Successful synthesis of metal–, semiconductor–, and metal/semiconductor–mordenite nanocomposites, using geothermal solid waste as precursor is reported. Powders of nanostructured composites, consisting of metal and/or semiconductor nanoparticles grown on a mordenite-type zeolitic matrix surface, were synthesized by a one-step solvent-free and organic template-free process. The developed methodology is capable of controlling and tuning the final properties of composites from their synthesis and is also reproducible and repeatable. For comparison and demonstration of the application of the final products, dye photocatalysis degradation tests were done using commercial TiO2 as reference (degradation reached ∼75% in 215min, k=0.004min−1), [M]–S–MOR samples revealed better performance (≥95% in 100min, k=0.009min−1).
Contemporary chemical industries are searching for new techniques that reduce manufacturing costs and mitigate environmental impact. Processes without emissions and free of risky chemicals have therefore become a challenge for researchers, technologists and engineers (Ambec, Cohen, Elgie, & Lanoie, 2013). The lagoon of mineralized waters at the Cerro Prieto geothermal plant, in Mexicali, Mexico (Fig. 1a), is an excellent source of silicon; in an area of approximately 12.5 km2, it is located between 115°12′ and 115°18′ west longitude and between 32°22′ and 32°26′ north latitude, 36km away from Mexicali city. Beside the process of geothermal energy conversion, the saturated silica water is conducted to the precipitation lagoon to separate the silica residues from the reinjection water. The silica salts precipitate as amorphous silica, which is used in this work.
(a) Aerial view of lagoon of mineralized waters at Cerro Prieto, Mexicali (INEGI-GOOGLE, 2015), (b) SEM image, and (c) DRX pattern of solid waste powders.
On the other hand, porous materials have potential applications in the chemical industry; likewise, the inclusion of transition metals and/or semiconductors into matrices to modify their properties has gained importance for the development of convenience materials (Bibby & Dale, 1985; Cooper et al., 2004). In the field of porous nanostructured materials, zeolites have been applied in areas such as catalysis, water treatment, H2 production, among others (Zaarour, Dong, Naydenova, Retoux, & Mintova, 2014).
In this work, nanostructured composites based on metal, semiconductor or metal/semiconductor nanoparticles were grown on a mordenite-type zeolite matrix from geothermal energy conversion solid waste materials by a solvent- and organic template-free process, with the inclusion of desired ion or ion combinations in a one step process leading to a series of materials with several potential applications. To demonstrate some of the potential applications, the use of [M]–S–MOR as photocatalyst is reported.
2Materials and methodsPrecursor SiO2 powders (Fig. 1(b)) were obtained from geothermal energy conversion solid waste materials at Cerro Prieto plant.
Solid materials obtained from Cerro Prieto were cleaned by two mechanical wash processes, briefly, consist of mixing by stirring the solid residue obtained from the geothermal plant with deionized water, these washings are necessary to remove the clay that may have been mixed with the residue. X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern analysis (Fig. 1(c)) revealed only an amorphous phase with the morphology shown in Fig. 1(b).
Elemental analysis by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) confirmed the absence of any other element that could come from clays (Table 1).
Weight percent obtained by SEM–EDS chemical analysis and superficial area values from representative synthesized materials.
| Weight percent | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste SiO2 | [Na]–MOR | [Mn]–MOR | [Fe]–MOR | [Ag]–MOR | [Ti,Ba,Sr]–MOR | [Cr,Ti,Fe]–MOR | [Ni, Co, Mo]–MOR | [Co,Mn]–S–MOR | [Cd,Zn,Ag]–S–MOR | [Cd,Zn]–S–MOR | |
| O | 33.2 | 51.8 | 51.3 | 51.3 | 44.9 | 49.3 | 48.4 | 50.4 | 50.3 | 50.8 | 49.9 |
| Na | 0 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 4.6 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 1.4 | 2.3 |
| Al | 0 | 5.5 | 4.4 | 5 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 3.9 | 4.9 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 5.0 |
| Si | 66.3 | 40.4 | 40.5 | 40 | 26.3 | 35.9 | 33.0 | 38.7 | 39.2 | 39.6 | 38.6 |
| M | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 7.4 | 10.3 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 5.2 | 1.5 |
| S | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.3 |
| Si/Al | N/A | 7 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 8 |
| S.A. | 1 | 328 | 240 | 275 | 210 | 247 | 185 | 301 | 83 | 74 | 101 |
S.A: superficial area (m2/g).
Using this amorphous SiO2 source, metal/mordenite ([M]–MOR) composites were synthesized with M=lithium, sodium, magnesium, titanium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, zinc, strontium, molybdenum, silver, cadmium, barium, lanthanum, gold, bismuth, and/or their mixtures, following the one-step route described in the MX/a/2012/013218 patent (Raymond, 2012). This process is solvent-, seed-, and organic template-free (avoiding the calcination processes to remove templates commonly used in the synthesis of zeolites), which involves 110mL of a mixture of 0.1M aqueous solutions of sodium silicate and aluminum sulfate (with SiO2/Al2O3 molar relation of 15) that was stirred for 30min; then, 30mL of 0.1–0.3M aqueous solution of desired ion salt was mixed with the first solution (this step is responsible to form nanoparticles in different concentrations). The final solution, with pH value of 9±1, was autoclaved at 155°C for 48h. It eliminates the typical ion exchange process (to clarify, ion exchange is the most followed route to embed nanoparticles in silicon matrices, briefly, matrices were exposed to an concentrated solutions of the desired ion salt for at least 48h then be washed) as it enables the inclusion of the desired ion (type and concentration) before the reaction. The possibility to select the ions before synthesis allows tuning the electro-optical properties and drastically reduces the obtaining time for this kind of materials because it does not require a calcination or evaporation process (Ren et al., 2012). The semiconductor/mordenite composites ([M]–S–MOR) are synthesized by exposure of the activated composites to an H2S atmosphere for 24h at room temperature.
Material composition, morphology and structure were studied by XRD with a Philips X’Pert diffractometer (CuKα radiation), by SEM using a JEOL JSM-5300 microscope with EDS attachment; by TEM with a JEOL JEM-2010 (with accelerating voltage of 200kV), and by N2 adsorption isotherms using a Tristar II 3020 Surface Area Analyzer. Optical properties were studied by UV–Vis spectroscopy using an AvaSpec-ULS2048-UA-50 spectrophotometer.
3Results and discussionXRD patterns of all synthesized composites exhibit a defined single phase which matches well with the ICSD 68445 file reported for Na-mordenite; Figure 2 shows patterns of some [M]–MOR samples.
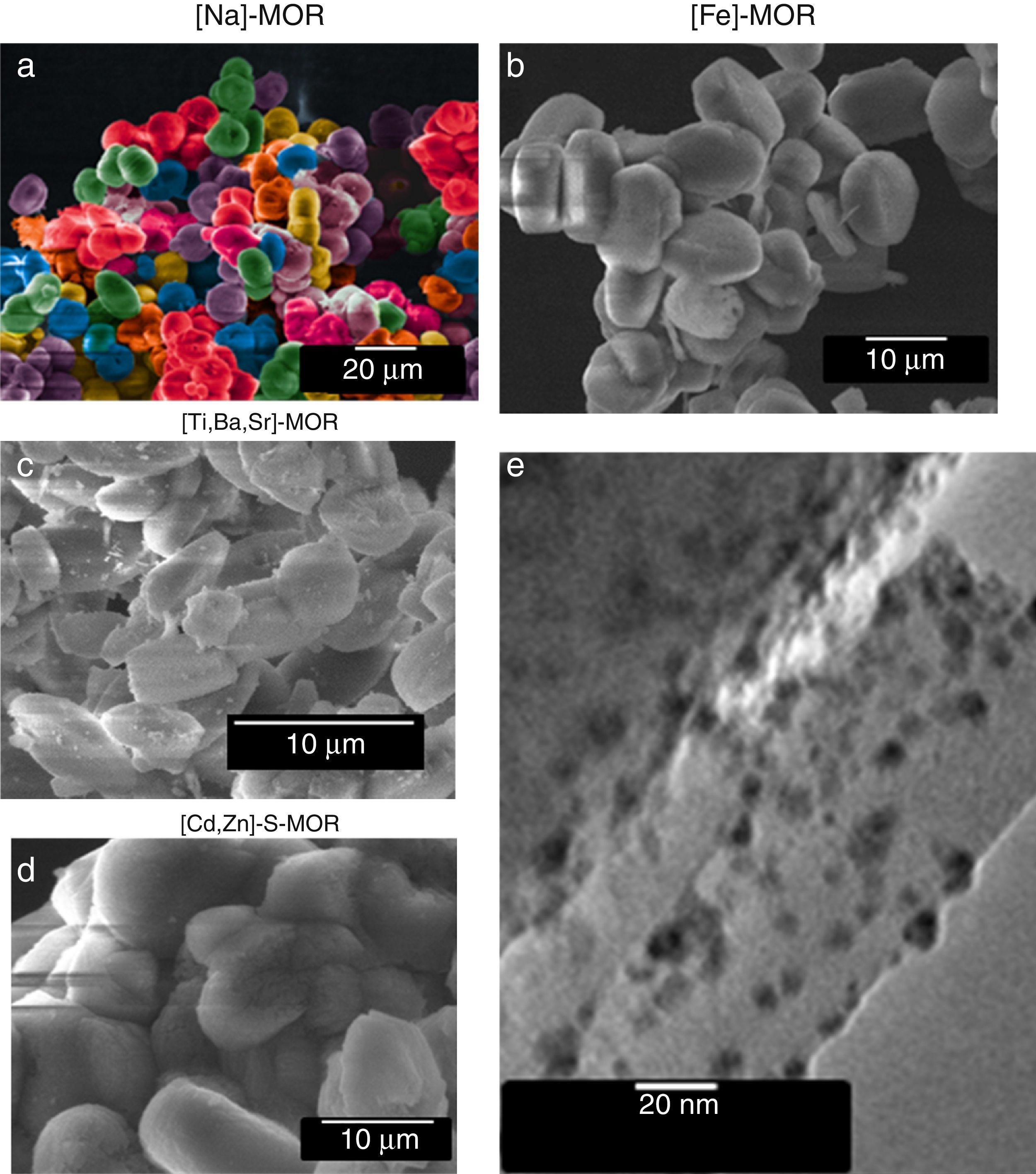
SEM and TEM analyses show the typical MOR morphology (Fig. 3), which consists of disc-shaped grains as arrangements of mordenite needle-like crystals. The SEM micrograph of sulfided [M]–S–MOR sample (Fig. 3(d), as representative case) shows the same morphology as [M]–MOR. The TEM micrograph (Fig. 3(e)) shows the general growth features of metal, semiconductor or metal/semiconductor nanoparticles (darker zones), strongly bonded to the mordenite matrix surface in all samples, which are homogeneously dispersed with an average size of 20nm. Such features significantly increase the active surface required for multiple applications in catalysis, water treatments, and others (Liu et al., 2016; Mota, Eliášová, Jung, & Ryoo, 2016).
Table 1 summarizes the weight percent of each element for all materials and geothermal silica, obtained by EDS. An average value of 8.3 for the Si/Al ratio, obtained from EDS analysis, means that the mordenites have several acid sites used as cleavage centers for the nanoparticles; the particular ion at these acid sites determines the size of the nanoparticles. Fig. 4 shows a demonstrative scheme of the metal and/or semiconductor–mordenite composite. Situations A and B illustrate possible clusters grown inside the mordenite framework channels. The nanoparticles that grow outside the framework are strongly oriented by the Si–O–Al surface of the zeolite matrix.
Figure 5 shows a representative N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm of the synthesized nanocomposite powders, which gives information about the micro- and mesoporosity structure and is closely related with the potential applications. Adsorption at very low partial pressures is associated with the zeolitic matrix micropore system (pore size<2nm), i.e., with the cavity and channel volumes inside the zeolite framework. Moreover, the N2 adsorption extends at higher pressures, and a slight continuous slope at medium relative pressures arises from the N2 adsorption on the external surface of the zeolite particles. An increase in the slope is also observed at high relative pressures (P/P0>0.8), describing a hysteresis cycle, which indicates the presence of mesoporosity (pore size between 2nm and 50nm), i.e., the porosity generated on the composite surface and on the inter-crystallites volume inside the grains as can be seen in Figure 3.
From the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm analysis (Table 1) we found that the [M]–MOR samples have an average surface area of 240m2/g, while sulfided [M]–S–MOR composites showed a lower average surface area of 60m2/g.
On the other hand, UV–Vis spectroscopy results (Fig. 6(a)) revealed the optical-electronic properties for different metal composite samples. The [Na]–MOR spectrum was subtracted from all spectra. The spectra showed that the optical behavior of the [M]–MOR nanocomposites can be tuned depending on the kind of metal.
Below are listed potential applications for representative samples, derived from the results in the spectra of Fig. 6(a).
A. For [Mn]–MOR two bands are evident, the band at ∼500nm is attributed to manganese coordination in Mn3O4 or MnO; the band at 250–270nm is associated to ligand-to-metal charge-transfer transition on tetrahedral coordination (Azizi & Ehsani Tilami, 2013; Selvaraj et al., 2005). Such Mn signals are related to the coexistence of the 2+ and 4+ oxidation states and their intensity is attributed to the existence of coordination with Si. It is known that [Mn]–MOR composites are used in the production of methylamines (Hidaka, Higuchi, & Kawai, 2003), in the water oxidation process, and in hydrocarbon oxidation (Meng et al., 2013).
B. The [Fe]–MOR sample displays a band at ∼240nm which may be attributed to metal–electron transfer transitions (Hailu et al., 2015). Moreover, a weak band at ∼500nm is related to high-spin tetrahedral complexes of Fe3+ (Fe2O3) (Hailu et al., 2015). [Fe]–MOR is suitable for Fenton treatments (Salazar, Brillas, & Sirés, 2012), in the oxidizing process on reformed gas (Watanabe, 2004), selective catalytic reduction on automotive emissions (Colombo, Koltsakis, Nova, & Tronconi, 2012), conversion of methane on methanol (Hammond et al., 2012), gasoline production by the Fischer–Tropsch reaction (Sun et al., 2012), among others.
C. For the [Co]–MOR sample, three bands appear at ∼230, ∼530 and ∼635nm; the two former transition bands correspond to Co2+ in octahedral coordination; while the transition at ∼635nm is due to tetrahedral of CoO4 coordination present when Co substitutes Si atoms on the mordenite framework (Azizi & Ehsani Tilami, 2013; Kato, Ikeda, Kodaira, & Takahashi, 2011). [Co]–MOR is presently being used as a Fischer–Tropsch catalyst, to make liquid fuels from biosyngas (Sartipi et al., 2013).
D. For the [Ni]–MOR sample the absorbance around 700nm is associated with the 2+ state of the Ni atoms. The absorbance between 270 and 300nm may be related to octahedral coordinated Ni ions, surrounded by oxygen atoms of zeolite in electron–donor–acceptor complexes. [Ni]–MOR has been used for oligomerizations from propene for lubricants and detergents (Mlinar, Shylesh, Ho, & Bell, 2014), and conversion of cellulose to polyols such as sorbitol and mannitol (Shrotri, Tanksale, Beltramini, Gurav, & Chilukuri, 2012).
E. The [Cu]–MOR sample shows a transition band at 240nm associated with Cu+; the shoulder at ∼500nm is attributed to copper nanoparticles on the mordenite surface which corresponds to the capacity of copper to occupy acid sites on the mesoporosity. The signal at ∼700nm corresponds to the spin-allowed d–d transition of Cu2+ on zeolite matrices (López-Bastidas, Petranovskii, & Machorro, 2012). [Cu]–MOR is used in the carbonylation process for organic molecule production, oxidations of organic molecules to obtain phenol (Tabler, Häusser, & Roduner, 2013), and inactivation of viruses (Imai et al., 2012).
F. The [Ag]–MOR shows a typical absorbance spectrum associated to a plasmon resonance in the 340–530nm region. [Ag]–MOR is used in pesticide degradation (Kanan & Nusri, 2013); in green chemistry, and in the production of important pharmacological molecules such as spiroketals (Borghèse, Drouhin, Bénéteau, Louis, & Pale, 2013).
Furthermore, the sulfided [M]–S–MOR UV–Vis absorbance spectra (Fig. 6(b)) show the modifications of the absorption spectrum for each example. These changes can be associated to the growth of sulfided nanoparticles as reported elsewhere (Jaime-Acuña et al., 2014). A noticeable increase of the sulfide samples absorption spectra is observed in the 225–550nm range. This effect is due to the formation of semiconductor nanoparticles which are strongly photoactive and are responsible for the high yield of UV–Vis light harvesting. This type of nanocomposites were tested in the photocatalytic degradation of the organic molecules reaction (Eqs. (1)–(5)); briefly, a 20ppm of some [M]–S–MOR nanocomposites and 50ppm of acid red 114 (AR114) dye were stirred under UV light (254nm). A commercial TiO2 sample was used as reference. Fig. 7 shows the residual concentration behavior of the AR114 dye as a function of time.
As shown in Figure 7, while for the commercial TiO2 the degradation reached ∼75% in 215min (k=0.004min−1), the [M]–S–MOR samples revealed a significantly better performance. The [Cd,Zn]–S–MOR sample shows the best performance with a degradation of ≥95% in only 100min (k=0.009min−1), the explanation of the calculation of the reaction rate could be found elsewhere (Trejo-Tzab, Alvarado-Gil, Quintana, & Bartolo-Pérez, 2012). Thus, the [M]–S–MOR nanocomposites here developed exhibit higher photoactivity and better harvesting of the light making our products industrially competitive.
4ConclusionsWaste solid materials, derived from the geothermal energy conversion process, were successfully used in solvent- and organic-free synthesis of nanostructured composites based on mordenite.
This route for synthesizing metal–MOR, semiconductor–MOR and metal/semiconductor–MOR nanostructured composites has the following advantages: (i) reduction of pollutants (no solvents are used); (ii) saving energy and simplifying synthetic procedures (no organic templates are used which means no calcination process is required); (iii) designation of the type and concentration of ion supported on MOR from the beginning of the synthesis. With these considerations, the proposed synthesis route becomes relevant for the industrial production of nanostructured composites based on synthetic zeolite.
The developed methodology allows control and tuning of the final properties of nanocomposites from their synthesis in addition to being reproducible and repeatable. Metal–semiconductor– and metal/semiconductor–MOR nanostructured composites could be widely used in industry and are strong candidates as materials for new developments in optoelectronics, catalysis, and especially in photocatalysis.
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Peer Review under the responsibility of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.















![Representative N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm of synthesized [M]–MOR for M=Mn. Representative N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm of synthesized [M]–MOR for M=Mn.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/16656423/0000001400000004/v2_201703180257/S1665642316300554/v2_201703180257/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr5.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w96p5LBcBpyJTqfwgorxm+Ow=)

