Family, peers and school are the three main contexts associated with school engagement. This study aims to analyze possible gender and age differences in these contextual variables and school engagement, as well as the relationship between the two. Participants were 1543 secondary school children aged between 12 and 18 years (M=14.24; SD=1.63). Of the total sample group, 728 (47.2%) were boys and 815 (52.8%) were girls. All completed the Family and Peer Support (FPS) scale, the Teachers’ Support scale of the Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) questionnaire, and the School Engagement Measure (SEM). The results reveal significant differences between boys and girls, with girls scoring higher in perceived peer support and behavioral and emotional engagement. Younger respondents were also observed to score significantly higher for perceived support from parents and teachers, as well as for school engagement. Significant correlation indexes were observed between contextual variables, as well as between these variables and school engagement, although it was for support from teachers that the strongest correlation was found.
La familia, los pares y la escuela constituyen los tres principales contextos asociados a la implicación escolar. Este estudio trata de analizar las posibles diferencias en función del sexo y de la edad en dichas variables contextuales y en la implicación escolar, así como la relación entre ellas. Participaron un total de 1543 estudiantes de Educación Secundaria, 728 hombres (47.2%) y 815 mujeres (52.8%) con edades comprendidas entre los 12 y los 18 años (M=14.24; SD=1.63). Todos ellos cumplimentaron la escala de Apoyo Familiar y de Amigos (AFA), la escala de apoyo de profesores del Cuestionario Health Behaviour in School aged Children (HBSC) y el School Engagement Measure (SEM). Los resultados muestran diferencias significativas a favor de las mujeres en la percepción del apoyo de los amigos, así como en la implicación comportamental y emocional. Se hallan a su vez, puntuaciones significativamente más altas para el grupo de menor edad en cuanto a la percepción del apoyo tanto de los padres como del profesorado, y en la implicación escolar. Por otro lado, se observan índices de correlación significativos entre las variables contextuales, así como entre éstas últimas y la implicación escolar, si bien es el apoyo del profesorado el que correlaciona con más intensidad.
The excessive emphasis that has placed classic psychology on students’ negative aspects has filtered through to the educational psychology also (Huebner & Gilman, 2003) focusing traditionally, psychoeducational research on a risk model. Among risk or maladjustment indicators further investigated (Buelga, Cava, & Musitu, 2012; Cava, Musitu, Buelga, & Murgui, 2010; Povedano, Jiménez, Moreno, Amador, & Musitu, 2012) are included school failure, expected school failure and interpersonal problems with peers.
In contrast to this approach that focused on maladjustment to the school environment, positive psychology is interested in adjustment, considering students’ engagement as a major factor of it. School engagement is considered a vital factor in social-personal development and in academic success (Motti-Stefanidi & Masten, 2013; Ros, Goikoetxea, Gairín, & Lekue, 2012), as well as a protective factor against poor achievement, disaffection and school dropout (Zimmer-Gembeck, Chipuer, Hanisch, Creed, & McGregor, 2006). It is viewed as a possible target for direct intervention during primary school, as part of an attempt to ensure school success and to avoid or at least minimize the occurrence of dropout during secondary school (Fredricks, Blumenfeld, & Paris, 2004).
The concept of school engagement varies from one author to another. There are some who consider it as the connection and commitment to their school and motivation to learn and perform (Simons-Morton & Chen, 2009); others, however, understand it as an active engagement, firm commitment and concentrated attention, in contrast to superficial participation, apathy or lack of interest (Newman, Wehlage, & Lamborn, 1992); or even as a centripetal experience of relating the student to the school (Veiga et al., 2012). Finn's participation-identification model (1989) proposes two elements of school engagement: behavioral and emotional. This model evolved later (Appleton, Christenson, & Furlong, 2008) with the inclusion of the cognitive component also. Today, it is widely accepted that school engagement is regarded as a meta-construct encompassing diverse related constructs, made up of emotional, behavioral and cognitive components (Fredricks et al., 2004).
The emotional dimension encompasses feelings toward school, teachers and fellow students; the behavioral dimension refers to observable acts or participation in extracurricular activities, finishing set tasks and mean overall grades; the cognitive dimension includes students’ perceptions and beliefs about themselves, their school, their teachers and their fellow students.
The term social support refers to the emotional, material and informational input and companionship perceived or received from diverse components of the individual's social network (Gracia, Herrero, & Musitu, 1995). It has been demonstrated that having people you can trust and to whom you can express emotions, difficulties and opinions while feeling listened to and accepted has a major impact on both school adjustment and school engagement (Suárez-Orozco, Pimentel, & Martin, 2009). From the perspective of ecological systems theory, three main social contexts are associated with school engagement: family, peers and school (Ou, 2005; Sinclair, Christenson, Lehr, & Reschly-Anderson, 2003). These three contexts have undergone, over recent years, numerous structural, legal, organizational and even philosophical changes, turning them into objects of renewed scientific interest.
The family constitutes an emotional hub that is vital to human beings’ full development. It is the child's first development environment (Cava, Musitu, & Murgui, 2006) and its importance for the academic achievement of adolescents is beyond any doubt (Martínez, 2009). It has been shown that parental support plays a key role in both school engagement (Veiga et al., 2012) and school adjustment (Rodríguez, Droguett, & Revuelta, 2012); parents who support their children and have high academic expectations of them prompt them to strive for results (Woolley & Grogan-Kaylor, 2006); although while parental influence is greater during children's initial years at school, later on, the adults in the school environment itself tend to become more significant (Woolley & Bowen, 2007).
The peer group becomes during adolescence the most influential socializing context, even though family relations continue to have a strong influence (Fernández del Valle & Bravo, 2000). Relationships with family members cede part of their influence to relationships with the peer group, which become increasingly intense and stable, constituting the priority socializing context and the primary source of support (Allen & Land, 1999; Hartup, 1993; Oliva, 1999). Studies indicate that peers have a considerable influence on several aspects of school adjustment (Studsrod & Bru, 2011), including attitude to school, school engagement and academic success (Wentzel & Caldwell, 1997). This remains true even in longitudinal studies (Buhs, Ladd, & Herald, 2006). Moreover, this relationship is even more intense when mediated by beliefs in academic self-efficacy (Buhs, 2005; Flook, Repetti, & Ullman, 2005; Thijs & Verkuyten, 2008). Some studies confirm a positive relationship between peer support and behavioral school engagement (Berndt & Keefe, 1995), affective school engagement (García-Reid, 2007), both these types (Furrer & Skinner, 2003) and general engagement (Perdue, Manzeske, & Estell, 2009); thus, a lack of engagement may signify a reaction to negative treatment by peers (Buhs & Ladd, 2001; Veiga et al., 2012). Nevertheless, not all studies have found a significative positive association (Rodríguez et al., 2012), showing inconsistent results when other contextual variables (parents and teachers) are taken into account also (Estell & Perdue, 2013).
There is also widespread consensus regarding the importance of school as a context which has a vital impact on the development of both adaptive and maladaptive behaviors (Otero-López, 2001). Numerous studies have highlighted the benefits of positive teacher–student relationships in connection with academic achievement (Voelkl & Frone, 2000; Wentzel, 1999), with support provided and expectations being two principal dimensions in this sense (Murdock, 1999). However, the importance of the teacher becomes even more evident when we take into consideration the fact that the social climate of the school is created mainly by the adults present in that environment (Woolley, 2006). Indeed, the support provided by adults is so influential that students’ positive perception of it may mitigate the effect of contextual risk factors posed by belonging to a certain social class or ethnic group (Woolley & Bowen, 2007). Thus, a good relationship between teachers and students has multiple benefits for school adjustment (Hughes & Kwok, 2007; Hughes, Luo, Kwok, & Loyd, 2008; Meehan, Hughes, & Cavell, 2003).
Despite this background, there is still requirement for further investigation in both interindividual variations in school engagement and its relationships with contextual factors.
As regards school engagement, most studies have found a decrease of the same during the change of education level (Urdan & Midgley, 2003, Wylie & Hodgen, 2011), and specifically in the transition between the primary school and the secondary (Eccles et al., 1997; Ros et al., 2012); on the other hand, adolescent girls score better in school engagement than boys (Freudenthaler, Spinath, & Neubauer, 2008; Lam et al., 2012; Salmela-Aro & Upadyaya, 2012; Wang, Willett, & Eccles, 2011), and more specifically in the behavioral and emotional dimensions, while in the cognitive dimension no significant sex differences have been observed (Escalante, Fernández-Zabala, & Elkoro, 2014). But these data need to be confirmed and clarified.
Regarding social support, adolescent girls perceive the support from friends and teachers they receive higher than boys (Bokhorst, Sumter, & Westenberg, 2010; Musitu & Cava, 2003), while in the perceived support from family no significant sex differences have been observed. It has been confirmed too that both the perceived support from family and from teachers decreases during adolescence (Bokhorst et al., 2010; Furman & Buhrmester, 1992; Musitu & Cava, 2003), thus increasing the importance attached to relations with peers (Colarossi & Eccles, 2003; DuBois et al., 2002).
Finally, it is worth highlighting that most studies that have attempted to relate these two large blocks of variables, social support from family, peers and teachers, on the one hand, and school engagement, on the other hand, do not consider the three dimensions of school engagement widely accepted by the scientific community (emotional, behavioral and cognitive). Relationships and, in general, contexts close to the subject foster academic competence (Ryan & Deci, 2000) and encourage school engagement (Roeser, Eccles, & Sameroff, 2000), but it is important to clarify whether the increase engagement occurs in all dimensions or not, in order to plan a much more specific and effective school intervention.
In order to clarify these questions, this study has a twofold aim. Firstly, to determine how school engagement and social support vary in accordance with sex and age. And secondly, to analyze the relationship between school engagement and three contextual factors: family, peers and school.
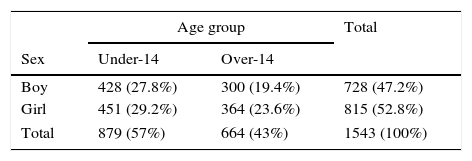
MethodParticipantsParticipants were 1543 students randomly selected from diverse public and private schools in the Autonomous Region of the Basque Country (Spain) (see Table 1). Of the total sample group, 728 (47.2%) were boys and 815 (52.8%) were girls. All were aged between 12 and 18 (M=14.24; SD=1.63) years. To analyze age differences, participants were divided into two groups: the under-14 group, which had 879 students (57%) and the over-14 group, which had 664 (43%).
Pearson's chi-squared test revealed no differences in the distribution of each sex between the two age groups (χ2=1.871, p>.05), indicating that the sample was well balanced.
InstrumentsSocial support perceived from parents and peers was calculated from the responses given to the Social Support Questionnaire (AFA; Landero & González, 2008). This instrument comprises 15 items, to which participants respond on a 5-point Likert-type scale. 8 of the 15 items measure the social support dimension, while the other 7 measure peer support. Together, the items explain 62.04% of the total variance, and offer good reliability: α=.92.
Support from teachers was assessed using the teacher support scale from the Health Behaviour in School aged Children (HBSC) questionnaire, by Moreno, Ramos, Rivera, Jiménez-Iglesias, and García (2012). This scale comprises 8 items with five response options for each. In this study, the percentage of total variance explained by the items was 44.18%. Cronbach's alpha was also found to be adequate, giving an index of .86.
School engagement was measured using the School Engagement Measure (SEM; Fredricks, Blumenfeld, Friedel, & Paris, 2005). This instrument comprises 19 items and responses are given on a 5-point Likert-type scale. The measure is further divided into three sub-scales, all of which have adequate internal consistency indexes: cognitive engagement (α=.55–.82), emotional engagement (α=.72–.77) and behavioral engagement (α=.83–.86).
ProcedureAfter obtaining the required permission from both the management team of the participating schools and the teachers and parents (in the case of the participants themselves being minors), the questionnaires were administered during lesson time in the students’ own classrooms in order to guarantee uniform application. The response time to the battery of questions oscillated between 20 and 30min, varying in accordance with participants’ age. The authors were present at all times during the administration of the questionnaires, in order to answer any questions and clear up any doubts. All participants were assured that their answers would be completely anonymous, although they were not told what the purpose of the project was in order to encourage them to be totally honest in their responses and to decrease the likelihood of social desirability bias.
Data analysisThe statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS 20.0 statistical package for Windows, with the significance level being .05 in all cases. In order to analyze the differences in scores obtained, in accordance with both sex and age, a means contrast was conducted for independent samples using Student's t test. The relationships between the contextual variables, i.e. social support perceived from parents, peers and teachers, and the different dimensions of school engagement (behavioral, emotional and cognitive) were analyzed using the Pearson correlation coefficient. Finally, a multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to identify the predictor variables of school engagement.
ResultsMeans differencesThe results of the means that contrast in accordance with sex are shown in Table 2 for both the contextual variables and the three dimensions of school engagement.
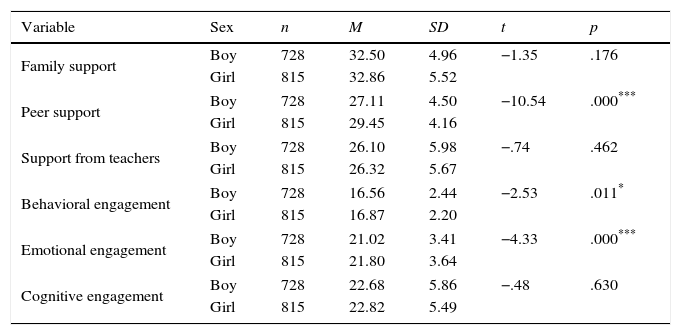
Differences in family context, school context and school engagement, in accordance with sex.
| Variable | Sex | n | M | SD | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family support | Boy | 728 | 32.50 | 4.96 | −1.35 | .176 |
| Girl | 815 | 32.86 | 5.52 | |||
| Peer support | Boy | 728 | 27.11 | 4.50 | −10.54 | .000*** |
| Girl | 815 | 29.45 | 4.16 | |||
| Support from teachers | Boy | 728 | 26.10 | 5.98 | −.74 | .462 |
| Girl | 815 | 26.32 | 5.67 | |||
| Behavioral engagement | Boy | 728 | 16.56 | 2.44 | −2.53 | .011* |
| Girl | 815 | 16.87 | 2.20 | |||
| Emotional engagement | Boy | 728 | 21.02 | 3.41 | −4.33 | .000*** |
| Girl | 815 | 21.80 | 3.64 | |||
| Cognitive engagement | Boy | 728 | 22.68 | 5.86 | −.48 | .630 |
| Girl | 815 | 22.82 | 5.49 | |||
The results reveal statistically significant differences between the sexes, with girls scoring higher on the peer support (t(1486.92)=−10.54; p<.001), behavioral engagement (t(1473.35)=−2.53; p<.05), and emotional engagement (t(1541)=−4.33; p<.001) scales. Although no statistically significant differences were observed in the support from parents (t(1541)=−1.35; p>.05), support from teachers (t(1541)=−.74; p>.05) and cognitive engagement (t(1494.01)=−.48; p>.05) scales, the results did show that, once again, the means were always higher for girls.
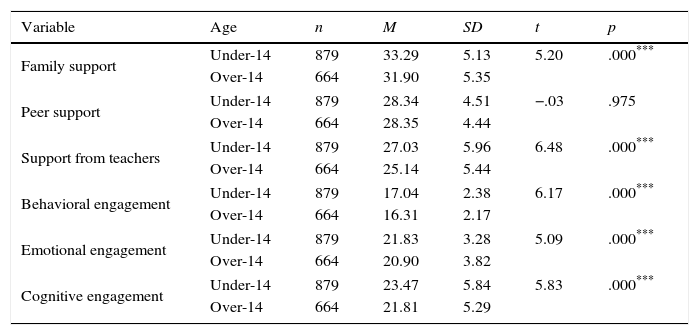
The differences between means in accordance with age (see Table 3) were found to be significant, with the younger age group scoring higher in the support from parents (t(1541)=5.20; p<.001), support from teachers (t(1487.80)=6.48; p<.001), behavioral engagement (t(1541)=6.17; p<.001), emotional engagement (t(1541)=5.09; p<.001), and cognitive engagement (t(1492.11)=5.83; p<.001) scales. No differences were found between the age groups as regards the peer support (t(1541)=−.03; p>.05) scale.
Differences in family context, school context and school engagement, in accordance with age.
| Variable | Age | n | M | SD | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family support | Under-14 | 879 | 33.29 | 5.13 | 5.20 | .000*** |
| Over-14 | 664 | 31.90 | 5.35 | |||
| Peer support | Under-14 | 879 | 28.34 | 4.51 | −.03 | .975 |
| Over-14 | 664 | 28.35 | 4.44 | |||
| Support from teachers | Under-14 | 879 | 27.03 | 5.96 | 6.48 | .000*** |
| Over-14 | 664 | 25.14 | 5.44 | |||
| Behavioral engagement | Under-14 | 879 | 17.04 | 2.38 | 6.17 | .000*** |
| Over-14 | 664 | 16.31 | 2.17 | |||
| Emotional engagement | Under-14 | 879 | 21.83 | 3.28 | 5.09 | .000*** |
| Over-14 | 664 | 20.90 | 3.82 | |||
| Cognitive engagement | Under-14 | 879 | 23.47 | 5.84 | 5.83 | .000*** |
| Over-14 | 664 | 21.81 | 5.29 | |||
Table 4 shows the correlation indexes between all the contextual variables and school engagement.
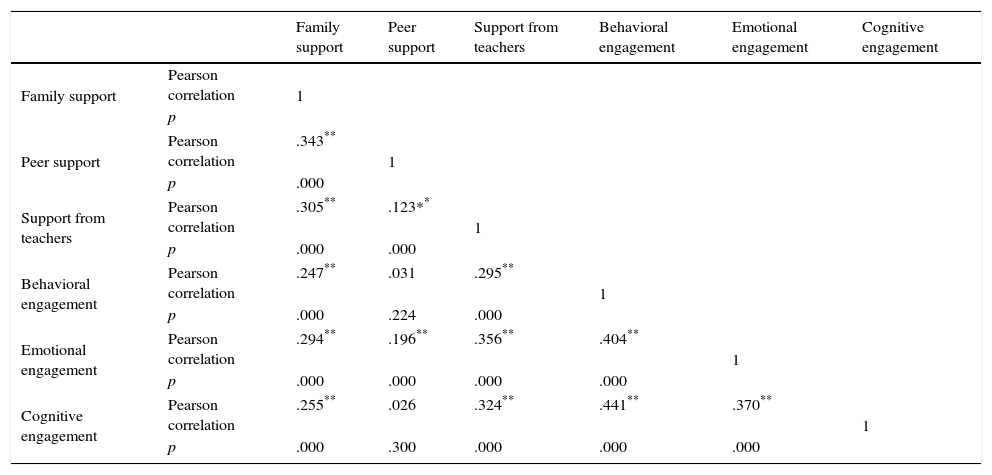
Pearson correlations between family context, school context and school engagement.
| Family support | Peer support | Support from teachers | Behavioral engagement | Emotional engagement | Cognitive engagement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family support | Pearson correlation | 1 | |||||
| p | |||||||
| Peer support | Pearson correlation | .343** | 1 | ||||
| p | .000 | ||||||
| Support from teachers | Pearson correlation | .305** | .123** | 1 | |||
| p | .000 | .000 | |||||
| Behavioral engagement | Pearson correlation | .247** | .031 | .295** | 1 | ||
| p | .000 | .224 | .000 | ||||
| Emotional engagement | Pearson correlation | .294** | .196** | .356** | .404** | 1 | |
| p | .000 | .000 | .000 | .000 | |||
| Cognitive engagement | Pearson correlation | .255** | .026 | .324** | .441** | .370** | 1 |
| p | .000 | .300 | .000 | .000 | .000 | ||
The results indicate that the majority of correlations are significant, with the exception of those between peer support and behavioral and cognitive engagement. It is worth highlighting that, more than support from parents or peers, it is support from teachers that correlates most with all three dimensions of school engagement.
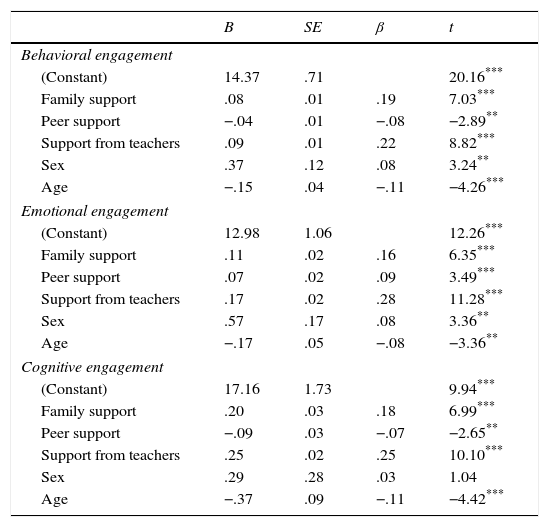
Predictor variables of school engagementTable 5 shows the results of the analysis that aimed to determine to what extent perceived social support from parents, peers and teachers predicts the three dimensions of school engagement.
Predictive capacity of the contextual variables for school engagement.
| B | SE | β | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Behavioral engagement | ||||
| (Constant) | 14.37 | .71 | 20.16*** | |
| Family support | .08 | .01 | .19 | 7.03*** |
| Peer support | −.04 | .01 | −.08 | −2.89** |
| Support from teachers | .09 | .01 | .22 | 8.82*** |
| Sex | .37 | .12 | .08 | 3.24** |
| Age | −.15 | .04 | −.11 | −4.26*** |
| Emotional engagement | ||||
| (Constant) | 12.98 | 1.06 | 12.26*** | |
| Family support | .11 | .02 | .16 | 6.35*** |
| Peer support | .07 | .02 | .09 | 3.49*** |
| Support from teachers | .17 | .02 | .28 | 11.28*** |
| Sex | .57 | .17 | .08 | 3.36** |
| Age | −.17 | .05 | −.08 | −3.36** |
| Cognitive engagement | ||||
| (Constant) | 17.16 | 1.73 | 9.94*** | |
| Family support | .20 | .03 | .18 | 6.99*** |
| Peer support | −.09 | .03 | −.07 | −2.65** |
| Support from teachers | .25 | .02 | .25 | 10.10*** |
| Sex | .29 | .28 | .03 | 1.04 |
| Age | −.37 | .09 | −.11 | −4.42*** |
The results revealed that all the variables considered (support from parents, peers and teachers, sex and age) were significant in the case of behavioral and emotional engagement. Sex, however, was not found to be a significant predictor of cognitive engagement among secondary school students. A medium level of variance was explained by these predictor variables in all three dimensions, with the specific percentages being 13% for behavioral engagement, 18% for emotional engagement and 15% for cognitive engagement. Of this variance, in all cases, perceived support from teachers was found to be the variable with the greatest explanatory capacity, followed by perceived support from parents. Another finding worth noting was that age was revealed as a negative predictor for school engagement. In other words, the older the child, the less engaged they are with their school.
DiscussionThe aim of this present study was firstly, to determine sex and age differences in both contextual variables (support from family, peers and teachers) and school engagement; and secondly, to analyze the relationships between said contextual variables and school engagement. This information is vital to the understanding of any psychological construct.
In relation to sex, the results confirm that which was found in previous studies, particularly as regards greater perceived peer support among girls (Musitu & Cava, 2003), and greater emotional and behavioral engagement (Escalante et al., 2014). In this sense, there is a study that concludes that the boys displayed fewer learning strategies and the girls take more responsibility for academic failure (Ghazvini & Khajehpour, 2011).
In relation to age, younger students were found to perceive more social support and have greater school engagement than their older counterparts. Although this is by no means a universal pattern (Li & Lerner, 2011), previous studies do indicate a decrease in school engagement during adolescence, specifically during secondary school (Green et al., 2012; Wang & Eccles, 2012). It is therefore vital to research the factors and processes that influence this important construct.
In short, bearing in mind that older children scored lower in perceived social support and school engagement, it is evident that interventions are required that are targeted specifically at that population.
A relationship was also observed between family context and school context (Moreno, Estevez, Murgui, & Musitu, 2009), as well as between both contexts and school engagement. However, the results fail to confirm a habitual trend during adolescence, namely the fact that family context loses ground to peer influence. In our study, the results showed no significant relationship between peer support and school engagement. Indeed, the factor that appears to have the most influence on school engagement is the support students perceive from their teachers, a result that has been found previously in other studies (Gruman, Harachi, Abbott, Catalano, & Fleming, 2008). In short, if the aim is to foster school engagement and adjustment during adolescence, then adults need to play a more prominent role in this process.
From this work is derived the possibility and desirability of study, together with contextual and psychological variables, in order to provide a more comprehensive understanding of adaptation of students to the school context (Rodríguez et al., 2012). In this way, it is interesting and innovative to analyze the impact that close contexts studied here (family and school) along with the psychological characteristics (e.g., self-concept, emotional intelligence and resilience) can have on the behavior of students in terms of engagement or academic performance.
Conflict of interestThe authors of this article declare no conflict of interest.
The authors of this paper form part of the Consolidated Research Group IT701-13 of the Basque University System. The study itself was carried out as part of the EHUA13/26 research project at the University of the Basque Country.