Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is the most frequent cause of portal hypertension in paediatric population. Baveno VI Consensus considers endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) as the second therapeutic option after Meso-Rex bypass (surgical shunt).
AimAnalyse the diagnostic profitability of non-invasive scales in order to predict the risk of esophageal varices (OV) in children with PVT.
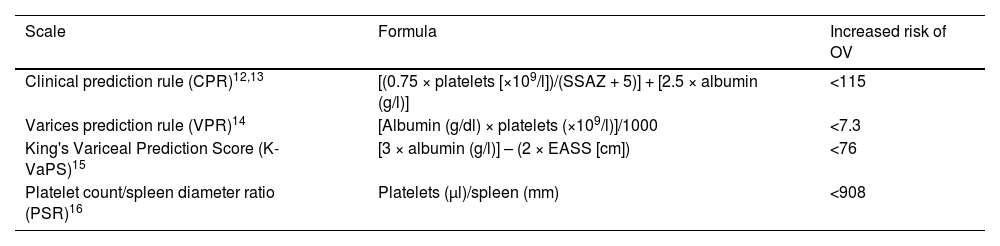
Materials and methodsDescriptive retrospective study where every upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (UGE) carried on patients <15 years old with non-cirrhotic PVT were included. There were divided according to the presence of OV and sex, cause, age, previous gastrointestinal bleeding or treatments, results of UGE and scales (Clinical Prediction Rule-CPR), Varices Prediction Rule-VPR), King’s Variceal Prediction Score-K-VaPS) and Platelet count / Spleen diameter Ratio-PSR). Qualitative variables were expressed as absolute frequency and percentage, and quantitative variables as median and intercuartilic range. U Mann–Whitney and Hanley–McNeil tests were used for comparisons.
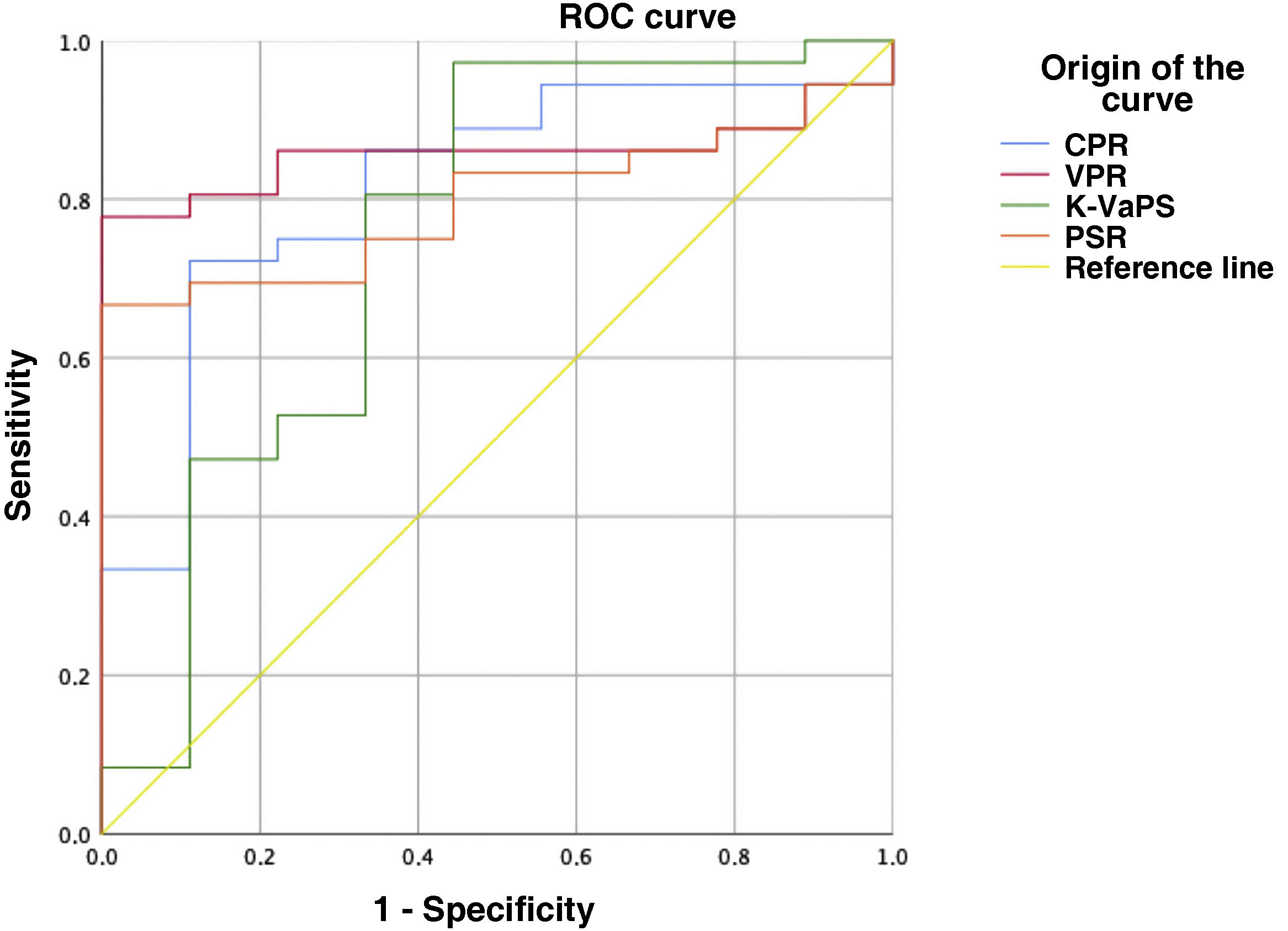
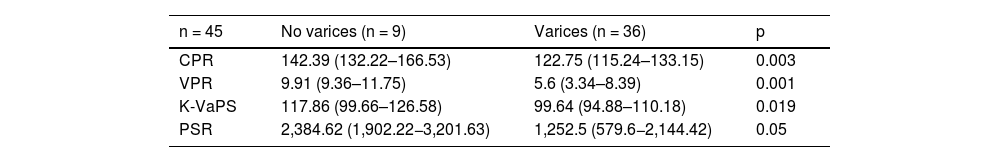
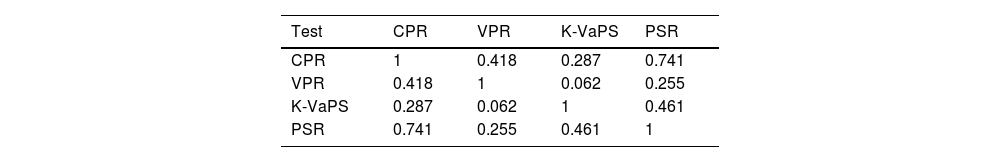
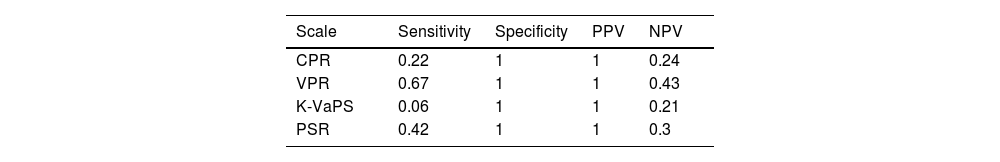
Results45 UGE were analysed. 80% (n = 36) presented OV: median of 3(2–3) and 33,3%(n = 12) required EVL. Statistical differences were demonstrated between both groups: CPR (142,39 (132,22–166,53) vs. 122,75 (115,24–133,15); p = 0,003), VPR (9,91 (9,36 – 11,75) vs. 5,6 (3,34–8,39) p = 0,001), K-VaPS (117,86 (99,66–126,58) vs. 99,64 (94,88–110,18) p = 0,019), PSR (2384,62 (1902,22–3201,63) vs. 1252,5 (579,6–2144,42) p = 0,05), with and area under the curve AUROC > 75%, without statistical differences between scales.
ConclusionsIn paediatric patients with non-cirrotic PVT non-invasive scales can be used as a tool to predict the presence of OV and raise the indication of UGE.
La trombosis portal (TVP) es la causa más frecuente de hipertensión portal en población pediátrica. El Consenso de Baveno VI considera la ligadura endoscópica de varices (LEV) como segunda opción terapéutica tras el Meso-Rex-bypass (shunt quirúrgico).
ObjetivoAnalizar la rentabilidad diagnóstica de escalas no invasivas para predecir el riesgo de varices esofágicas (VE) en niños con TVP.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo retrospectivo donde se incluyeron endoscopias digestivas altas (EDA) en pacientes <15 años con TVP no cirróticos. Se dividieron según la presencia de VE y se estudiaron sexo, etiología, edad, hemorragia digestiva o tratamientos previos, resultados de EDA y las escalas (Regla Predicción Clínica-CPR, Regla Predicción Varices-VPR, King’s Variceal Prediction Score-K-VaPS y ratio plaquetas/bazo-RPB). Las variables cualitativas se expresaron mediante frecuencia absoluta y porcentaje, y las cuantitativas mediante mediana y rango intercuartílico. Para las comparaciones se emplearon los test U de Mann–Whitney y Hanley–McNeil.
ResultadosSe realizaron 45 EDA. Un 80%(n = 36) presentaron VE: mediana de 3 (2–3) y un 33,3% (n = 12) precisó LEV. Se demostraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre ambos grupos: CPR (142,39 (132,22–166,53) vs. 122,75 (115,24–133,15) p = 0,003), VPR (9,91 (9,36 – 11,75) vs. 5,6 (3,34 – 8,39) p = 0,001), K-VaPS (117,86 (99,66–126,58) vs. 99,64 (94,88–110,18) p = 0,019), RPB (2384,62 (1902,22–3201,63) vs. 1252,5 (579,6–2144,42) p = 0,05), con un área bajo la curva >75%, sin demostrarse diferencias entre escalas.
ConclusionesEn pacientes pediátricos con TVP no cirróticos se pueden emplear escalas no invasivas como herramienta para predecir la presencia de VE y plantear con ello la indicación de EDA.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora