The socioemotional wealth (SEW) related to emotional endowments accumulated in the business by the family, is one of the most important features that differentiate the family firms of other organizations. However, there are few studies developed in the context of the antecedents and consequences of the building and use of SEW in the family business. Therefore, this study, using a sample of Spanish family firms that are non-publicly traded, explains how family influence affects the building and use of SEW and, thus, the organizational effectiveness of the family firm. The results indicate mixed results regarding the impact of the family involvement on the essence. Those suggest a positive relationship between building and use of SEW and organizational effectiveness of the family business.
La riqueza socioemocional se relaciona con las dotaciones emocionales que la familia acumula en la empresa. Es una de las características más importantes que diferencian a las empresas familiares de otros tipos de organizaciones. Sin embargo, existen pocos estudios desarrollados en el contexto de los antecedentes y consecuencias de la creación y uso de la riqueza socioemocional en la empresa familiar. Por tanto, en este estudio, utilizando una muestra de empresas familiares españolas que no cotizan en bolsa, se explica cómo la influencia familiar afecta la creación y uso de la riqueza socioemocional y, de este modo, a la efectividad organizativa de la empresa familiar. Los resultados indican resultados mixtos con respecto al impacto de la participación familiar en la esencia de la empresa familiar. Además, sugieren una relación positiva entre la creación y uso de la riqueza socioemocional y la efectividad organizativa de la empresa familiar.
The management of family firms is related to feelings and emotions (Morgan & Gómez-Mejía, 2014). This influence has to do with family owners willing to preserve family ties over time (Chrisman, Chua, & Sharma, 2005; Litz, 1995; Zellweger, Eddleston, & Kellermanns, 2010). Family introduces in the firm other than economic objectives that literature refers to as socioemotional wealth (SEW) (Berrone, Cruz, & Gómez-Mejía, 2012; Cennamo, Berrone, Cruz, & Gómez-Mejía, 2012; Gómez-Mejía, Cruz, Berrone, & De Castro, 2011; Gómez-Mejía, Haynes, Núñez-Nickel, Jacobson, & Moyano-Fuentes, 2007).
The specificities of each family managing a firm (familiness) make them heterogeneous in their SEW (Chirico & Nordqvist, 2010; Chrisman, Chua, Pearson, & Barnett, 2012; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2011). In fact, those differences in power, experience, and culture are the basis for family firm diversity as the participation and essence approaches state (Chua, Chrisman, & Sharma, 1999). Therefore, the familiness is affecting priorities in terms of SEW (Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007).
Previous literature offers evidence of family ownership and managerial activities related to SEW (Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007). However, previous literature has not evaluated the relational perspective in the family firms (Milton, 2008). In this paper, we evaluate for family firms, the effects of family involvement and essence on SEW and, the consequences on organizational effectiveness. In order to accomplish this research objective, we conduct a study of representative non-listed Spanish family firms during 2013.
We use the literature based on socioemotional wealth (Astrachan & Jaskiewicz, 2008; Berrone, Cruz, Gómez-Mejía, & Larraza-Kintana, 2010; Berrone et al., 2012; Chrisman & Holt, 2016; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2011; Martin & Gómez-Mejía, 2016; Zellweger & Astrachan, 2008), literature based on involvement and essence approaches (Chua et al., 1999; Chrisman et al., 2005; Litz, 1995; Sharma, Chrisman, & Chua, 1997), and literature on organizational effectiveness (Gold, Malhotra, & Segars, 2001; Zheng, Yang, & Mclean, 2010).
Overall, this study advances theoretically and empirically our understanding of the family firms and, we continue the research by Berrone et al. (2012), Astrachan (2010) and Chrisman et al. (2005). In particular, this study advances theoretically and empirically our understanding of the family firms by (i) improving the comprehension of how the specific resources of the family in the firm affect SEW, (ii) providing empirical evidence and support for the impact of SEW on organizational effectiveness, and (iii) focusing on non-listed Spanish family firms.
In the sections that follow, we first present the theoretical model and the hypotheses. Second, we explain the methodology, sample, variables, and measurement. Finally, we discuss the results, implications and future research.
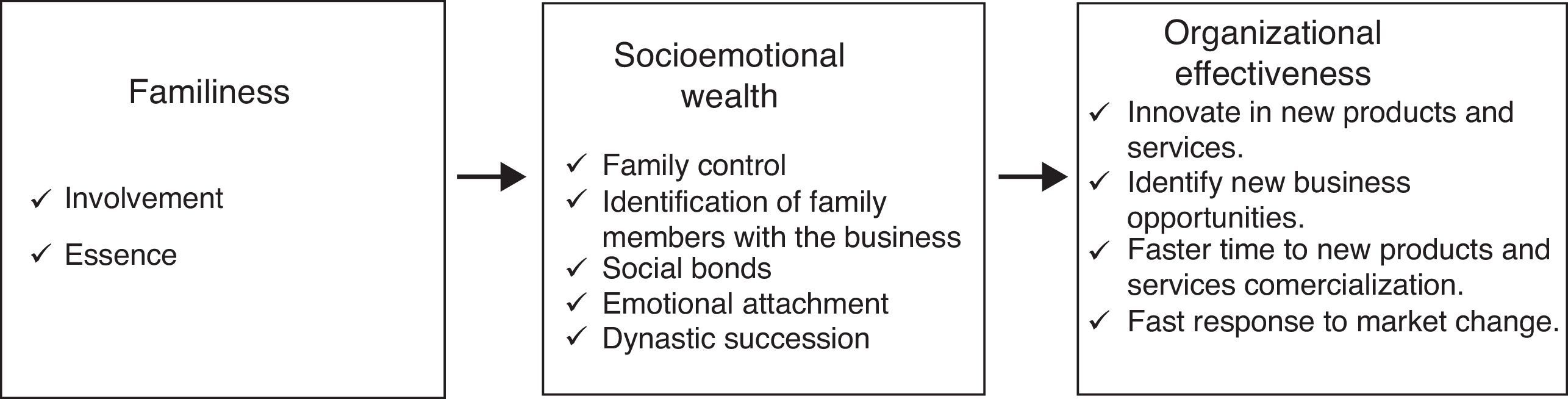
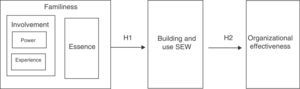
Theory and hypothesesSEW in family firmsRecent literature on family firms reveals that their non-economic objectives are a consequence of preferences of the dominant coalition in the firm (Berrone et al., 2012). This is a characteristic that differentiates those firms to the non-family firms which have mainly an economic purpose. Furthermore, family firms are not homogeneous in preferences related to perceptions, values, attitudes, and intentions of the family (Westhead & Howorth, 2007). Fig. 1 shows the model based on SEW to explain the antecedents and consequences of non-economic objectives (Berrone et al., 2012; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007).
SEW is defined as ‘the nonfinancial aspects of the firm that meet the family's affective needs, such as identity, the ability to exercise family influence, and the perpetuation of family dynasty’ (Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007). Therefore, the process of aggregating family emotions derives the emotional or socioemotional value for the firm (Astrachan & Jaskiewicz, 2008; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007). From the involvement and essence approaches, researchers claim that the key elements affecting this emotional process are the family ownership and control, and the generational control intentions (Chua et al., 1999; Chrisman et al., 2005). Those idiosyncratic characteristics (familiness) help to preserve the firm SEW (Astrachan & Jaskiewicz, 2008; Berrone et al., 2010; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007; Gómez-Mejía, Makri, & Kintana, 2010; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2011; Zellweger & Astrachan, 2008). To the best of our knowledge, there is not empirical research relating familiness to SEW.
Creating SEW relates to the decision process in the firm (Berrone et al., 2012). In fact, only SEW can explain some managerial decisions that are not efficient from a purely financial analysis (Zellweger, Kellermanns, Chrisman, & Chua, 2012). Moreover, those decisions could be the desires of the family to preserve and increase SEW (Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007). Several empirical analysis shows that opportunities that are sensed cannot be exploited due to SEW preservation (Berrone et al., 2012). Empirical research based on the consequences of SEW approach is scarce. Gómez-Mejía et al. (2010) observe that family firms have a lower propensity for diversification strategies. The needs to hire non-family members for the success of this kind of strategies are not aligned with the desire to preserve SEW of the family. Therefore, family firms are not prone to diversification. The same results when a sample is a group of firms operating in a high-tech industry. Family firms decide not to implement technological diversification decisions to avoid venture capitalists in the firm ownership. SEW affects environmental strategies due to the family trying to protect the environment for their stakeholders (Berrone et al., 2010). Vandekerkhof, Steijvers, Hendriks, and Voordeckers (2015) recognize the positive effect of organizational characteristics on the integration of non-family managers decreases when family-related objectives. Therefore, SEW could have deleterious effects for the family firms (Habbershon & Williams, 1999).
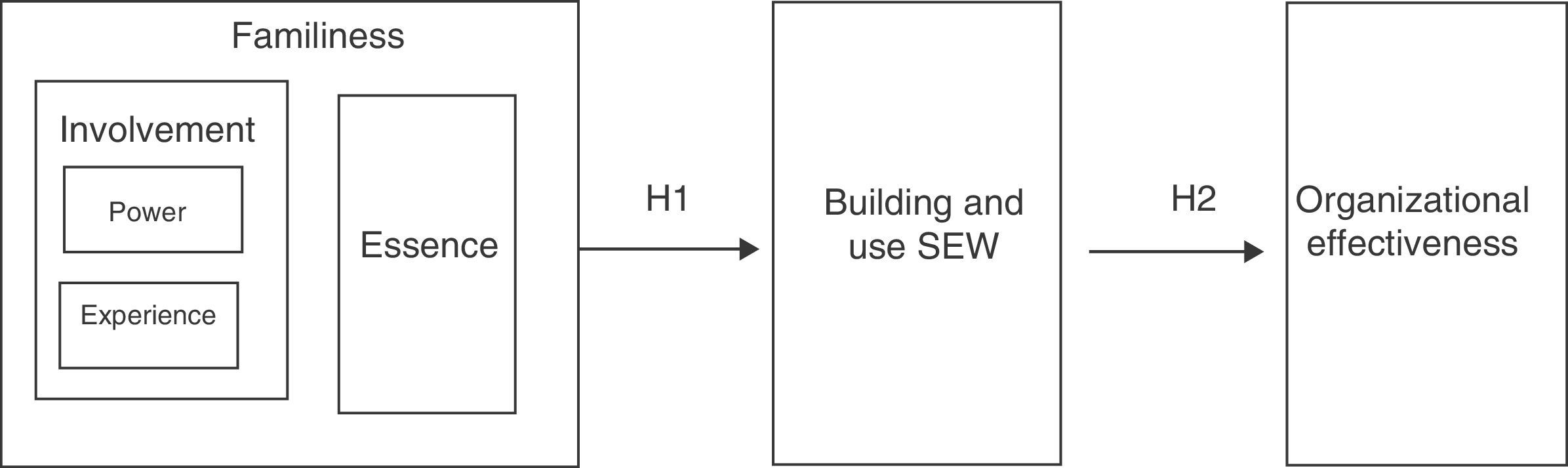
Family involvement and essence and SEWThe involvement of the family in the firm affects the generational control intentions (Chua et al., 1999). Therefore, family involvement is a precondition of the family essence and both explain heterogeneity of family firms (Chrisman et al., 2005, 2012). This heterogeneity, as stated by Gómez-Mejía et al. (2007), brings to different combinations of SEW.
Family involvement determines the level of SEW (Zellweger & Astrachan, 2008). Particularly, family ownership or the generations involved in the management influences SEW (Astrachan & Jaskiewicz, 2008). This relationship could be reinforced by the family social capital, reputation or status (Zellweger et al., 2012). For instance, there is a link between a high family ownership concentration and brand reputation (Dyer & Whetten, 2006). Both involvement and essence reinforce each other and affect SEW (Zellweger et al., 2012).
As family experience increases – as part of family involvement – the emotional link of the individuals with the firm is stronger and contributes to the SEW (Zellweger et al., 2012). The creation of relational capital between family members is the mediator variable that links family experience with SEW as commitment, membership feelings, affects, intimacy, altruism involve the family relationships in the firm – Fig 2 (Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007). However, those claims reverse if the relational capital could not be built (Naldi, Cennamo, Corbetta, & Gómez-Mejía, 2013; Zellweger & Astrachan, 2008). Based on this previous literature, we postulate the following hypothesis:H1 Family essence has a mediation effect over the relationship between family involvement and building and use of SEW.
Threats to the SEW of the family firm induce to managerial decisions that could be contrary to financial objectives (Berrone et al., 2012; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007), even though not all decisions affected by SEW are related to financial losses (Berrone et al., 2010). However, in situations of financial crisis, the family is willing to sacrifice personal economic wealth in support of firm survival, firm rebuilding and organizational recovering (Berrone et al., 2012; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007; Martin & Gómez-Mejía, 2016).
Therefore, the literature is not clear about the relationship between socioemotional wealth and organizational effectiveness (Habbershon & Williams, 1999). Based on contradictory effects of socioemotional wealth and organizational effectiveness – Fig. 2 – we posit that:H2 Building and use SEW has an effect on the organizational effectiveness of the family firm.
Spain is the country chosen to test the research model given the importance of the family firms in this context. In Spain, there are 2.9 million family firms that produce more than 70% of the GDP and create 13.9 million jobs. Moreover, family firms are an important lobby organized by the Family Business Institute from 1992. More specifically, our area of interest is non-listed medium and large family firms. However, as it has been noted, there is little research on this kind of family firms, since 80% of the research has concentrated on listed family firms (Sharma & Carney, 2012).
The source of information was the ranking of the 5000 largest firms in Spain, published in 2012 by the renowned magazine specialized in business and finance ‘Actualidad Económica’ (ranking defined by sales volume). The final sample included 1656 firms. The information collected with a questionnaire took place between May and September of 2013. This is a very interesting period since Spanish firms dealt with a very complex and dynamic environment due to the crisis from 2008 to 2013. The financial crisis (the financial system was in a restructuring process) and the international crisis made family firms to work in a completely unknown context. 135 surveys were received, representing a response rate of 8.15%, similar to that obtained in other studies of family firms (Lindow, Stubner, & Wulf, 2010; Zellweger et al., 2012). There were 125 valid surveys, of which 17 were identified as non-family firms and 6 as listed firms, resulting finally in 102 usable surveys.
The usable surveys matched the objectives of the research as 100% of the sample corresponds to unlisted family firms. Furthermore, 99% of the respondents indicated that their firms were family-owned, with family members on their management boards (95%) and on their boards of directors (98%); in addition, 93% of them anticipated that the future CEO of their firm would be a family member. These aspects are included in the operational definition adopted for the present study (family involvement in the ownership, management, and direction of the firm and the intention for trans-generational control).
In order to check for the non-response bias, we divided the sample into three groups and compared the first responses received with the last to respond to the survey. The underlying assumption is that those in the group that responded last are similar to those who didn’t respond at all. The completed ANOVA shows statistically insignificant differences between the first and last respondents at a 99% level of significance. Thus, we can confirm that there are no problems with respect to the non-response bias.
On the other hand, the possible limitation that our data is based on the subjective evaluation of the main informant can lead to common methods bias (Doty & Glick, 1998). This was rectified by applying the Harman single-factor test that no factor registered a significant portion of variance; our analysis suggests that the common method variance is not a problem. In addition, to avoid the reduction construct validity due to the participation of an informant, we follow the suggestion Podsakoff, Mackenzie, Lee, and Podsakoff (2003) to keep the questions as simple as possible and clearly separate dependent and independent variables in our questionnaire. We have concluded that the sample used is of good quality.
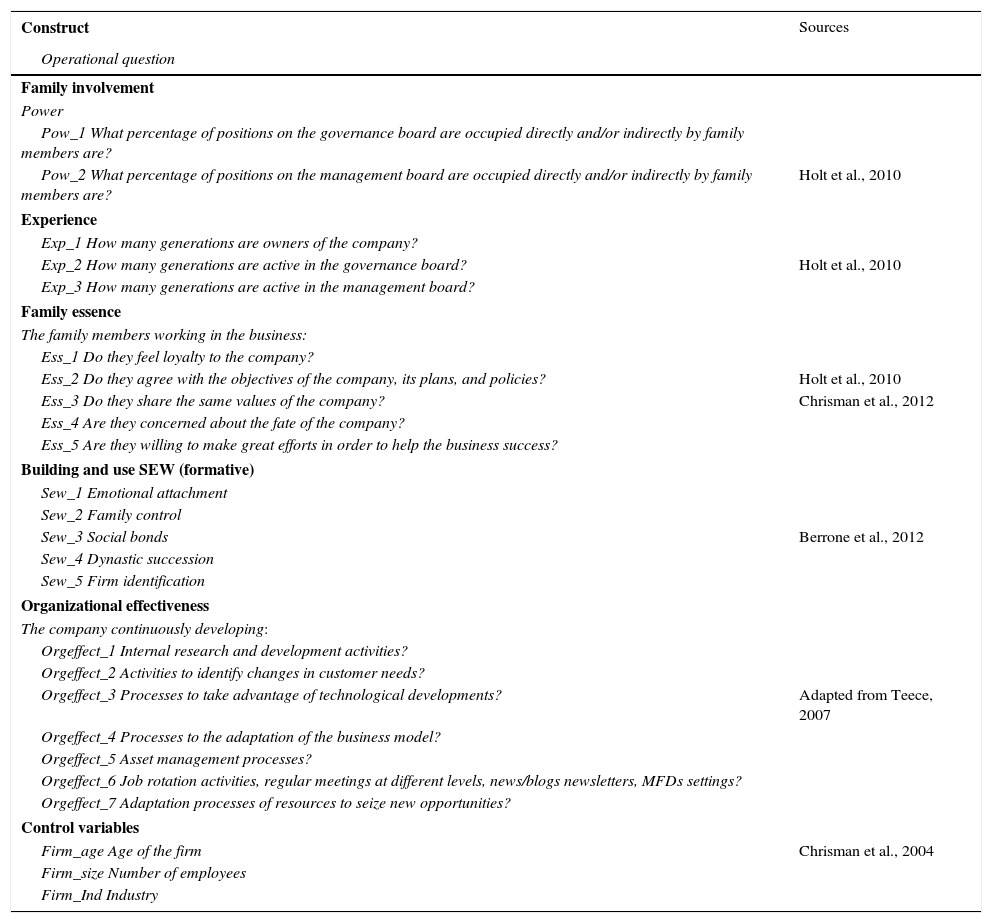
Dependent and independent variablesThe concept of ‘familiness’ was first developed by Habbershon and Williams (1999) and then measured by Astrachan et al. (2002), creating the familiness scale Power Experience Culture Scale (F-PEC). The scale has subsequently received some validation by Klein, Astrachan, and Smyrnios (2005) and Holt, Rutherford, and Kuratko (2010) among others. The three elements of the F-PEC scale include power (family ownership, governance, and management), experience (the generation and the number of family members involved in the firm), and culture (family commitment to the firm and the overlap of family and business values). We use the two first elements to measure the involvement of the family in the firm and the third one to measure the essence of the family in the firm.
To measure family firm power, we used two items of the F-PEC sub-scale of power: (1) the percentage of management board positions occupied directly and/or indirectly by family members and (2) the percentage of governing board positions occupied directly and/or indirectly by family members.
The experience was measured by three items of the F-PEC subscale of experience: (1) the number of generations involved in the ownership of the firm, (2) the number of generations involved in the board of management and (3) the number of generations of family members involved on the board of directors.
To measure family culture a version of the F-PEC sub-scale of culture was used. Consistent with Holt et al. (2010) and Chrisman et al. (2012) the representative elements of the F-PEC sub-scale of culture refer to whether the family members (a) feel a loyalty toward the family business, (b) are in agreement with the family firm's objectives, plans and politics, (c) have and share the same firm values, (d) are concerned about the future/destiny of the firm, and (e) are willing to exert great efforts in order for the firm to be successful. The measurement of these five items was done using the Likert 1–5 scale (where 1 means “strongly disagree/never” and 5 means “strongly agrees/always”).
The measurement of building and use SEW has been done with the scale proposed by Berrone et al. (2012) using five dimensions: (a) family control and influence (Klein et al., 2005; Lee & Rogoff, 1996); (b) family identification with the firm (Allen & Meyer, 1990; Carlock & Ward, 2001; Klein et al., 2005; O’Reilly & Chatman, 1986), (c) family social bonds (Cruz, Gómez-Mejía, & Becerra, 2010; Miller & Le Breton-Miller, 2005; Miller, Lee, Chang, & Le Breton-Miller, 2009); (d) emotional links of family members (Allen & Meyer, 1990; Carlock & Ward, 2001; Eddleston & Kellermanns, 2007; O’Reilly & Chatman, 1986) and (e) generational links by generational renewal (Lee & Rogoff, 1996; Zellweger et al., 2012). Using several items for each dimension (Likert scale), the factor analysis confirms the five dimensions: family control, firm identification, social bonds, emotional attachment, and dynastic succession.
The organizational effectiveness was constructed consistent with the micro-fundamentals proposed by Teece (2007). The items included are in order to identify organizational effectiveness by means of the development of permanent organizational activities and processes derived from learning and knowledge capabilities of the firm. Thus the items used are related to continuous development: (a) internal activities of research and development, (b) activities to identify changes in customer needs, (c) processes to take advantage of technological developments, (d) adaptation processes for the business model, (e) processes of asset management, (f) activities such as job rotation, regular multi-level meetings, information bulletins/blogs, configuration of multi-functional teams and, (g) processes of resource adaptation to take advantage of new opportunities. These routines have been recognized as evidence of organizational effectiveness (Gold et al., 2001; Zheng et al., 2010). The measurement of these items was again done using the Likert 1–5 scale.
Control variablesWe include three control variables that have normally been utilized in prior research related to the behavior of family firms: age, size and industry (Chrisman, Chua, & Litz, 2004). The age was measured by the years in business; the family can have a deeper attachment to the firm over time (Zellweger & Astrachan, 2008), which can affect its disposition toward SEW. The size was evaluated based on the number of employees. A firm that grows in size may affect SEW preservation. The relationship between the family and the firm can become more distant when the size of the firm grows, for example, due to the need to professionalize the firm (Chrisman et al., 2012). The research indicates that family firms compete better in some industries than in others (Pollak, 1985), which could affect their predisposition toward SEW. Industries were measured classifying the firms in accordance with the categories proposed by the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC Code). The categories include agriculture, construction, manufacturing, transportation, commerce, service and others.
The mean of age of the sample is 3.2 standard deviation 1.11 (scalemin. 1 max 5). The number of employees on average is 3.48 standard deviation 1.33 (scalemin. 1 max 5). The main industries in the sample were manufacturing at 43% and services 29%. The variables are summarized in Table 1.
Operationalization of the constructs.
| Construct | Sources |
|---|---|
| Operational question | |
| Family involvement | |
| Power | |
| Pow_1 What percentage of positions on the governance board are occupied directly and/or indirectly by family members are? | |
| Pow_2 What percentage of positions on the management board are occupied directly and/or indirectly by family members are? | Holt et al., 2010 |
| Experience | |
| Exp_1 How many generations are owners of the company? | |
| Exp_2 How many generations are active in the governance board? | Holt et al., 2010 |
| Exp_3 How many generations are active in the management board? | |
| Family essence | |
| The family members working in the business: | |
| Ess_1 Do they feel loyalty to the company? | |
| Ess_2 Do they agree with the objectives of the company, its plans, and policies? | Holt et al., 2010 |
| Ess_3 Do they share the same values of the company? | Chrisman et al., 2012 |
| Ess_4 Are they concerned about the fate of the company? | |
| Ess_5 Are they willing to make great efforts in order to help the business success? | |
| Building and use SEW (formative) | |
| Sew_1 Emotional attachment | |
| Sew_2 Family control | |
| Sew_3 Social bonds | Berrone et al., 2012 |
| Sew_4 Dynastic succession | |
| Sew_5 Firm identification | |
| Organizational effectiveness | |
| The company continuously developing: | |
| Orgeffect_1 Internal research and development activities? | |
| Orgeffect_2 Activities to identify changes in customer needs? | |
| Orgeffect_3 Processes to take advantage of technological developments? | Adapted from Teece, 2007 |
| Orgeffect_4 Processes to the adaptation of the business model? | |
| Orgeffect_5 Asset management processes? | |
| Orgeffect_6 Job rotation activities, regular meetings at different levels, news/blogs newsletters, MFDs settings? | |
| Orgeffect_7 Adaptation processes of resources to seize new opportunities? | |
| Control variables | |
| Firm_age Age of the firm | Chrisman et al., 2004 |
| Firm_size Number of employees | |
| Firm_Ind Industry | |
As in other studies in the field of family firms (Chua et al., 1999; Vallejo, 2009) and as recommended by recent literature (Binz, Patel, & Wanzenried, 2014; Sarstedt, Ringle, Smith, Reams, & Hair, 2014) we used partial least squares (PLS) in order to validate our research model. PLS is a model of structural equations based on variance. Our selection was made for several reasons. First, this technique allows including latent variable with reflective and formative indicators (Henseler, Ringle, & Sinkovics, 2009). Second, one of the advantages of PLS-SEM is that it establishes assumptions of normality of the data (Chin, 1998) and can be used in small samples (Kyu Kim, Yul Ryoo, & Dug Jung, 2011). Third, it can analyze structural models with multi-item constructs and direct and indirect relationships (Vallejo, 2009). Finally, this technique is more suitable during the first stages of the development of a theory, supporting exploratory and confirmatory research (Premkumar & Bhattacherjee, 2008), primarily in complex research and in research in which the theoretical knowledge is scarce (Wold, 1982). The program SmartPLS 2.0 M3 (Ringle, Wende, & Will, 2005) was used.
The estimation process with PLS is done through simple and multiple regressions, thus the required sample will be the one that provides a basis for the most complex multiple regression that can be found (Barclay, Higgins, & Thompson, 1995). It can be determined by multiplying by 10 the best result that is obtained from the following options: (1) the number of indicators in the most complex formative construct, or (2) the greatest number of structural paths directed to whichever of the model constructs (Chin, 1998). In our model, there is five formative construct, and at least two structural paths exist that go toward whichever construct, therefore the minimum required size for a sample in our study is 50. Thus the sample of 102 observations is adequate.
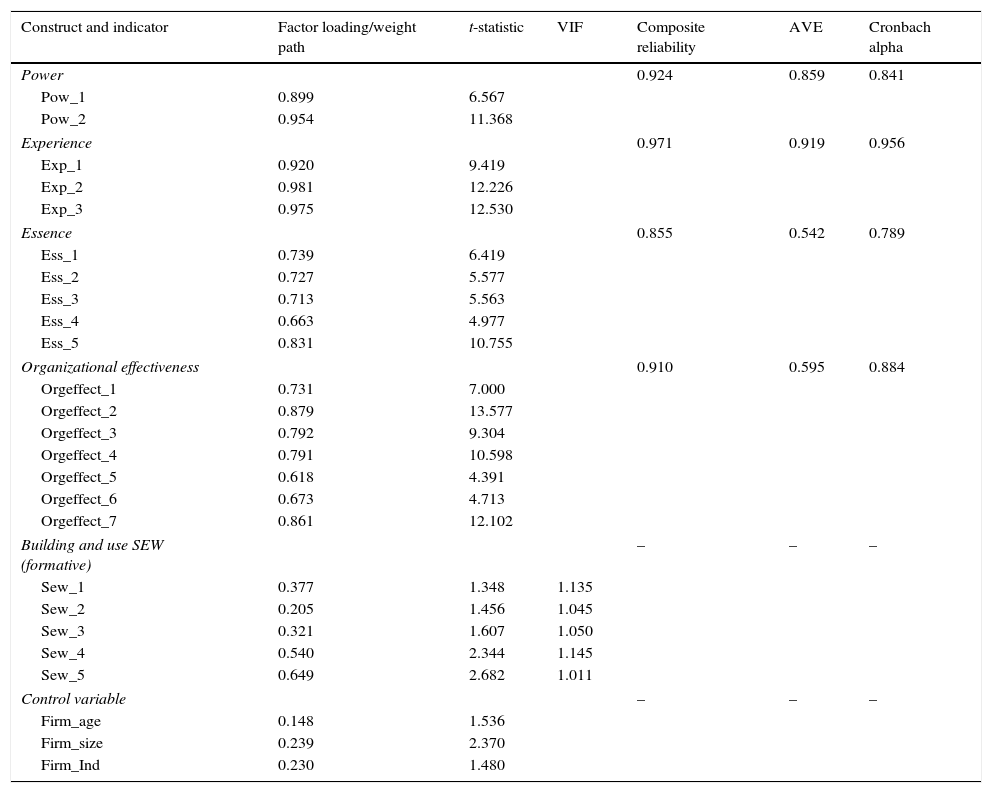
Measurement modelBefore estimating the structural model, we did a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) in order to verify the measurement model. The CFA confirms our measurement model, clearly identifying the representative factors of the F-PEC scale, SEW and organizational effectiveness.
The research model includes reflective (F-PEC and organizational effectiveness) and formative constructs (building and use SEW) – Table 2. The measurement model of the reflective constructs was evaluated by examining the reliability of each item, the internal consistency, and the convergent and discriminate validity (Roldán & Leal, 2003). The internal reliability of each item is determined by the items loading for the case of the constructs with reflective indicators and is expressed as a percentage of the variance of the item compared to the construct. In order for an item to have good reliability, all the loadings must be greater than 0.7 (Carmines & Zeller, 1979). All of the loadings of the items exceeded the 0.7 limit with the exception of one of the construct of the essence and two of construct organizational effectiveness whose loadings were near 0.6; these are considered acceptable when the scales are in the first stages of development (Chin, 1998).
Latent variable, measurement item, composite reliability, AVE, and Cronbach alpha.
| Construct and indicator | Factor loading/weight path | t-statistic | VIF | Composite reliability | AVE | Cronbach alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power | 0.924 | 0.859 | 0.841 | |||
| Pow_1 | 0.899 | 6.567 | ||||
| Pow_2 | 0.954 | 11.368 | ||||
| Experience | 0.971 | 0.919 | 0.956 | |||
| Exp_1 | 0.920 | 9.419 | ||||
| Exp_2 | 0.981 | 12.226 | ||||
| Exp_3 | 0.975 | 12.530 | ||||
| Essence | 0.855 | 0.542 | 0.789 | |||
| Ess_1 | 0.739 | 6.419 | ||||
| Ess_2 | 0.727 | 5.577 | ||||
| Ess_3 | 0.713 | 5.563 | ||||
| Ess_4 | 0.663 | 4.977 | ||||
| Ess_5 | 0.831 | 10.755 | ||||
| Organizational effectiveness | 0.910 | 0.595 | 0.884 | |||
| Orgeffect_1 | 0.731 | 7.000 | ||||
| Orgeffect_2 | 0.879 | 13.577 | ||||
| Orgeffect_3 | 0.792 | 9.304 | ||||
| Orgeffect_4 | 0.791 | 10.598 | ||||
| Orgeffect_5 | 0.618 | 4.391 | ||||
| Orgeffect_6 | 0.673 | 4.713 | ||||
| Orgeffect_7 | 0.861 | 12.102 | ||||
| Building and use SEW (formative) | – | – | – | |||
| Sew_1 | 0.377 | 1.348 | 1.135 | |||
| Sew_2 | 0.205 | 1.456 | 1.045 | |||
| Sew_3 | 0.321 | 1.607 | 1.050 | |||
| Sew_4 | 0.540 | 2.344 | 1.145 | |||
| Sew_5 | 0.649 | 2.682 | 1.011 | |||
| Control variable | – | – | – | |||
| Firm_age | 0.148 | 1.536 | ||||
| Firm_size | 0.239 | 2.370 | ||||
| Firm_Ind | 0.230 | 1.480 | ||||
The measurement model of the formative constructs was evaluated by examining the item weights (Chin, 1998). Weights indicate the value for each item in the construct (Cepeda & Roldán, 2004). We controlled for multicollinearity (Diamantopoulos & Winklhofer, 2001) with the VIF index (lower than 5). The values are close to 1, therefore, multicollinearity is not a problem.
The internal consistency of the constructs was evaluated by examining the Cronbach alpha and the composite reliability. The indicators obtained for the constructs exceeded 0.8 for the composite reliability and 0.5 for the Cronbach alpha, which suggests that both measures are acceptable when the scales are in the first stages of development (Nunnally, Bernstein, & Berge, 1967). The convergent validity of the construct is expressed in the degree that all the items in a construct are measured by the same concept and are evaluated by examining the average variance extracted (AVE). In our analysis, the AVE indicator exceeds the 0.5 recommended by Fornell and Larcker (1981).
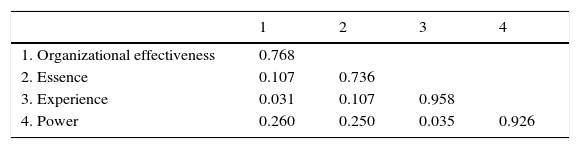
The discriminant validity was evaluated by examining the degree to which the square root of AVE is greater than the inter-construct correlations (Fornell & Larcker, 1981). Table 3 shows this relation. Thus we are able to state that all the indicators obtained have good measurement properties.
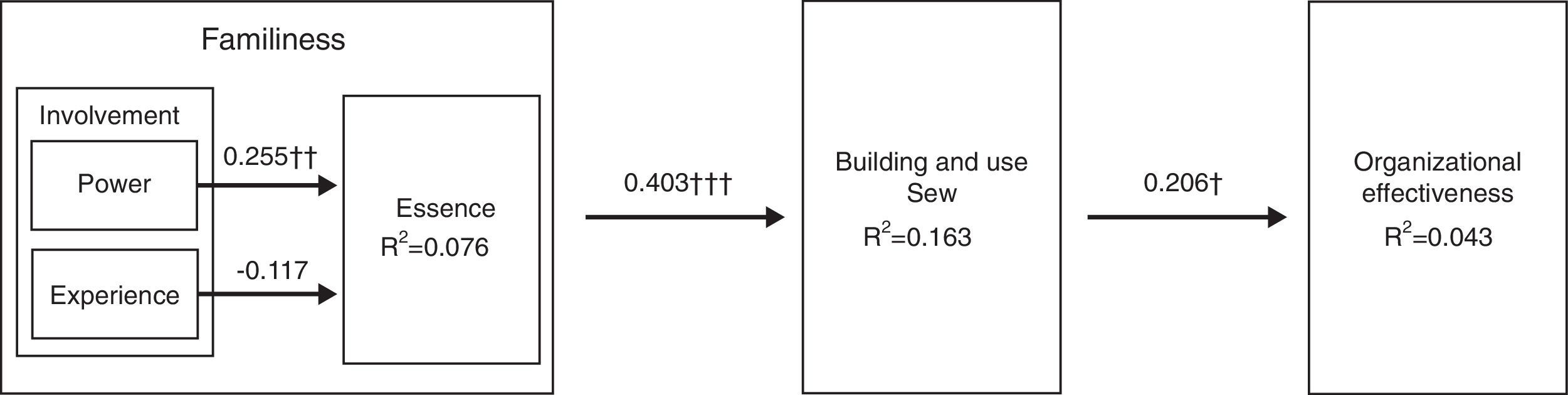
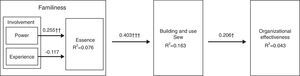
Structural modelFig. 3 shows the explained variance (R2) in the dependent constructs and the path coefficients β for the model. In agreement with Chin (1998), a bootstrapping (1000 samples) was used to generate standard errors and the t-statistics. The R2 for the endogenous variables were: essence (0.076); building and use SEW (0.163) and organizational effectiveness (0.043).
Fig. 3 shows that power has a positive and significant effect on essence (0.255; t=2.504) and experience has a non-significant and negative impact on essence (0.117; t=1.488). Table 4 presents the results testing the model. There is a positive and significant relationship in the path involvement→essence→building and use SEW (0.403; t=3.363). However, it is necessary to evaluate the individual effects of the elements of involvement on the essence – eight additional analyses (Tables 5 and 6) as Baron and Kenny (1986) recommend.
Results of hypothesis testing.
| Hypotheses | Path coefficient | t-value | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Power→Essence | 0.255 | 2.504†† | Partial supported |
| Experience→Essence | −0.117 | 1.488 | ||
| Essence→Building and use SEW | 0.403 | 3.363††† | ||
| H2 | Building and use SEW→Organizational effectiveness | 0.206 | 1.986† | Supported |
Note: Path coefficients; (t statistic two tailed) †p<0.05, ††p<0.02, †††p<0.01.
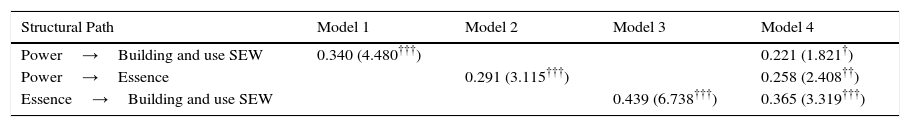
Mediating effect Power→Essence→Building and use SEW.
| Structural Path | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power→Building and use SEW | 0.340 (4.480†††) | 0.221 (1.821†) | ||
| Power→Essence | 0.291 (3.115†††) | 0.258 (2.408††) | ||
| Essence→Building and use SEW | 0.439 (6.738†††) | 0.365 (3.319†††) |
Note: Path coefficients; (t-statistic two tailed) †p<0.1, ††p<0.02, †††p<0.01.
Mediating effect Experience→Essence→Building and use SEW.
| Structural Path | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experience→Building and use SEW | −0.181 (2.598††) | −0.072 (0.884) | ||
| Experience→Essence | −0.164 (2.024†) | 0.101 (1.226) | ||
| Essence→Building and use SEW | 0.439 (6.616††) | 0.431 (6.353††) |
Note: Path coefficients; (t-statistic two tailed) †p<0.05, ††p<0.01.
Model 1 (Table 5) shows a positive relationship between power and building and use SEW (0.340; t=4.480). Model 2 relates power to essence – mediation variable (0.291; t=3.115). Model 3 shows a direct, positive and significant relationship between essence and building and use SEW (0.439; t=6.738). Finally, model 4 analyzes the simultaneous relationship between power, essence, and building and use SEW. The relationship between power and building and use SEW reduce its significance when the mediator variable – essence – is in the model (0.221; t=1.821). The rest of the structural path is significant. Therefore, there is a partial mediation effect of the essence when considering power and building and use SEW.
Related to experience (Table 6), model 5 evaluates the relationship between experience and building and use SEW (−0.181; t=2.598). Model 6 examines the relationship between experience and essence (−0.164; t=2.024). Model 7 relates essence to building and use SEW (0.439; t=6.616). Finally, model 8, include all the relationships. The relationship between experience and building and use SEW reduce its significance when the mediator variable – essence – is introduced into the analysis (−0.072; t=0.884). However, at the same time the structural path experience,→essence reduces its significance (0.101; t=1.226). Therefore, there is no mediation effect of essence between experience and building and use SEW.
In brief, hypothesis H1 is partially supported. The essence partially mediates the relationship between power and building and use of SEW, while is not mediating the relationship between experience and building and use of SEW.
Hypothesis H2 is supported. The results show that there is a positive and significant relationship between building and use SEW and organizational effectiveness (0.206; t=1.986) (Table 4).
Finally, the size of the firm as a control variable has a positive and significant relationship with organizational effectiveness (0.239; t=2.370).
Discussion and conclusionsThe objective of this paper is to empirically test a model of SEW to evaluate the effects of family involvement and essence on SEW, and, therefore on organizational effectiveness.
First, we study how power and experience – involvement – relate to the essence. Results indicate that family involvement in ownership and managerial boards have a positive impact. However, the generational transfer does not have a positive but negative effect on essence. This result shows that new generations are not assuming and integrating the family objectives and values to the firm.
Second, results show that both, involvement by the means of power and essence, have an impact on building and use SEW. This is consistent with the previous literature (Berrone et al., 2010; Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007), as ownership has been considered to impact on the SEW. The lack of effect of experience needs further analysis as previous research claims that generational renewal could have deleterious effects on SEW (Le Breton-Miller and Miller, 2013).
Third, there is a positive and significant relationship between building and use of SEW and organizational effectiveness. In line with previous studies, SEW preservation is related to firm survival (Berrone et al., 2012; Morgan & Gómez-Mejía, 2014). Therefore, managerial decisions driven by the desire to preserve SEW could be related to competitive advantages (Gómez-Mejía et al., 2007). This result is consistent with Zheng et al. (2010) claims about the impact of dynamic capabilities creation on abnormal returns. In fact, additional analysis with our sample indicates a positive and significant relationship between organizational effectiveness and perceived returns (0.295; t=3.782). Therefore, SEW preservation guarantees organizational effectiveness and firm performance. Closeness in relationships, communication, and commitment between family and non-family members could explain those superior returns.
This empirical research contributes to the literature in several directions. First, in the family firm literature, we contribute evaluating the antecedents and consequences of SEW, in line with the claims of Berrone et al. (2012) and Kellermanns, Dibrell, and Cruz (2014). Second, we combine the involvement and essence approaches, along with Basco (2013) recommendations, using the global concept of familiness. Third, we add empirical support in a sample of non-listed family firms, according to Sharma and Carney (2012) statements.
Our results have implications for practice. In fact, managers have to deal with SEW as a way to achieve organizational effectiveness in this particular type of firms. They have to facilitate a climate in which emotional resources could be used and toward higher performance. The goal is to avoid conflict between family members related to personal relationships to guarantee family firm survival.
Although this study is one of the first steps in quantitative research on the building and use SEW in the family firm, and offers important implications for the theory and practice, we recognize that this type of study has some inevitable limitations. First, it refers to a cross-sectional study that is particularly problematic when it attempts to measure a phenomenon over time. The static nature of this type of study doesn’t allow the establishment of causal relationships, making it impossible to capture the dynamic essence and the effects of the building and use SEW. Second, the use of a questionnaire in data collection can be problematic. The characteristics of the variables of the study and the unavailability of appropriate databases made it necessary to use this type of instrument. Third, on a purely methodological level, data were obtained based on the subjective evaluation of a survey respondent, which can lead to the common method bias. To solve this problem, we used the procedures recommended by the literature. Finally, the use of the PLS method does not establish causal relationships but rather the predictability between the independent and dependent variables, since it deals with a flexible modeling. However, the state of the development of the theory and the complexity of the model make this method appropriate.
This research opens interesting avenues for further research. First, a case study can be developed to capture the evolution of the variables included in the model of SEW. Second, our model could be evaluated in other contexts and cultures, contributing to its mainstreaming and adaptation. Third, further studies could be devoted to study the possible moderating effect of experience, in the relationship between the essence and building and use SEW.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
We acknowledge the financial support to this study from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (Plan Nacional de I+D+i) of Spain [ECO2012-32075], and the policy of academic improvement of the Universidad Austral de Chile.