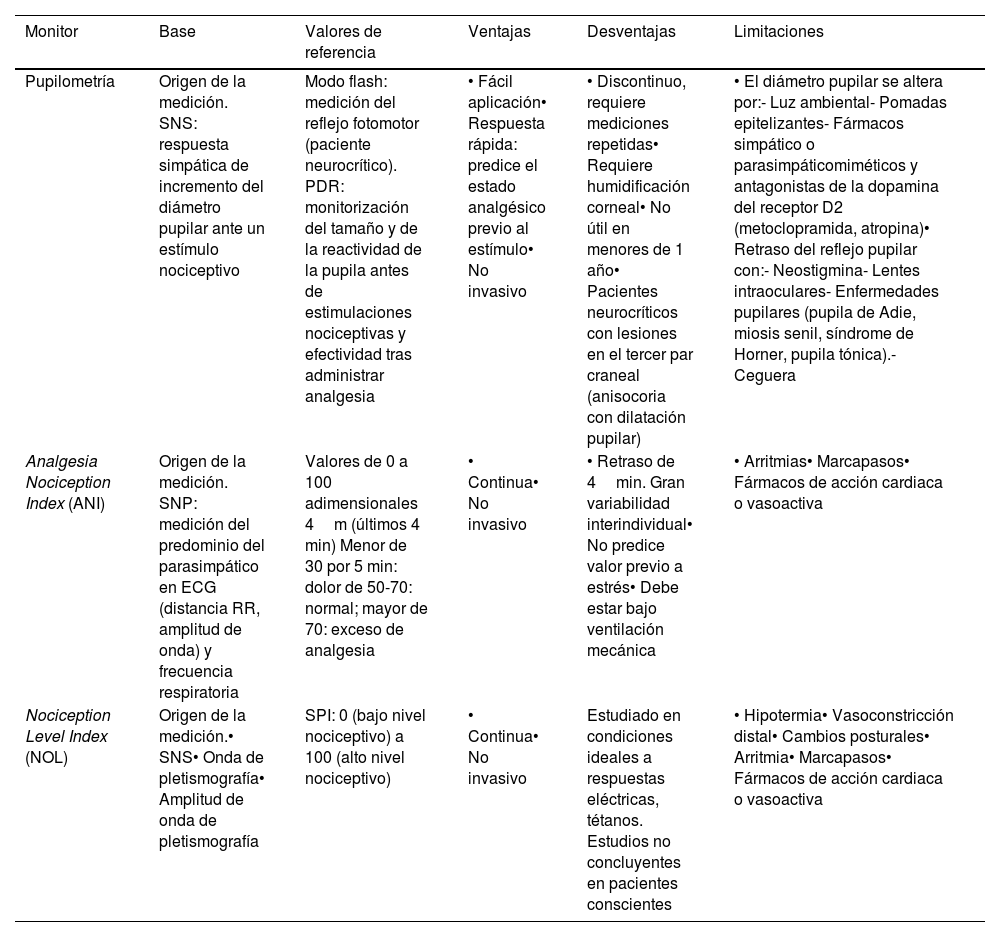
Entre los dispositivos electrofisiológicos disponibles destacan la pupilometría de infrarrojos automatizada, Analgesia Nociception Index (ANI) y Nociception Level Index (NOL®). Estos sistemas de medición no invasivos analizan la respuesta del sistema nervioso simpático o parasimpático ante estímulos dolorosos mediante la observación de la dilatación pupilar y su reactividad (pupilómetro), el ritmo cardiaco durante la respiración (ANI) o la combinación de múltiples parámetros del circuito medular nociceptivo-autonómico (NOL®). Estos métodos se han utilizado principalmente en la monitorización de la nocicepción relacionada con procedimientos en pacientes críticos. Además, han permitido predecir, ajustar y personalizar la administración de analgesia antes de realizar un procedimiento doloroso.
Para obtener mediciones precisas y hacer una buena interpretación de los valores que aportan estos dispositivos, es importante tener en cuenta algunas limitaciones en su uso, como puede ser la administración de determinados fármacos o la presencia de ciertas patologías, por su influencia en la respuesta del sistema nervioso autónomo. También es importante tener en cuenta que, al no disponer de ensayos clínicos aleatorizados en el contexto de unidades de cuidados intensivos sobre estos dispositivos, el nivel de evidencia reportado es limitado.
Electrophysiological monitoring of pain provides objective measures that allow for pain control and adjustment of analgesia in non-communicative patients.
Among the available electrophysiological devices, automated infrared pupillometry, Analgesia Nociception Index (ANI), and Nociception Level Index (NOL®) stand out. These non-invasive measurement systems analyze the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system response to painful stimuli by observing pupillary dilatation and reactivity (pupillometry), heart rate during respiration (ANI), or a combination of multiple parameters from the nociceptive-autonomic medullary circuit (NOL®). These methods have mainly been used in the monitoring of nociception related to procedures in critically ill patients.
Furthermore, they have allowed for the prediction, adjustment, and customization of analgesia administration prior to painful procedures. To obtain accurate measurements and properly interpret the values provided by these devices, it is important to consider certain limitations in their use, such as the administration of specific medications or the presence of certain pathologies, due to their influence on the autonomic nervous system response. It is also important to note that the reported level of evidence is limited, as randomized clinical trials in the context of intensive care unit regarding these devices are currently lacking.
Artículo
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora