Attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common neuro-behavioural disorder with onset in childhood. These children have impaired emotional self-control, self-regulation of drive and motivation. Numerous studies have reported cognitive disabilities in memory, executive functions, spatial abilities and language skills. The main objective of this work is to determine whether a socio-emotional intervention programme could improve executive functions in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. The sample of this study consisted of 25 children (8 female and 17 male) aged between 8 and 12 years, diagnosed with ADHD and who were not taking any psychopharmacological treatment at the time of the study, and had not taken medication previously. Executive functioning was assessed through the Zoo Map test and Tower of Hanoi puzzle in pre-/post-test design. A socio-emotional intervention programme was implemented. The training consisted of 8 one-hour weekly sessions, on an individual basis. Results indicate that such a programme does lead to improved performance in the execution of tasks that evaluate executive functions. After the intervention, the children took less time to resolve the Zoo Map test. Results for the Hanoi Tower puzzle were also improved after intervention. The children needed a lower number of movements to complete the task.
El Trastorno por Déficit de Atención e Hiperactividad (TDAH) es el trastorno más frecuentemente diagnosticado durante la infancia. Uno de los modelos explicativos es el desarrollado por Barkley (1990), que considera que la capacidad de inhibición de una respuesta estaría mediatizada por la capacidad de inhibir una respuesta hacia un objeto que atrae nuestra atención, la capacidad para interrumpir una conducta que se está llevando a cabo y la competencia para cambiar el foco de nuestra atención. De esta forma, una baja capacidad de inhibición repercutiría negativamente en las capacidades cognitivas. Desde este modelo, se considera que dicha incapacidad de inhibición está producida por una alteración en la Función Ejecutiva. La muestra de nuestro estudio está formada un grupo de 25 niños con edades comprendidas entre 8 y 12 años diagnosticados de déficit de atención que no están tomando medicación en la actualidad ni la han tomado anteriormente. Se realizó un programa de intervención socio-emocional de una duración de 8 semanas y una frecuencia semanal de una hora. Durante estas sesiones se trabajó el autocontrol, la tolerancia a la frustración y la resiliencia. Los resultados muestran una mejora en la Función Ejecutiva que se traducían en una mejor inhibición conductual.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a common neurobehavioral disorder with onset in childhood (Weyandt, 2007), is characterized by developmentally inappropriate levels of hyperactivity, impulsivity in motor, emotional and social responses, a general lack of inhibition and pervasive inattention (DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
ADHD is associated with greater risks for low academic achievement (Rodríguez et al., 2009), poor school performance, retention in grade, school suspension and expulsions, poor peer and family relation, anxiety and depression, aggression, conduct problems and delinquency, early substance experimentation and abuse, driving accidents and speeding violations, as well as difficulties in adult social relationship, marriage and employment. Often, these children have impairment in emotional self-control, self-regulation of drive and motivation. Numerous studies have reported cognitive disabilities in memory, executive functions, spatial abilities and language skills (Barkley, 2006; Goldstein & Naglieri, 2006; Goldstein & Schwebach, 2004).
From a psychological perspective, many theories of ADHD have been proposed depending on whether they emphasize motivational or energic factors (“bottom-up” theories) or emphasize some form of cognitive control (“top-down” theories). Classic bottom-up theories proposed that ADHD arises from a deficit in sensitivity to reinforcement (Haenlein & Caul, 1987) or as involving a steep reward-discounting gradient (Sagvolden, Johansen, Aase, & Russell, 2005). Early top-down theories were Still's (1902) notion of defective volitional inhibition and moral regulation of behaviour; and Douglas's (1972) theory of deficient attention, inhibition, arousal and preference for immediate reward. The most comprehensive articulation of a top-down model has come from Barkley (1997). He has outlined a theory of ADHD that attempts to integrate numerous observations into a more comprehensive theory. This author proposes that self-regulation requires the ability to inhibit a behavioural response, and that four other executive functions are dependent upon this for their own effective execution. These four executive functions provide for self-regulation, bringing behaviour progressively more under the control of time and the influence of future over immediate consequences. The interaction of these executive functions permits far more effective adaptive functioning towards the social future (social self-sufficiency). In this model, the term Executive Function refers to this mainly private (cognitive) self-directed actions that contribute to self-regulation (Hughes, Russell, & Robbins, 1994).
The model developed by Barkley, DuPaul, and McMurray (1990) hypothesized that the ability to inhibit a response would be mediated by the competence to inhibit a response to an object that attracts our attention, the ability to stop a behaviour that is taking place and the capability to change the focus of our attention. Thus, low inhibition ability would have a negative impact on cognitive performances. According to this model, the ability to inhibit the behaviour would act as moderator for four executive mechanisms: self-regulation of emotion, motivation and arousal; internalization of speech; nonverbal working memory and reconstitution. These executive functions influence the motor system in the service of goal-directed behaviour.
In this sense, recent studies have reported that children with ADHD have many difficulties in self-regulation of affect, motivation and arousal (Pacheco, Díez, & García, 2010). Several studies have found that these children show a lower motivation, effort capacity and reward discounting (Barber, Milich, & Welsh, 1996; Barkley et al., 1990; Douglas, 1988). This difficulty in self-regulation of motivation may explain the need for short-term reinforcers (Haenlein & Caul, 1987; Sagvolden, Wultz, Moser, Moser, & Morkrid, 1989). Neuroimaging research had suggested brain underactivity, particularly in functioning related to the frontal lobes (Klorman, 1992; Rothenberger, 1995).
Self-directed speech is believed to provide a means for reflection and description, by which the individual covertly labels, describes, and verbally contemplates the nature of an event or situation prior to responding to that event. Private speech also provides a means for self-questioning through language, creating an important means for self-interrogation of the past and thereby a source of problem-solving ability, as well as a means of formulating rules and plans. Children with ADHD have greater difficulty following directions (Luk, 1985) and rules (Hinshaw, Simmel, & Heller, 1995), using strategies for achieving a goal (August, 1987) and deficient rule-governed behaviour (Conte & Regehr, 1991). These difficulties related to planning are also well documented in patients with damage in the frontal lobe (Gershberg & Shimamura, 1995; Kesner, Hopkins, & Fineman, 1994). Studies focusing on brain morphology have found that patients with ADHD had significantly smaller brain volumes in all regions (Castellanos et al., 2002). Neuropsychological findings suggest that deficits in response inhibition, delay aversion, and executive functioning are presumed to be linked to dysfunction of frontal-striatal-cerebellar circuits (Krain & Castellanos, 2006).
Nonverbal working memory is defined as the capacity to maintain internally represented information in mind or online that will be used to control a subsequent response. It represents covert sensing towards oneself. The retention of a sequence of events in the working memory appears to provide the basis for the human sense of time and could explain the incapacity that children with ADHD have to manage behaviour relative to time. Also, it has been largely demonstrated that these children have a poorer performance in tasks related to memorizing digits (Barkley, Murphy, & Kwasnik, 1996) and spatial memory tasks (Grodzinsky & Diamond, 1992). An early study (Cantwell & Satterfield, 1978) found a high prevalence of academic performance problems in boys with ADHD as compared to age-matched boys with similar Intelligence quotient. Swanson and Saez (2003) reported similar findings and highlighted the importance of the working memory and the executive functions in learning disabilities.
The reconstitution component represents activities of “analysis” and “synthesis”. “Analysis” means the ability to take the units of behavioural sequences apart. These behavioural units can then be recombined to create novel behaviours and sequences of behaviours out of previously learned responses, in a process Bronowski called “synthesis.” The last executive mechanism stated from this model refers to the ability of analysis and synthesis. Several studies have found that children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder have greater difficulty analysing verbal (Fischer, Barkley, Edelbrock, & Smallish, 1990) and nonverbal information (Funk, Chessare, Weaver, & Exley, 1993).
From this perspective, the ineffectiveness of such mechanisms would lead to uncontrolled and inefficient motor behaviour. Some studies associated disability in behavioural inhibition with an inadequate control of movement, leading to hyperactivity (Hartsough & Lambert, 1985; Szatmari, 1992). This alteration of behavioural inhibition could explain, in part, the psychomotor difficulties in children with ADHD (Grodzinsky & Diamond, 1992; Seidman et al., 1995, 1997, 2005).
Thus, the model proposed by Barkley, not only explains the core symptoms of ADHD (inattention-hyperactivity-impulsivity), but also gives an explanation to the behaviours that often accompany this symptom triad, having a high comorbidity with other disorders (mood disorders, learning disorders, communication disorders, emotional disorders and disorders related to the development of coordination).
ADHD is a valid clinical disorder that can be distinguished from coexisting conditions (although it is most commonly comorbid) and the normal spectrum. ADHD differs from the normal spectrum because there is a high level of hyperactivity/impulsivity and/or inattention that result in significant psychological, social and/or educational or occupational impairment, occurring across multiple domains and settings and persisting over time. A diagnosis of ADHD should only be made on the basis of a full clinical and psychosocial assessment of the person; this should include discussion about behaviour and symptoms in the different domains and settings of the person's everyday life, and a full developmental and psychological history, as well as observational reports and assessment of the person's mental state.
Treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) includes parents-training interventions, behavioural interventions and pharmacotherapy. The family-centred interventions are based on providing parents the necessary training to handle difficult behaviours. Referring to specific pharmacological treatment for ADHD, we found that the treatments most widely used in Spain nowadays is based on the administration of methylphenidate or atomoxetine, whose effects cause an increase in dopamine in the brain. Cognitive behavioural therapy has shown beneficial effects. Being able to understand for themselves the causes of their difficulties as well as the having the possibility of learning mechanisms to avoid failure and frustration seems to be relevant. Ramsay and Rostain (2008) conducted a programme of 16 sessions carried out during six months, where teaching focused on symptoms, learning to regulate their own behaviour. The results indicated an improvement in the core symptoms of ADHD. In a similar way, Antshel et al. (2012) conducted a programme with 68 adolescents diagnosed with ADHD where briefings on ADHD, communication skills, recognition and control of emotions were included. Data from this study indicate an improvement in symptoms of inattention, better school performance and a gain in social and family relationships. In addition, interventions aimed at improving behavioural self-regulation in ADHD lead to a better academic performance (Chronis et al., 2006).
In recent years, Emotional Intelligence programmes have been implemented providing positive outcomes in children with ADHD. These programmes have been carried out in schools with children aged between 7 and 10 years and have focused on training in social skills and communication; emotional self-control skills; cooperative work strategies and strategies on learning how to think. The results of these studies show that students with ADHD who attend these programmes improved their academic performance and their intellectual competence (Girón, 2005).
Recently, in order to improve self-regulation in children with ADHD, mindfulness training for both children and their parents has been found to be effective (Cassone, 2015). With regard to higher education, Parker et al. (2011) launched a pioneering training that consisted of the implementation of a coaching programme in college students with ADHD. During 10 sessions the students had sessions periodically with a coach specifically trained in the care of subjects with ADHD. Coaching appears to strengthen students’ executive functioning skills, promote their autonomy, and enhance their sense of well-being.
The aim of this study was to test whether a social-emotional intervention can improve executive function in children with ADHD.
MethodParticipantsThe sample of this study consisted of 25 children (8 female and 17 male) aged between 8 and 12 years, diagnosed with ADHD-predominantly hyperactive/impulsive presentation and who were not taking any psychopharmacological treatment at the time of the study, and had not taken medication previously. The participants are students from various schools in the province of Zaragoza, Spain. All of them were unaware of the purpose of the intervention and agreed to participate voluntarily. Subjects received no compensation for participating in the study. Compliance with the standards contained in the Declaration of Helsinki on human experimentation was guaranteed at all times. Inclusion criteria included being aged between 8 and 12, attending any school in the province of Zaragoza (Spain) and having been diagnosed with ADHD. Exclusion criteria included presenting some kind of mental disorder, intellectual disability or visual/hearing impairment. Students who were taking, or had been taking, psychopharmacological treatment for Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder and those students who had previously attended psychological therapy were also excluded.
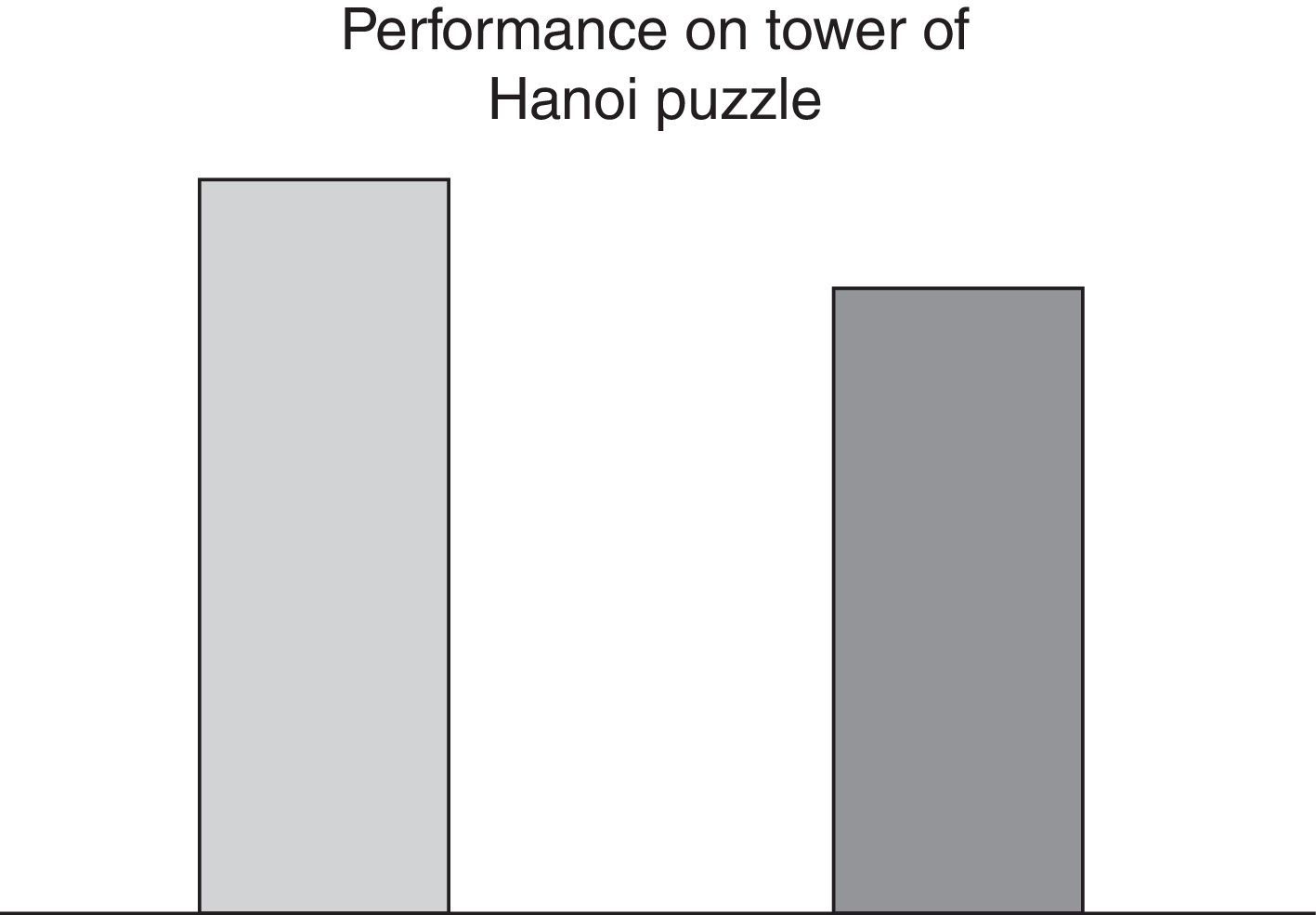
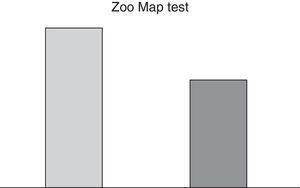
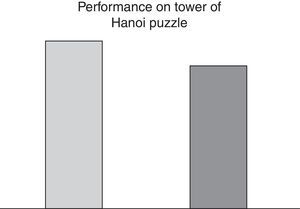
VariablesAs dependent variables, executive functioning was assessed through the Zoo Map test (version A in pre-test phase and B in post-test phase in order to avoid any memory effect) and the test of the Tower of Hanoi. The Zoo Map Test is one of the subtests of behavioural assessment of dysexecutive syndrome (BADS), a battery of tests aimed at predicting the difficulties in daily life as a result of dysexecutive syndrome. The test of the Tower of Hanoi is another test widely used to assess executive functioning and resolution of a complex task that requires problem solving strategies (Díaz et al., 2012). Two measurements were taken, one before applying the socio-emotional training and the other after its application. In the Zoo Map test the duration in solving the task was evaluated and in the test of the Tower of Hanoi the number of attempts before solving the task was measured.
As independent variable, a training of a socio-emotional intervention was implemented. The training consisted of 8 one-hour weekly sessions, on an individual basis. In the first session we worked on the recognition of basic emotions. During the second session, diverse situations were showed and the child analyzed how he/she had felt, as well as talking about how they behaved in such situations and a model of an appropriate behaviour was given. The third session focused on self-awareness of strengths and weaknesses. Appropriate and inappropriate behaviours were addressed along with a proposal on how to improve the weaknesses through the use of their strengths. In the fourth session, we worked on the feeling of belonging to a group. We analysed how they behave in groups and possible difficulties experienced with peers. The fifth session was dedicated to working on Social Skills through training in empathy, active listening and assertiveness. The sixth session focused on learning relaxation techniques. During the seventh session we worked on how we can shift our emotions. The association between emotion and thought was addressed and we worked on substituting negative emotions with positive ones through our thoughts. During the eighth session a summary of what had been worked on in previous sessions took place.
ProcedureBefore initiating the study, parents were interviewed and informed about the programme. They were then asked if they were willing to participate in the study and given the informed consent. The participants initiated the first phase of the study with individual sessions. The tests were conducted in a soundproof room adapted for the administration of this type of assessment. At this stage, the Zoo Map Test and the test of the Tower of Hanoi were administered individually to assess executive functioning. Once finished this part of the study, the socio-emotional intervention programme was administered to the group. Finally, the assessment tests of executive functioning, the test of the Tower of Hanoi and the Map Zoo, were administrated again, now in their B version to avoid possible memory effects on the task.
ResultsData were analyzed with SPSS 20.0. The statistical techniques were descriptive (arithmetic mean and standard deviation) and group comparative (student “t”). No statistically significant differences were found with regards to sex and age. The results showed an improvement in both tests after socioemotional intervention (Table 1).
After the intervention, the children took less time to resolve the Zoo Map test (Fig. 1).
Results for the Hanoi Tower puzzle were also improved after intervention. The children needed a lower number of movements to complete the task (Fig. 2).
DiscussionIt is increasingly recognized that ADHD is a lifelong disorder and the focus of school-based interventions needs to be long-term: individualized education and behavioural plans that require ongoing evaluation, modification, and implementation, over months and years. Currently, medication is the predominant treatment for children with ADHD (Hill & Turner, 2015) in spite of the fact that the NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, 2013) recommend that the first treatment option should be psychological interventions.
Reducing the severity of ADHD and its associated difficulties requires effective interventions that address problems at home, school and in the community. Effective management programmes link the nature of the problems to specific treatments management by objectives). On a broad diagnostic level, therapy can be targeted to specific subtypes of ADHD and comorbid disorders. For effective behavioural interventions that are tailored to the specific needs of the child, one must go beyond diagnosis and identify the behaviours for which change is desired (e.g. deportment, academic problems, social skills etc.), as well as the function that these behaviours serve for the individual.
The main objective of this work was to determine if a socioemotional intervention programme could improve executive functions in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Results indicate that such a programme does lead to improved performance in the execution of tasks that evaluate executive functions. Barkley (1997) has theorized that problems with executive functioning (EF) specifically and self-regulation more generally are central to ADHD and give rise to the more obvious surface behavioural symptoms represented in the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. We found no significant differences with regards to the sex of the subjects; a number of previous studies have shown that although ADHD is more prevalent among males, there are no differences in the carrying out of executive function evaluation tests (Seidman et al., 2005).
Because of their decreased sensitivity to reward and their failure to sustain effort when reinforcement is inconsistent and weak, students with ADHD usually require more frequent and more powerful reinforcement (often in the form of special privileges or activities) in order to modify classroom performance (Pfiffner et al., 1985). Reward programmes can be designed for individual children or the entire class. Individual or classwide programmes in which students earn rewards for their behaviour are often best for the student with ADHD. Involving the entire class may be particularly effective when peer contingencies are competing with teacher contingencies (e.g. when peers reinforce disruptive students by laughter or joining in their off-task pursuits).
In our study, we chose individual therapy in order to focus on the characteristics of the child. The success of token programmes in numerous studies and their success with a wide range of problem behaviours have led to their widespread use in school settings.
Efforts to involve peers in modifying the disruptive and intrusive behaviour of a child with ADHD have concentrated on strategies to discourage peers from reinforcing their classmate's inappropriate behaviour and to encourage positive, prosocial behaviour. Cunningham (1998) have developed a student-mediated conflict resolution programme that involves peers’ acting as playground monitors. The implementation of this programme has been associated with reductions in playground violence and negative interactions throughout the school.
Self-management interventions, which include self-monitoring, self-reinforcement, and more comprehensive self-instruction and problem solving, were originally developed to directly treat the impulsive, disorganized, and non-reflective manner in which children with ADHD approach academic tasks and social interactions. With emphasis on self-control, it was thought that these interventions would reduce the need for extrinsic rewards and would result in better maintenance and generalization of gains made by children with ADHD than those achieved with contingency management programmes. Social skills training (SST) has achieved some positive results for assisting children with ADHD in their social adjustment, but they are usually limited to settings with active behavioural programmes in place to promote the skills. The grouping of children in SST is an important consideration, since aggressive behaviour may increase in some children if nonaggressive and aggressive children participate together in groups (Hinshaw et al., 1995).
Several early studies examined the combined effects of stimulant medication and cognitive-behavioural therapy. Horn et al. (1983) examined the separate and combined effects of dextroamphetamine and self-instructional training for a 9-year-old inpatient child with ADHD. The combined programme was more effective in increasing on-task behaviour during classwork as well as decreasing teacher ratings of ADHD symptoms. However, academic productivity was only improved by the use of direct reinforcement for correct responses. Some success for combined medication and self-evaluation procedures was reported (Hinshaw et al., 1984) when social skills, such as cooperation, were targets of the intervention. In contrast, using group comparison designs, Brown et al. (1986) found no benefits of combined drug and cognitive-behavioural therapy over either treatment alone on similar domains of functioning in children with ADHD.
The aforementioned works combine psychological and pharmacological approaches. In these cases, it is very difficult to determine the degree to which each one contributes to the improvements. It is for this reason that our study has only included psychological therapy. Previous works have focused on behavioural and/or cognitive aspects; one of the original features or our work is the incorporation of more diverse considerations. We examined the importance of making sure that the child understands the process. In the programme, we clearly explained the nature of ADHD and its consequences. We worked on the concepts of strengths and weaknesses to later link them to the ideas of tolerance and frustration. Another aim was to improve the child's control over emotions and social skills as a lack of inhibition can provoke difficulties in relationships with peers and adults. In short, we encouraged the children to believe in their own abilities and we acted as a guide that aimed to help them overcome their problems by means of an optimistic interpretation of any given situation.
There continues to be a need for a better understanding of how to match specific instructional materials and behaviour management techniques to the individual characteristics of the child, and how to enhance academic performance and improve maintenance and generalization of intervention effects.
Conflict of interestWe declare no conflict of interest.